Содержание
- 2. Lecture 1 “Phonetics as a Branch of Linguistics” 1. Theoretical phonetics as a science 2. Branches
- 3. References: Соколова М.А.Теоретическая фонетика английского языка. М.1996 Леонтьева С.Ф. Теоретическая фонетика английского языка. М.1988 Dickushina D.
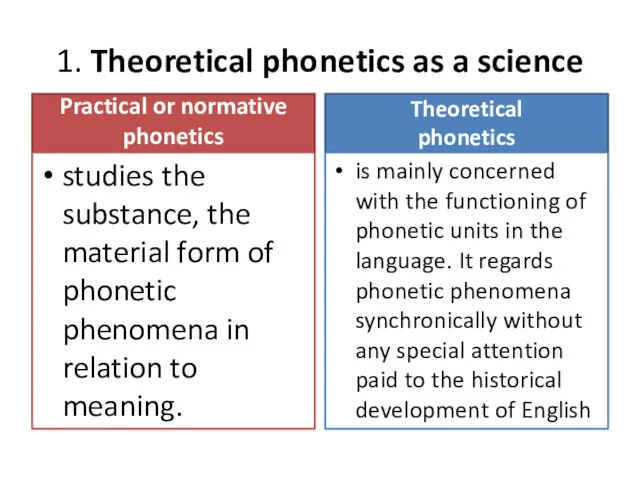
- 4. 1. Theoretical phonetics as a science Practical or normative phonetics studies the substance, the material form
- 5. Definition of theoretical phonetics (TP) The term phonetics comes from the Greek word φωνή (phõnē) meaning
- 6. The origin of Phonetics Baudouin de Courtenay (1845-1929) was the first one who introduced the term
- 7. Theoretical phonetics studies only such sound sequences, which are produced by a human vocal apparatus, which
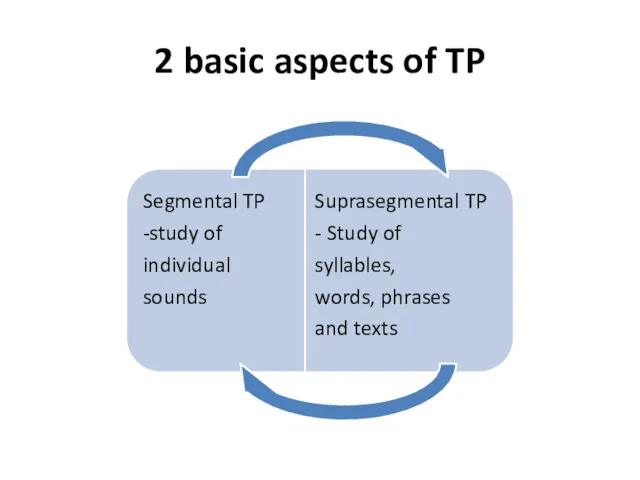
- 8. 2 basic aspects of TP
- 9. What is ‘norm’ in English phonetics? What do we imply for the term ’norm’?
- 10. A norm in English phonetics ‘Norm’ is a "neutral" style. ‘Norm’ is a complex of all
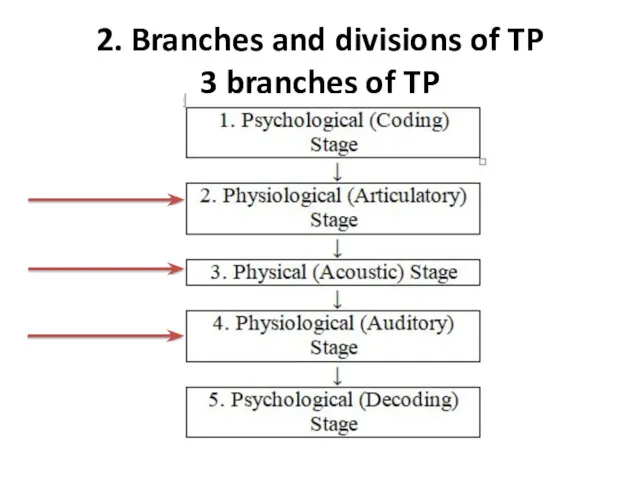
- 11. 2. Branches and divisions of TP 3 branches of TP
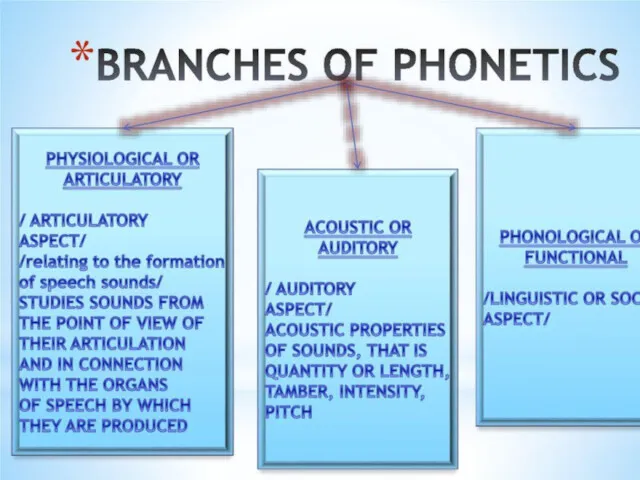
- 12. Articulatory phonetics is the branch of phonetics “which is concerned with the study, description and classification
- 13. Acoustic phonetics is the branch of phonetics that studies the physics of the air vibrating between
- 14. Auditory phonetics is the branch of phonetics which main concern is the investigation of the hearing
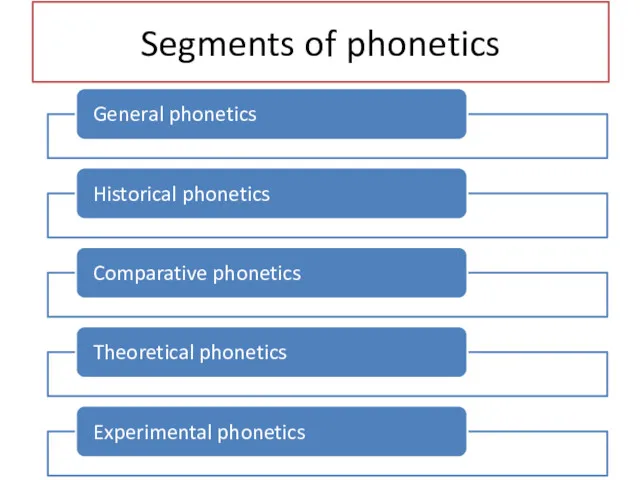
- 16. Segments of phonetics
- 17. General phonetics is a section studying all the sound-producing possibilities of human speech apparatus (organs) in
- 18. Historical phonetics is a section that traces and establishes the successive changes in the phonetic system
- 19. Comparative phonetics studies the correlation between the phonetic systems of two or more languages, especially kindred
- 20. Theoretical phonetics deals with theoretical problems of a particular language. It gives students the latest theories
- 21. Experimental phonetics is a section that studies various phonetic phenomena in the laboratory conditions by means
- 22. 3. Methods in Phonetics 1) direct observation method; 2) experimental method; 3) instrumental methods; 4) method(s)
- 23. The direct observation method is the method of observing the facts of a language in their
- 24. The experimental method is the method of obtaining data and facts of a language through constructing
- 25. Instrumental methods are sometimes called experimental, which is not quite correct because, on the one hand,
- 26. The method(s) of phonological analysis (sometimes called proper linguistic method or functional method of phonetics) includes
- 27. 4. Phonetics and Other Disciplines What are the branches of other linguistic study where Phonetics can
- 28. Phonetics and Grammar 1) the differences in pronunciation of morpheme -ed after voiced and voiceless consonants
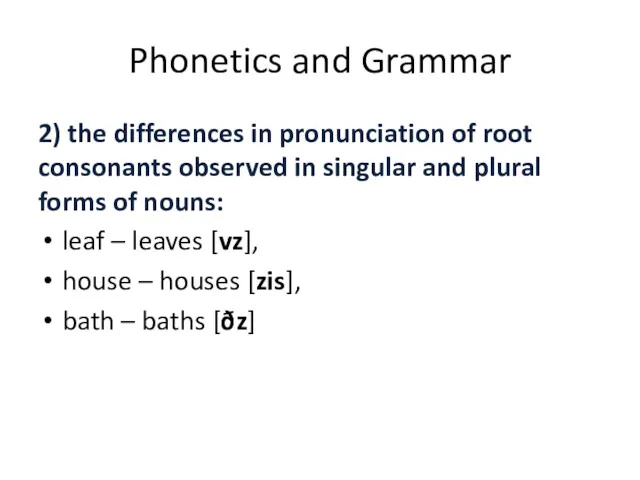
- 29. Phonetics and Grammar 2) the differences in pronunciation of root consonants observed in singular and plural
- 30. Phonetics and Grammar 3) the vowel interchanges helping to distinguish the singular and plural forms of
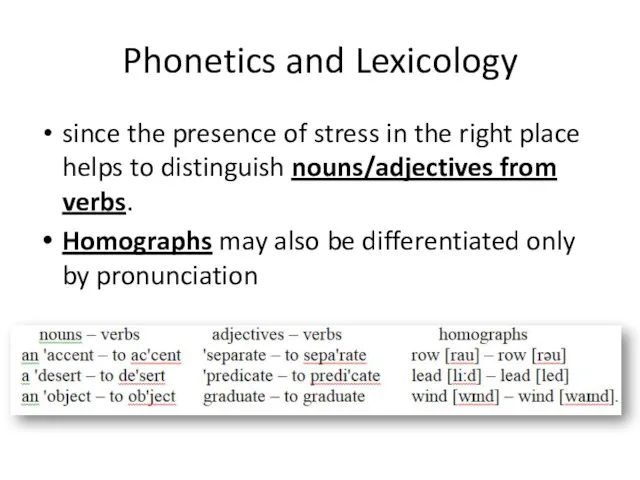
- 31. Phonetics and Lexicology since the presence of stress in the right place helps to distinguish nouns/adjectives
- 32. Theoretical phonetics and Stylistics Intonation patterns (the purpose of the utterance) Rhythm and rhyme Alliteration and
- 33. 5. Phonetics vs Phonology The field of science that studies phonemes is called phonology (the term
- 34. Various views on Phonetics and Phonology “Phonetics has two main divisions; on the one hand, phonology,
- 35. Traditional view
- 36. Alternative view
- 37. Distribute into two categories – Phonetics and Phonology Sounds [a:] Phonemes Stress Accommodation Assimilation 0 reduction
- 38. Distribute into two categories Phonetics Sounds Phonemes [a:] [p] Phonology Stress Intonation Accommodation Assimilation 0 reduction
- 40. Скачать презентацию



























![Distribute into two categories – Phonetics and Phonology Sounds [a:]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/146428/slide-36.jpg)
![Distribute into two categories Phonetics Sounds Phonemes [a:] [p] Phonology Stress Intonation Accommodation Assimilation 0 reduction](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/146428/slide-37.jpg)
 Візова орієнтаційна зустріч
Візова орієнтаційна зустріч The weather forecasts are very important for people
The weather forecasts are very important for people Глагол to be
Глагол to be Present simple: learn the rule (questions)
Present simple: learn the rule (questions) Job hunting
Job hunting Образование порядковых числительных
Образование порядковых числительных Викторина по английскому языку
Викторина по английскому языку Brilliant-2, animals
Brilliant-2, animals Future simple
Future simple Help me with the weather report
Help me with the weather report Past simple regular verbs game fun activities games
Past simple regular verbs game fun activities games Modal verbs
Modal verbs Idioms
Idioms Yale university
Yale university What can you do
What can you do Valentine's Day
Valentine's Day Sport. Types of sports
Sport. Types of sports What are you going to do in summer?
What are you going to do in summer? Distinctive features of the functional styles. Lecture 10
Distinctive features of the functional styles. Lecture 10 There is/there are. 3 класс “Spotlight”
There is/there are. 3 класс “Spotlight” Do you clean the territory
Do you clean the territory The conditionals. The questions
The conditionals. The questions Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland My pet
My pet Exam practice (part 2). Tasks 1-2-3-4
Exam practice (part 2). Tasks 1-2-3-4 Как правильно употреблять предлоги и наречия места в английском языке
Как правильно употреблять предлоги и наречия места в английском языке Opposites sonic game
Opposites sonic game So many countries. so many customs
So many countries. so many customs