Содержание
- 2. Radionuclide diagnostics methods Noninvasive Are primarily physiologic Functional Does not provide the same anatomic details As
- 3. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Glomerular filtration ⬜ 99mTc DTPA
- 4. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Nuclear medicine is a medical
- 5. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol
- 6. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Three basic classes of radionuclide
- 7. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol DTPA and MAG3 are filtered
- 8. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol MAG3 and Hipuran are excreted
- 9. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol DMSA and Glucoheptonate are accumulated
- 10. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol There are two main radionuclide
- 11. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol
- 12. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Radiopharmaceticals 99mTc-DTPA – Diethylentriamine pentaacetic
- 13. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Radiopharmaceticals 99mTc-MAG3 - Mercapto-acetyltriglycine -is
- 14. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Dynamic renal study Radiopharmaceutical 99mTc
- 15. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol
- 16. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol
- 17. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol
- 18. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Area of interest This is
- 19. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Normally, the curves show rapid
- 20. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol A II. III. Vascular phase
- 21. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol A čas normal obstructed pattern
- 22. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol ANT POST RPO LPO Normal
- 23. Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Evaluation - number of kidneys
- 25. Скачать презентацию
 Пропедевтика. Клиническая симптоматология холециститов, холангита
Пропедевтика. Клиническая симптоматология холециститов, холангита Анафилактический шок
Анафилактический шок Уильям Гарвей (1578 – 1657)
Уильям Гарвей (1578 – 1657) Социальное медицинское страхование в Республике Казахстан
Социальное медицинское страхование в Республике Казахстан Hygiene of children and teenagers
Hygiene of children and teenagers Иммунитет у детей и подростков
Иммунитет у детей и подростков Репродуктивное здоровье населения и национальная безопасность России
Репродуктивное здоровье населения и национальная безопасность России ДВС-синдром
ДВС-синдром САП (malleus)
САП (malleus) Бел-омыртқа жарығы
Бел-омыртқа жарығы Жұлынның құрылысы және қызметтері
Жұлынның құрылысы және қызметтері Заболевания, диагностируемые неонатальным скринингом
Заболевания, диагностируемые неонатальным скринингом Аллергодерматозы. Синдром Стивенса-Джонсона. Микозы
Аллергодерматозы. Синдром Стивенса-Джонсона. Микозы Что нужно знать для купирования боли
Что нужно знать для купирования боли Металлопластмасса
Металлопластмасса Клинический случай (плановой, экстренной анестезии)
Клинический случай (плановой, экстренной анестезии)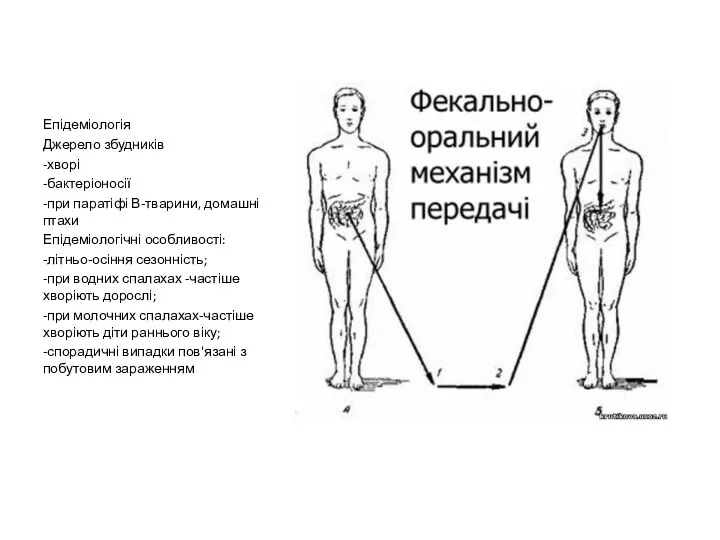 Епідеміологія. Джерело збудників
Епідеміологія. Джерело збудників Diagnostic diferenţial în sindromul de hipertensiune portală
Diagnostic diferenţial în sindromul de hipertensiune portală Аналитикалық эпидемиология зерттеу. Оқиға бақылау, когорттық, және кәлденелік зерттеу
Аналитикалық эпидемиология зерттеу. Оқиға бақылау, когорттық, және кәлденелік зерттеу Структурная организация кроветворения
Структурная организация кроветворения Организация работы медицинских организаций по предотвращению возникновения аварийных ситуаций
Организация работы медицинских организаций по предотвращению возникновения аварийных ситуаций Стрельниковская дыхательная гимнастика
Стрельниковская дыхательная гимнастика Парентеральное питание
Парентеральное питание ДВС - синдром у детей
ДВС - синдром у детей Физиологиялық рефлекстер
Физиологиялық рефлекстер Роль медсестры поликлиники в реабилитации недоношенных детей
Роль медсестры поликлиники в реабилитации недоношенных детей Обследование пациентов с заболеваниями органов дыхания
Обследование пациентов с заболеваниями органов дыхания Феохромоцитома: трудности диагностики и лечения
Феохромоцитома: трудности диагностики и лечения