Содержание
- 2. There are 3 basic parts to a rocket: the structural and mechanical parts (engines, storage spaces,
- 3. Like most engines, rockets burn fuel. Most rocket engines turn the fuel into hot gas. The
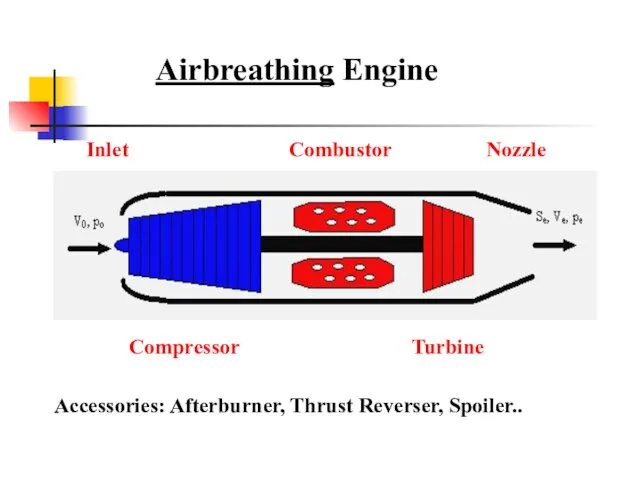
- 4. Airbreathing Engine Compressor Combustor Turbine Inlet Nozzle Accessories: Afterburner, Thrust Reverser, Spoiler..
- 5. In space, an engine has nothing to push against. So how do rockets move there? Rockets
- 6. Propellant Rocket propellant is mass that is stored, usually in some form of propellant tank or
- 7. A rocket design can be as simple as a cardboard tube filled with black powder, but
- 8. There are actually many different types of rockets including: tiny models such as balloon rockets, water
- 9. Rockets or other similar reaction devices carrying their own propellant must be used when there is
- 11. Скачать презентацию






 Peters family. Game
Peters family. Game It is... 4 класс
It is... 4 класс The law of contract
The law of contract Questions-game
Questions-game Proper names in translation
Proper names in translation Rheumatic Endocarditis
Rheumatic Endocarditis Формування іншомовної граматичної компетентності
Формування іншомовної граматичної компетентності Interactive repetition simulator. Grade 2
Interactive repetition simulator. Grade 2 The city of USA - Boston
The city of USA - Boston Indian cuisine
Indian cuisine Английский язык на улицах Кемерово
Английский язык на улицах Кемерово Begin with an outline or agenda to give a big picture view
Begin with an outline or agenda to give a big picture view My personal profile, my lifestyle
My personal profile, my lifestyle Man and nature
Man and nature Распространение Американского английского языка
Распространение Американского английского языка My house
My house Past simple vs past continuous
Past simple vs past continuous My room. A flat
My room. A flat Summer holidays (1)
Summer holidays (1) Past Tenses
Past Tenses Movers Bright Ideas
Movers Bright Ideas The person I admire Steve Jobs
The person I admire Steve Jobs Welcome to Disneylend
Welcome to Disneylend Ecological city of the future
Ecological city of the future Food
Food What does “can” mean
What does “can” mean National Research Tomsk State University
National Research Tomsk State University New York City Attractions Достопримечательности Нью-Йорка
New York City Attractions Достопримечательности Нью-Йорка