Содержание
- 2. The basis of CLIL is that content subjects are taught and learnt in a language which
- 3. The advantages of CLIL CLIL helps to: Introduce the wider cultural context Prepare for internationalisation Access
- 4. INTERRELATED TYPES OF LANGUAGE The balance between language and content involves three kinds of language, which
- 5. DEVELOPING THINKING SKILLS
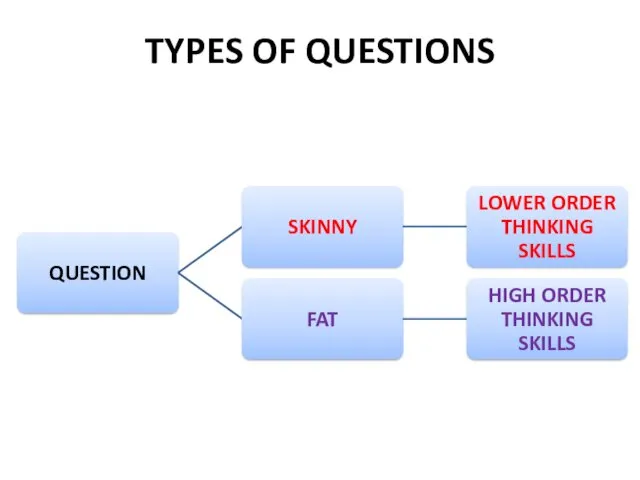
- 6. TYPES OF QUESTIONS
- 7. TYPES OF QUESTIONS LOTS How would you use …? How would you plan to …? What
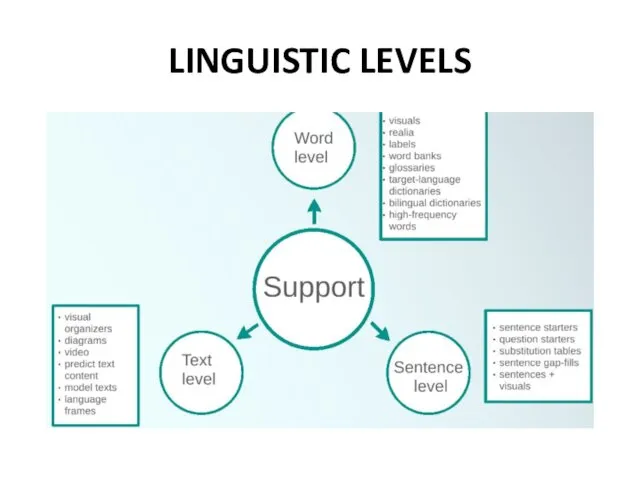
- 8. LINGUISTIC LEVELS
- 9. LINGUISTIC LEVELS
- 10. ADAPTING MATERIAL
- 11. Requirements for texts 1. Texts must be accompanied by illustrations so that learners can visualise what
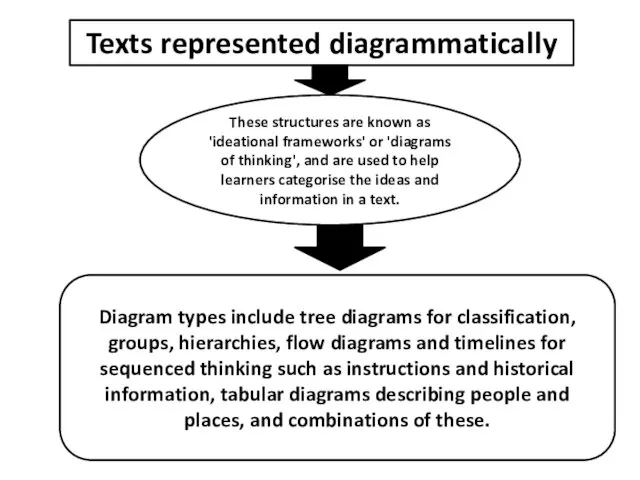
- 12. Texts represented diagrammatically These structures are known as 'ideational frameworks' or 'diagrams of thinking', and are
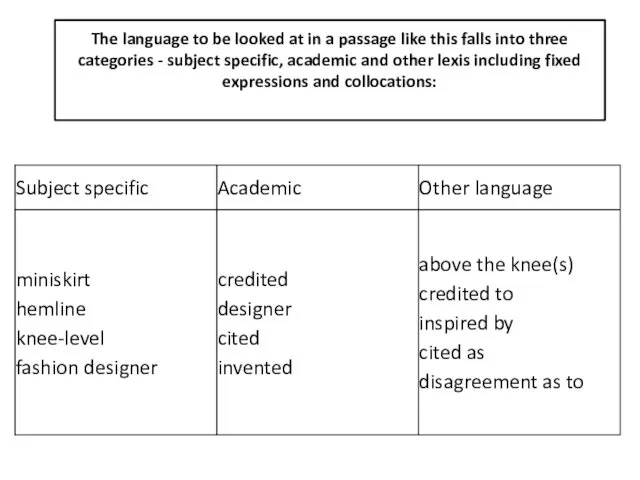
- 13. Here is a paragraph from a text on fashion:
- 14. The language to be looked at in a passage like this falls into three categories -
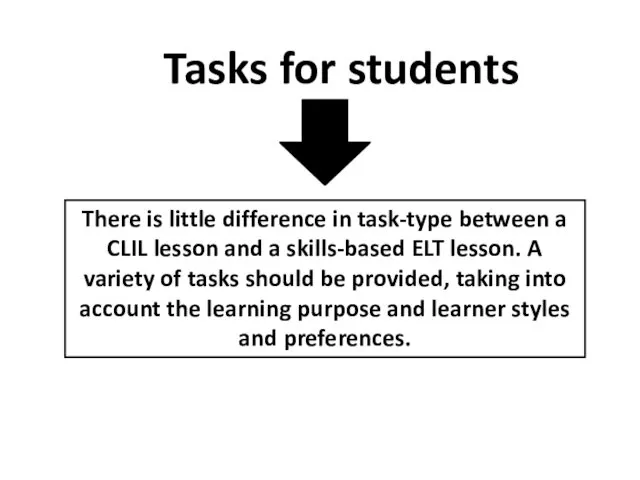
- 15. Tasks for students There is little difference in task-type between a CLIL lesson and a skills-based
- 16. The treatment of this lexis has the following features: Noticing of the language by the learners
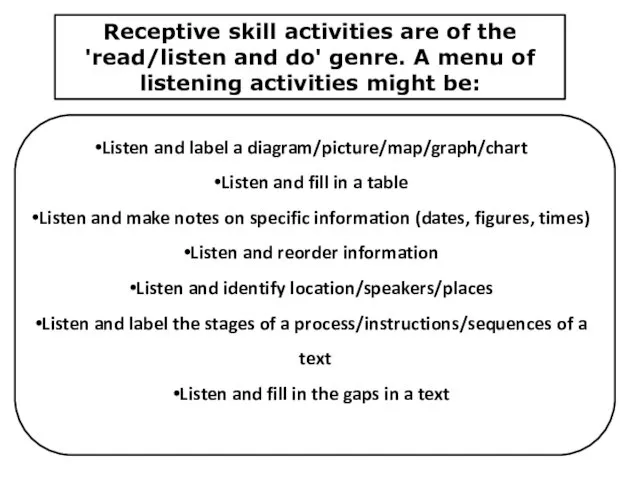
- 17. Receptive skill activities are of the 'read/listen and do' genre. A menu of listening activities might
- 18. Tasks designed for production need to be subject-orientated, so that both content and language are recycled.
- 19. Assessment in CLIL lessons
- 20. Assessing Content o Factual knowledge (checking detail) o General understanding (major points) o Ability to manipulate
- 21. We need to be sure which aspect of language we are assessing: It could be the
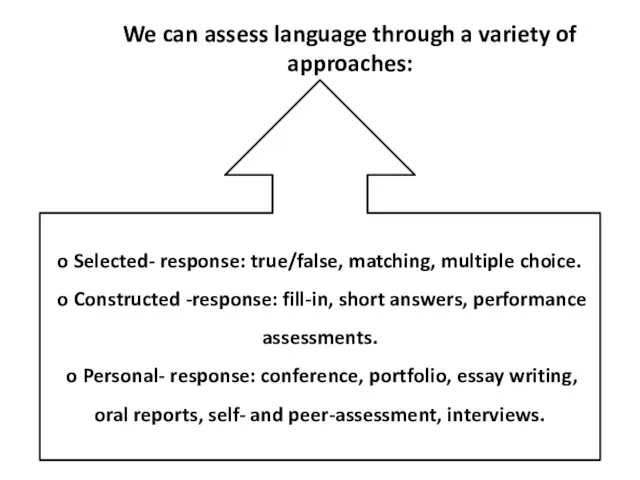
- 22. We can assess language through a variety of approaches: o Selected- response: true/false, matching, multiple choice.
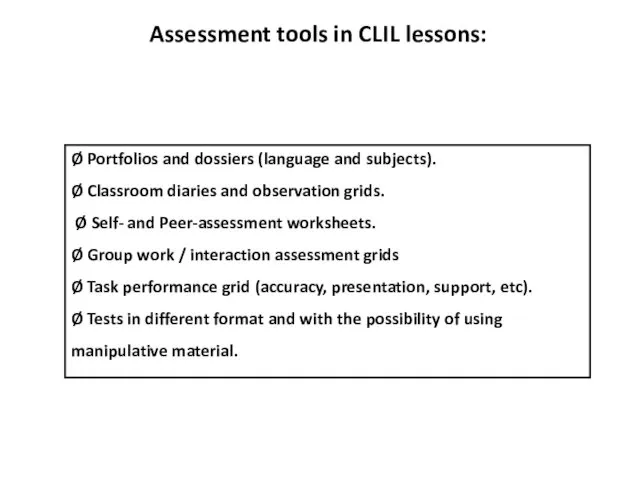
- 23. Assessment tools in CLIL lessons: Ø Portfolios and dossiers (language and subjects). Ø Classroom diaries and
- 25. Скачать презентацию














 Интонация в английском языке
Интонация в английском языке IT Школа. Программа изучения базовых английских слов
IT Школа. Программа изучения базовых английских слов Дополнительная общеразвивающая программа Поговорим по-английски (8– 9 лет, 9-10 лет )
Дополнительная общеразвивающая программа Поговорим по-английски (8– 9 лет, 9-10 лет ) Monologue in interpersonal communication
Monologue in interpersonal communication Free time activity
Free time activity Розбираємо, коли вживати Have got і Has got
Розбираємо, коли вживати Have got і Has got The role play staged by BS-065-RP-021
The role play staged by BS-065-RP-021 Физминутки и игры на уроках английского языка
Физминутки и игры на уроках английского языка Английские цифры от 1 до 10
Английские цифры от 1 до 10 My profession is an auto mechanic. Professional skills
My profession is an auto mechanic. Professional skills 10 вариантов. Тренажер по подготовке к ОГЭ по английскому языку. Устная часть. (Задания 1-3)
10 вариантов. Тренажер по подготовке к ОГЭ по английскому языку. Устная часть. (Задания 1-3)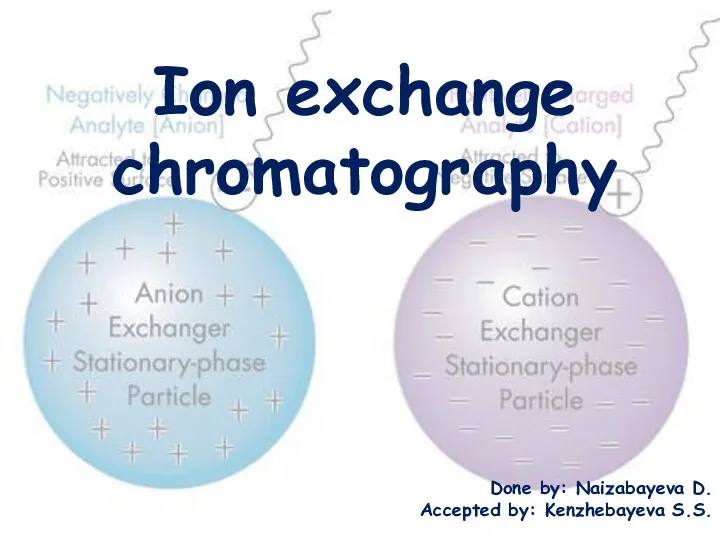 Ion exchange chromatography
Ion exchange chromatography My profession
My profession The Adjective
The Adjective REGEN-I_BK-350S Educational data
REGEN-I_BK-350S Educational data Pakistan. Cinema and theater
Pakistan. Cinema and theater My Favorite Book
My Favorite Book My belt wrestling “Dream Team”
My belt wrestling “Dream Team” My future profession teacher
My future profession teacher Things to do. Chall-2
Things to do. Chall-2 Mr. Grammar Tenses Active Voice
Mr. Grammar Tenses Active Voice Real relationships
Real relationships Biotechnology as my future profession
Biotechnology as my future profession Old english phonetic system
Old english phonetic system Present Perfect
Present Perfect Have to, has to
Have to, has to Old English noun
Old English noun City of London
City of London