Содержание
- 2. Aims of the meeting TO LEARN SOME ONCOLOGY TERMS AND WIDEN YOUR MEDICAL VOCABULARY TO FORM
- 3. Breast Cancer Awareness It's an annual campaign organized in octover: to increase awareness of the disease
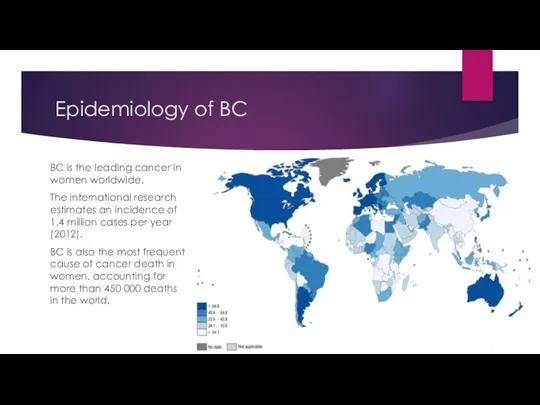
- 4. Epidemiology of BC BC is the leading cancer in women worldwide. The international research estimates an
- 5. Risks factors Classical risk factors: age sex ethnic origin reproductive factors (nulliparity and delayed pregnancy) hormone
- 6. Diagnosis The gold standard for diagnosis is the triple diagnosis: I. Clinical examination history palpation and
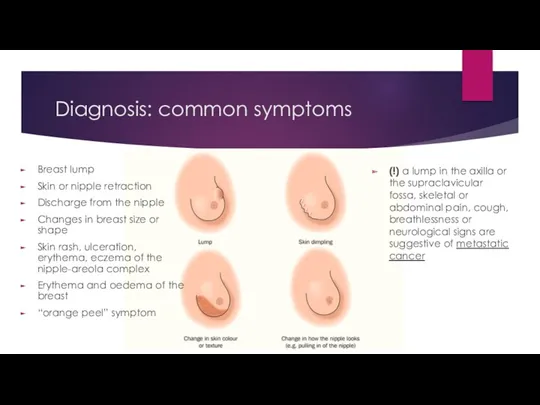
- 7. Diagnosis: common symptoms Breast lump Skin or nipple retraction Discharge from the nipple Changes in breast
- 8. Diagnosis: clinical examination 1. History taking family history of BC age of menarche number of births
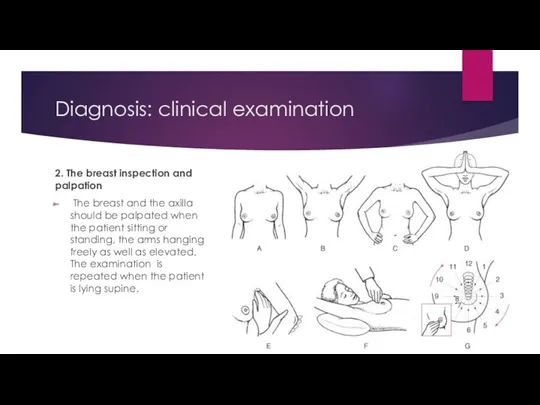
- 9. Diagnosis: clinical examination 2. The breast inspection and palpation The breast and the axilla should be
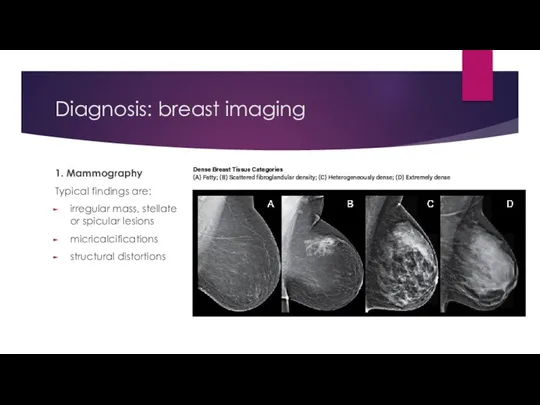
- 10. Diagnosis: breast imaging 1. Mammography Typical findings are: irregular mass, stellate or spicular lesions micricalcifications structural
- 11. Diagnosis: breast imaging 2. Breast and axillary ultrasound BC usually causes an echo-poor irregular lesion in
- 12. Diagnosis: breast imaging 3. Breast MRI MRI may identify BCs not detected by mammography or ultrasonography.
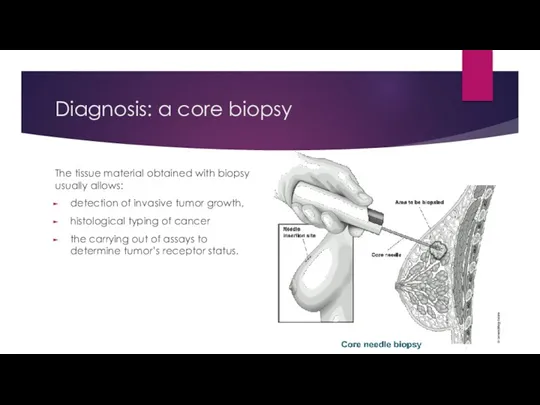
- 13. Diagnosis: a core biopsy The tissue material obtained with biopsy usually allows: detection of invasive tumor
- 14. Multidisciplinary work The team should include: a breast surgeon a medical oncologist a radiation oncologist a
- 15. Screening for BC Breast self-examination and clinical breast examination is important in BC detection, but are
- 16. What does the breast cancer awareness mean for you?
- 17. Attitude is a little thing that makes a big difference. © Winston Churchill
- 18. Thank you for your attention! YOU ARE AWESOME AUDIENCE!
- 20. Скачать презентацию










 Kid's box 1
Kid's box 1 Современные лакуны-заимствования в русском языке как средство познания мировоззрения носителей английского языка
Современные лакуны-заимствования в русском языке как средство познания мировоззрения носителей английского языка Personal letter
Personal letter Подготовка к ВПР. Грамматические формы (задание № 3)
Подготовка к ВПР. Грамматические формы (задание № 3) London
London Daily routine
Daily routine The History of The Simpsons
The History of The Simpsons Christmas in Great Britain
Christmas in Great Britain Quiz household items furniture
Quiz household items furniture Past simple
Past simple Kid's box 1. Unit 1. Hello!
Kid's box 1. Unit 1. Hello! University of Toronto
University of Toronto Everyday products
Everyday products Будущее простое время. Future Simple tense
Будущее простое время. Future Simple tense Дополнительная общеразвивающая программа для детей 4-5 лет Путешествие в Англию с Куки и его друзьями
Дополнительная общеразвивающая программа для детей 4-5 лет Путешествие в Англию с Куки и его друзьями Do we have the same hobbies
Do we have the same hobbies There is are - furniture (game)
There is are - furniture (game) Alexander Aleksandroviсh Alyabyev
Alexander Aleksandroviсh Alyabyev Christmas advent calendar
Christmas advent calendar Debate in English
Debate in English About newspapers
About newspapers Present Perfect VS Present Perfect Continuous
Present Perfect VS Present Perfect Continuous Development of electronics
Development of electronics Etymology. Lexicology. Lecture 2
Etymology. Lexicology. Lecture 2 Spotlight 4. Module 5 (Unit 9). Where were you yesterday?
Spotlight 4. Module 5 (Unit 9). Where were you yesterday? London Eye
London Eye Cheburashka. Present Simple
Cheburashka. Present Simple Harry Potter Simple Board Game
Harry Potter Simple Board Game