Содержание
- 2. is a system of expressing a generalised grammatical meaning by means of paradigmatic correlation of grammatical
- 3. grammatical category is generally represented by at least two grammatical forms, otherwise it cannot exist Singular
- 4. A grammatical category is a unit of grammar based on a morphological opposition of grammatical meanings
- 5. Grammatical categories may be influenced by the lexical meaning
- 6. The most general meanings rendered by language and expressed by systemic correlations of word-forms are interpreted
- 7. is a system of expressing the grammatical meaning through the paradigm of grammatical forms expressed by
- 8. For example, the class of nouns has the grammatical meaning of thingness. table its individual lexical
- 10. explicitly The book reads well Implicitly lexico-grammatical meanings of countability / non-countability of nouns Grammatical meaning
- 11. is the sum total of all the formal means constantly employed to render this or that
- 12. Synthetic Types. Inflexions (actor, studying) Sound-alternation (mouse – mice, meet - met ) Analytical Types (extra
- 13. The paradigmatic correlations of grammatical forms in a category are exposed by the so-called "grammatical oppositions"
- 14. The minimal (two-member) opposition is called binary.
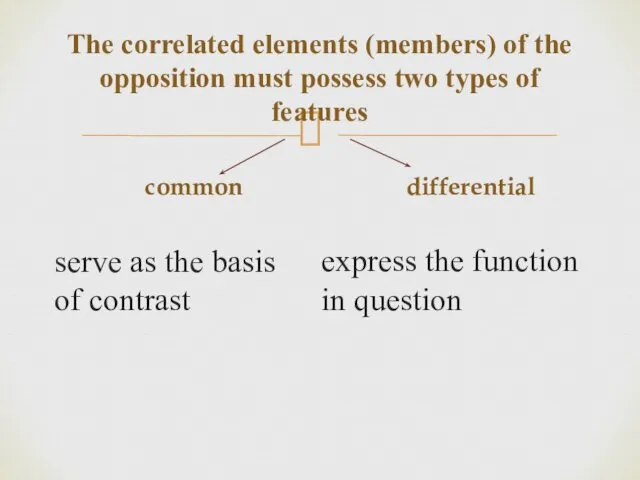
- 15. The correlated elements (members) of the opposition must possess two types of features common serve as
- 16. Privative Equipollent Gradual Types of oppositions were established in phonology
- 17. One member has a certain distinctive feature. This member is called marked, or strong (+). The
- 18. both members of the opposition are marked opposition is formed by a contrastive pair or group
- 19. members of the opposition differ by the degree of certain property strong - stronger - strongest
- 20. morphological oppositions unlike those of phonological oppositions possess both the plane of expression and the plane
- 21. one member of an opposition can be used in the position of the other Reduction of
- 23. Скачать презентацию



















 Food commodities. Offal introduction
Food commodities. Offal introduction Object pronouns
Object pronouns English-speaking countries
English-speaking countries Colours. Click pn the options
Colours. Click pn the options Friendship. Who is a true friend?
Friendship. Who is a true friend? In harmony with myself
In harmony with myself Present Simple. Настоящее неопределенное время
Present Simple. Настоящее неопределенное время Фразовый глагол to get
Фразовый глагол to get My idol-Gina Carano
My idol-Gina Carano Phrasal verbs. Get
Phrasal verbs. Get Let`s celebrate. Module 5b
Let`s celebrate. Module 5b Time. What time is it
Time. What time is it Michael Jackson
Michael Jackson Semantics. Introduction to English linguistics
Semantics. Introduction to English linguistics Passive voice
Passive voice Cheetah. Appearance. Hunting
Cheetah. Appearance. Hunting Music in our life. Урок английского языка в 10 классе
Music in our life. Урок английского языка в 10 классе Augmented reality
Augmented reality Spelling. Vocabulary. Present simple. Past simple. Future simple
Spelling. Vocabulary. Present simple. Past simple. Future simple Tell the truth
Tell the truth The Present Simple Tense
The Present Simple Tense Jobs
Jobs ВПР. 7 класс. Английский язык. Задание 3. Как описать картинку
ВПР. 7 класс. Английский язык. Задание 3. Как описать картинку Present simple tense. Настоящее простое время
Present simple tense. Настоящее простое время Основы перевода. Уровни перевода и переводческие трансформации
Основы перевода. Уровни перевода и переводческие трансформации Robert Burns
Robert Burns Обучение написанию делового и личного письма на английском языке
Обучение написанию делового и личного письма на английском языке City of London
City of London