The Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL) describes computational linguistics as the
scientific study of language from a computational perspective.
Computational linguistics (CL) combines resources from linguistics and computer science to discover how human language works.
Computational linguists create tools for important practical tasks such as Machine translation, Natural language interfaces to computer systems, Speech recognition, Text to speech generation, Automatic summarization, E-mail filtering, Intelligent search engines .
What is computational linguistics?








 Going Shopping. Shopping Vocabulary
Going Shopping. Shopping Vocabulary American major cities
American major cities parts-of-the-house-ppt-flashcards-fun-activities-games-games-picture-desc_51437
parts-of-the-house-ppt-flashcards-fun-activities-games-games-picture-desc_51437 Gastronomic kaleidoscope
Gastronomic kaleidoscope Welcome to Great Britain
Welcome to Great Britain The Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous Tense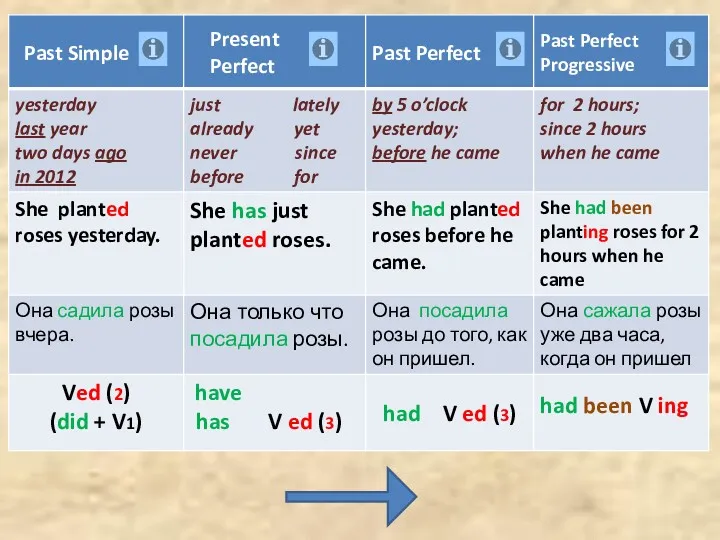 Past Simple Present Perfect
Past Simple Present Perfect How the police operate in England
How the police operate in England Present perfect и past simple
Present perfect и past simple Лексические проблемы перевода
Лексические проблемы перевода Sounds and Letters
Sounds and Letters Guessing game
Guessing game The famous writers of Great Britain
The famous writers of Great Britain She's got blue eyes
She's got blue eyes [i] [i:] [ɔ] [ɔ:]
[i] [i:] [ɔ] [ɔ:] Present Simple. Настоящее постоянное время
Present Simple. Настоящее постоянное время Los Angeles
Los Angeles The Solar System
The Solar System Правила пользования симулятором для подготовки к устной части по английскому языку ЕГЭ. Вариант 4
Правила пользования симулятором для подготовки к устной части по английскому языку ЕГЭ. Вариант 4 Перевод на русский язык английских имен собственных
Перевод на русский язык английских имен собственных This person is
This person is Swimming. It’s my life
Swimming. It’s my life Гастрит. Условные предложения. Виды условных предложений
Гастрит. Условные предложения. Виды условных предложений Speaking Games (тренажёр)
Speaking Games (тренажёр) Роль учителя в развитии навыков говорения на уроках английского языка в начальной школе
Роль учителя в развитии навыков говорения на уроках английского языка в начальной школе My toys. (Module 4, lesson 45)
My toys. (Module 4, lesson 45) Do the test to check if you understand Present Tenses + Past Simple (active, passive)
Do the test to check if you understand Present Tenses + Past Simple (active, passive) There is a parlamentary republic in the Italy
There is a parlamentary republic in the Italy