Содержание
- 2. Today at our classes we study and practice Gerund: its formation and use; get information and
- 3. STUDY THE TERMS: 1. изобретать 2. делать, производить 3. запустить 4. смесь 5. испытывать 6. делать
- 4. STUDY THE WORD EQUIALENTS: 1. A small device 2.To make bright or brighter 3. Absolutely necessary
- 5. GERUND ГЕРУНДИЙ Неличная форма глагола (non-finite form of the verb) выражает название действия и обладает признаками
- 6. Функции герундия в предложении Drinking tea is good – подлежащее, I hate making people cry –
- 7. Герундий в английском языке можно переводить: Существительным, которое передает процесс (reading – чтение, walking – прогулка,
- 8. Make up sentences using gerund 1.She is interested a) being ill. 2.We really enjoy b) laughing
- 9. Quotations: “If you think that you are able to do something, you are right. If you
- 10. INVENTIONS New inventions appear every day to make our lives easier, longer, warmer, faster, and so
- 11. OUTSTANDING INVENTORS OF RUSSIA For thousands of years people's mode of life was primitive. In a
- 12. Alexander Fedorovich Mozhaisky Mozhaisky's aero plane was the 1st in the world. 1825 -1890. Was a
- 13. Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev in 1869. All future discoveries in the field of chemistry and physics are
- 14. Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky Tsiolkovsky is the father of rocket flying. He worked out the theory of
- 15. Igor Ivanovich Sikorsky A helicopter and aircraft designer. 1889 - 1972 Igor Sikorsky was considered to
- 16. VLADIMIR ZWORYKIN Russian inventor, Vladimir Zworykin invented kinescope in 1929. Zworykin was one of the first
- 17. Sergei Pavlovich Korolyov S. Korolyov devoted his life to rocket research, constructing artificial satellites. 1907 -
- 18. Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov Born in 1921 Sakharov an outstanding scientist and public figure worked on hydrogen
- 19. ANDREW KONSTANTINOVICH NARTOV (1693 – 1756) born in Moscow Was a “personal turner” of Peter I
- 20. IVAN KULIBIN (1735— 1818) was born in Nizhniy Novgorod Russian mechanic and self-educated person designed clocks
- 21. PYOTR KOZMICH FROLOV (1775—1839) worked in Altai, studied Primary Metal Manufacturing (металлургическое производство) founded a Picture
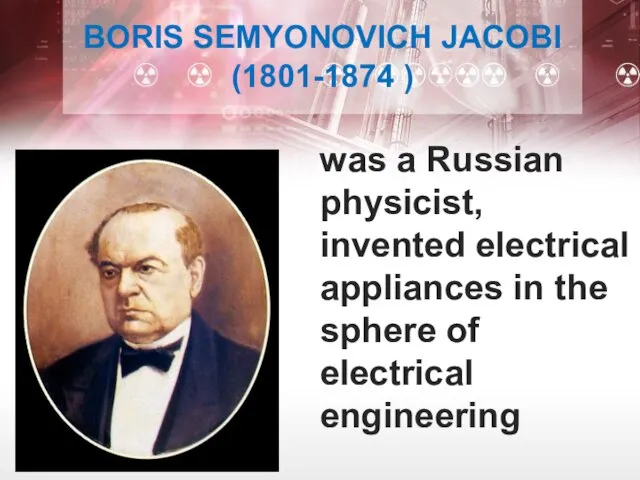
- 22. BORIS SEMYONOVICH JACOBI (1801-1874 ) was a Russian physicist, invented electrical appliances in the sphere of
- 23. ALEXANDER STEPANOVICH POPOV (1859 -1906) was a Russian physicist invented radio
- 24. Useful sites for you: http://inventors.about.com http://subscribe.ru/archive/history.izobretatel/200607/24125712.html http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sgQzD7ALVnc http://rangevoting.org/BInventions.html http://englishrussia.com/tag/russian-inventions/
- 25. unsatisfaction irritation anxiety fear sadness boredom What emotions do you feel after our lesson ? joy
- 26. Hometask: Portfolio “Great Russian scientists” (biography, main inventions, their meaning in the development of Russian science.
- 28. Скачать презентацию
























 Our grammar school program for this year
Our grammar school program for this year Артикли A и The
Артикли A и The Past progressive tense
Past progressive tense The Speech Mechanism
The Speech Mechanism Present Indefinite (simple) Tense. Настоящее Неопределенное (простое) Время
Present Indefinite (simple) Tense. Настоящее Неопределенное (простое) Время Диалоги о Лондоне. Урок английского языка в 5 классе
Диалоги о Лондоне. Урок английского языка в 5 классе Fitness. A sound mind in a sound body
Fitness. A sound mind in a sound body Времена группы past
Времена группы past Conditionals
Conditionals Tongue twisters
Tongue twisters Present perfect. Active or passive
Present perfect. Active or passive Tag questions wasn’t he
Tag questions wasn’t he English lesson (конспект 3)
English lesson (конспект 3) The formation of aesthetic values in elementary school students on the example of Gorodets painting
The formation of aesthetic values in elementary school students on the example of Gorodets painting The Future of Nuclear Energy: Nuclear Safety and Security
The Future of Nuclear Energy: Nuclear Safety and Security Smiles. 4 класс 1 урок
Smiles. 4 класс 1 урок CANADA
CANADA Morphological structure of the english word. English word-formation. Compound words. Lecture 2
Morphological structure of the english word. English word-formation. Compound words. Lecture 2 Speaking activity using adjectives ed and ing conversation topics dialogs
Speaking activity using adjectives ed and ing conversation topics dialogs Освітній округ Шлях до успіху. Розвиток міжнародних відносин. Подорож до Англії
Освітній округ Шлях до успіху. Розвиток міжнародних відносин. Подорож до Англії Music in our Life
Music in our Life Present настоящее, Past прошедшее, Tenses Времена, Future будущее
Present настоящее, Past прошедшее, Tenses Времена, Future будущее Introduction to Articulatory Phonetics. The production of speech: The Physiological Aspect
Introduction to Articulatory Phonetics. The production of speech: The Physiological Aspect The philosophy of education. (Chapter 5)
The philosophy of education. (Chapter 5) My own game. Categories
My own game. Categories Гастрит. Условные предложения. Виды условных предложений
Гастрит. Условные предложения. Виды условных предложений To be going to…
To be going to… Reasons for travelling
Reasons for travelling