Содержание
- 2. Lecture 10: Composite sentence. Complex sentence. 1. Definition of the complex sentence. 2. Subject clause and
- 3. Find the complex sentence, please: I see them coming. They insisted on staying there. Being introduced
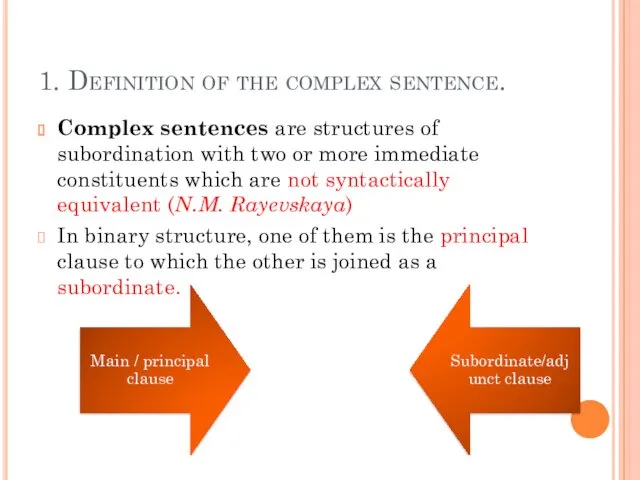
- 4. 1. Definition of the complex sentence. Complex sentences are structures of subordination with two or more
- 5. Means of expression of subordination in complex sentence: a) conjunctions; b) conjunctive words; c) asyndeton; d)
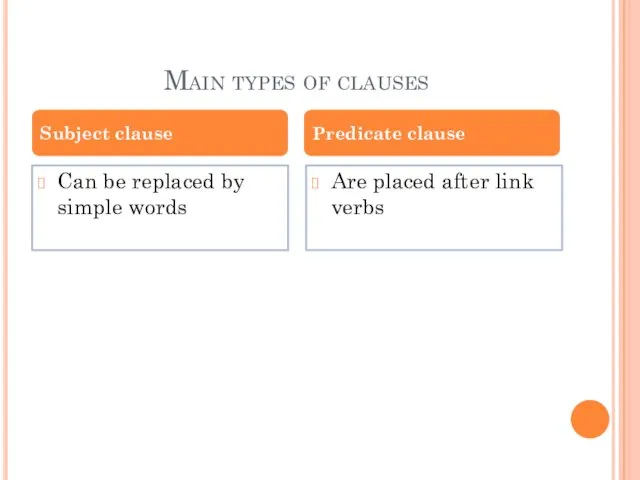
- 6. Main types of clauses Can be replaced by simple words Are placed after link verbs Subject
- 7. Examples of subject clause: That he will help us leaves no doubt. That he had not
- 8. Examples of predicate-clause: This was what had happened to himself! (Galsworthy) What surprised me most was
- 9. 3. Types of subordinate clauses(N.Raevskaya).
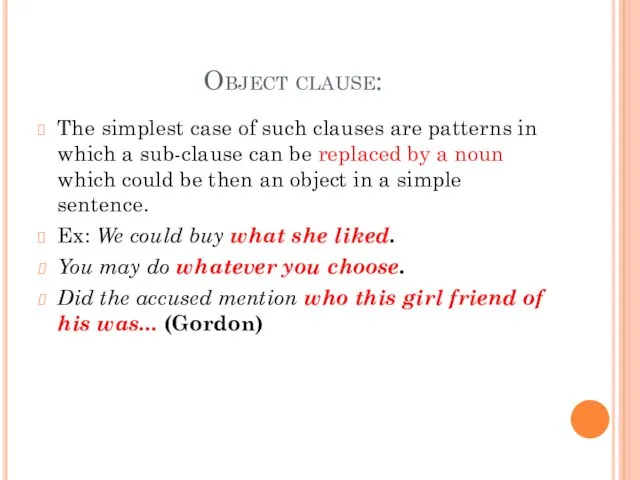
- 10. Object clause: The simplest case of such clauses are patterns in which a sub-clause can be
- 11. Attributive Clauses attributive clauses qualify the thing denoted by its head word through some actions, state
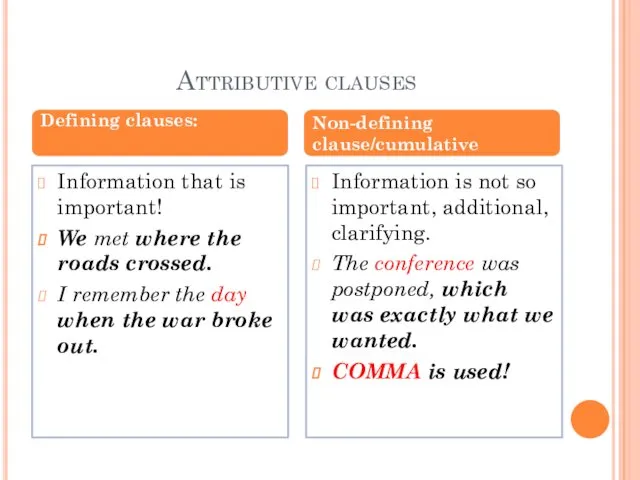
- 12. Attributive clauses Information that is important! We met where the roads crossed. I remember the day
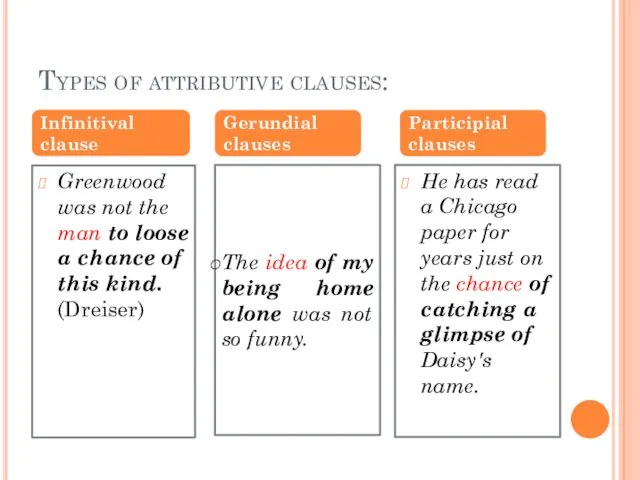
- 13. Types of attributive clauses: Greenwood was not the man to loose a chance of this kind.
- 14. Clauses of Cause indicate purely causal relations Conjunctions: Because As Since For Ex: 1.I could not
- 15. Subordinate clauses of cause have their synonymic alternatives: Infinitival nominals: She was angry now to think
- 16. Clauses of Place Clauses of place do not offer any difficulties of grammatical analysis; they are
- 17. Temporal Clauses (the clause of time) Express the Relations of time between the action of the
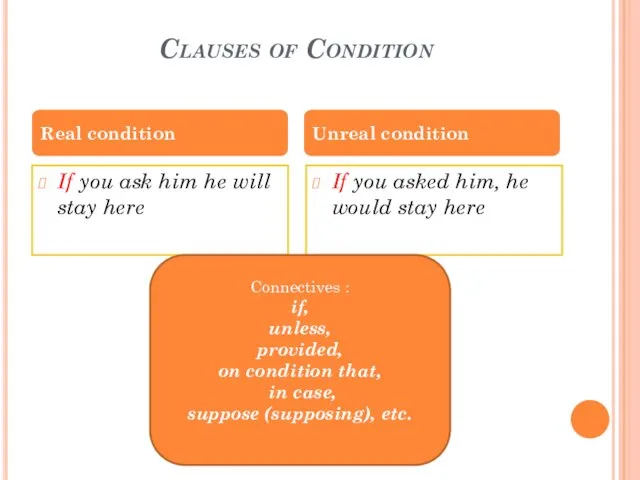
- 18. Clauses of Condition If you ask him he will stay here If you asked him, he
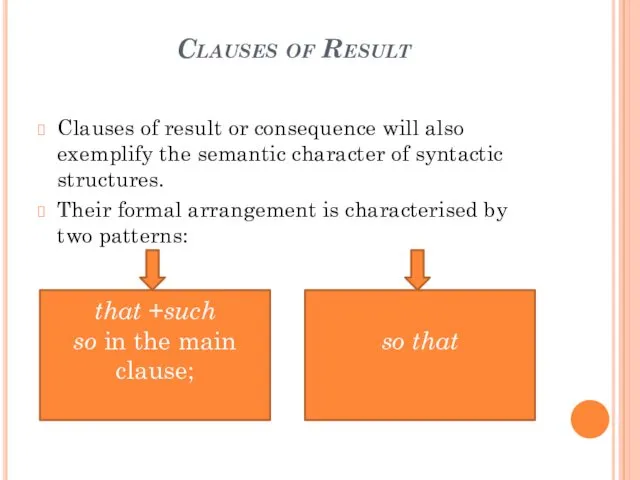
- 19. Clauses of Result Clauses of result or consequence will also exemplify the semantic character of syntactic
- 20. Examples of the Clauses of Result: Her misery was so terrible that she pinned it on
- 21. Clauses of Purpose Clauses expressing purpose are known to be introduced by the conjunction: that lest
- 22. Clauses of Concession - уступка though – хотя, although, nevertheless He extracted great happiness, though it
- 23. Clauses of Manner and Comparison as - как Sub-clauses of manner and comparison characterise the action
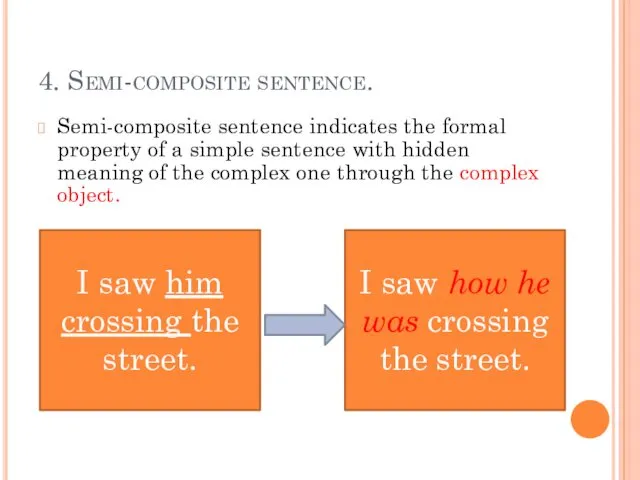
- 24. 4. Semi-composite sentence. Semi-composite sentence indicates the formal property of a simple sentence with hidden meaning
- 25. Practical tasks: Identify the types of subordinate clauses: If you have already made such arrangements I
- 26. Practical task – continuation 9. They tried to help, though it gave much pain. 10. I
- 28. Скачать презентацию

















 Модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты
Модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты Types of questions in english
Types of questions in english Filofei Leszczynski
Filofei Leszczynski (Academic) IELTS PREPARATION WORKSHOP. Henry Robinson (NIS, Shymkent)
(Academic) IELTS PREPARATION WORKSHOP. Henry Robinson (NIS, Shymkent) Письмо другу
Письмо другу The seventh continent
The seventh continent Countries and nationalities
Countries and nationalities Issues of translation of official documents. Lecture 8
Issues of translation of official documents. Lecture 8 Guess the word
Guess the word The noun
The noun Farm animals 2
Farm animals 2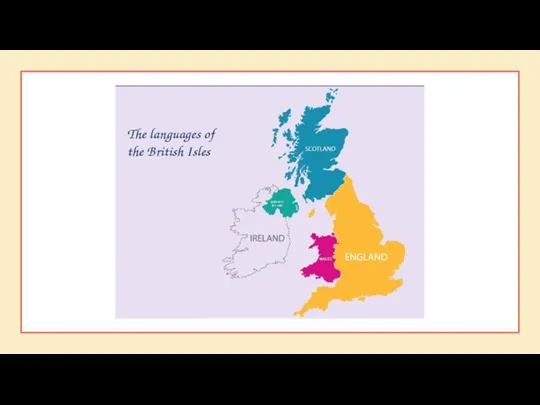 Languages. Answer the
Languages. Answer the The Beatles music
The Beatles music American Families
American Families Australia. Flag and National Emblem
Australia. Flag and National Emblem Module 5. Art & Literature. Lesson 5f
Module 5. Art & Literature. Lesson 5f House
House The middle english period
The middle english period Single Round Robin
Single Round Robin IELTS/TOEFL. SAT/ACT
IELTS/TOEFL. SAT/ACT Fruit And Vegetable Riddles Fun Activities Games
Fruit And Vegetable Riddles Fun Activities Games English for kids
English for kids The english alphabet a-i. Game 1
The english alphabet a-i. Game 1 Canadian english (Mainland)
Canadian english (Mainland) Contrastive lexicology 6. Pragmatic connotation, irony, understatement, hyperbole, oxymora
Contrastive lexicology 6. Pragmatic connotation, irony, understatement, hyperbole, oxymora Form of government
Form of government Wonders of nature
Wonders of nature Edgar Degas
Edgar Degas