Содержание
- 2. Introduction-con’t John Stacey Adams behavioral psychologist ‘Give and take affair’
- 3. Introduction Equity- fair and being impartial calls for a fair balance to be struck between an
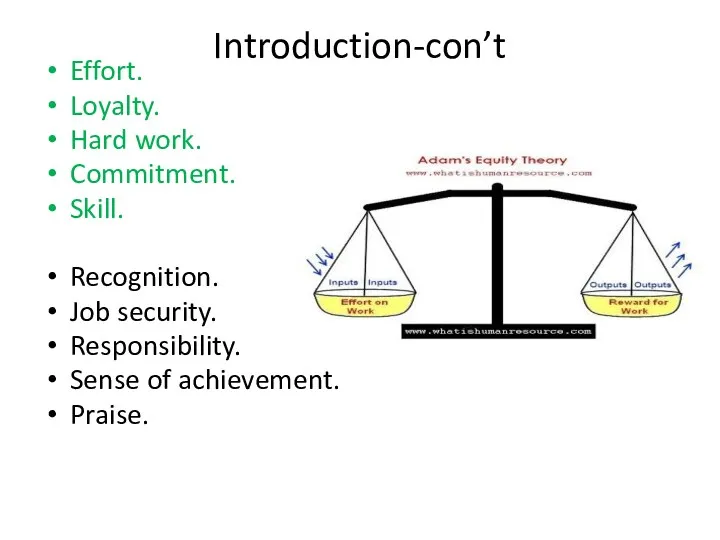
- 4. Introduction-con’t Effort. Loyalty. Hard work. Commitment. Skill. Recognition. Job security. Responsibility. Sense of achievement. Praise.
- 5. M.Deutsch’s notions about the determinants of the justice value base: In cooperative relations in which economic
- 6. Inequity in social exchange Relative deprivation – felt injustice: response discrepancy between what is perceived to
- 7. Inequity in social exchange Antecedents of inequity: inputs (recognition and relevance) outcomes (positive/negative valence and recognition
- 8. Inequity in social exchange Consequences of inequity, cognitive dissonance approach: the presence of IQ in Person
- 9. Equity, equality, and need as a basis of distributive justice justice equity ≈ Morton Deutsch: it
- 10. Equity, equality, and need as a basis of distributive justice The sense of injustice. Grounds (M.
- 12. Скачать презентацию








 Historical attractions of Kyiv
Historical attractions of Kyiv English tenses. Указатели времени
English tenses. Указатели времени A Lesson About Jobs
A Lesson About Jobs Participles phrasal verb “check”
Participles phrasal verb “check” Употребление местоимений some, any
Употребление местоимений some, any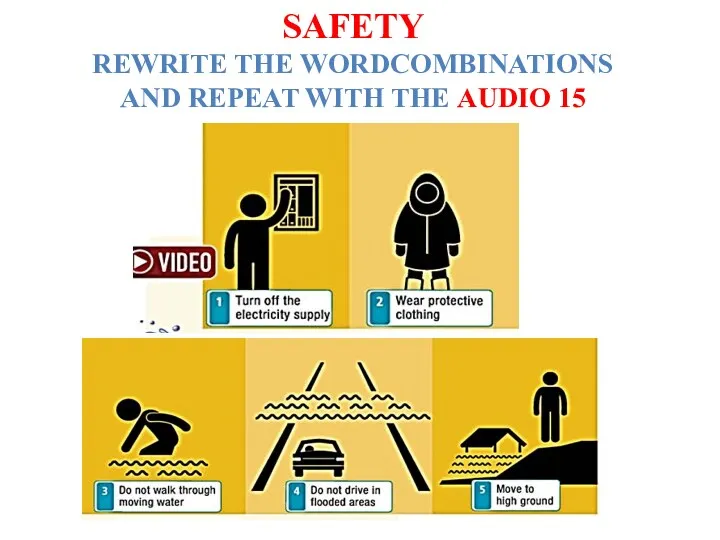 Safety
Safety The Verb
The Verb Consolidation Unit 1. Preparation For Testing
Consolidation Unit 1. Preparation For Testing Appearance. Well - dressed, elegant
Appearance. Well - dressed, elegant My holidays. 2 класс
My holidays. 2 класс Countable or Uncountable?
Countable or Uncountable? Rainbow Art Pointillism
Rainbow Art Pointillism Eсonomy of Belarus
Eсonomy of Belarus Switzerland the country of peace
Switzerland the country of peace Jeopardy Game - Great Britain
Jeopardy Game - Great Britain Условные предложения
Условные предложения The judicial system of Great Britain
The judicial system of Great Britain Creating a survey about the hobbies of either family and friends or of the class or the whole school
Creating a survey about the hobbies of either family and friends or of the class or the whole school The present simple Tense
The present simple Tense Changes to LPDIMM Rev 02
Changes to LPDIMM Rev 02 Английские идиомы. Трудности перевода
Английские идиомы. Трудности перевода Irregular verbs make
Irregular verbs make Family conflicts
Family conflicts Физминутки и игры на уроках английского языка
Физминутки и игры на уроках английского языка Special Easter Lesson
Special Easter Lesson Typical English House
Typical English House How about jogging
How about jogging Animals
Animals