Содержание
- 2. Why culture is a business issue More than 80% of cross-border mergers fail to add value
- 3. Individuals are more than generalities or stereotypes YOU Inborn factors National culture Corporate & professional culture
- 4. Culture: the shared assumptions, values and beliefs of a group of people that result in characteristic
- 5. ABOVE THE SURFACE Language and style Ellen Hake
- 6. Language: ‘global English’ Speak slowly and pause often Consider British versus US English Use native speaking
- 7. Consider communication style
- 8. BELOW THE SURFACE Values and assumptions Ellen Hake
- 9. Key research on culture in business Trompenaars/Hampden-Turner Universalism-Particularism (rules versus relationships) Communitarianism-Individualism (group versus individual) Neutral-Emotional
- 10. Context in cultural analysis Highly Low Context- Monochronic cultures (such as U.S., Germany, Scandinavia): time is
- 11. Values impact communication Approximation based on research by Hall, Hofstede, Trompenaars, Hampden-Turner and others LOW CONTEXT
- 12. Context in communication Ellen Hake
- 13. Tolerance for change Approximation based on research by Fons Trompenaars, Charles Hampden-Turner and others ACCEPT UNCERTAINTY
- 14. Analyze and describe behavior—don’t judge it. (“They don’t queue” versus “They are rude”…how do I choose
- 15. Resources Riding the Waves of Culture: Understanding Cultural Diversity in Business, Trompenaars/Hampden-Turner, Nicholas Brealey Publishing Cultures
- 16. Relative rankings of some sample countries, based on research by Geert Hofstede LARGE POWER DISTANCE SMALL
- 17. Relative rankings of some sample countries, based on research by Fons Trompenaars/Charles Hampden-Turner UNIVERSALISM PARTICULARISM COMMUNITARIANISM
- 18. Relative rankings of some sample countries, based on research by Geert Hofstede LARGE POWER DISTANCE SMALL
- 20. Скачать презентацию
 Past Simple. Present Simple
Past Simple. Present Simple The Lorax by Dr. Seuss
The Lorax by Dr. Seuss Past continuous
Past continuous Career choice
Career choice Spotlight 3. Module 5 (Unit 10). Furry friends
Spotlight 3. Module 5 (Unit 10). Furry friends Эквивалентность. Закономерные соответствия. Трансформации при переводе
Эквивалентность. Закономерные соответствия. Трансформации при переводе What is the weather like in Britain?
What is the weather like in Britain? The Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction
The Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction Test Execution
Test Execution The importance of carbohydrates in animal nutrition
The importance of carbohydrates in animal nutrition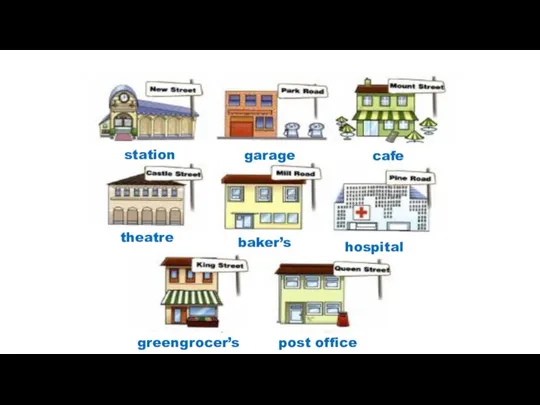 Places. Spotlight 4
Places. Spotlight 4 Guess these animal idioms
Guess these animal idioms To be
To be Duvan Mechetlino 102. My small homeland
Duvan Mechetlino 102. My small homeland Alexander Fleming
Alexander Fleming English. Oral texts
English. Oral texts Traditions of Belarus
Traditions of Belarus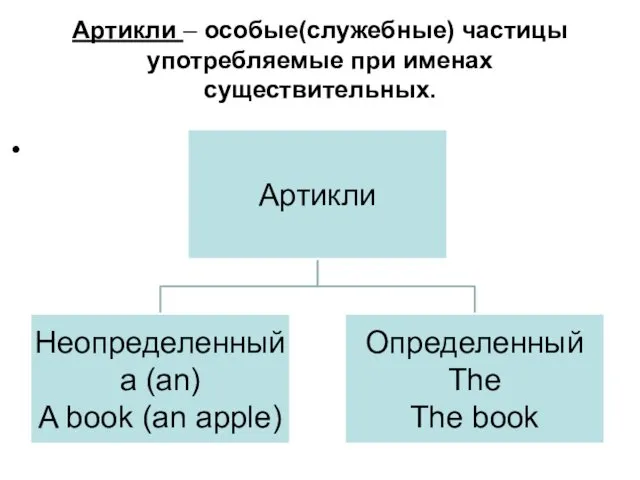 Артикли – особые (служебные) частицы, употребляемые при именах существительных
Артикли – особые (служебные) частицы, употребляемые при именах существительных -ing форма глагола
-ing форма глагола Job hunting
Job hunting Stop terrorism
Stop terrorism Prepositions
Prepositions Etymology
Etymology Contrastive lexicology 2. Understanding metaphorical expressions
Contrastive lexicology 2. Understanding metaphorical expressions New Year Game
New Year Game Federal Reserve System
Federal Reserve System ЕГЭ. Английский язык. Вариант 2
ЕГЭ. Английский язык. Вариант 2 Clothes Hidden Pictures Game
Clothes Hidden Pictures Game