Содержание
- 2. Sylviun fissure, to whom we owe, in this part, everything that the brain has the most,
- 3. Definition The sylvian fissure ,is the most distinct & consistent landmark on the lateral surface, that
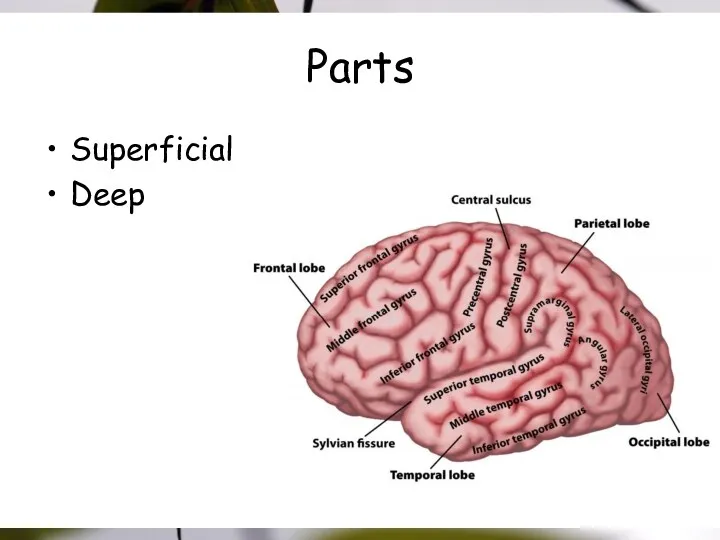
- 4. Parts Superficial Deep
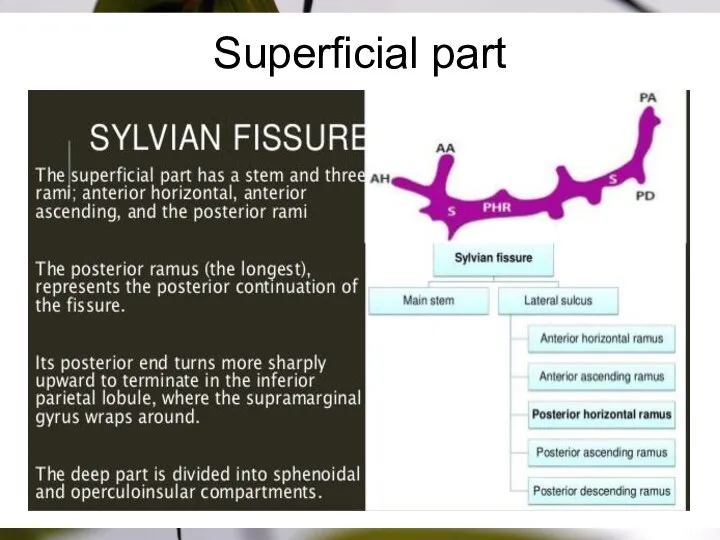
- 5. Superficial part
- 6. Deep Part (Sylvian Cistern) Sphenoidal Operculoinsular compartment
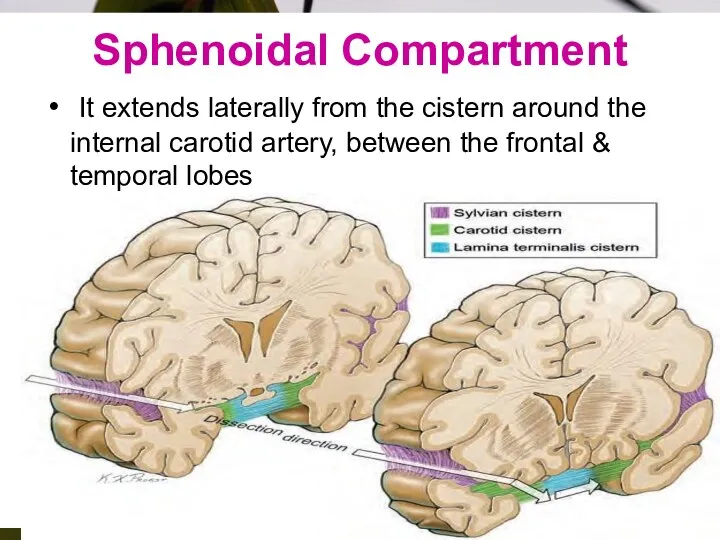
- 7. Sphenoidal Compartment It extends laterally from the cistern around the internal carotid artery, between the frontal
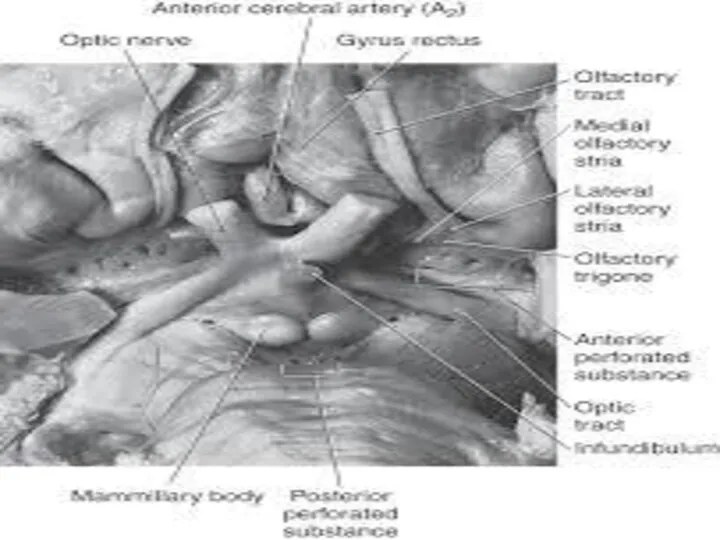
- 8. Sphenoidal Compartment Roof is formed by: Post. orbital surface of the frontal lobe Anterior perforated substance.
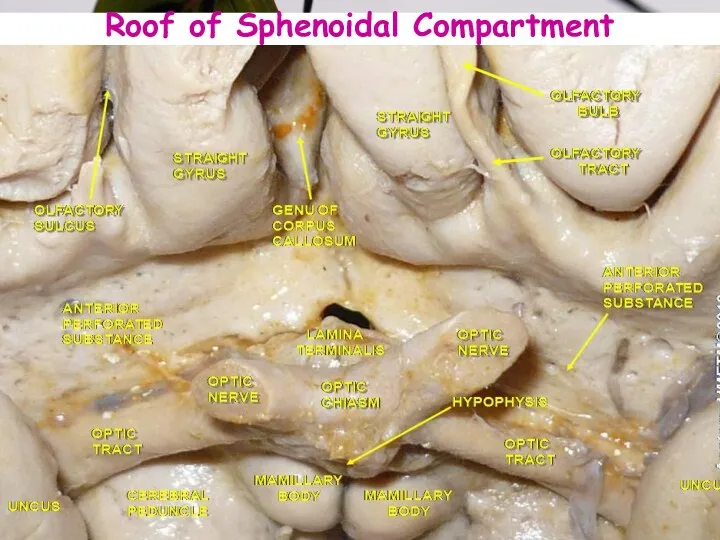
- 9. Roof of Sphenoidal Compartment
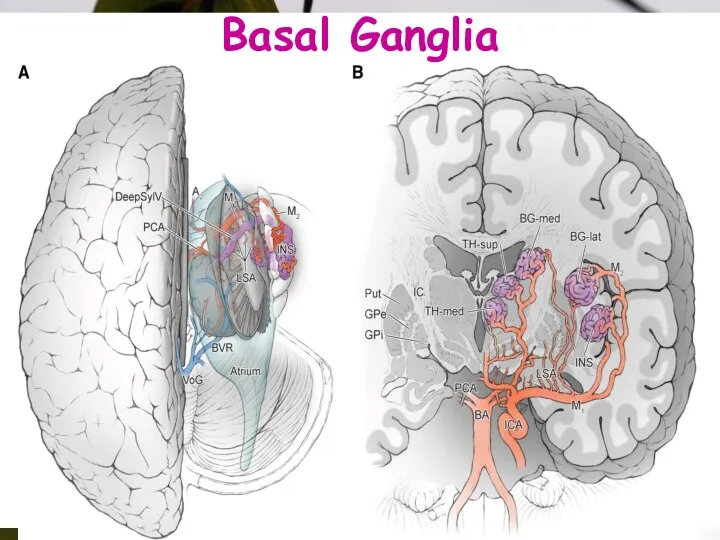
- 11. Basal Ganglia
- 12. Floor: anterior part of the planum polare, an area free of gyri on the upper temporal
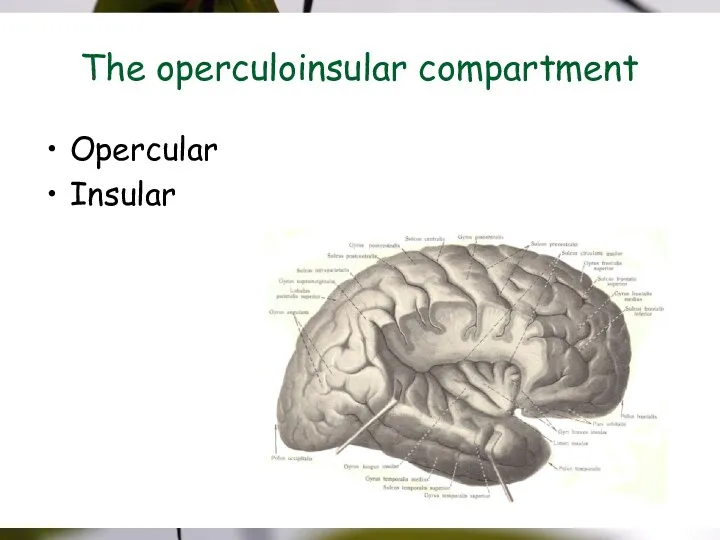
- 13. The operculoinsular compartment Opercular Insular
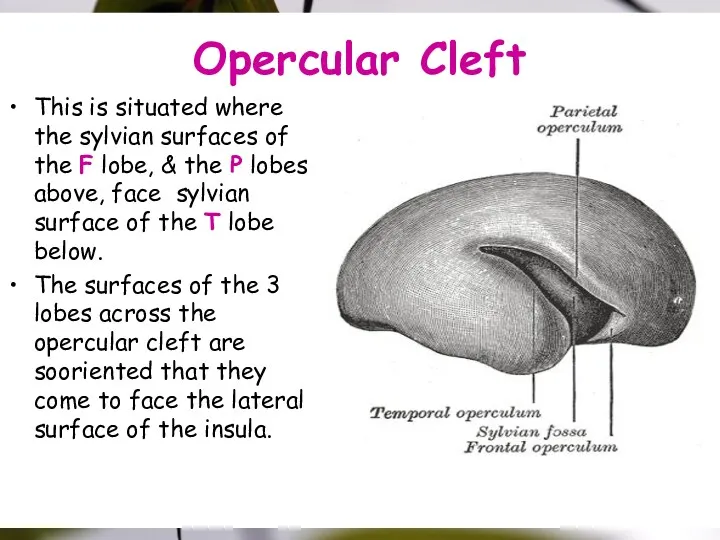
- 14. Opercular Cleft This is situated where the sylvian surfaces of the F lobe, & the P
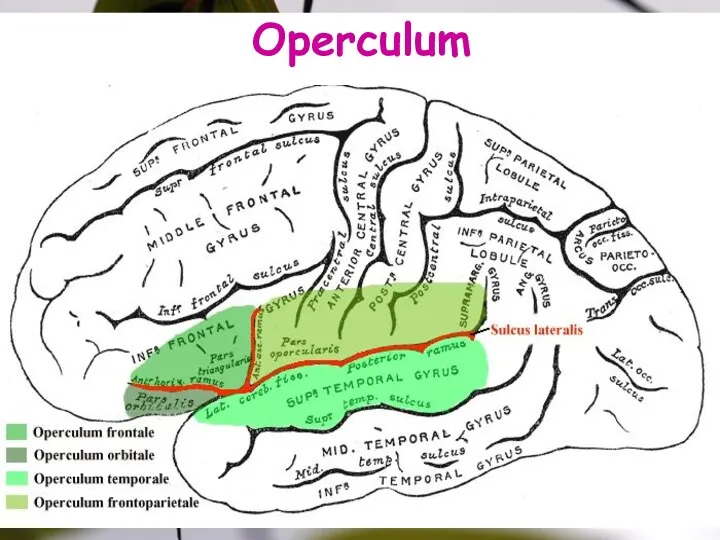
- 15. Operculum
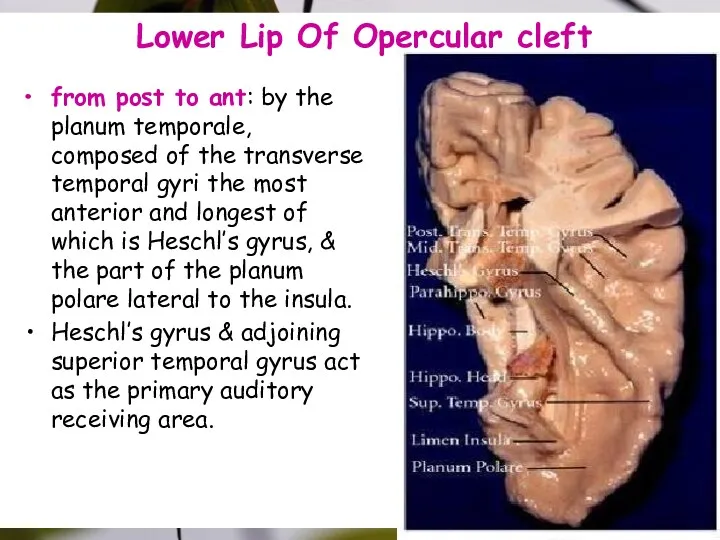
- 16. Lower Lip Of Opercular cleft from post to ant: by the planum temporale, composed of the
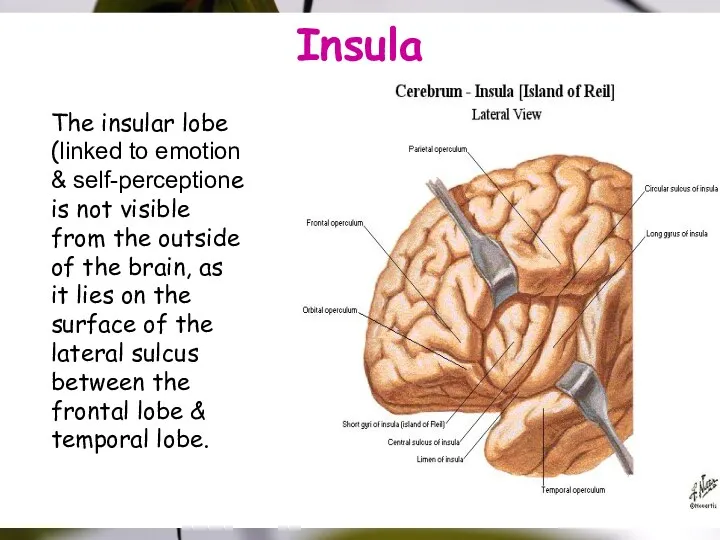
- 17. Insula The insular lobe (linked to emotion & self-perceptione is not visible from the outside of
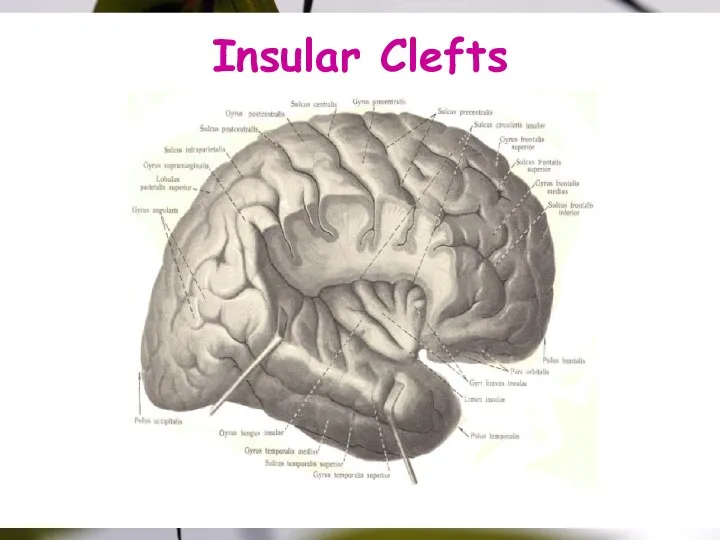
- 18. Insular Clefts
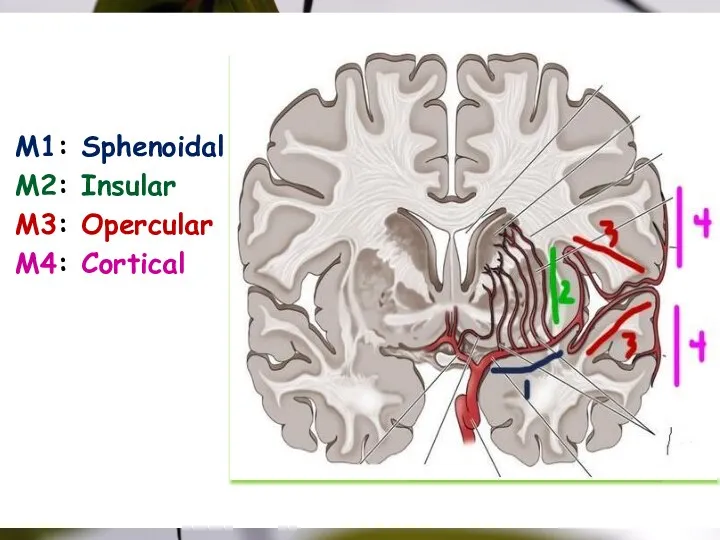
- 19. Picture slide M1: Sphenoidal M2: Insular M3: Opercular M4: Cortical
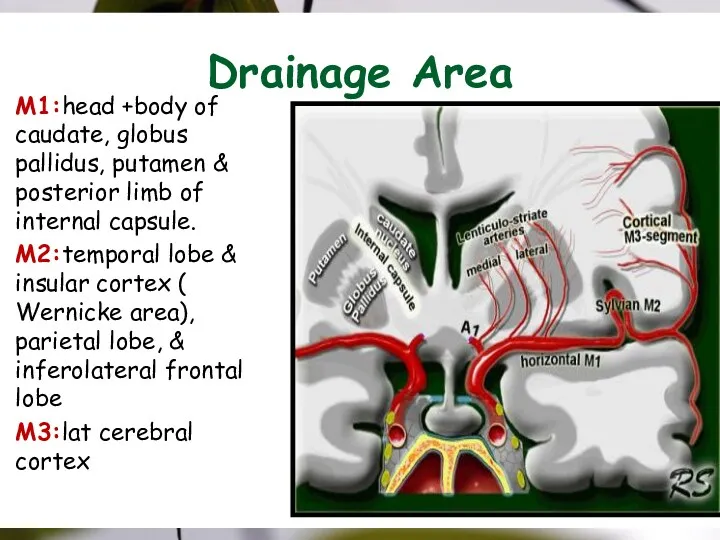
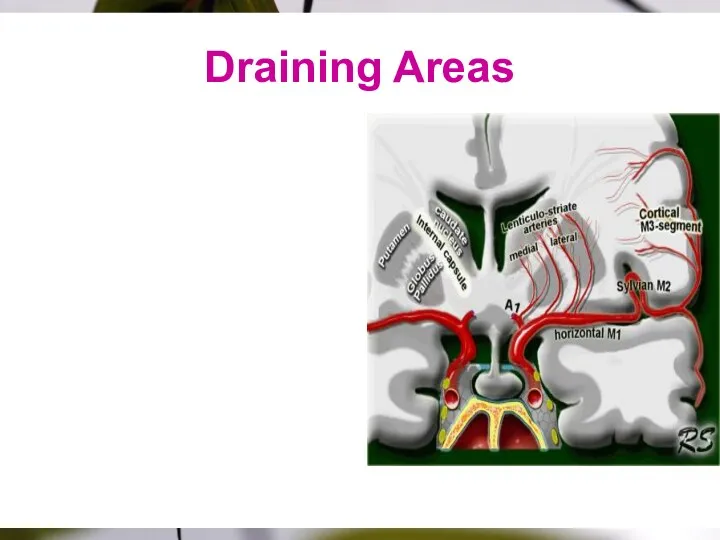
- 20. Drainage Area M1:head +body of caudate, globus pallidus, putamen & posterior limb of internal capsule. M2:temporal
- 21. Radiographic Classification M1: before bifurcation M2: after bifurcation
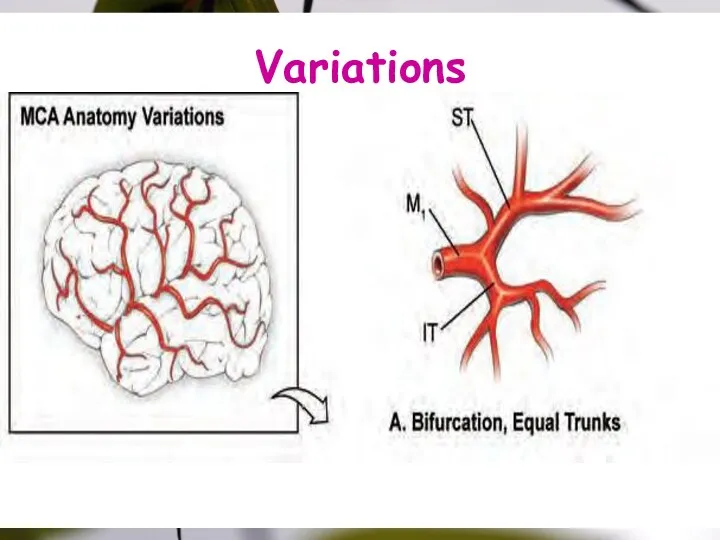
- 22. Variations
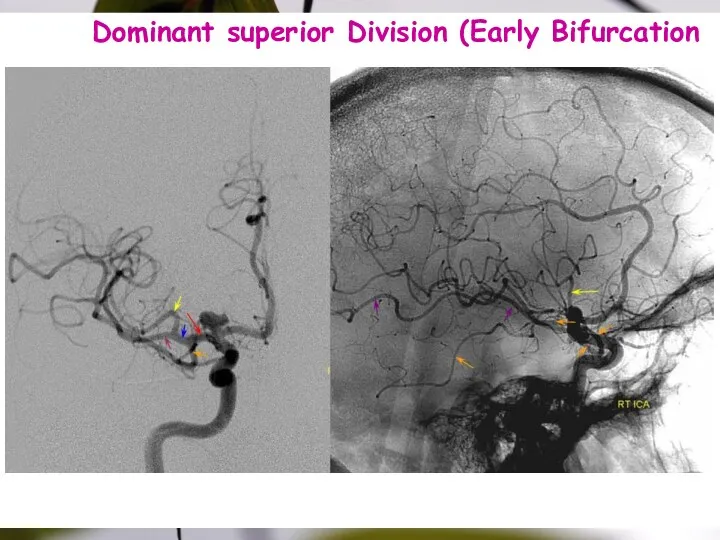
- 23. Dominant superior Division (Early Bifurcation 187
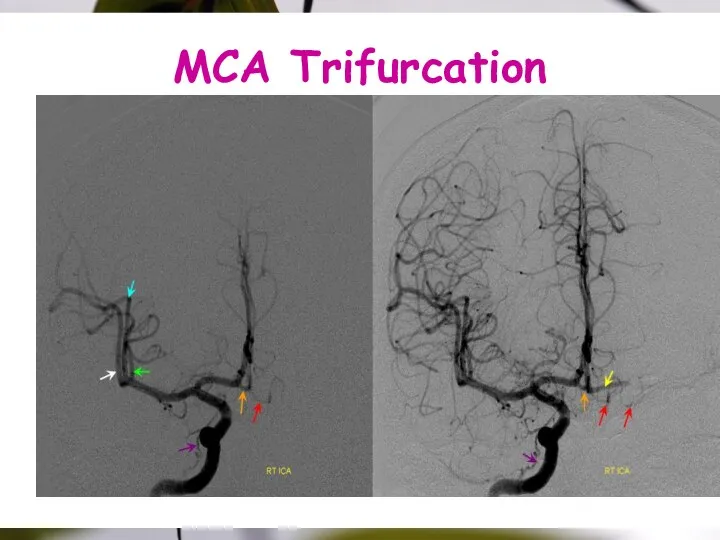
- 24. MCA Trifurcation
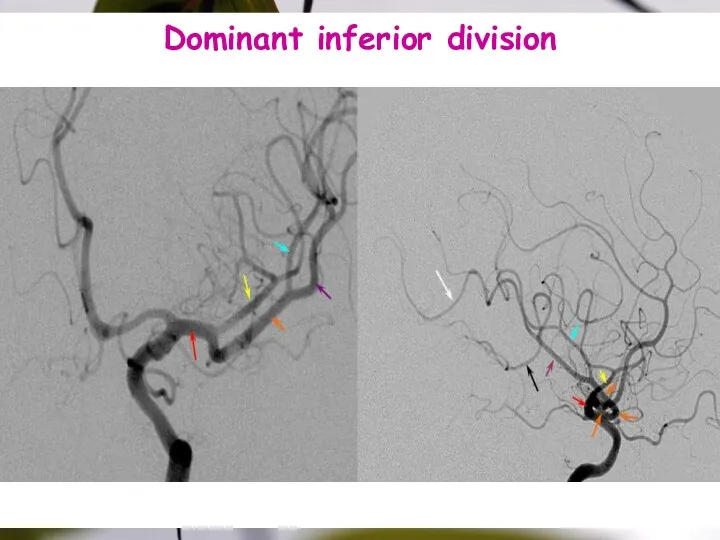
- 25. Dominant inferior division
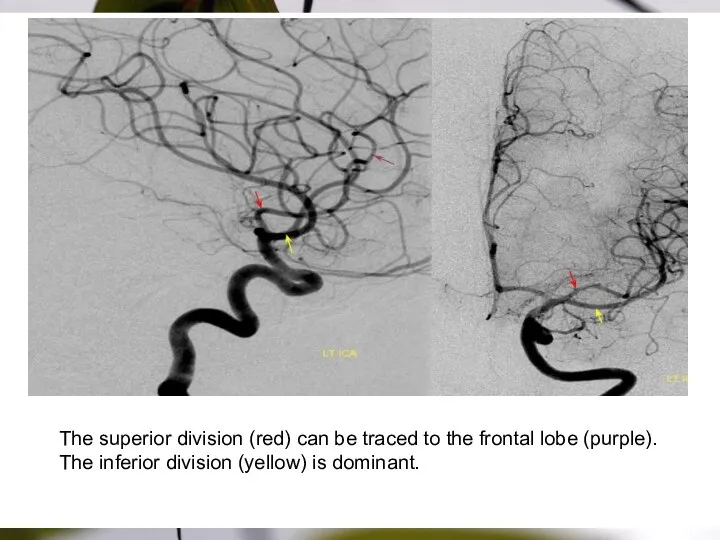
- 26. The superior division (red) can be traced to the frontal lobe (purple). The inferior division (yellow)
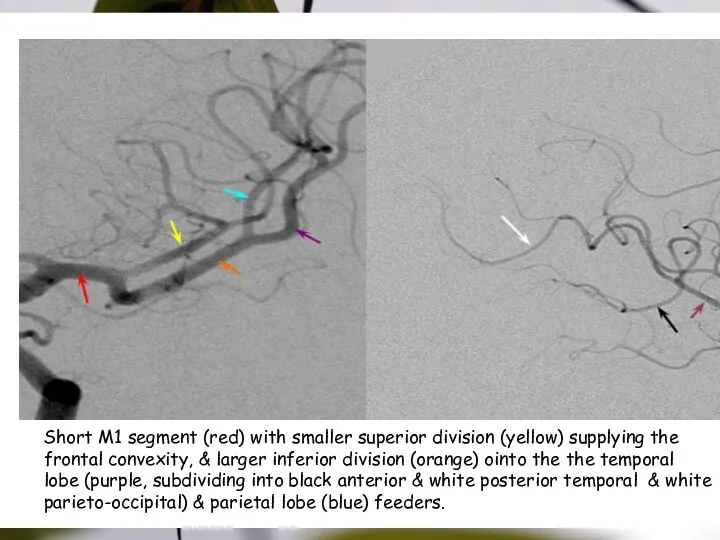
- 27. Short M1 segment (red) with smaller superior division (yellow) supplying the frontal convexity, & larger inferior
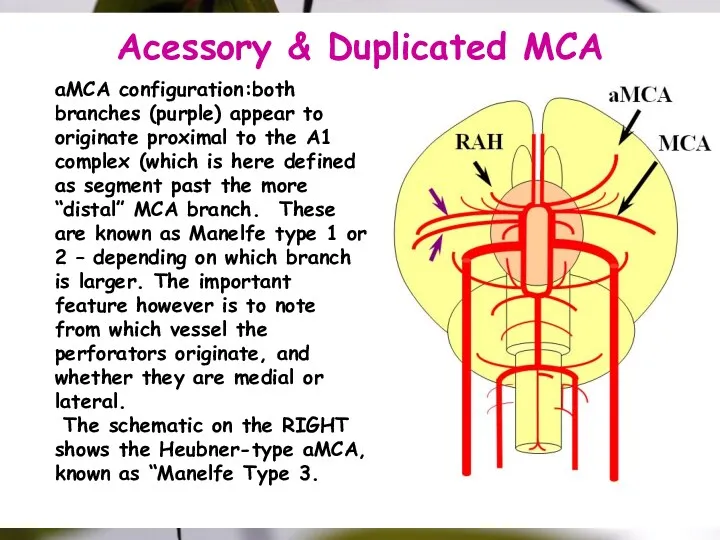
- 28. Acessory & Duplicated MCA aMCA configuration:both branches (purple) appear to originate proximal to the A1 complex
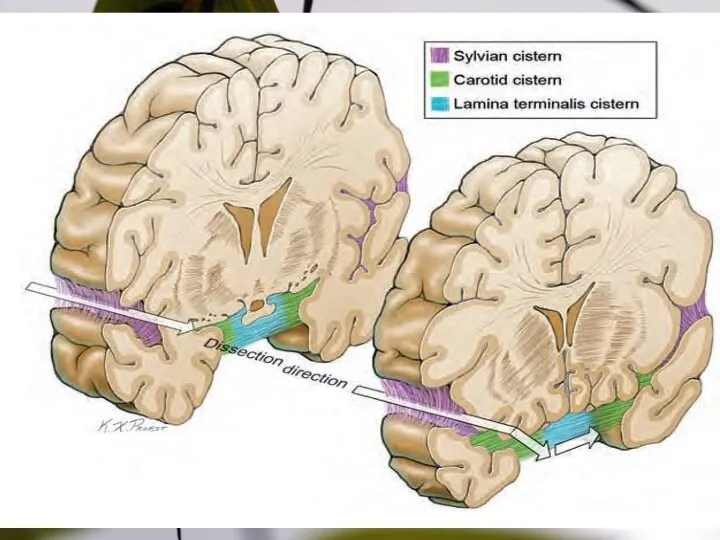
- 29. SYLVIAN FISSURE Splitting
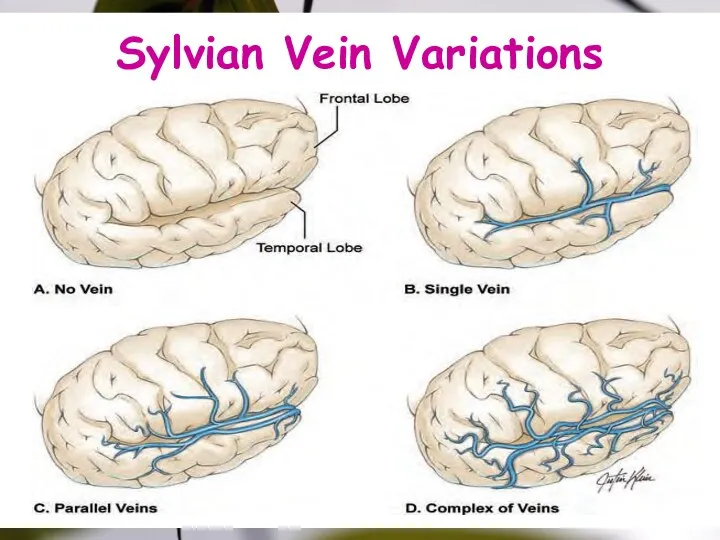
- 30. Sylvian Vein Variations
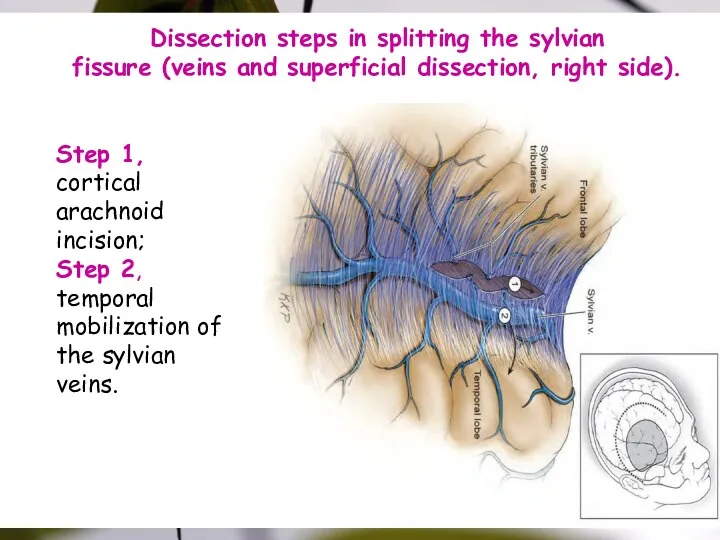
- 31. Step 1, cortical arachnoid incision; Step 2, temporal mobilization of the sylvian veins. Dissection steps in
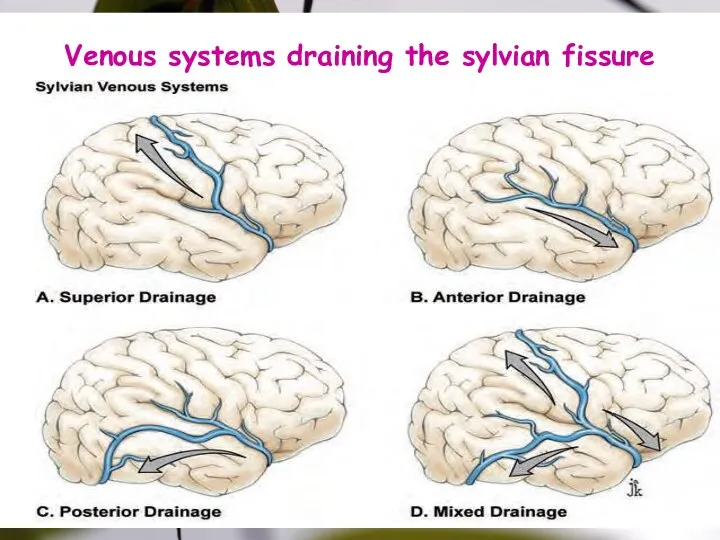
- 32. Venous systems draining the sylvian fissure
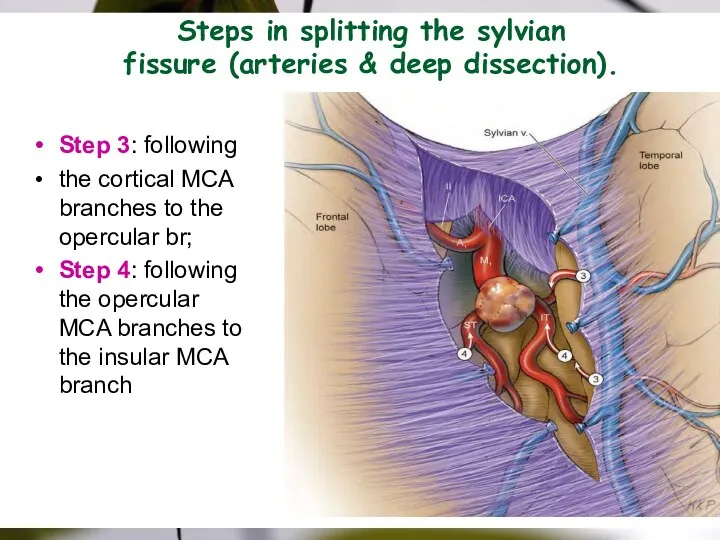
- 34. Steps in splitting the sylvian fissure (arteries & deep dissection). Step 3: following the cortical MCA
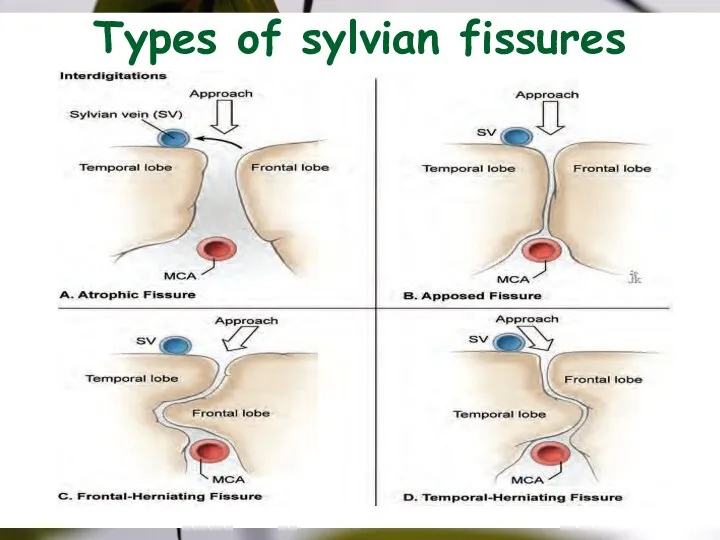
- 35. Types of sylvian fissures
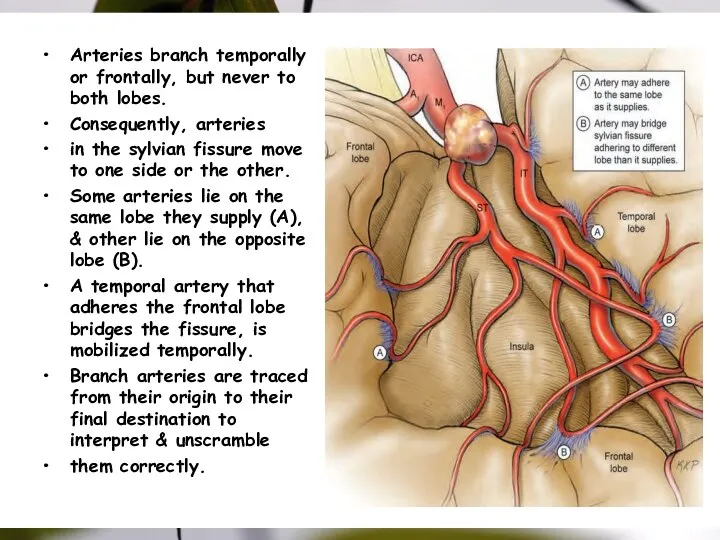
- 36. Arteries branch temporally or frontally, but never to both lobes. Consequently, arteries in the sylvian fissure
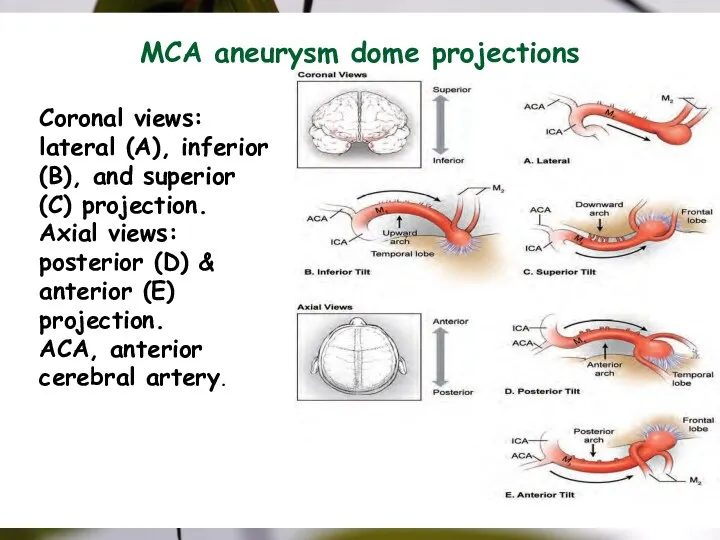
- 37. MCA aneurysm dome projections Coronal views: lateral (A), inferior (B), and superior (C) projection. Axial views:
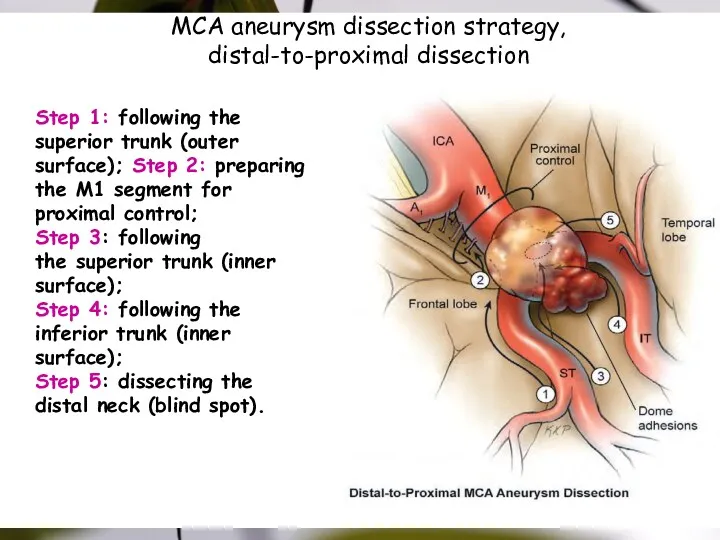
- 38. MCA aneurysm dissection strategy, distal-to-proximal dissection Step 1: following the superior trunk (outer surface); Step 2:
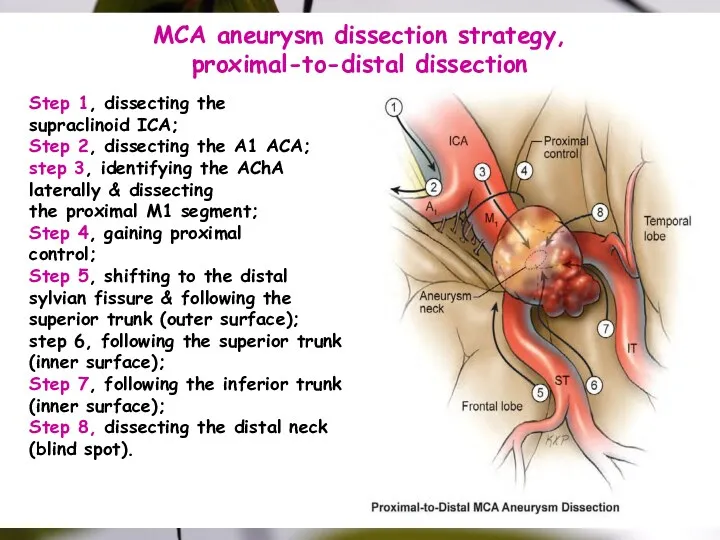
- 39. MCA aneurysm dissection strategy, proximal-to-distal dissection Step 1, dissecting the supraclinoid ICA; Step 2, dissecting the
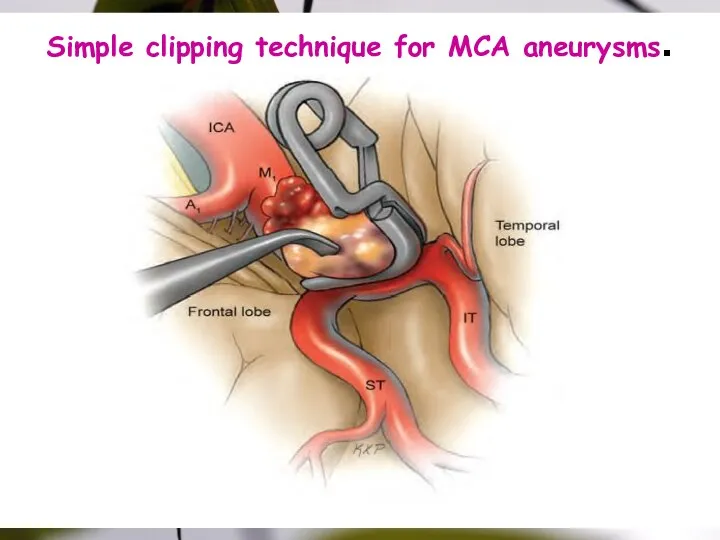
- 40. Simple clipping technique for MCA aneurysms.
- 41. Draining Areas
- 42. Thank You
- 43. Colour scheme
- 44. Sample Graph (3 colours)
- 45. Process Flow Bullet 1 Bullet 2 Bullet 3 Bullet 1 Bullet 2 Bullet 3 Bullet 1
- 46. Example of a table Note: PowerPoint does not allow you to have nice default tables -
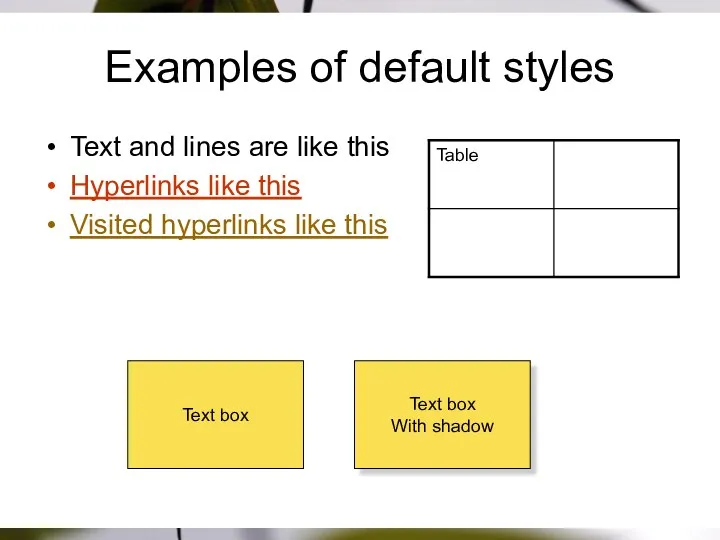
- 47. Examples of default styles Text and lines are like this Hyperlinks like this Visited hyperlinks like
- 49. Скачать презентацию









 I like school
I like school An Englishman`s House Is His Castle
An Englishman`s House Is His Castle Philippines
Philippines My native town Arzamas
My native town Arzamas Цвета. Сolours
Цвета. Сolours My summer holidays
My summer holidays Существительное в притяжательном падеже
Существительное в притяжательном падеже The Adjective. The Pronoun. Lecture 8
The Adjective. The Pronoun. Lecture 8 Past simple tense
Past simple tense What number is this
What number is this Job Interview in English. Guestions
Job Interview in English. Guestions Present Cont
Present Cont Emirates society. (Сhapter 3)
Emirates society. (Сhapter 3) Science: insects
Science: insects Global warming
Global warming Раздел грамматики синтаксис. (Лекция 10)
Раздел грамматики синтаксис. (Лекция 10) Etymology
Etymology Gerund Infinitive
Gerund Infinitive My family
My family Проблемы больших гоодов
Проблемы больших гоодов Устная часть ЕГЭ. Тренировочные картинки для описания и сравнения. Задания 3,4
Устная часть ЕГЭ. Тренировочные картинки для описания и сравнения. Задания 3,4 Relative pronouns and adverbs
Relative pronouns and adverbs Ecological problems
Ecological problems Прошедшее совершенное время
Прошедшее совершенное время To say, to tell, to speak, to talk
To say, to tell, to speak, to talk Can and Can’t
Can and Can’t Look at the pictures and be ready to compare them
Look at the pictures and be ready to compare them Adjective or Adverb
Adjective or Adverb