Содержание
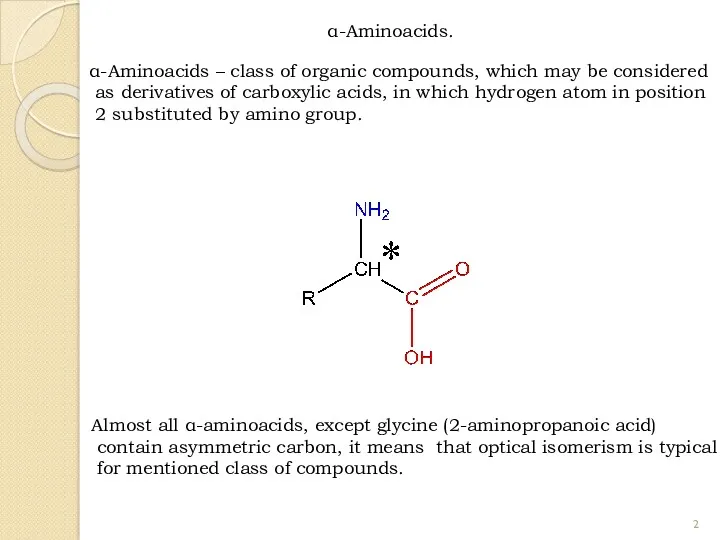
- 2. α-Aminoacids. α-Aminoacids – class of organic compounds, which may be considered as derivatives of carboxylic acids,
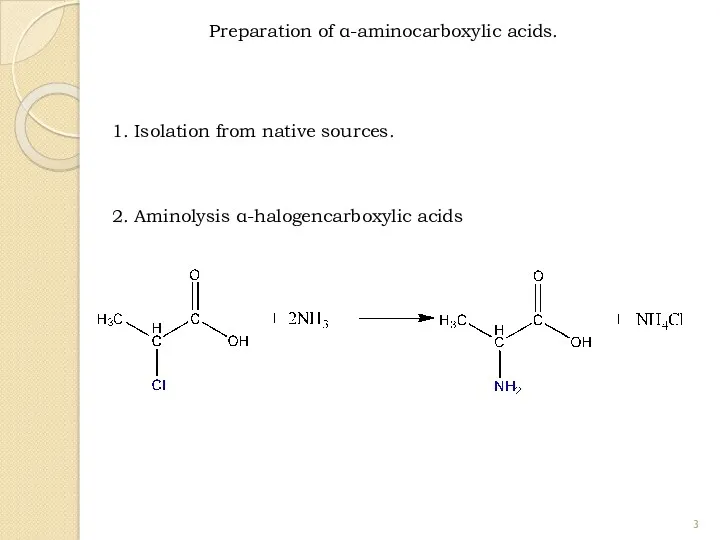
- 3. Preparation of α-aminocarboxylic acids. 2. Aminolysis α-halogencarboxylic acids 1. Isolation from native sources.
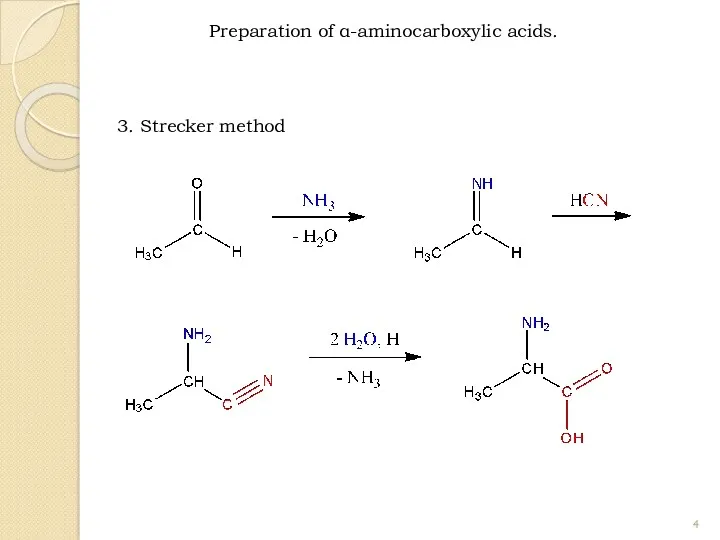
- 4. 3. Strecker method Preparation of α-aminocarboxylic acids.
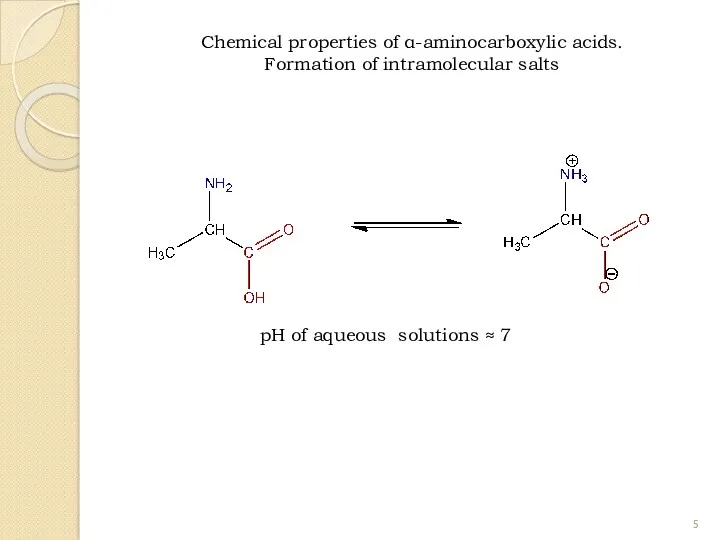
- 5. Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Formation of intramolecular salts pH of aqueous solutions ≈ 7
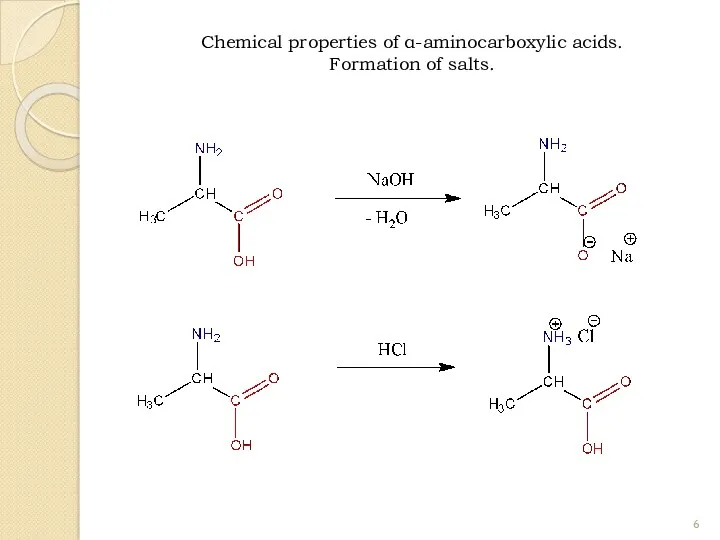
- 6. Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Formation of salts.
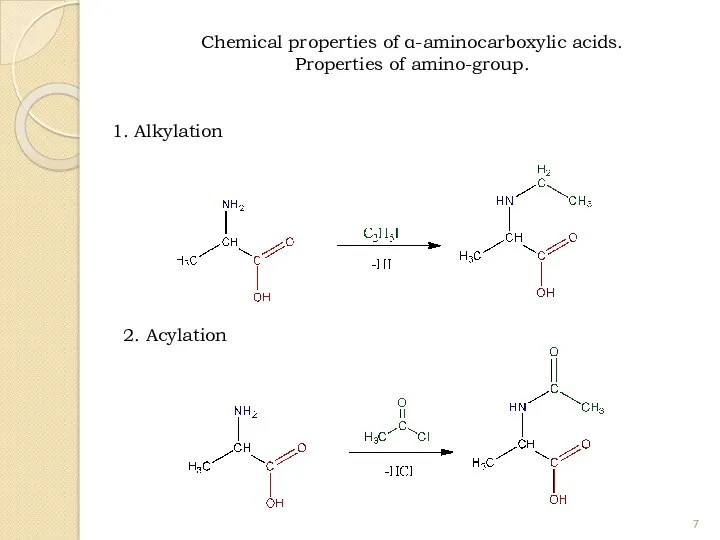
- 7. 1. Alkylation 2. Acylation Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Properties of amino-group.
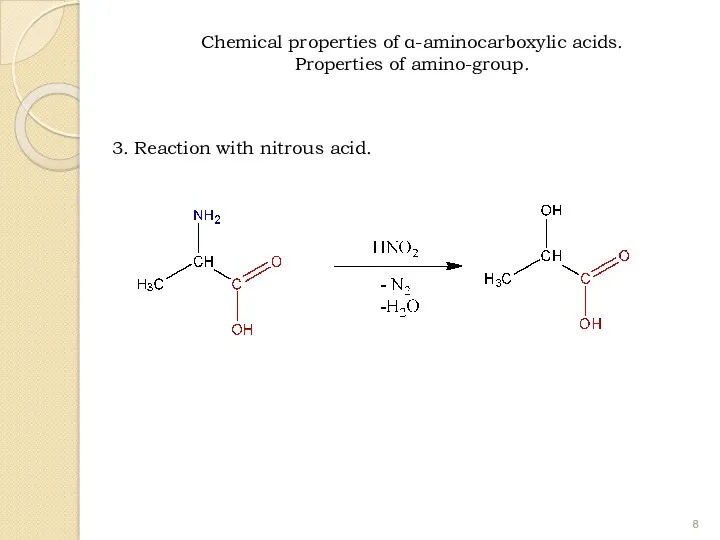
- 8. 3. Reaction with nitrous acid. Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Properties of amino-group.
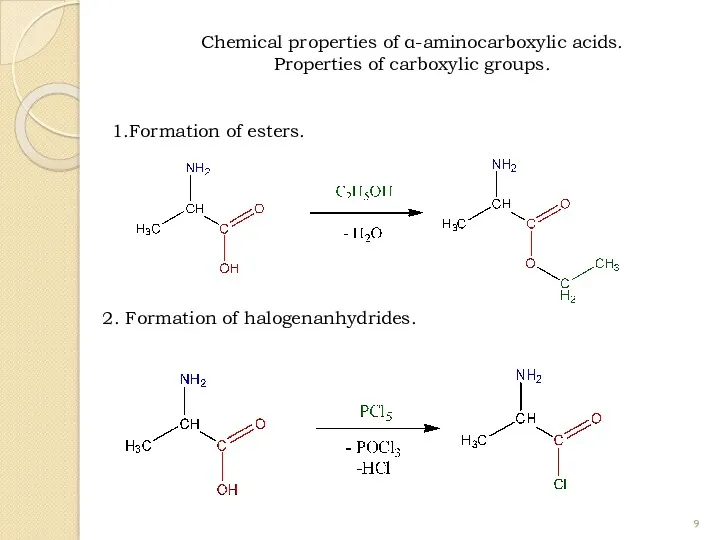
- 9. 1.Formation of esters. 2. Formation of halogenanhydrides. Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Properties of carboxylic groups.
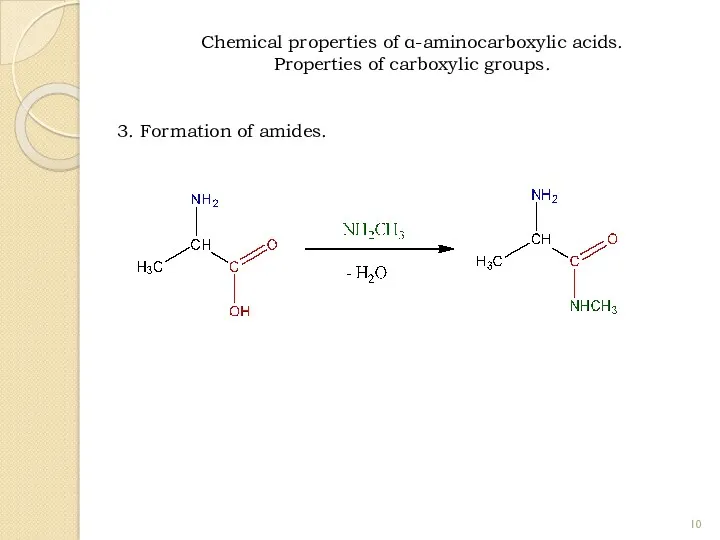
- 10. 3. Formation of amides. Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Properties of carboxylic groups.
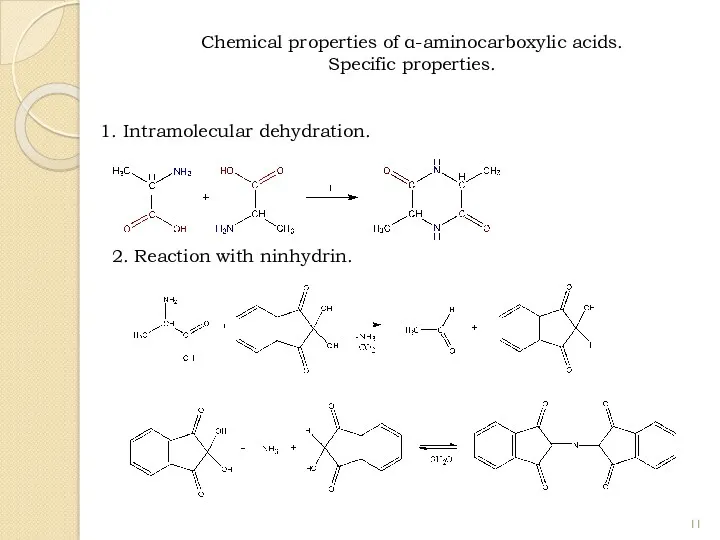
- 11. 1. Intramolecular dehydration. 2. Reaction with ninhydrin. Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Specific properties.
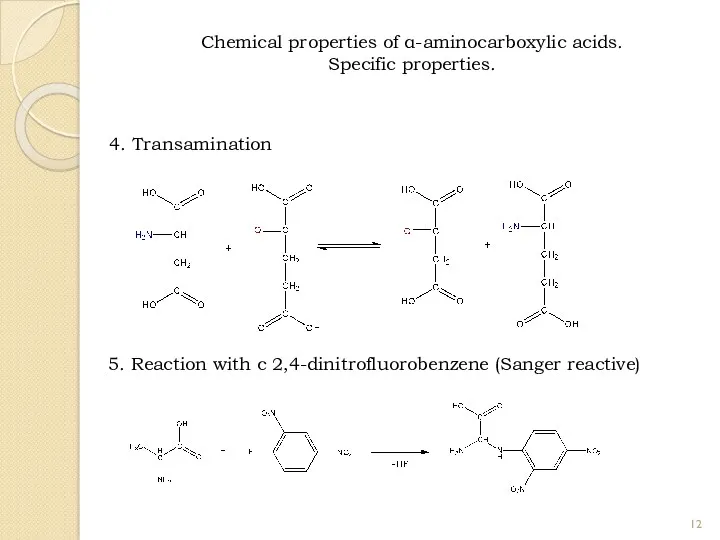
- 12. 4. Transamination 5. Reaction with с 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (Sanger reactive) Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Specific properties.
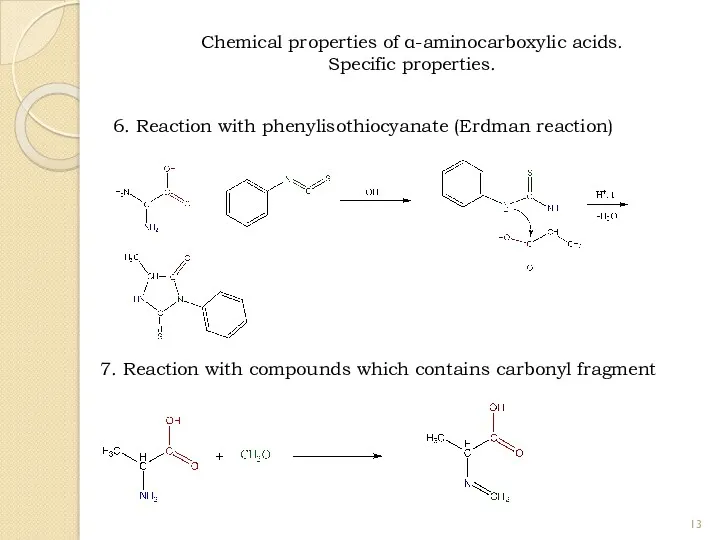
- 13. 6. Reaction with phenylisothiocyanate (Erdman reaction) 7. Reaction with compounds which contains carbonyl fragment Chemical properties
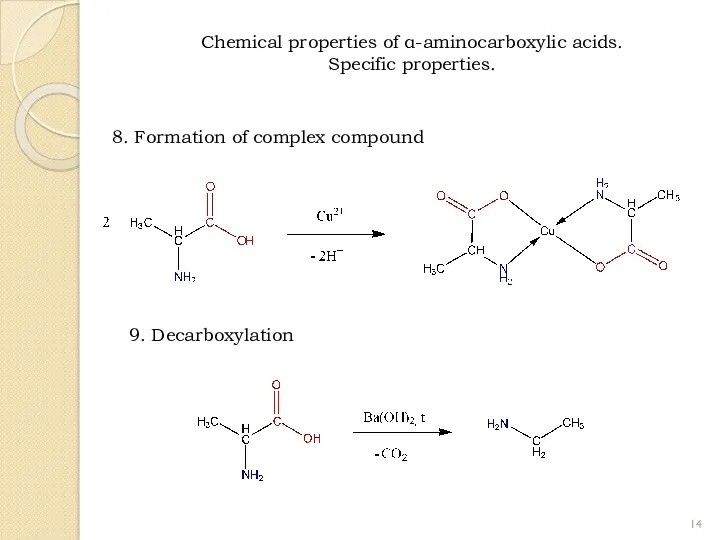
- 14. 8. Formation of complex compound 9. Decarboxylation Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Specific properties.
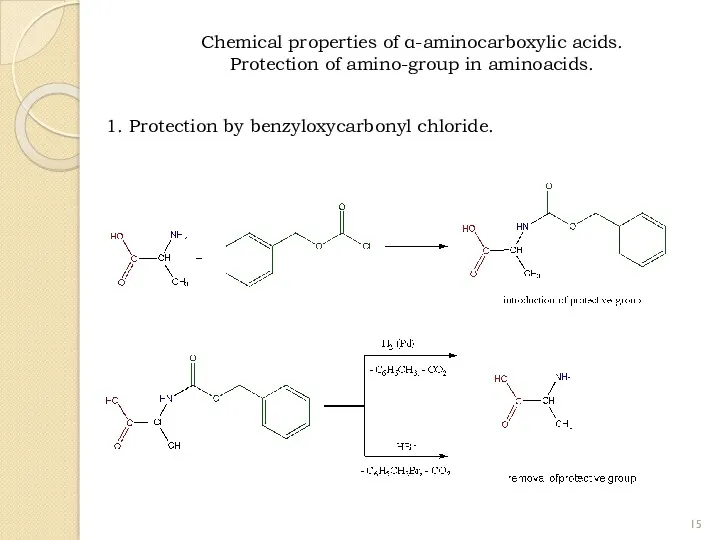
- 15. 1. Protection by benzyloxycarbonyl chloride. Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Protection of amino-group in aminoacids.
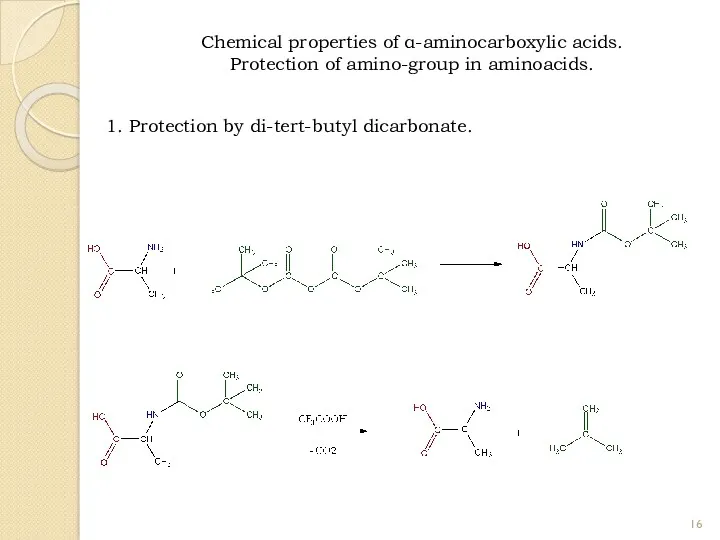
- 16. Chemical properties of α-aminocarboxylic acids. Protection of amino-group in aminoacids. 1. Protection by di-tert-butyl dicarbonate.
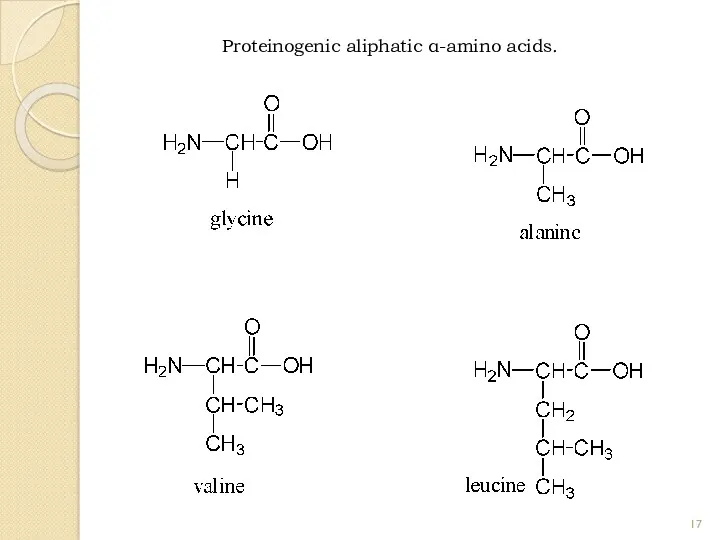
- 17. Proteinogenic aliphatic α-amino acids.
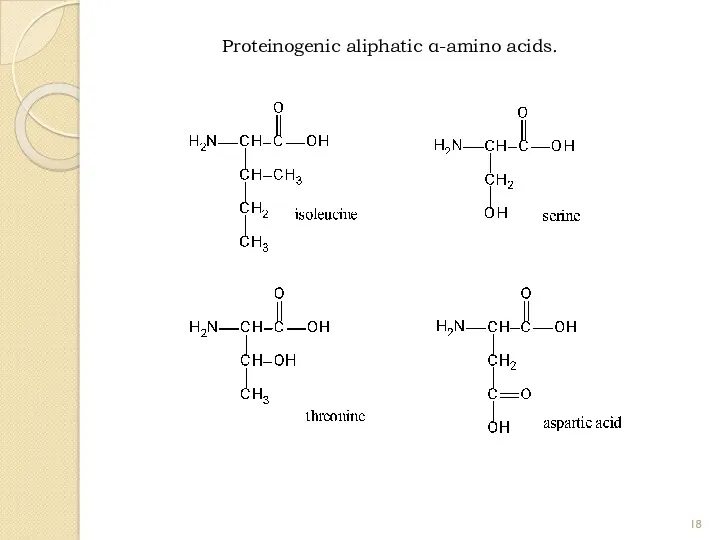
- 18. Proteinogenic aliphatic α-amino acids.
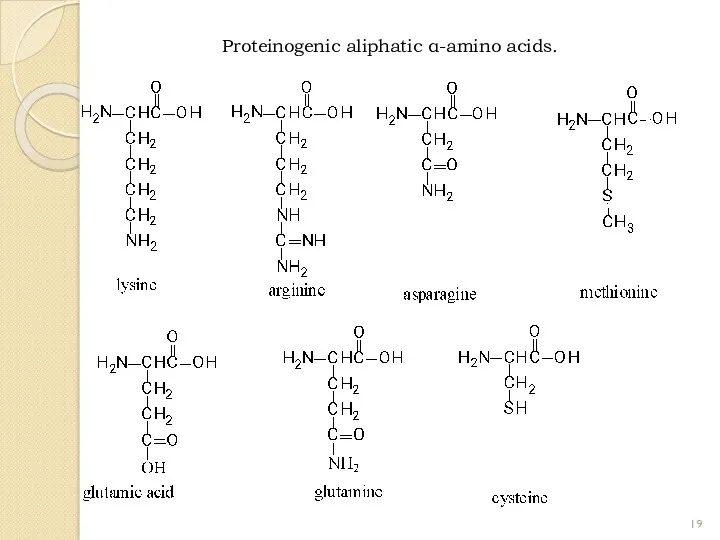
- 19. Proteinogenic aliphatic α-amino acids.
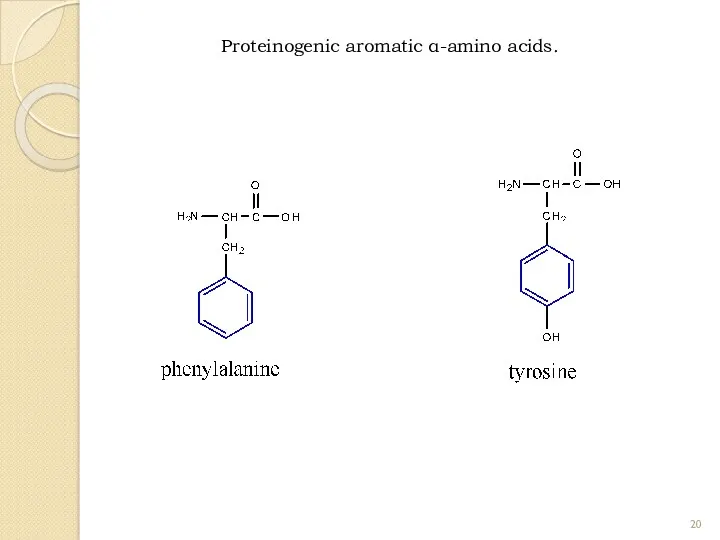
- 20. Proteinogenic aromatic α-amino acids.
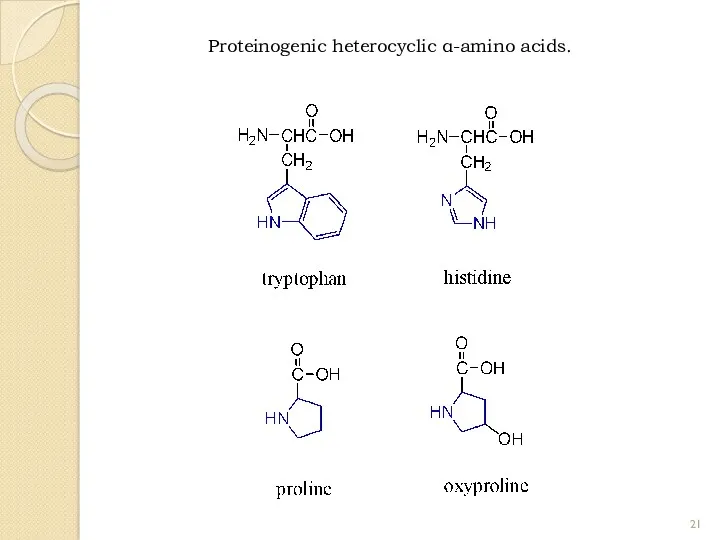
- 21. Proteinogenic heterocyclic α-amino acids.
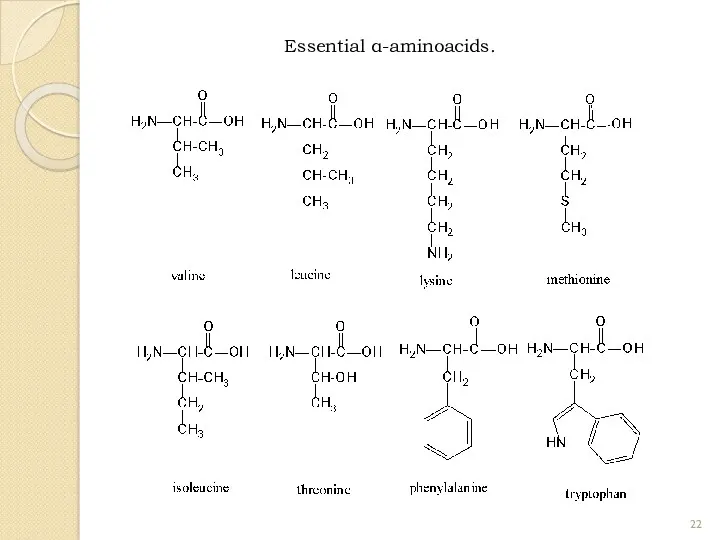
- 22. Essential α-aminoacids.
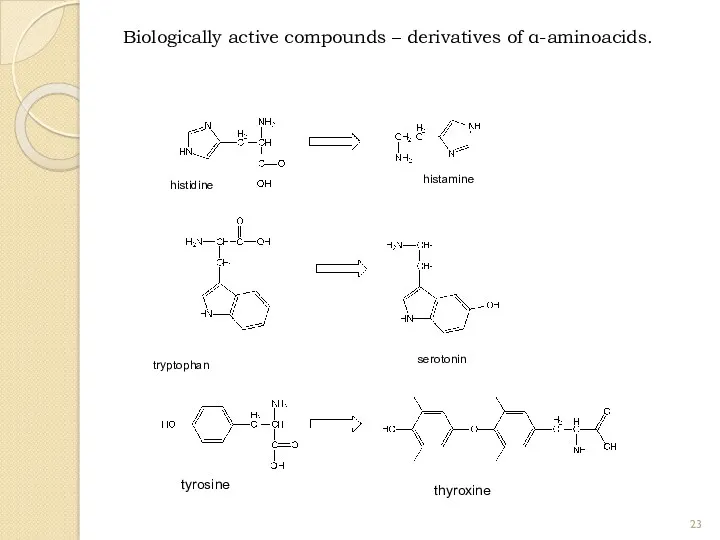
- 23. Biologically active compounds – derivatives of α-aminoacids. histidine histamine tryptophan serotonin thyroxine tyrosine
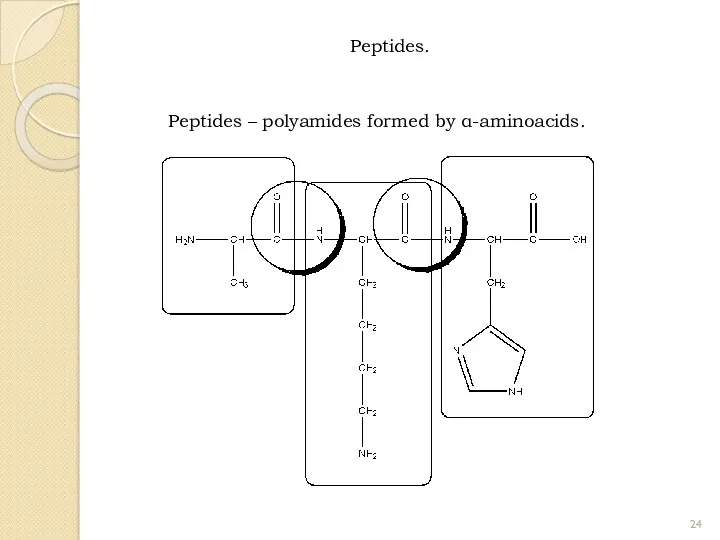
- 24. Peptides. Peptides – polyamides formed by α-aminoacids.
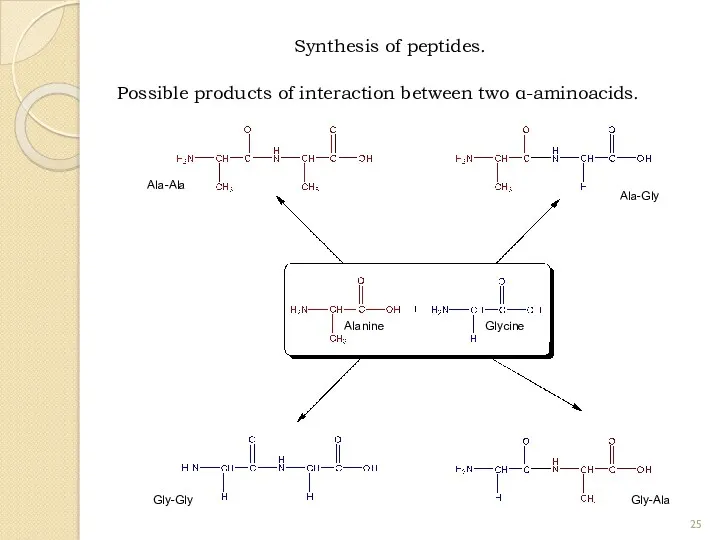
- 25. Synthesis of peptides. Possible products of interaction between two α-aminoacids. Alanine Glycine Ala-Ala Ala-Gly Gly-Gly Gly-Ala
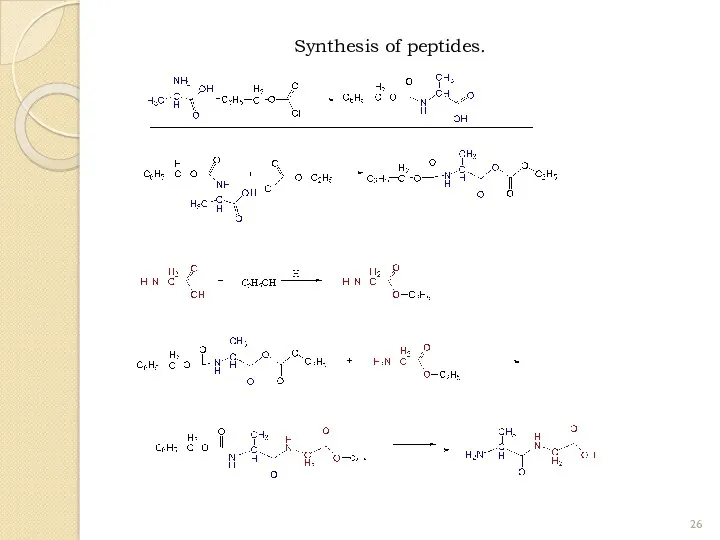
- 26. Synthesis of peptides.
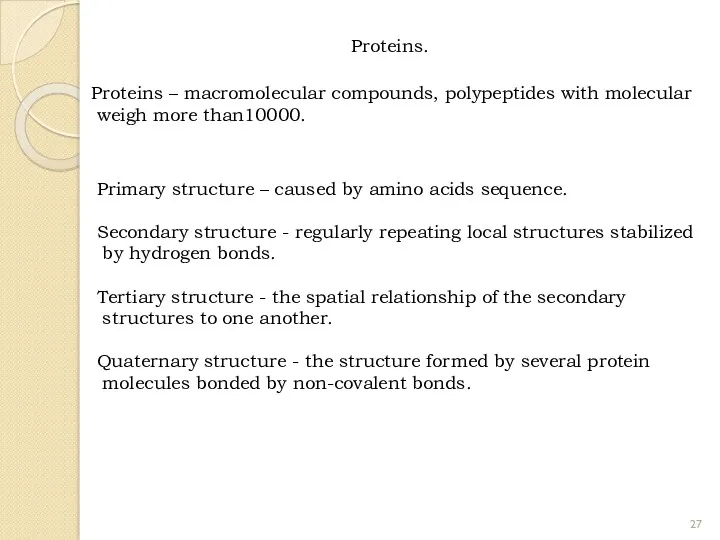
- 27. Proteins. Proteins – macromolecular compounds, polypeptides with molecular weigh more than10000. Primary structure – caused by
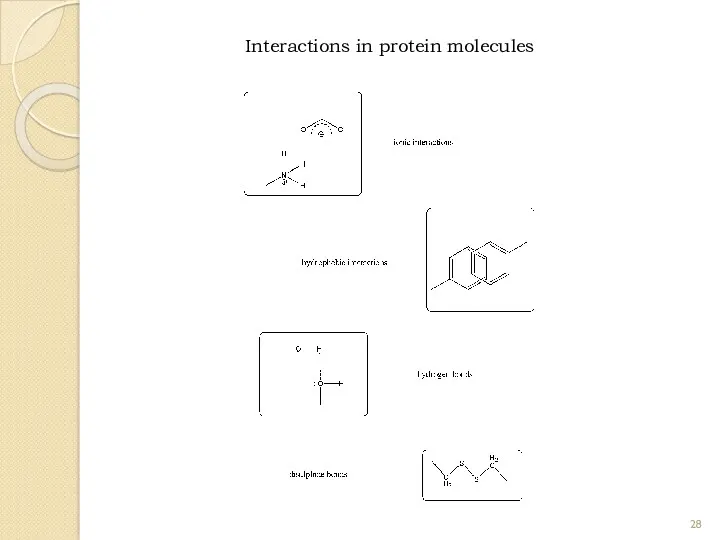
- 28. Interactions in protein molecules
- 30. Скачать презентацию
 Самые необычные животные
Самые необычные животные Путешествие по материкам. Животный мир Евразии
Путешествие по материкам. Животный мир Евразии Многообразие и происхождение пресмыкающихся
Многообразие и происхождение пресмыкающихся Слюнные железы
Слюнные железы Жизнь диких животных зимой
Жизнь диких животных зимой Морфологическая характеристика лекарственных и ядовитых растений
Морфологическая характеристика лекарственных и ядовитых растений Движение. 6 класс
Движение. 6 класс Мозжечок (cerebellum). Сагиттальный разрез головного мозга
Мозжечок (cerebellum). Сагиттальный разрез головного мозга Тихоходки. Что? Как? Почему?
Тихоходки. Что? Как? Почему? Проект Судогда - река, город, жизнь...
Проект Судогда - река, город, жизнь... Интересное о растениях
Интересное о растениях Класс Ракообразные
Класс Ракообразные Строение клетки. Растительная и животная клетки. (9 класс)
Строение клетки. Растительная и животная клетки. (9 класс) презентация Интеллектуальный марафон
презентация Интеллектуальный марафон Виды корней и типы корневых систем (7 класс)
Виды корней и типы корневых систем (7 класс) Химические элементы и неорганические вещества клетки
Химические элементы и неорганические вещества клетки Размножение растений семенами. 5 класс
Размножение растений семенами. 5 класс Антропогенез. Этапы эволюции человека
Антропогенез. Этапы эволюции человека Физиология высшей нервной деятельности. Формирование поведения в онтогенезе
Физиология высшей нервной деятельности. Формирование поведения в онтогенезе Вода, її роль у життєдіяльності організмів
Вода, її роль у життєдіяльності організмів Питание клетки
Питание клетки Мифы и легенды о животных
Мифы и легенды о животных Лекарственные растения Томской области
Лекарственные растения Томской области Животные Красной Книги. Белый медведь
Животные Красной Книги. Белый медведь Класс рыбы: Хрящевые, Костные
Класс рыбы: Хрящевые, Костные Биологические мембраны. Транспорт веществ через мембраны
Биологические мембраны. Транспорт веществ через мембраны Сцепленное наследование генов
Сцепленное наследование генов Отряд Рукокрылые
Отряд Рукокрылые