Содержание
- 2. Outline 2.1 Data and Software Application Concepts 2.2 Types of Information Systems and Support 2.3 Supply
- 3. Learning Objectives Understand the types of information systems and how they process data. Understand the types
- 4. 2.1 Data and Software Application Concepts Organizations have different types of information systems that collect and
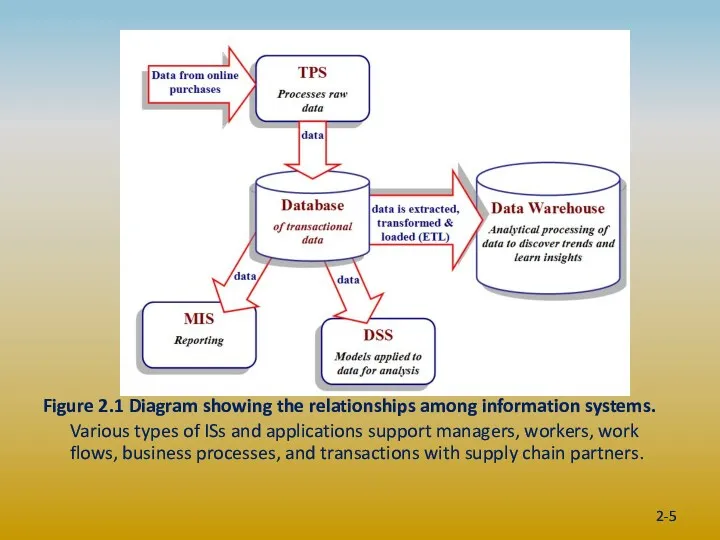
- 5. Figure 2.1 Diagram showing the relationships among information systems. Various types of ISs and applications support
- 6. Data, Information, and Knowledge Data: raw data ( details of subjects and processes) Database: stores data
- 7. 2- Figure 2.2. Example of data, information, and knowledge.
- 8. 2.2 Types of Information Systems and Support ISs classified into 2 categories based on type of
- 9. Operations support system Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) Data is processed by a TPS—e.g., sales orders, payroll,
- 10. TABLE 2.1 Business Transactions in a Manufacturing Company Payroll and personnel Employee time cards Employee pay
- 11. Operations support system Batch vs. Online Real-Time Processing Processing of transactions is done in one of
- 12. Management support system Management Information Systems (MIS) General purpose reporting systems are referred to as management
- 13. Support unstructured and semi-structured decisions, such as whether to make or buy products or what new
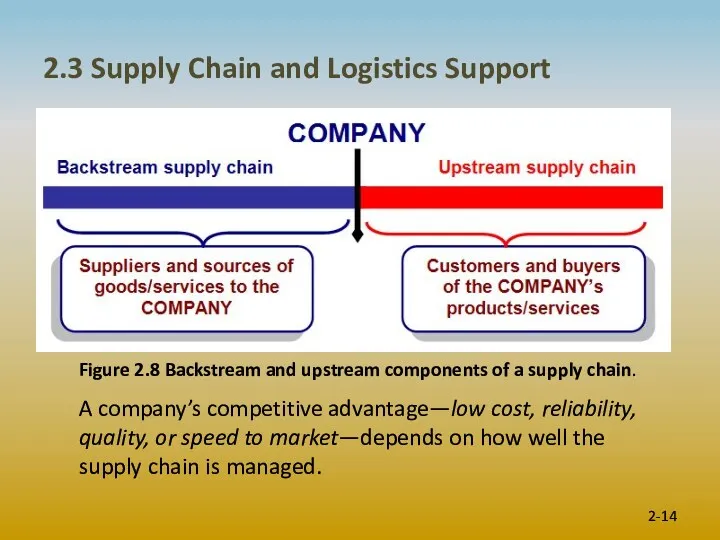
- 14. 2.3 Supply Chain and Logistics Support 2- Figure 2.8 Backstream and upstream components of a supply
- 15. Logistics & RFID Managing material and information flows to optimize supply chain operations. Logistics has been
- 16. Wal-Mart’s Global Sourcing Strategy for its Backstream Supply Chain Because Wal-Mart has thousands of suppliers and
- 17. 2.4 IT Infrastructures, Cloud Computing, & Services A company’s IT infrastructure determines the workload that its
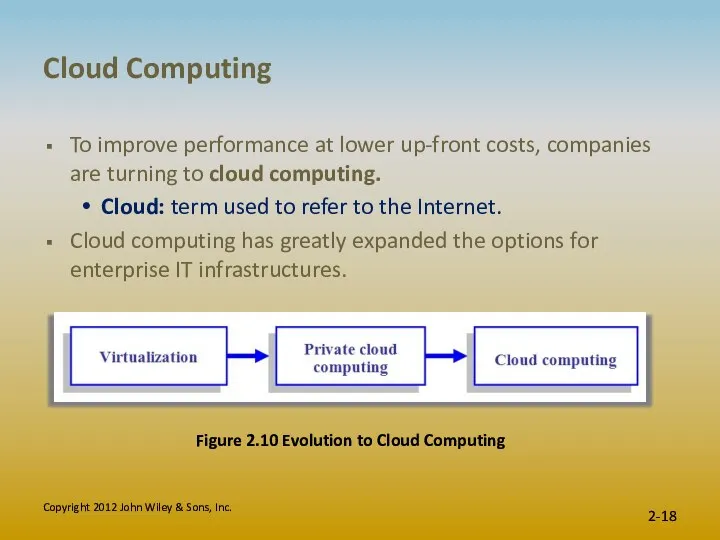
- 18. Cloud Computing To improve performance at lower up-front costs, companies are turning to cloud computing. Cloud:
- 19. IT at Work U.S. government spent about $68.1 billion in 2012 on IT, with 1/3 spent
- 20. What Services are Available in the Cloud? Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): popular IT model in which software is
- 21. Moving to the Cloud raises questions Which workloads should be exported to the cloud? Which set
- 22. Cloud computing limitations & trade-offs Cloud computing runs on a shared infrastructure so the arrangement is
- 23. Link Library Blog on cloud computing http://infoworld.com/blogs/david-linthicum Planners Lab, for building a DSS http://plannerslab.com Supply Chain
- 25. Скачать презентацию
















 A critical analysis of the basic concepts of post-nonclassical stage of scientific development
A critical analysis of the basic concepts of post-nonclassical stage of scientific development Compound Nouns
Compound Nouns Event Met Gala
Event Met Gala Writing a Summary of an Article/Text
Writing a Summary of an Article/Text English Lesson. Peer pressure
English Lesson. Peer pressure Adverbs of frequency
Adverbs of frequency Passive Voice Страдательный залог
Passive Voice Страдательный залог Pregnancy and bad habits
Pregnancy and bad habits Expressive means of language
Expressive means of language Проект Мое любимое животное 3 класс
Проект Мое любимое животное 3 класс Общий вопрос
Общий вопрос Adjective in English
Adjective in English Guitar music
Guitar music Проект по английскому язык. Англия
Проект по английскому язык. Англия Глагол to be
Глагол to be Spotlight 7. Module 4. In the news
Spotlight 7. Module 4. In the news My favorite places to visit in Moscow
My favorite places to visit in Moscow Phonetic drill
Phonetic drill Forget + to inf
Forget + to inf Указатели Past Simple
Указатели Past Simple National dishes of Germany
National dishes of Germany Английский язык (ОГЭ): написание электронного письма
Английский язык (ОГЭ): написание электронного письма Сослагательное наклонение и страдательный залог
Сослагательное наклонение и страдательный залог The past simple tense
The past simple tense My family and I
My family and I Урок английского языка в 5 классе
Урок английского языка в 5 классе Russian Federation
Russian Federation Rural tourism in France
Rural tourism in France