Слайд 2

Chemical kinetics studies the rate and mechanism of chemical reactions
Слайд 3

In homogeneous reactions all the reactants exist in the same phase
in which the reaction itself occurs. Na2CO3 + HCl ↔ NaHCO3 + NaCl
Heterogeneous reactions take place only in the interphase.
Fe + HCl⭢FeCl2 +H2
Слайд 4

Single-stage reactions are called simple
(or elementary) reactions.
Multistage reactions include few
simple reactions and are called complex
(or non-elementary) reactions.
All biochemical reactions are non-elementary.
Слайд 5

The dependence of the reaction rate on the concentration of reactants
is described by the law of mass action discovered by N.Beketov, C. Guldberg and P. Waage in 1967:
«At constant temperature the rate of chemical reaction is in direct proportion to the product of reactant concentrations in the degree of their stoichiometric coefficients».
Слайд 6

Mathematical expression of the law of mass action is called a
kinetic
equation
or
rate law of the reaction.
Слайд 7

Molecularity of the reaction
is determined by the number of molecules
which interact and take part in an elementary act of the reaction.
Слайд 8

Arrenius Equation
establishes a connection between the reaction rate constant, activation
energy and temperature:
e is base of natural logarithm;
R is universal gas constant (8.314 J / mol · K);
T is absolute temperature, K;
A is pre-exponential factor.
Слайд 9

Catalysis is the change of chemical reactions rate under the influence
of substances, the amount and nature of which, after completion of the reaction are the same as before the reaction.
Catalyst is a substance that influences the rate of chemical processes without changing its own chemical composition.








 Возрастная изменчивость мышечных качеств
Возрастная изменчивость мышечных качеств Декоративные качества листьев
Декоративные качества листьев Физиология и биохимия микроорганизмов. Биохимическая идентификация бактерий (часть 2)
Физиология и биохимия микроорганизмов. Биохимическая идентификация бактерий (часть 2) Мы - друзья пернатых
Мы - друзья пернатых Биосфера эволюциясы
Биосфера эволюциясы Систематика растений. Многообразие растений
Систематика растений. Многообразие растений Мышцы. Работа мышц
Мышцы. Работа мышц Как разные животные готовятся к зиме
Как разные животные готовятся к зиме Всероссийские проверочные работы по биологии
Всероссийские проверочные работы по биологии Лабораторные, микробиологические и иммунологические исследования. Окраска препаратов по методу Грама
Лабораторные, микробиологические и иммунологические исследования. Окраска препаратов по методу Грама Понятие биологического вида
Понятие биологического вида Презентация Системы органов в организме биология 8 класс
Презентация Системы органов в организме биология 8 класс Анатомия мышечной системы
Анатомия мышечной системы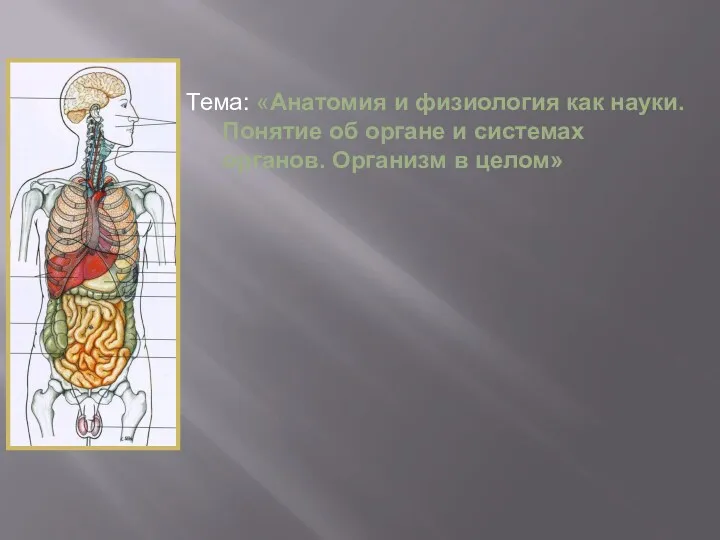 Анатомия и физиология, как науки. Понятие об органе и системах органов. Организм в целом
Анатомия и физиология, как науки. Понятие об органе и системах органов. Организм в целом Анатомия лошади
Анатомия лошади Немембранные и двумембранные органоиды
Немембранные и двумембранные органоиды Общая и медицинская генетика
Общая и медицинская генетика Белки - важнейшие компоненты клеток
Белки - важнейшие компоненты клеток Урок по биологии 8 класс Строение органа слуха
Урок по биологии 8 класс Строение органа слуха Развитие представлений о происхождении жизни на Земле. Гипотеза Опарина-Холдейна
Развитие представлений о происхождении жизни на Земле. Гипотеза Опарина-Холдейна Презентация к уроку по теме :Водоросли
Презентация к уроку по теме :Водоросли Презентация Систематика растений.
Презентация Систематика растений. Двумембранные органоиды клетки
Двумембранные органоиды клетки Что такое экосистема
Что такое экосистема Растительный и животный мир Донецкого края
Растительный и животный мир Донецкого края Суспільна, групова, територіальна, репродуктивна поведінка тварин
Суспільна, групова, територіальна, репродуктивна поведінка тварин The theory of phylembryogenesis
The theory of phylembryogenesis Биологические негативные факторы
Биологические негативные факторы