Содержание
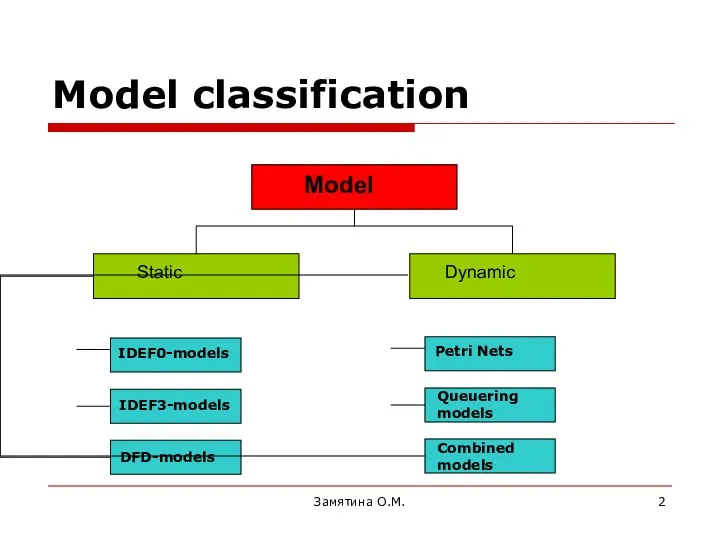
- 2. Замятина О.М. Model classification
- 3. Petri Nets Petri nets were developed in the early 1960s by Carl Adam Petri in his
- 4. What is a Petri net? 1. A bipartite graph G(V,E) where V = P υ T
- 5. 2. Marking function M. Given µ belongs to M, each µ is a function which assigns
- 6. 3. f(p) is the marking of the place p. Marking is represented on the graph with
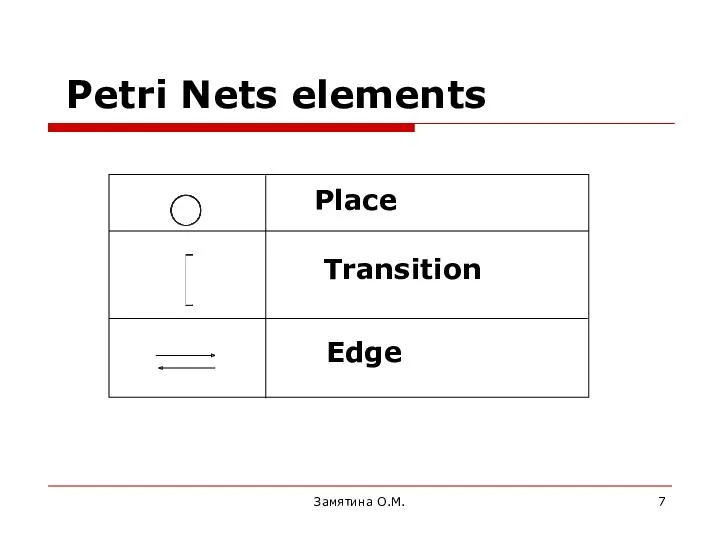
- 7. Замятина О.М. Petri Nets elements
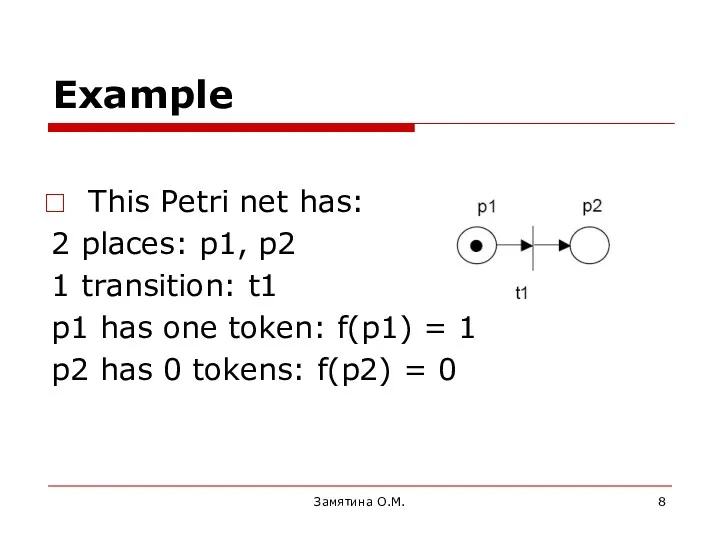
- 8. Example This Petri net has: 2 places: p1, p2 1 transition: t1 p1 has one token:
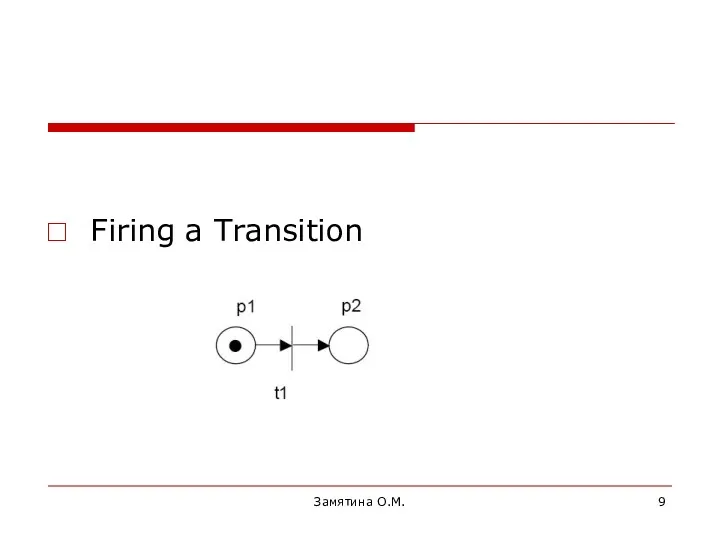
- 9. Firing a Transition Замятина О.М.
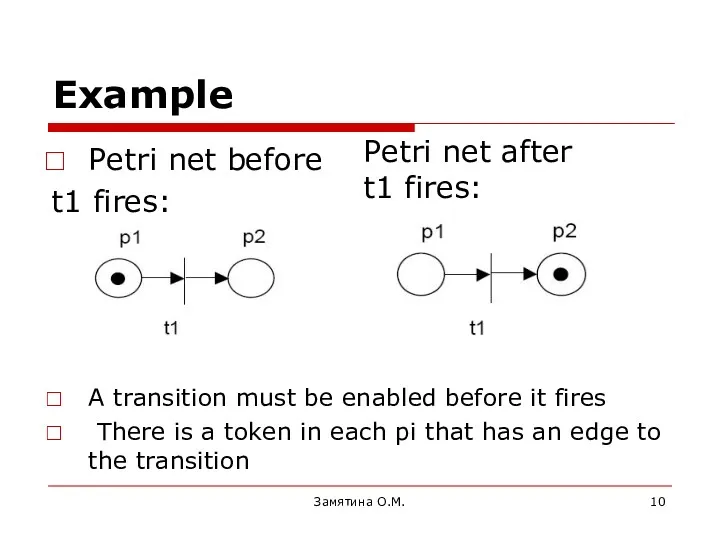
- 10. Example Petri net before t1 fires: before t1 fires: A transition must be enabled before it
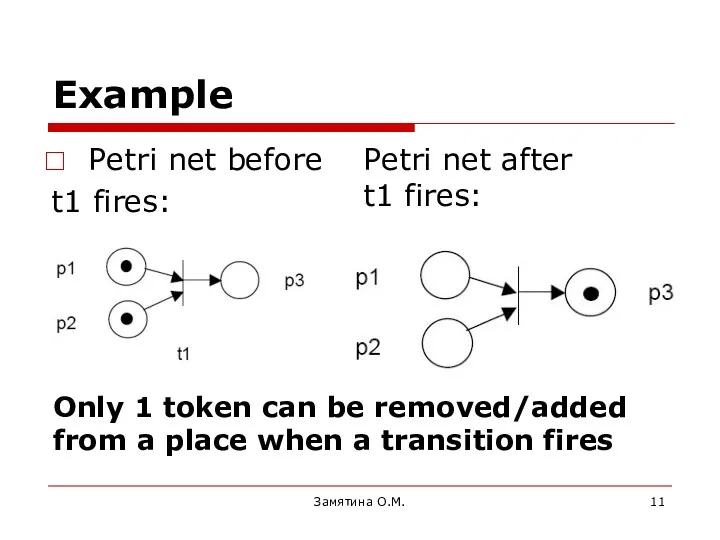
- 11. Example Petri net before t1 fires: Замятина О.М. Petri net after t1 fires: Only 1 token
- 12. Other Types of Petri Nets Petri nets have been extended over the years in many directions
- 13. Time Extended Petri nets First developed in the mid 1970s For real systems it is often
- 14. Time Extended Petri nets There are 3 basic ways to introduce time into the Petri net.
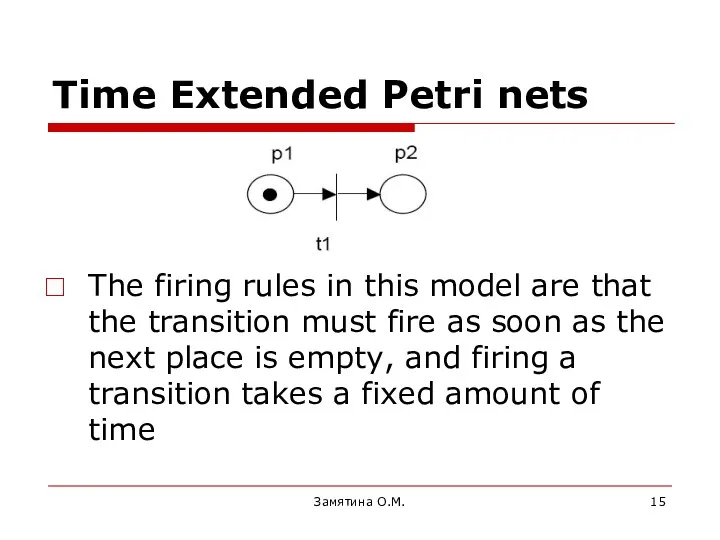
- 15. Time Extended Petri nets The firing rules in this model are that the transition must fire
- 16. Coloured Petri Nets Developed in the late 1970s by K. Jensen, “Coloured Petri nets and the
- 17. Coloured Petri Nets To represent attributes of these objects, the Petri net model is extended with
- 18. Hierarchical Petri Nets Developed in the late 1980s Specifications for real systems have a tendency to
- 19. Hierarchical Petri Nets The hierarchy construct is called a subnet A subnet is an aggregate of
- 20. Hierarchical Petri Nets Such a construct can be used to structure large processes At one level
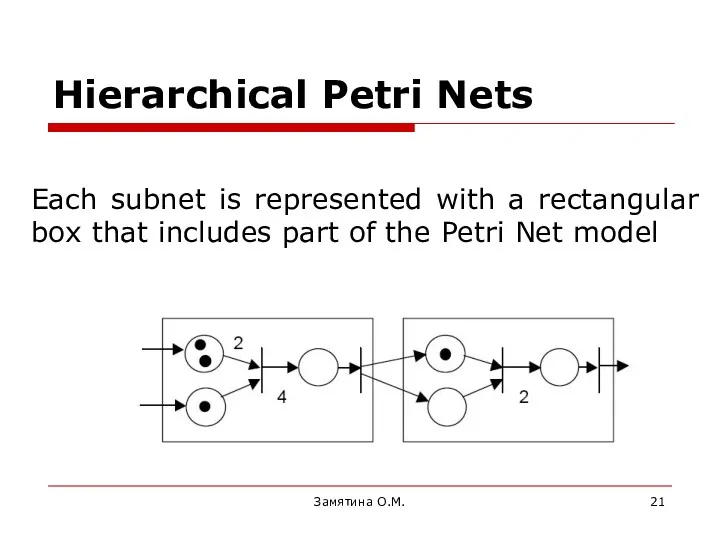
- 21. Each subnet is represented with a rectangular box that includes part of the Petri Net model
- 22. Properties of a Petri Net Terminate Does the Petri Net terminate? Immediately Reachable Is a state
- 23. Properties of a Petri Net Deadlock Is there a state in which none of the transitions
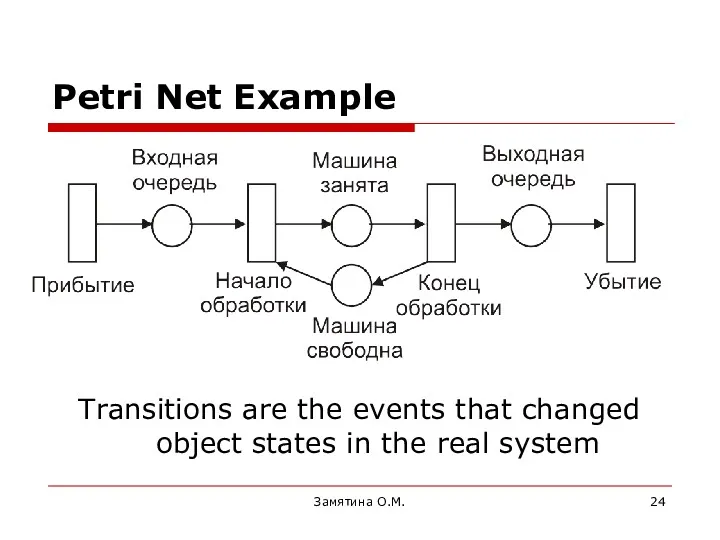
- 24. Замятина О.М. Petri Net Example Transitions are the events that changed object states in the real
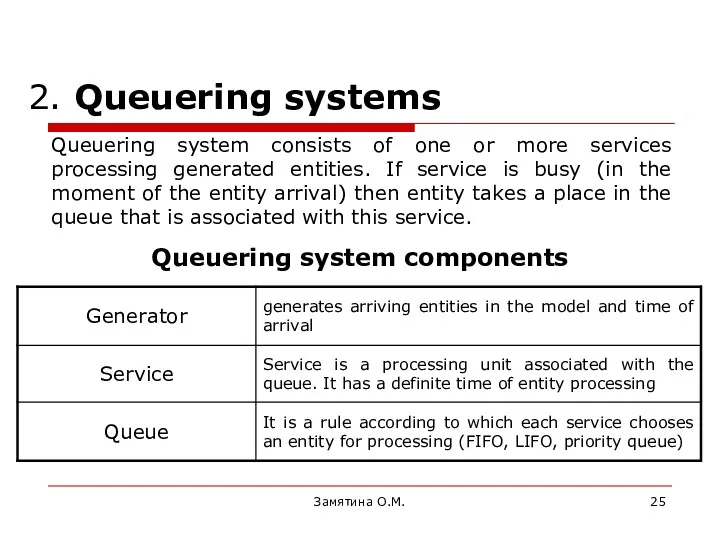
- 25. Замятина О.М. 2. Queuering systems Queuering system components Queuering system consists of one or more services
- 26. Замятина О.М. 3. Combined models Usually combined model is a complex model that is based on
- 27. Замятина О.М. Simulation tool Arena 7.0 Arena 7.0 was developed by Systems Modeling (Rockwell Software)
- 28. Замятина О.М. Arena 7.0 allows to 1. Formalize and visualize dynamics of complex processes and systems
- 29. Замятина О.М. Arena 7.0 allows to 4. Find an optimal recourses distribution (humans, equipments, finances) 5.
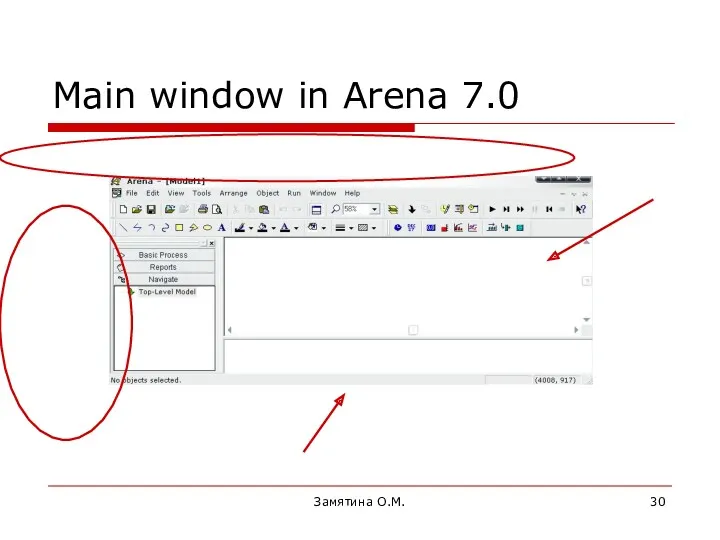
- 30. Замятина О.М. Main window in Arena 7.0
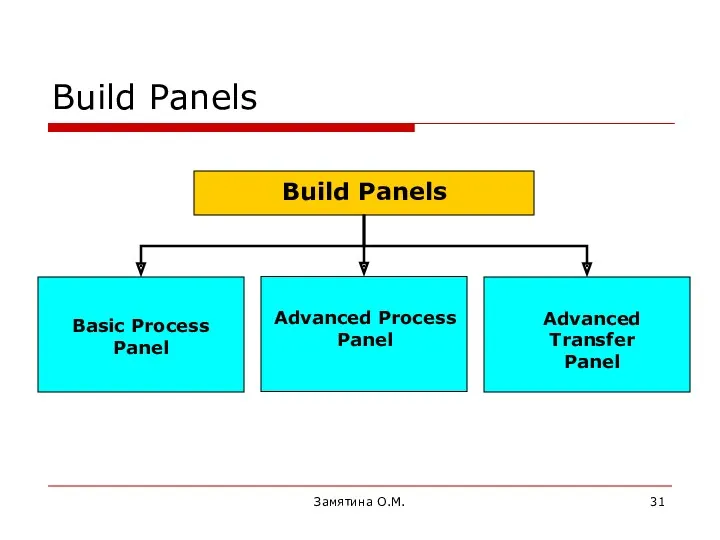
- 31. Замятина О.М. Build Panels
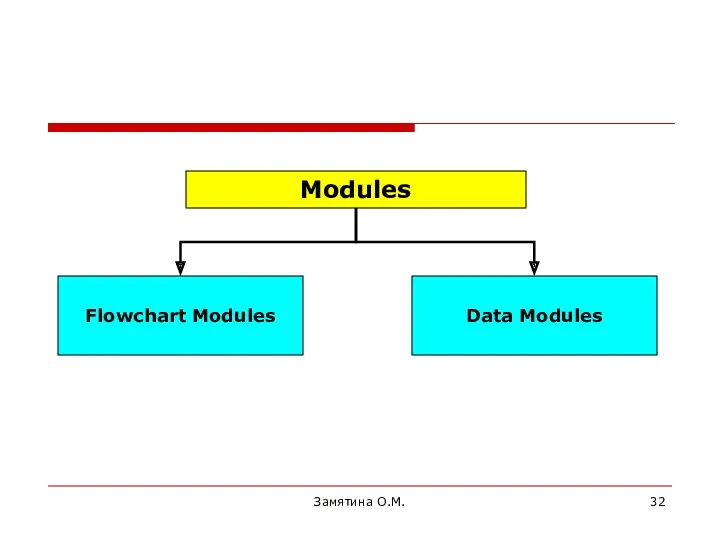
- 32. Замятина О.М. Modules
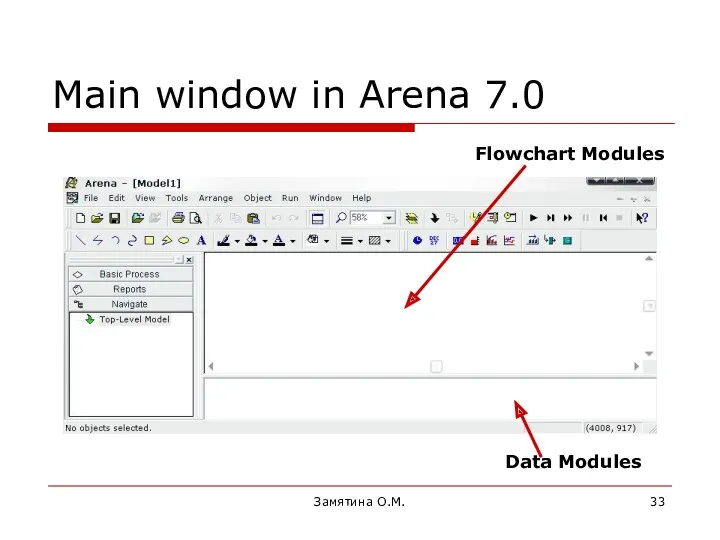
- 33. Замятина О.М. Main window in Arena 7.0 Flowchart Modules Data Modules
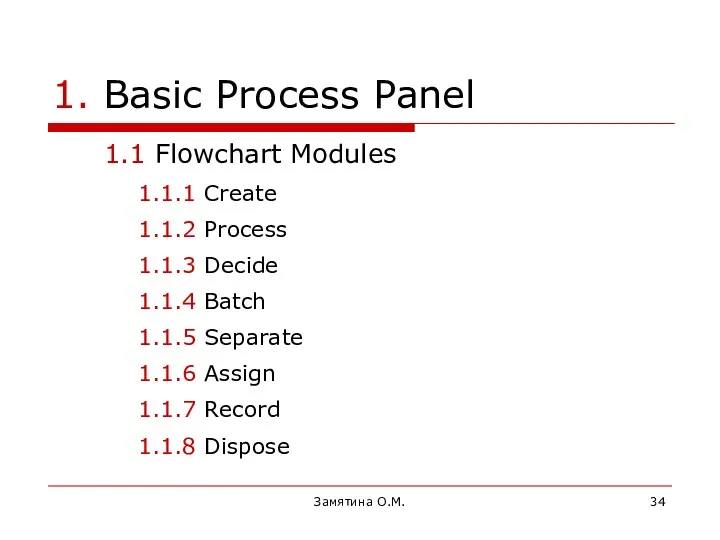
- 34. Замятина О.М. 1. Basic Process Panel 1.1 Flowchart Modules 1.1.1 Create 1.1.2 Process 1.1.3 Decide 1.1.4
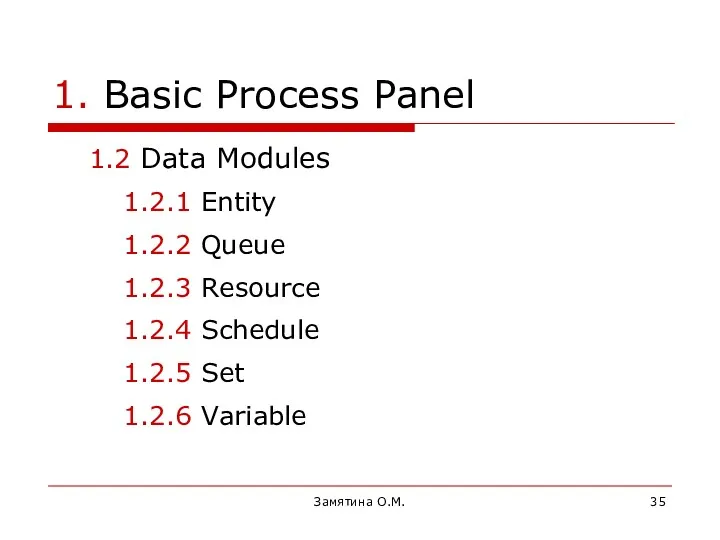
- 35. Замятина О.М. 1. Basic Process Panel 1.2 Data Modules 1.2.1 Entity 1.2.2 Queue 1.2.3 Resource 1.2.4
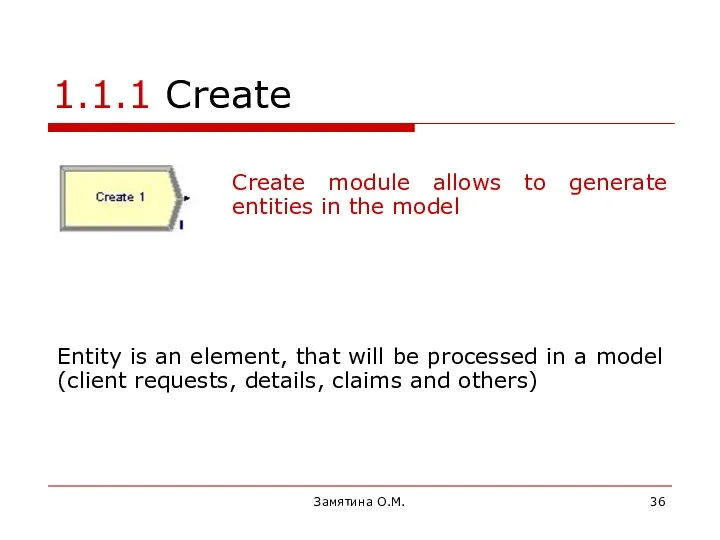
- 36. Замятина О.М. 1.1.1 Create Entity is an element, that will be processed in a model (client
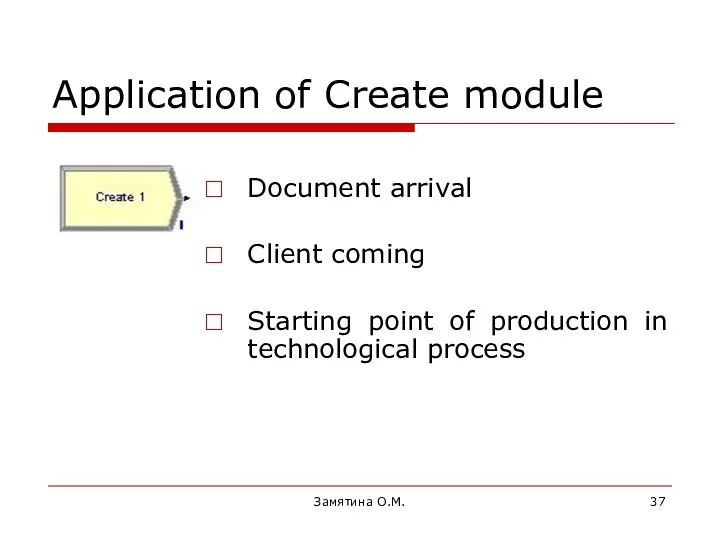
- 37. Замятина О.М. Application of Create module Document arrival Client coming Starting point of production in technological
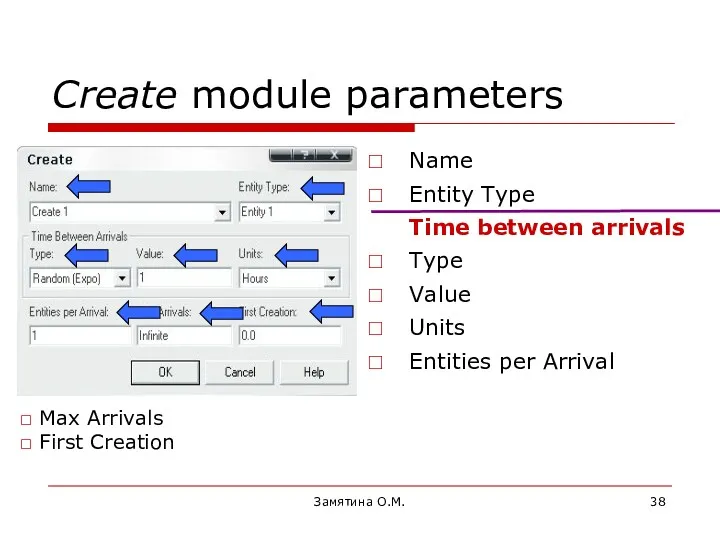
- 38. Замятина О.М. Create module parameters Name Entity Type Time between arrivals Type Value Units Entities per
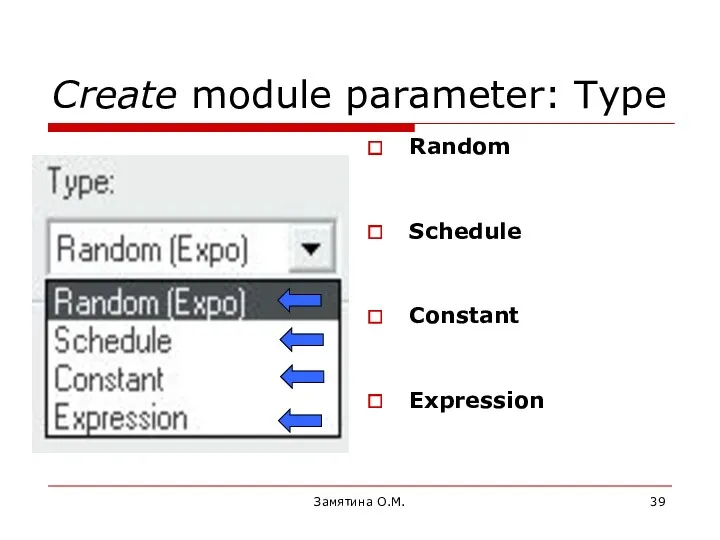
- 39. Замятина О.М. Create module parameter: Type Random Schedule Constant Expression
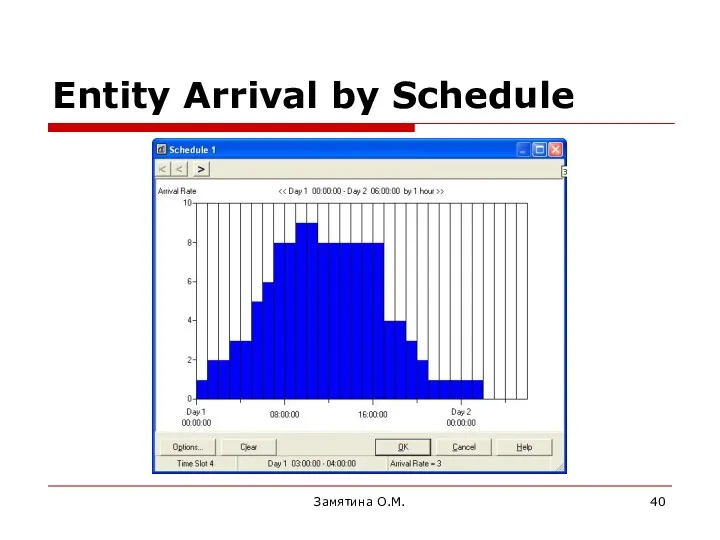
- 40. Замятина О.М. Entity Arrival by Schedule
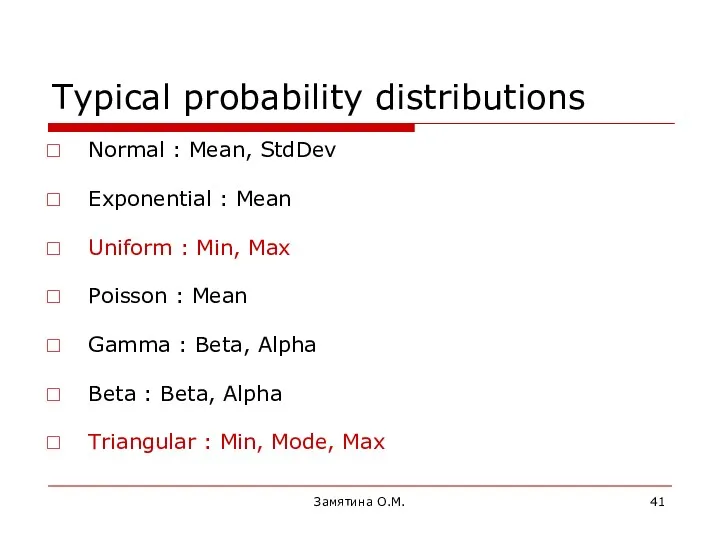
- 41. Замятина О.М. Typical probability distributions Normal : Mean, StdDev Exponential : Mean Uniform : Min, Max
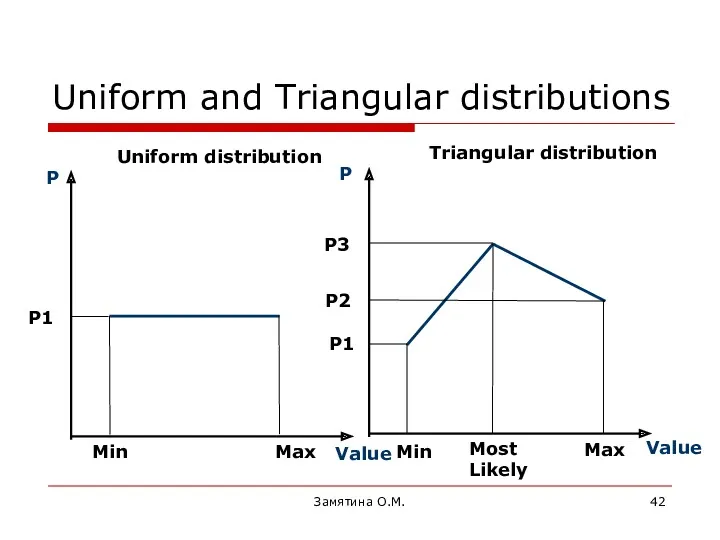
- 42. Замятина О.М. Uniform and Triangular distributions Uniform distribution Triangular distribution
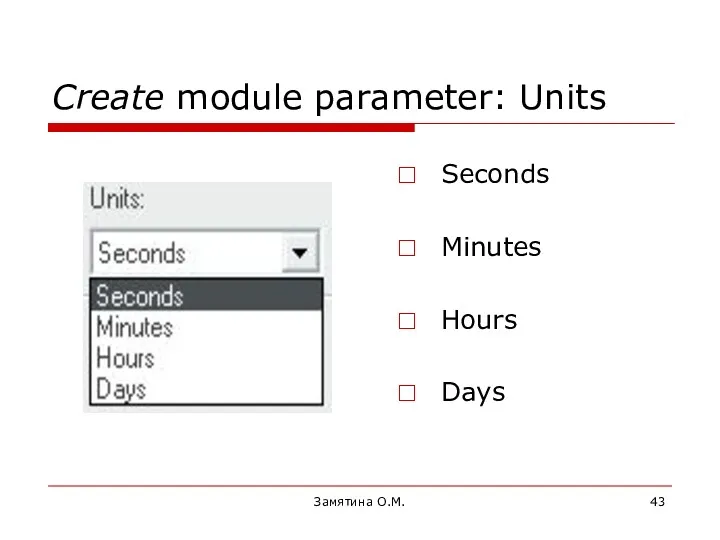
- 43. Замятина О.М. Create module parameter: Units Seconds Minutes Hours Days
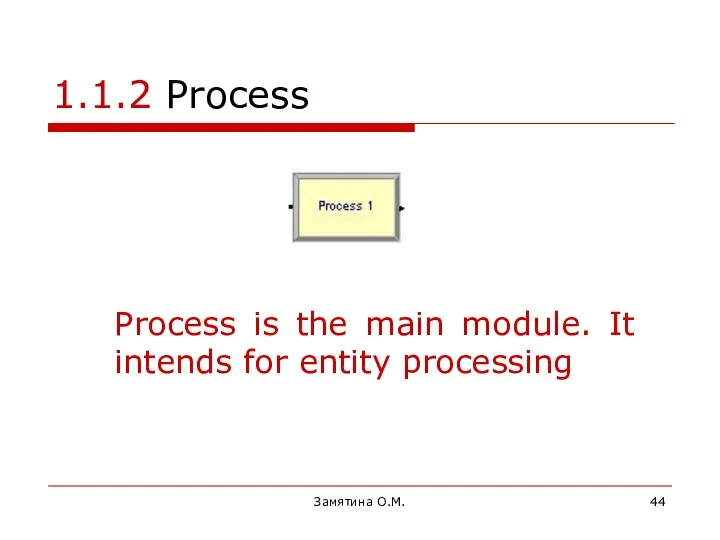
- 44. Замятина О.М. 1.1.2 Process Process is the main module. It intends for entity processing
- 45. Замятина О.М. Application of Process module Document checking Order performing Client service Part cutting
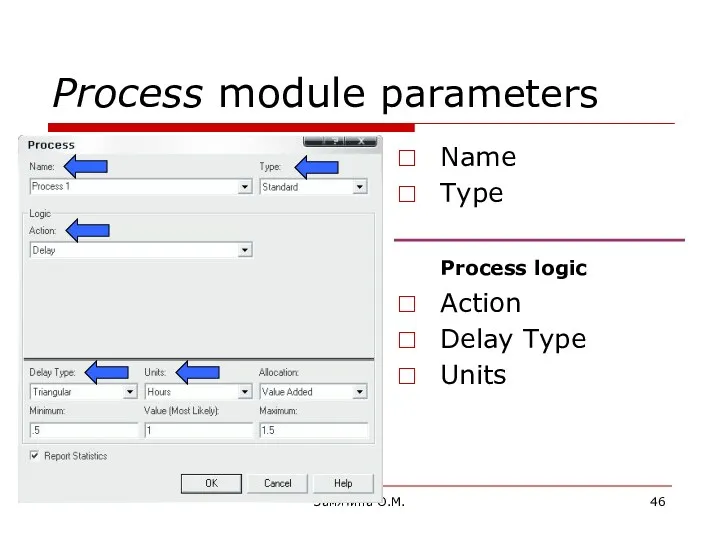
- 46. Замятина О.М. Process module parameters Name Type Process logic Action Delay Type Units
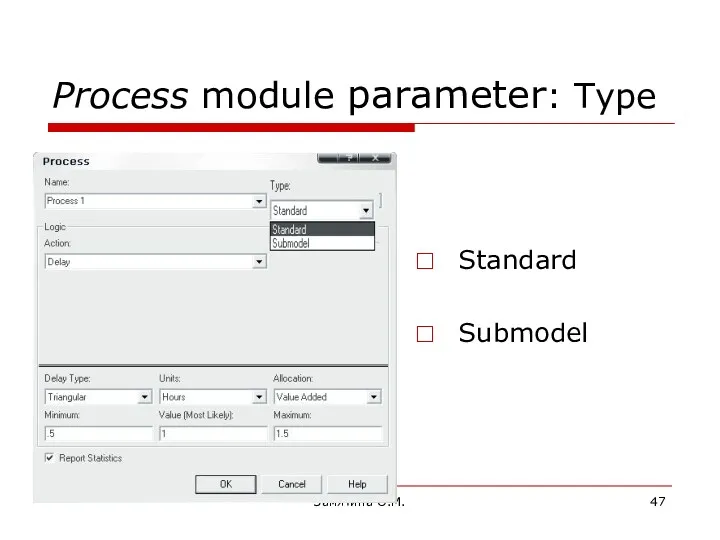
- 47. Замятина О.М. Process module parameter: Type Standard Submodel
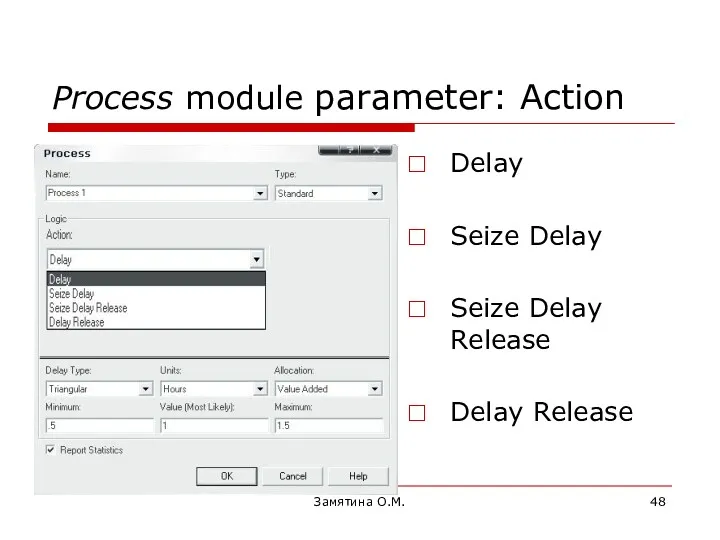
- 48. Замятина О.М. Process module parameter: Action Delay Sеize Delay Sеize Delay Release Delay Release
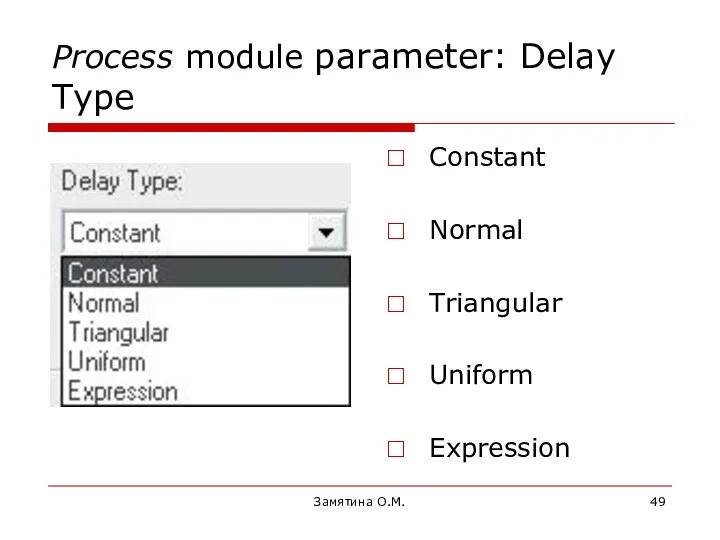
- 49. Замятина О.М. Process module parameter: Delay Type Constant Normal Triangular Uniform Expression
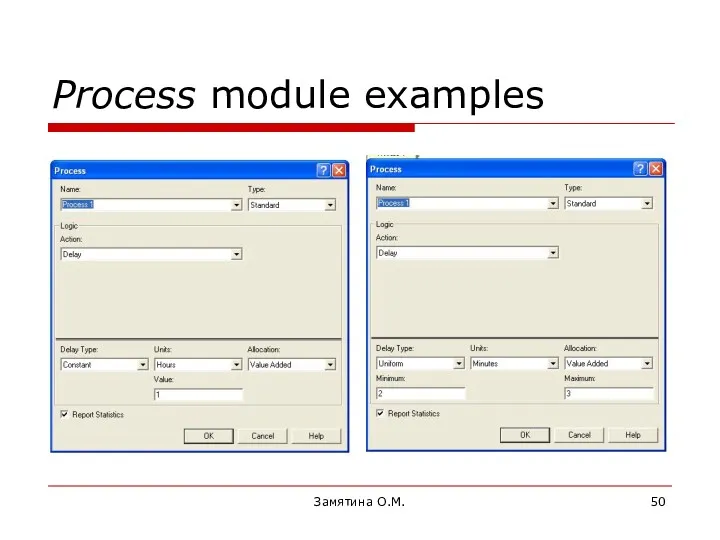
- 50. Замятина О.М. Process module examples
- 51. Замятина О.М. Process module examples
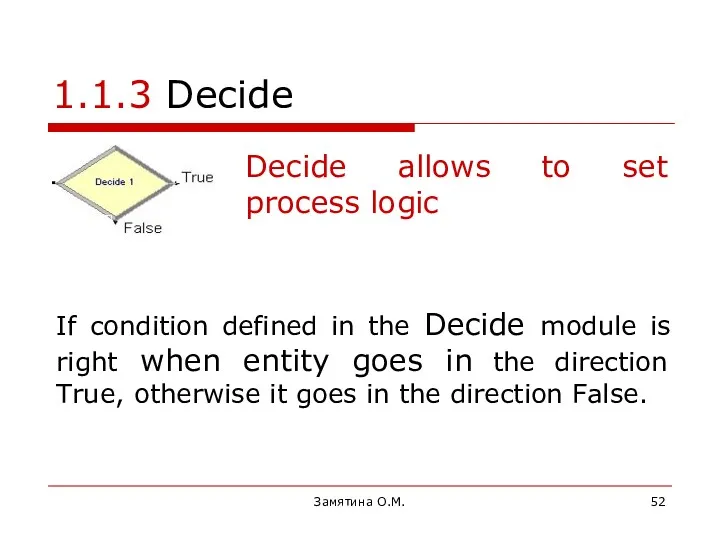
- 52. Замятина О.М. 1.1.3 Decide Decide allows to set process logic If condition defined in the Decide
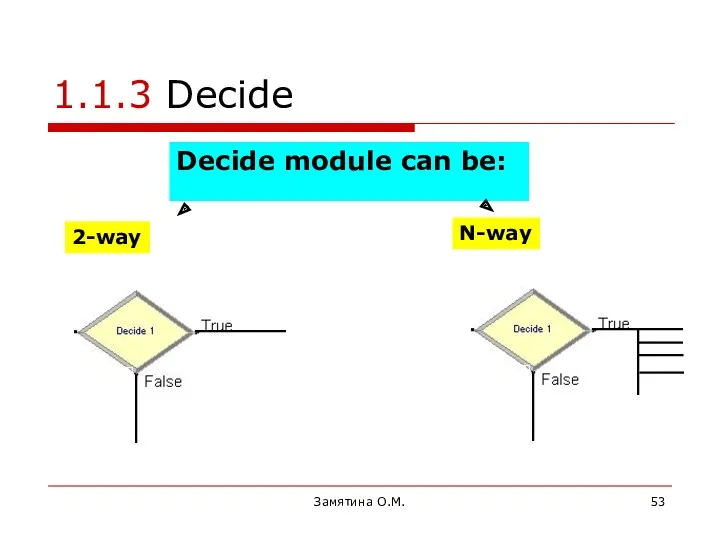
- 53. Замятина О.М. 1.1.3 Decide Decide module can be: N-way 2-way
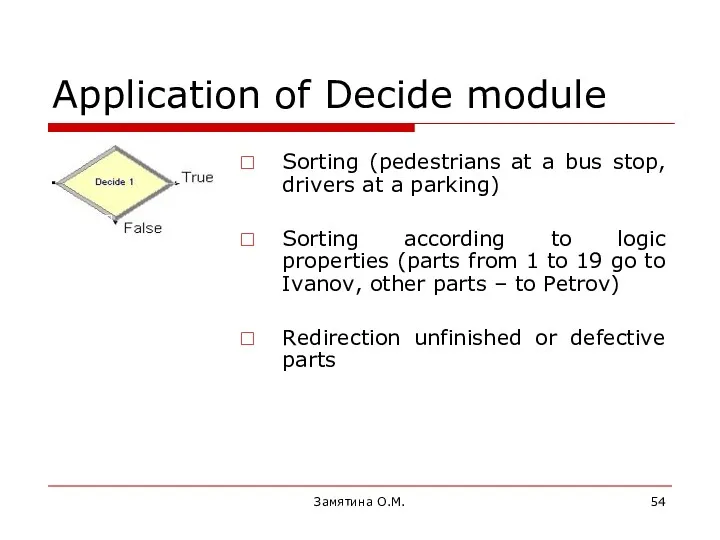
- 54. Замятина О.М. Application of Decide module Sorting (pedestrians at a bus stop, drivers at a parking)
- 55. Замятина О.М. Decide module parameters Name Type
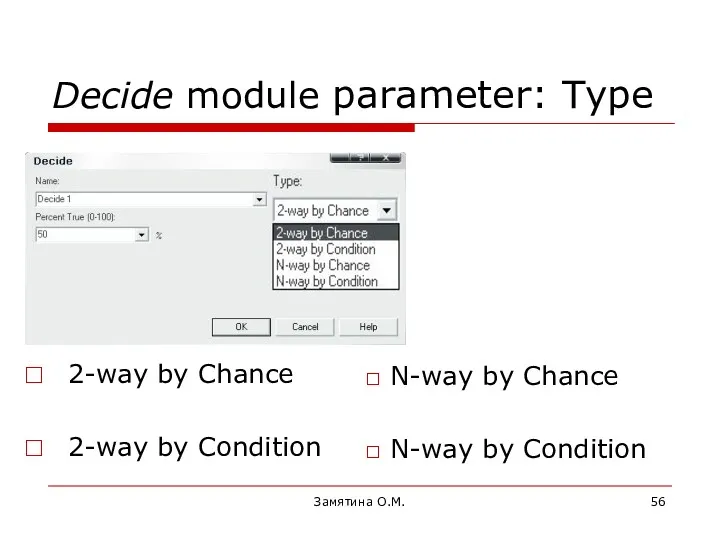
- 56. Замятина О.М. Decide module parameter: Type 2-way by Chance 2-way by Condition N-way by Chance N-way
- 57. Замятина О.М. 2-way by Chance 10 25 33 50 66 75 90
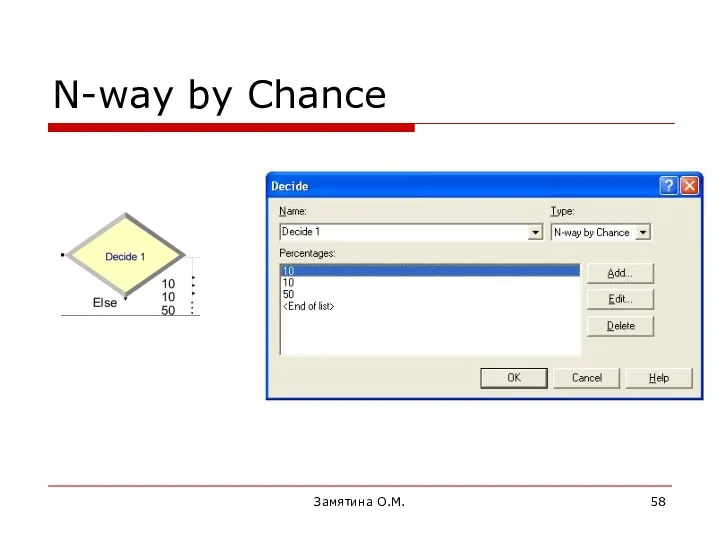
- 58. Замятина О.М. N-way by Chance
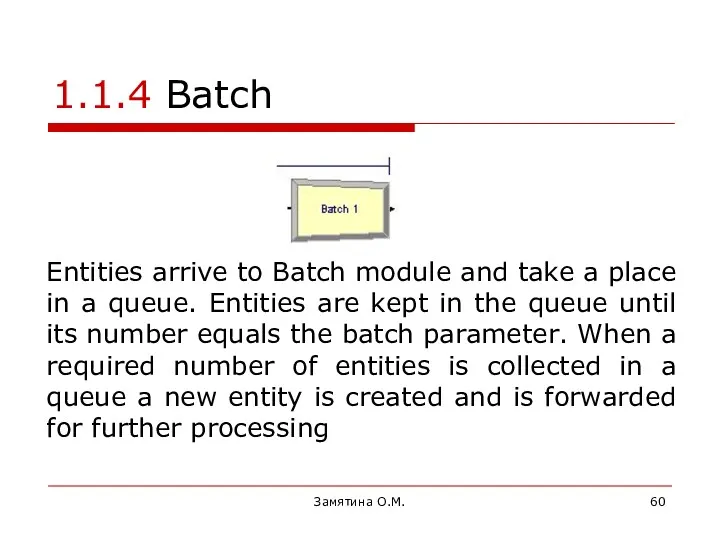
- 59. Замятина О.М. 1.1.4 Batch Batch module allows to create groups in a model
- 60. Замятина О.М. 1.1.4 Batch Entities arrive to Batch module and take a place in a queue.
- 61. Замятина О.М. Application of Batch module Collect necessary number of parts/data for their processing Collect earlier
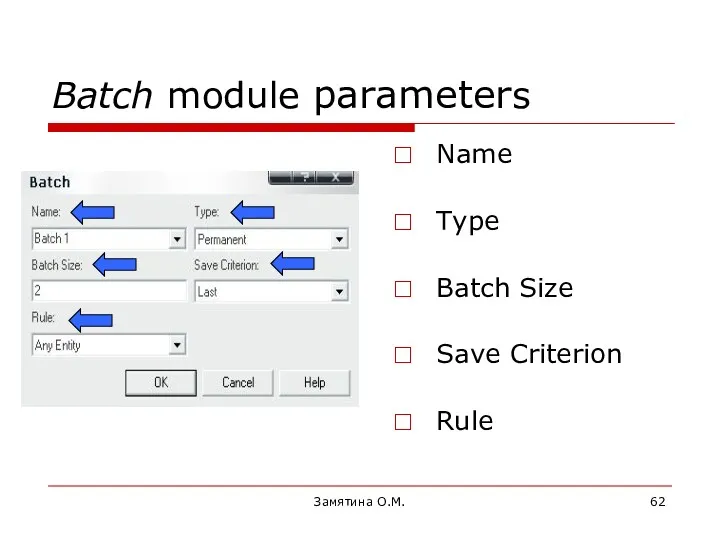
- 62. Замятина О.М. Batch module parameters Name Type Batch Size Save Criterion Rule
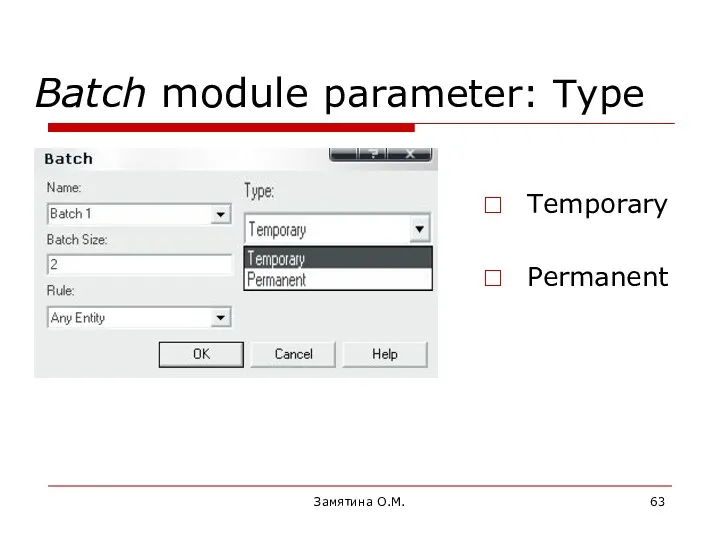
- 63. Замятина О.М. Batch module parameter: Type Temporary Permanent
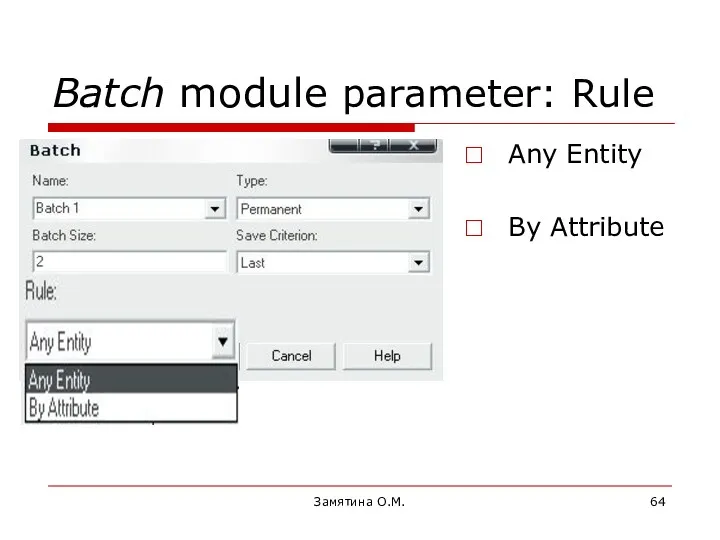
- 64. Замятина О.М. Batch module parameter: Rule Any Entity By Attribute
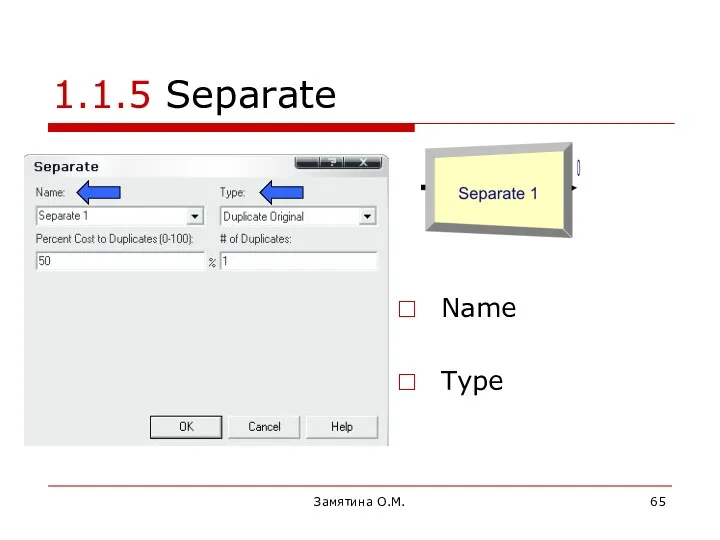
- 65. Замятина О.М. 1.1.5 Separate Name Type
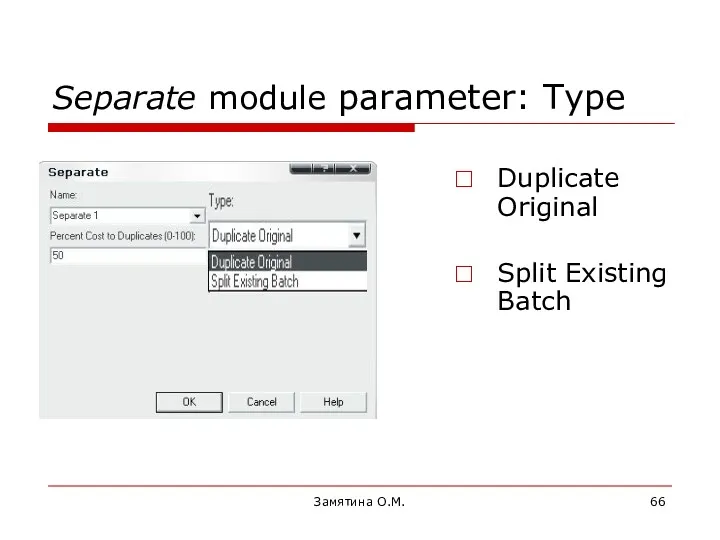
- 66. Замятина О.М. Separate module parameter: Type Duplicate Original Split Existing Batch
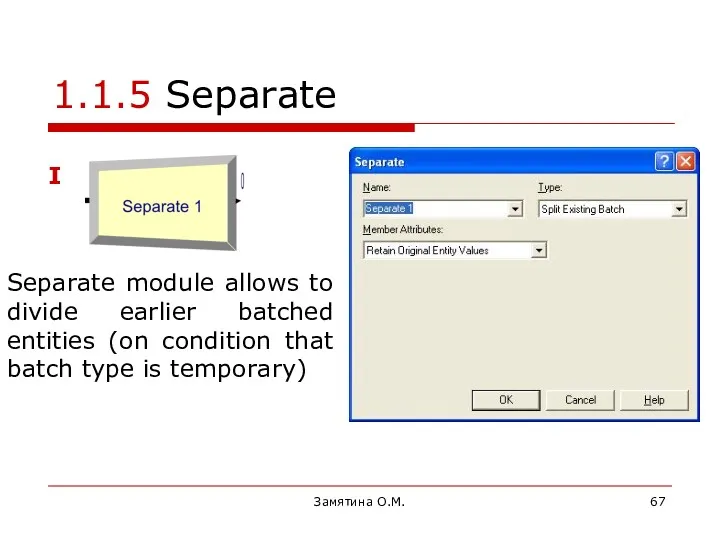
- 67. Замятина О.М. 1.1.5 Separate Separate module allows to divide earlier batched entities (on condition that batch
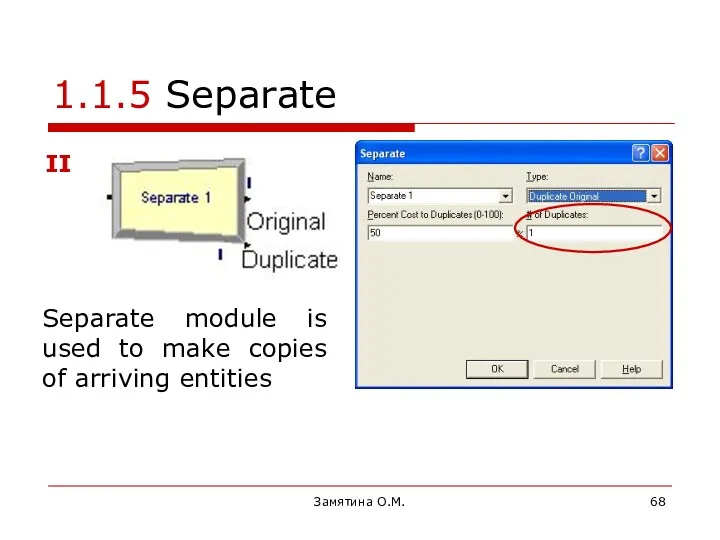
- 68. Замятина О.М. 1.1.5 Separate II Separate module is used to make copies of arriving entities
- 69. Замятина О.М. Application of Separate module Separation of earlier batched entities Parallel processing of documents (invoices)
- 70. Замятина О.М. 1.1.6 Assign Assign module allows to set new value of attributes (entity’s type, entity’s
- 71. Замятина О.М. Application of Assign module Identification of entity number Changing of animation picture Setting of
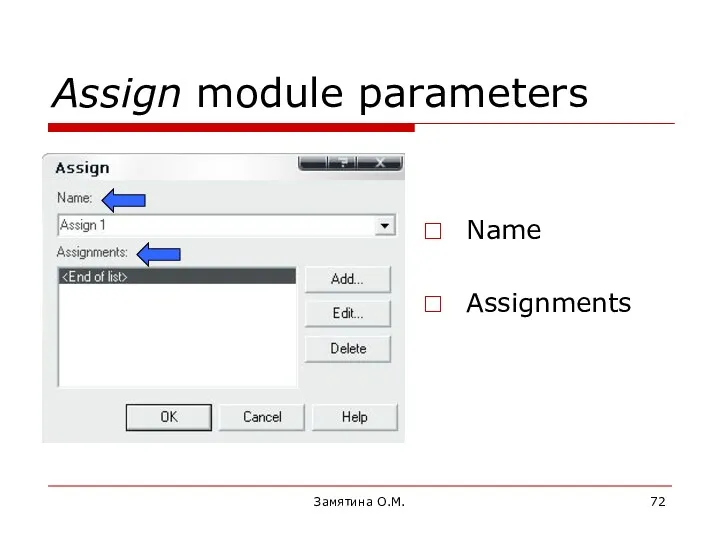
- 72. Замятина О.М. Assign module parameters Name Assignments
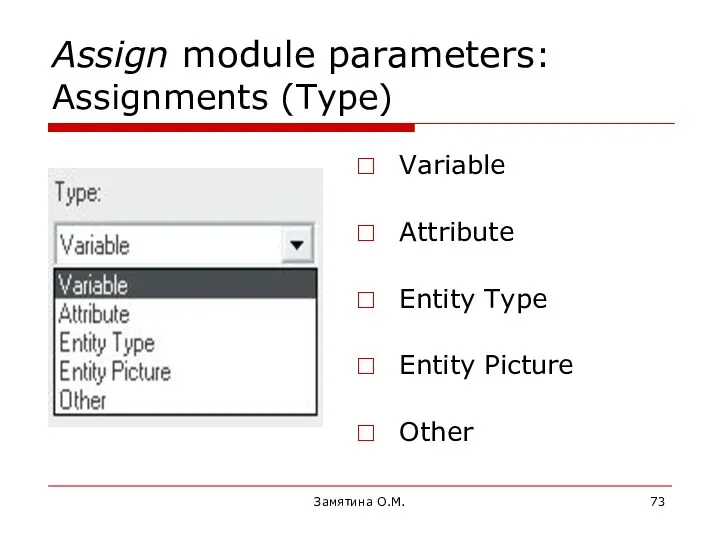
- 73. Замятина О.М. Assign module parameters: Assignments (Type) Variable Attribute Entity Type Entity Picture Other
- 74. Замятина О.М. 1.1.7 Record Record module intend for specific statistic data collection. It needs when it
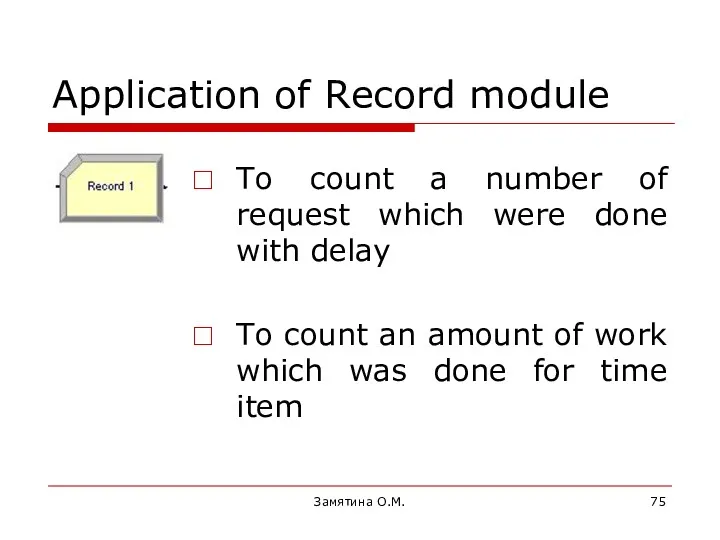
- 75. Замятина О.М. Application of Record module To count a number of request which were done with
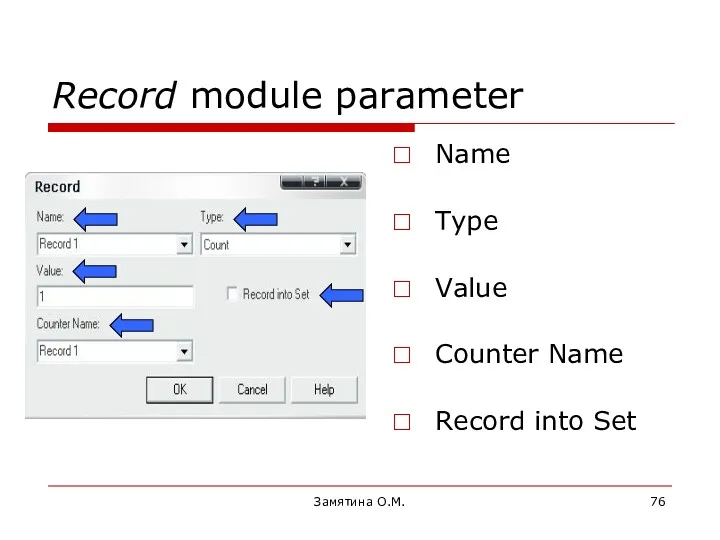
- 76. Замятина О.М. Record module parameter Name Type Value Counter Name Record into Set
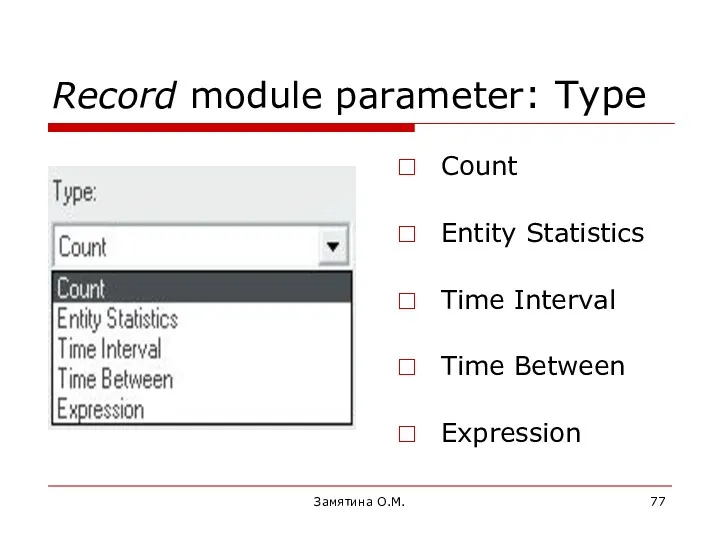
- 77. Замятина О.М. Record module parameter: Type Count Entity Statistics Time Interval Time Between Expression
- 78. Замятина О.М. 1.1.8 Dispose Dispose module is end point for entity leaving from simulating model
- 79. Замятина О.М. Application of Dispose module Documents processed Clients come out
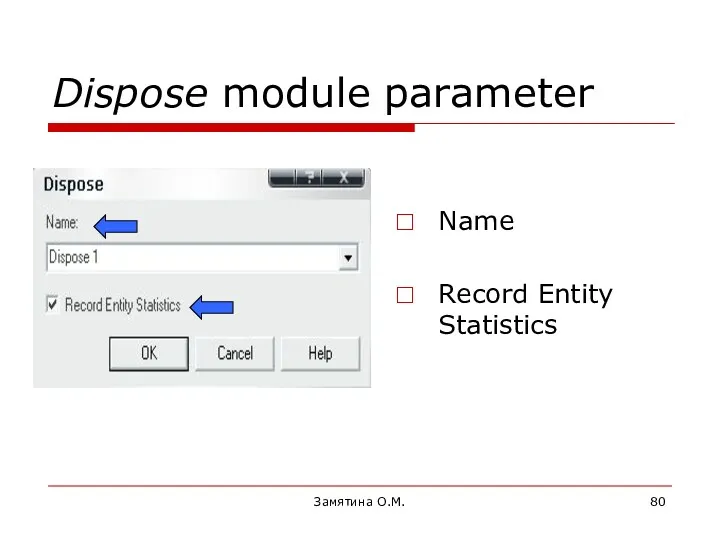
- 80. Замятина О.М. Dispose module parameter Name Record Entity Statistics
- 81. Замятина О.М. 1.2 Data Modules
- 82. Замятина О.М. 1.2.1 Entity Entity module sets entity type and entity initial picture in the model
- 83. Замятина О.М. Application of Entity module Documents: faxes, letters, reports and etc. People: workers, managers, men
- 84. Entity type Initial picture Замятина О.М. Entity module parameters
- 85. 1.2.2 Queue Queue module uses for setting of queue types: First in First out (FIFO) Last
- 86. Замятина О.М. Application of Queue module Queue in the supermarket where people are waiting cashier service
- 87. Замятина О.М. 1.2.3 Resource Resource module allows to set recourse which is associated with certain process
- 88. Замятина О.М. Application of Resource module People: workers, managers, men, salespeoples and etc. Equipment: telephone loop,
- 89. Resource module parameters Замятина О.М. Resource type (Fixed Capacity, Based on Schedule ) Capacity
- 90. Замятина О.М. 1.2.4 Schedule Schedule module can be uses for setting of the time interval: Generation
- 91. Замятина О.М. Application of Schedule module Time-table of staff Number of buyers are arrived at supermarket
- 92. Замятина О.М. Schedule module parameter Type Capacity (Process module), Arrival (Create module) Other Time units
- 93. Замятина О.М. 1.2.5 Set Set module is defined recourse set, which will be associated with Process
- 94. Замятина О.М. Set module parameter Members Cyclical Preferred Order Resource Name
- 95. Замятина О.М. 1.2.6 Variable Variable module defines variable names and variable initial values
- 96. Замятина О.М. Application of Variable module To count a number of documents which were processed during
- 97. Замятина О.М. Variable module parameter Initial Value Rows Columns Clear Option Statistics System None Statistics
- 99. Скачать презентацию

















 Profession is a logistician
Profession is a logistician What belongs to the cat
What belongs to the cat Independent work
Independent work Books in our life
Books in our life Особенности перевода фразеологизмов и передачи модальности в переводе
Особенности перевода фразеологизмов и передачи модальности в переводе to_be___
to_be___ Shopping
Shopping Система вправ для навчання ІМ
Система вправ для навчання ІМ H, b, f, l. Initial sounds
H, b, f, l. Initial sounds Sightseeing in St. Petersburg
Sightseeing in St. Petersburg Shops and shopping in Britain
Shops and shopping in Britain General characteristics of English vocabulary
General characteristics of English vocabulary Aleksei Brusilov distinguished commander of the First World War
Aleksei Brusilov distinguished commander of the First World War So many countries. so many customs
So many countries. so many customs Categories. Construction
Categories. Construction The future tenses and other ways of expressing future actions
The future tenses and other ways of expressing future actions How do you treat the Earth?
How do you treat the Earth? Present Simple Tense (настоящее простое время)
Present Simple Tense (настоящее простое время) Future simple 1
Future simple 1 Historical perspectives. Popular methodology
Historical perspectives. Popular methodology Countable and uncountable nouns
Countable and uncountable nouns Судебные источники публичного права зарубежных стран
Судебные источники публичного права зарубежных стран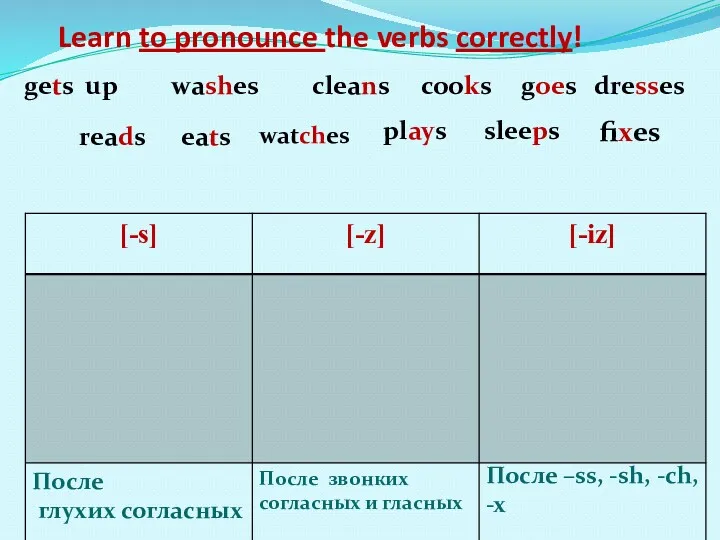 Learn to pronounce the verbs correctly
Learn to pronounce the verbs correctly Побег из волшебного банка Гринготтс. Условные предложения 0 и 1 типов
Побег из волшебного банка Гринготтс. Условные предложения 0 и 1 типов Personal letter
Personal letter School subjects game
School subjects game Present Perfect and Past Simple
Present Perfect and Past Simple Present perfect continuous progressive tense
Present perfect continuous progressive tense