Содержание
- 2. PLAN I. Lexicology as a branch of linguistics a) Its object and aims b) Branches of
- 3. III. The semantic structure of word meaning 1) Approaches to meaning 2) Types of meaning a)
- 4. Definition Lexicology – ‘lexi(ko)s’ - a word; ‘logos’ - a science/learning; literally: the science of the
- 5. Definition Lexicology is the part of linguistics dealing with the vocabulary of the language and the
- 6. What does it aim at?
- 8. The main problems investigated in lexicology systematic description of the word-stock in respect to its origin,
- 9. The main problems investigated in lexicology 2. the problems of word structure and word formation; E.g.,
- 10. The main problems investigated in lexicology 3. semantics of English words; semantic structure of the meaning;
- 11. The main problems investigated in lexicology 4 )relationships of lexical units in speech; E.g. a blind
- 12. Branches of lexicology 1.General & Special Lexicology; Contrastive Lexicology 2. Historical / diachronic/ & Synchronic lexicology
- 13. Branches of lexicology Synchronic lexicology: Word building or Word formation Semantics or Semasiology Phraseology Applied Lexicology
- 14. A Word A word is the basic/ smallest significant unit of a given language capable of
- 15. Approaches to meaning A word is a linguistic sign (F.de Saussure) Interpretations of the structure of
- 16. Referential approach The 3 components are closely connected with meaning: the sound-form of the linguistic sign
- 17. Functional approach The meaning of a linguistic unit can be studied only through its relation to
- 18. The operational or information-oriented approach The operational or information-oriented definitions of meaning are centered on defining
- 19. Meaning Meaning is a linguistic component reflecting concept or naming emotions by means of a definite
- 20. Types of meaning Grammatical Lexical Lexico-grammatical meaning
- 21. Types of meaning Grammatical meaning is an expression of relationships between words Milk shake – shake
- 22. Types of meaning Lexical meaning is a realisation of a concept or emotion by means of
- 23. Types of meaning Lexico-grammatical meaning = Part-of-speech meaning
- 24. Aspects of lexical meaning De’notative (denotational) ‘Connotative (connotational) Pragmatic
- 25. Aspects of lexical meaning The denotative meaning reflects the concept or the object referred to by
- 26. Aspects of lexical meaning The connotative meaning is supplementary meaning which is added to the word’s
- 27. Types of connotations Stylistic Emotional Evaluative Imagery Intensifying (expressive, emphatic) Pragmatic
- 28. Motivation Motivation is a direct connection between the phonemic, morphemic composition, the structural pattern of the
- 29. Types of motivation Phonetic Morphological Semantic Faded Folk etymology Non-motivated words
- 30. Types of motivation Phonetic motivation is the connection between the phonetic composition of the word and
- 31. Types of motivation Morphological motivation is the connection between the morphemes and the meaning of the
- 32. Types of motivation Semantic motivation is based on the co-existence of direct and indirect meaning of
- 33. The structure of meaning A meaning is a combination of minimal sense units – semes or
- 35. Скачать презентацию
 Grammar test
Grammar test Present Simple Tense. Простое настоящее время. 2 класс
Present Simple Tense. Простое настоящее время. 2 класс Виды письменного перевода
Виды письменного перевода Reported speech. Intermediate level
Reported speech. Intermediate level Test health vocabulary - dictation and collocations
Test health vocabulary - dictation and collocations Всероссийская олимпиада школьников. Английский язык
Всероссийская олимпиада школьников. Английский язык Word formation Phrasal verb GET and dependent prepositions
Word formation Phrasal verb GET and dependent prepositions Do you have the same hobby?
Do you have the same hobby? English for Business Communication
English for Business Communication Present Continuous Tense. Настоящее длительное время
Present Continuous Tense. Настоящее длительное время Relationship. Human relationships are complex and varied
Relationship. Human relationships are complex and varied Describing events
Describing events The english alphabet j-r. Game 2
The english alphabet j-r. Game 2 Present simple vs. present continuous
Present simple vs. present continuous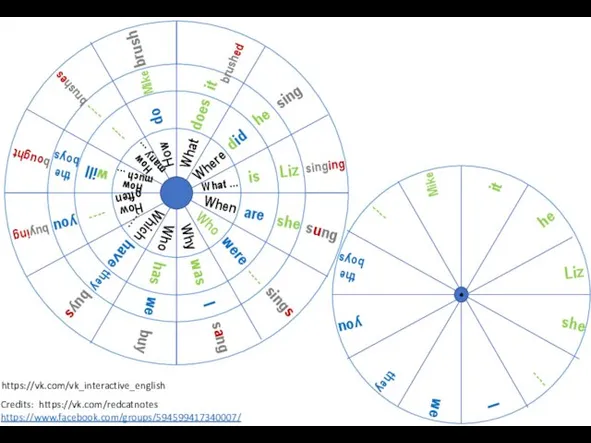 Wh-questions vk interactive english
Wh-questions vk interactive english Ideal holiday!
Ideal holiday! Английский как международный язык общения
Английский как международный язык общения Australian English
Australian English George Washington
George Washington Sweden cross cultural management
Sweden cross cultural management My favorite sportsman
My favorite sportsman Colours
Colours Spotlight 4. Module 5 (Unit 10). Where were you yesterday?
Spotlight 4. Module 5 (Unit 10). Where were you yesterday? Spotlight 4. Module 7 (Unit 13). Days to remember
Spotlight 4. Module 7 (Unit 13). Days to remember Present simple
Present simple Конструкция There is/are
Конструкция There is/are Past Simple. Употребление Past Simple
Past Simple. Употребление Past Simple What is she going to do?
What is she going to do?