Содержание
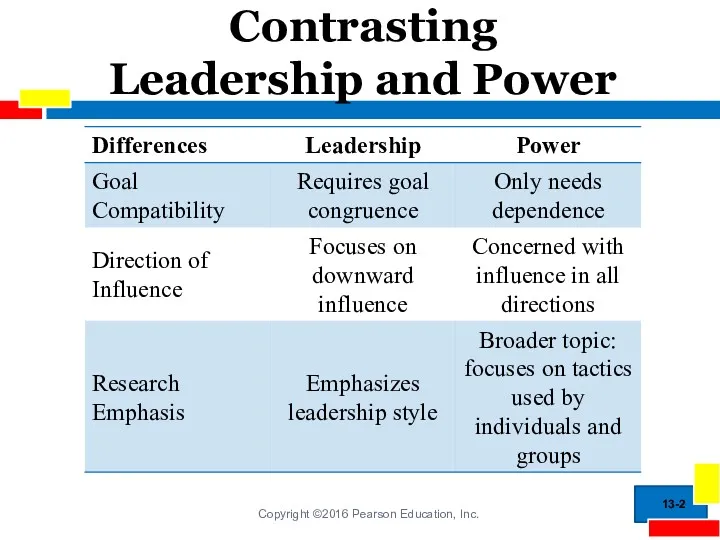
- 2. Contrasting Leadership and Power 13-
- 3. Formal Bases of Power Formal power is based on an individual’s organizational position Coercive Power: Complies
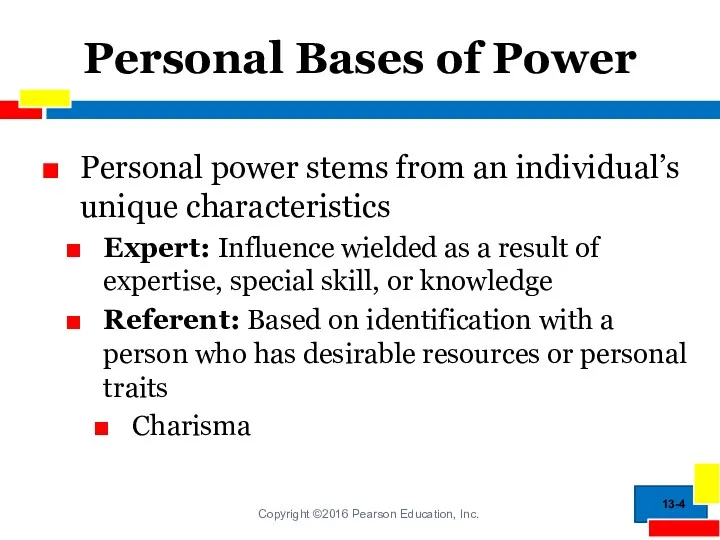
- 4. Personal Bases of Power Personal power stems from an individual’s unique characteristics Expert: Influence wielded as
- 5. Effective Power Bases Expert and referent power are positively related to performance and commitment Reward and
- 6. Power Tactics Power tactics: Used to translate power bases into specific actions that influence others Some
- 7. Nine Influence Tactics Legitimacy Rational persuasion Inspirational appeals Consultation Exchange Personal appeals Ingratiation Pressure Coalitions 13-
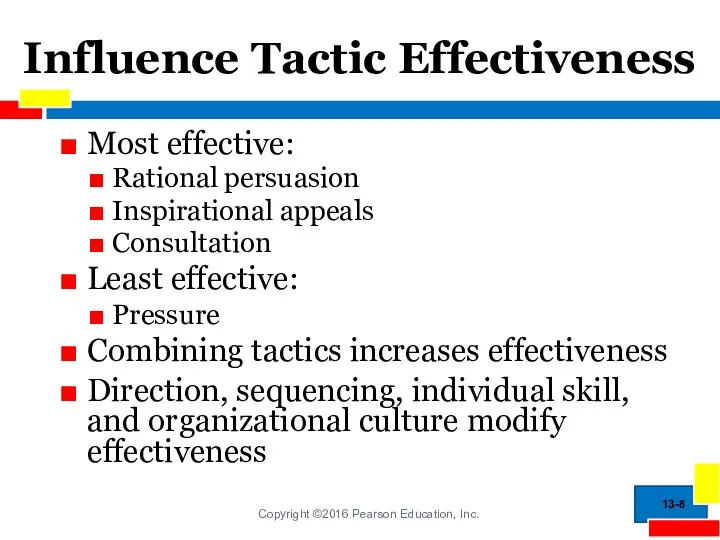
- 8. Influence Tactic Effectiveness Most effective: Rational persuasion Inspirational appeals Consultation Least effective: Pressure Combining tactics increases
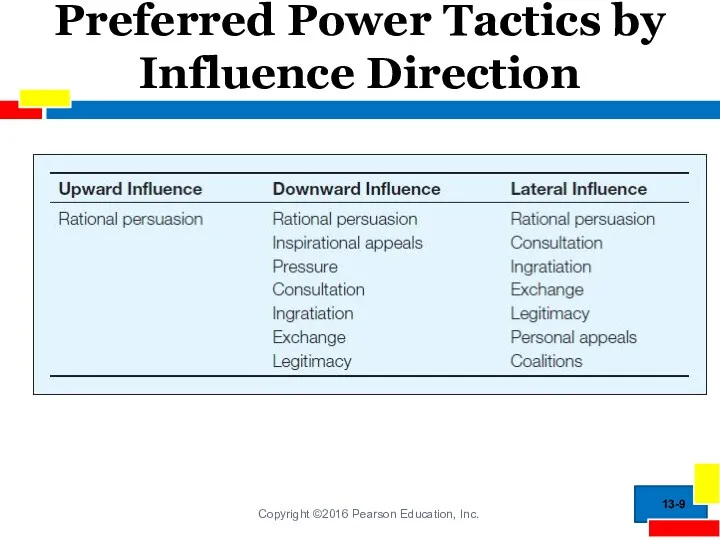
- 9. Preferred Power Tactics by Influence Direction 13-
- 10. Global Implications Culture affects preference for power tactics Individualistic cultures See power in personalized terms and
- 11. Political Skill Political skill: ability to influence others to enhance one’s own objectives Politically skilled are
- 12. How Power Affects People People with power: Put their interests ahead of others Objectify others React
- 13. Organizational Politics Political behavior: consists of activities that are not required as part of an individual’s
- 14. The Reality of Politics Politics arise in organizations because of: Conflicting interests Limited resources Ambiguity in
- 15. Individual Factors Contributing to Political Behavior Traits that encourage political action: High self-monitors Internal locus of
- 16. Organizational Factors Contributing to Political Behavior Organizational resources declining or distribution shifting Opportunity for promotion exists
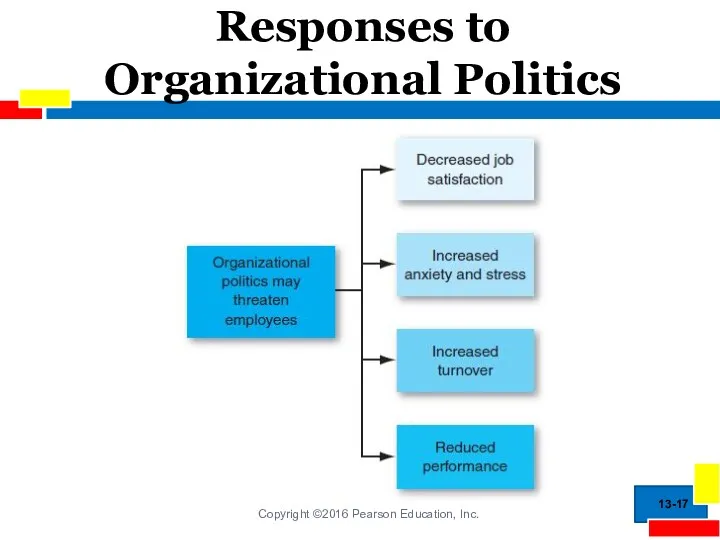
- 17. Responses to Organizational Politics 13-
- 18. Qualifiers to Responses to Organizational Politics The politics-performance relationship is moderated by individual’s understanding of who
- 19. Impression Management Impression Management: The process by which individuals attempt to control the impression others form
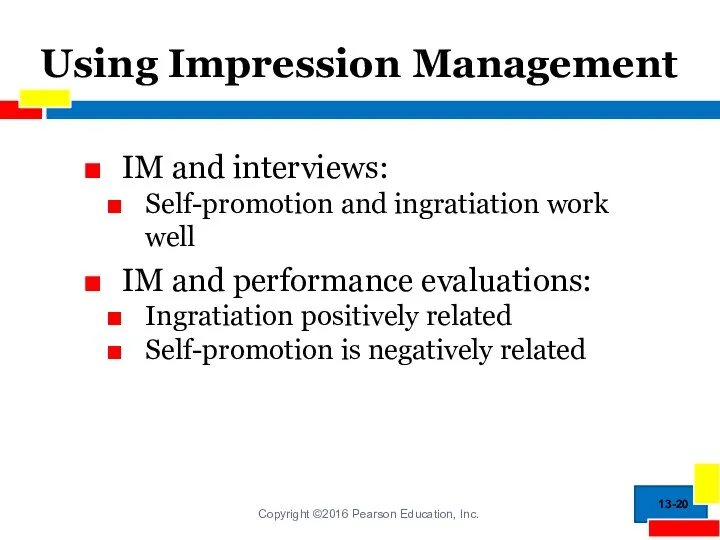
- 20. Using Impression Management IM and interviews: Self-promotion and ingratiation work well IM and performance evaluations: Ingratiation
- 21. The Ethics of Behaving Politically Questions to consider: What is the utility of engaging in politicking?
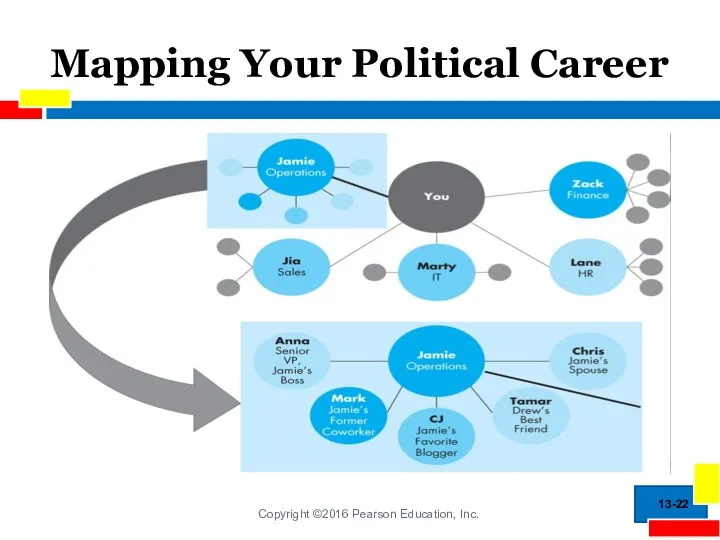
- 22. Mapping Your Political Career 13-
- 23. Implications for Managers As a manager who wants to maximize your power, you will want to
- 25. Скачать презентацию















 Gerund Infinitive
Gerund Infinitive Степени сравнения прилагательных Adjectives Degrees of Comparison
Степени сравнения прилагательных Adjectives Degrees of Comparison Правила в английском языке
Правила в английском языке The climate of Great Britain
The climate of Great Britain Self-Determination Theory
Self-Determination Theory Riddles
Riddles Travel Kazan
Travel Kazan Задания по английскому языку
Задания по английскому языку Причастие – неличная форма глагола, сочетающая свойства глагола, прилагательного и наречия
Причастие – неличная форма глагола, сочетающая свойства глагола, прилагательного и наречия Welcome to Wales
Welcome to Wales Алфавит. Буква и транскрипция. Типы чтения
Алфавит. Буква и транскрипция. Типы чтения The Humboldt University of Berlin
The Humboldt University of Berlin Present Continuous
Present Continuous Gate way unit. Vocabulary people
Gate way unit. Vocabulary people University of Cambridge and Lomonosov Moscow State University
University of Cambridge and Lomonosov Moscow State University Family and friend 4. Class book. Interactive. Starter module
Family and friend 4. Class book. Interactive. Starter module Irregular Verbs (game)
Irregular Verbs (game) The english alphabet j-r. Game 2
The english alphabet j-r. Game 2 American TV families
American TV families Нарисовать себя и действия
Нарисовать себя и действия The best product of the 21st century
The best product of the 21st century Страна Уэльс
Страна Уэльс To Have. The Affirmative Form
To Have. The Affirmative Form Television
Television Monologue in interpersonal communication
Monologue in interpersonal communication Read the clues and guess the food
Read the clues and guess the food Soil. Types of soils of Kazakhstan
Soil. Types of soils of Kazakhstan The Beatles were a legendary English rock band
The Beatles were a legendary English rock band