Содержание
- 2. What do we mean by reading? What is reading? What happens when we read? What kind
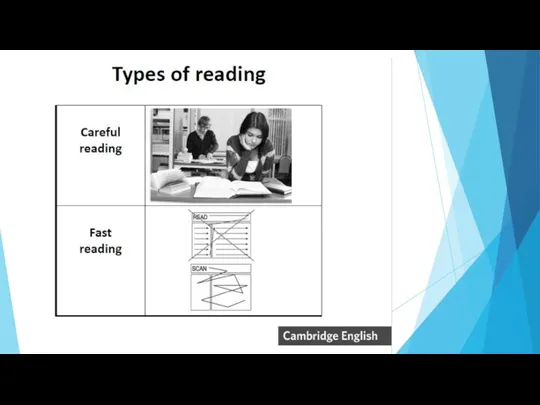
- 3. What reading skills do we employ when reading… a timetable? a newspaper article? a poem? Skimming
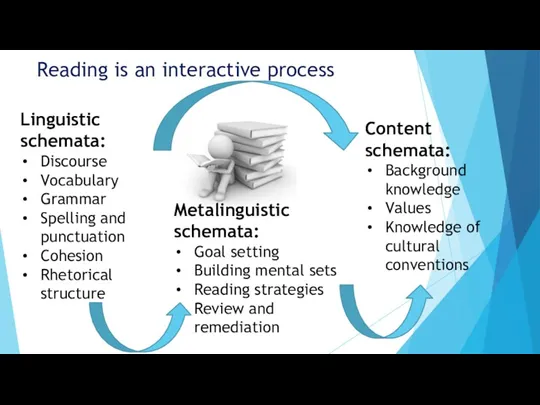
- 6. Reading is an interactive process Linguistic schemata: Discourse Vocabulary Grammar Spelling and punctuation Cohesion Rhetorical structure
- 7. Bottom-Up Reading
- 12. Top-down reading
- 13. Reading bottom-up vs top-down style BU takes 3 times longer: more fixations and movement back and
- 14. Reading: What are your objectives? Macro skills Reading quickly to skim for gist Scan for specific
- 15. What macro skills do you want to assess? How are you going to do it? Macro
- 16. What micro skills do you want to assess? How are you going to do it? Micro
- 17. What do we read?
- 18. Some considerations in designing reading tasks Use both prose texts and non-linear texts Collect appropriate reading
- 19. Flesch Reading Ease
- 20. Readability level
- 21. Instructions Formulate questions in a slightly lower level than the reading passage Follow the same order
- 22. Formats for assessing reading Recognition and selection Multiple choice, true/false/not given, matching Reduce guessing factor, avoid
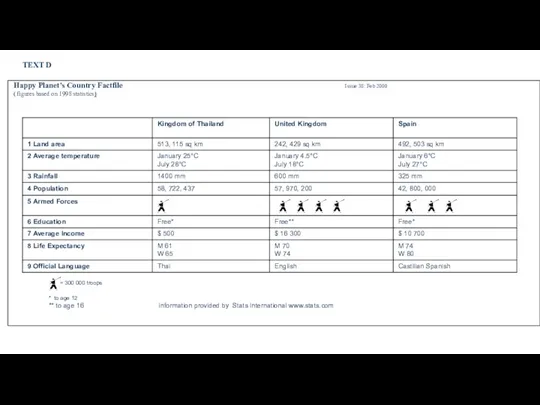
- 23. TEXT D Happy Planet’s Country Factfile Issue 38: Feb 2000 ( figures based on 1998 statistics)
- 24. Use Text D on the next page to answer the questions. Write short answers on the
- 26. Скачать презентацию




















 Present & past
Present & past Assessing writing (Part 1). Lecture 8
Assessing writing (Part 1). Lecture 8 Interactive repetition simulator. Grade 2
Interactive repetition simulator. Grade 2 ЕГЭ. Говорение
ЕГЭ. Говорение Independent work. Pneumonia
Independent work. Pneumonia Походження англійської мови
Походження англійської мови Clothes vocabulary review 4
Clothes vocabulary review 4 Подготовка к ОГЭ. Пробник. Christmas and New Year
Подготовка к ОГЭ. Пробник. Christmas and New Year Princeton university
Princeton university FIFA 2018
FIFA 2018 ¿Qué es esto? Что это?
¿Qué es esto? Что это? Pollution in the world
Pollution in the world Old english period. Lecture 3
Old english period. Lecture 3 My favorite book
My favorite book Произношение гласных и согласных звуков
Произношение гласных и согласных звуков Transportation More esl games
Transportation More esl games Welcome to English-speaking country. Students’ Exchange Programs
Welcome to English-speaking country. Students’ Exchange Programs Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Устная часть
Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Устная часть Country I want to visit is Canada. Канада
Country I want to visit is Canada. Канада Cosmonauts are Discoverers of the Universe
Cosmonauts are Discoverers of the Universe Bedroom, bathroom, kitchen, living room
Bedroom, bathroom, kitchen, living room Modern building materials
Modern building materials Школьные принадлежности. 2 класс
Школьные принадлежности. 2 класс Non-continuous verbs list. Verbs of feeling and perception
Non-continuous verbs list. Verbs of feeling and perception Структура английского предложения. Вспомогательный глагол to be
Структура английского предложения. Вспомогательный глагол to be Communicative Language Teaching Vocabulary (lecture 3)
Communicative Language Teaching Vocabulary (lecture 3) Weather. Seasons. Game
Weather. Seasons. Game He loves jelly (lesson 20)
He loves jelly (lesson 20)