Содержание
- 2. Outline of today’s lecture Challenges of speaking assessment Speaking as a skill and subskills Types of
- 3. Why assess speaking? Speaking is part of language curricula, esp. in communicative LT if we teach
- 4. Why assess speaking? Linking language production to real-world contexts Valuing communication over knowledge about the language
- 5. Inherent challenges and practicalities of assessing speaking Inherent challenges: What exactly is the construct of speaking?
- 6. Theory of speaking assessment Speaking is a complex skill (Harris, 1977) Pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, purpose, fluency
- 7. Classifying oral skills (based on Weir 1993) Repertoire of routines Exchanging information Provide personal information, give
- 8. Speaking subskills based on Brown H (2010) Micro-skills Creation of sounds Chunks of speech Stress Reduced
- 9. Assessing interactive speech: Includes long stretches of interactive discourse. Can take two forms: Transactional language: to
- 10. Assessing interactive speech: Interview Direct face-to-face exchange and proceeding through a protocol of questions and directives
- 11. Example: Interviews
- 12. Assessing interactive speech: Role play Popular activity in communicative language teaching classes. Controlled or ‘’guided’’ by
- 13. Assessing interactive speech: Discussions and conversations Difficult to specify and even more difficult to score. Offer
- 14. Assessing interactive speech: Discussions and conversations (ctd.) Discussions may be specially appropriate tasks through which to
- 15. Assessing extensive speech: Complex, relatively lengthy stretches of discourse. Variations on monologues, an interlocutor’s role is
- 16. Assessing extensive speech: Oral Presentations TTs present a report, a paper, a marketing plan, a sales
- 17. Oral Presentations (ctd.)
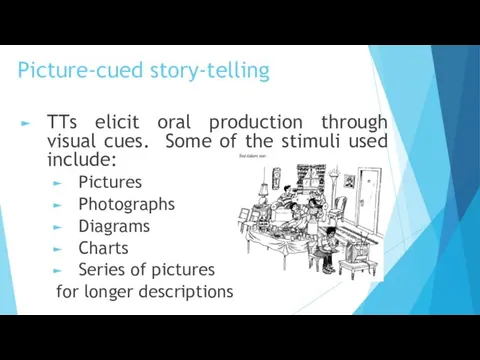
- 18. Picture-cued story-telling TTs elicit oral production through visual cues. Some of the stimuli used include: Pictures
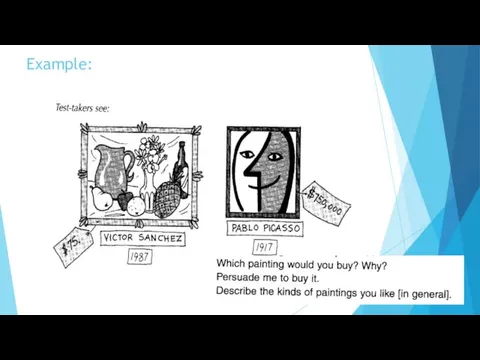
- 19. Example:
- 20. Retelling a story or news event In these tasks test-takers hear or read a story or
- 21. Validity issues Test what you teach, how you teach it Think about: The type of English
- 22. Matching test to objectives The skills you choose to test should match your program’s objectives Within
- 23. Conditions of assessing speaking How many people? Effective to test 2 : 2 Even with pairs,
- 24. Grading a productive skill What are the key subskills? Communication of meaning Comprehension Appropriateness, relevance Fluency:
- 25. Grading a productive skill Holistic Use a banding scheme Assign 1 overall mark based on impression
- 27. Скачать презентацию






















 Astana
Astana Prevention of respiratory diseases
Prevention of respiratory diseases Genito-Urinary Examination
Genito-Urinary Examination The Present Perfect
The Present Perfect Instructions for use
Instructions for use Глагол to have got (иметь)
Глагол to have got (иметь) Victoria State in Australia
Victoria State in Australia Singapore Changi Airport
Singapore Changi Airport Christmas in Britain
Christmas in Britain Complex Object
Complex Object How are you? - I am…
How are you? - I am… Clothes Hidden Pictures Game
Clothes Hidden Pictures Game My house is my castle
My house is my castle Sights of Donbass. Welcome to Donetsk
Sights of Donbass. Welcome to Donetsk Артикль: определённый и неопределённый
Артикль: определённый и неопределённый Tourist attractions in Moscow
Tourist attractions in Moscow Kids
Kids My flat
My flat The house of my dream
The house of my dream The United States of America
The United States of America Airport departures
Airport departures How to talk about yourself in English
How to talk about yourself in English Past progressive tense
Past progressive tense To have forms and functions. Формы и функции
To have forms and functions. Формы и функции Happy New Year!
Happy New Year! Своя игра. English-speaking countries
Своя игра. English-speaking countries Food born illness. (Chapter 1)
Food born illness. (Chapter 1) Welcome to Great Britain
Welcome to Great Britain