Слайд 2
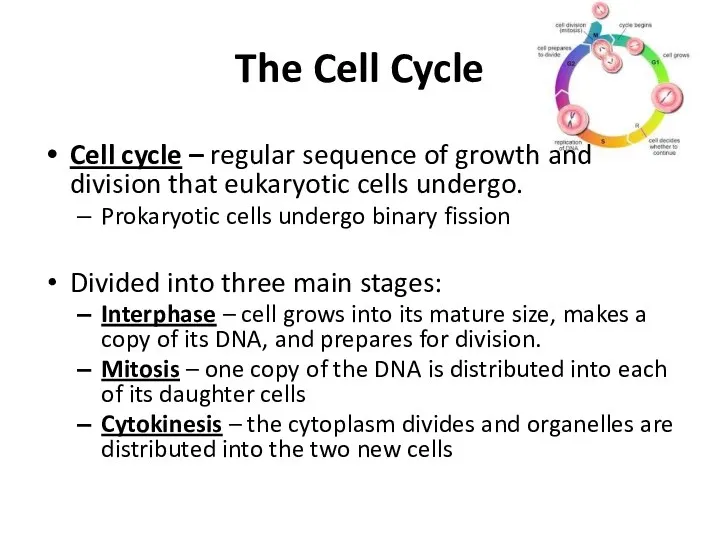
The Cell Cycle
Cell cycle – regular sequence of growth and division
that eukaryotic cells undergo.
Prokaryotic cells undergo binary fission
Divided into three main stages:
Interphase – cell grows into its mature size, makes a copy of its DNA, and prepares for division.
Mitosis – one copy of the DNA is distributed into each of its daughter cells
Cytokinesis – the cytoplasm divides and organelles are distributed into the two new cells
Слайд 3

Слайд 4
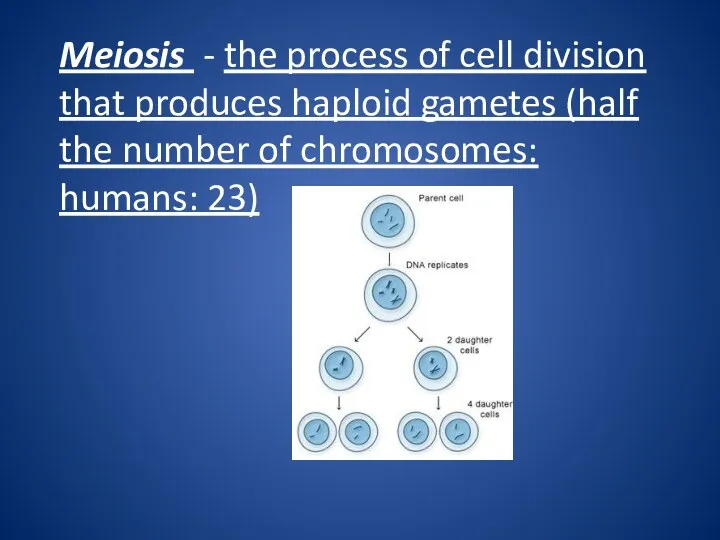
Meiosis - the process of cell division that produces haploid gametes
(half the number of chromosomes: humans: 23)
Слайд 5

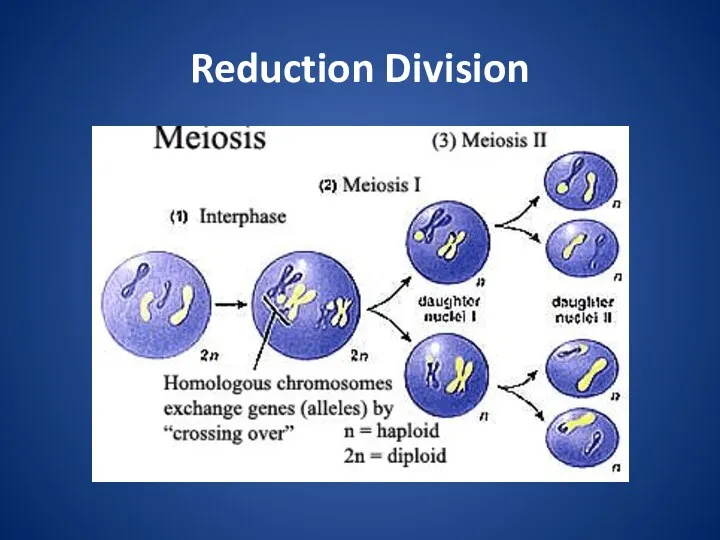
Reduction Division
Since the sperm and the egg contain only half the
number of chromosomes, they cannot be formed from mitosis.
Meiosis - the process of cell division that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes as somatic cells
Cell undergoes 2 rounds of cell division:
Meiosis 1
Meiosis 2
Humans have 46 chromosomes in their somatic cells.
Слайд 6
Слайд 7

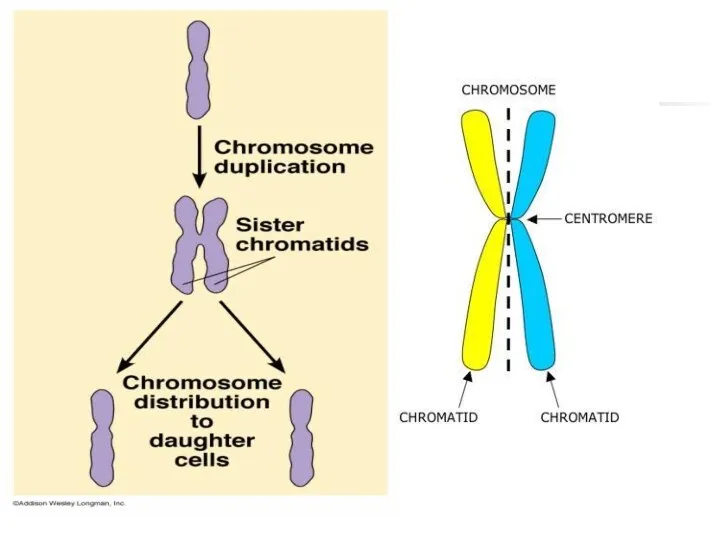
Meiosis I
Preceded by Interphase- chromosomes are replicated to form sister chromatids
Sister
chromatids are genetically identical and joined at centromere
Слайд 8
Слайд 9
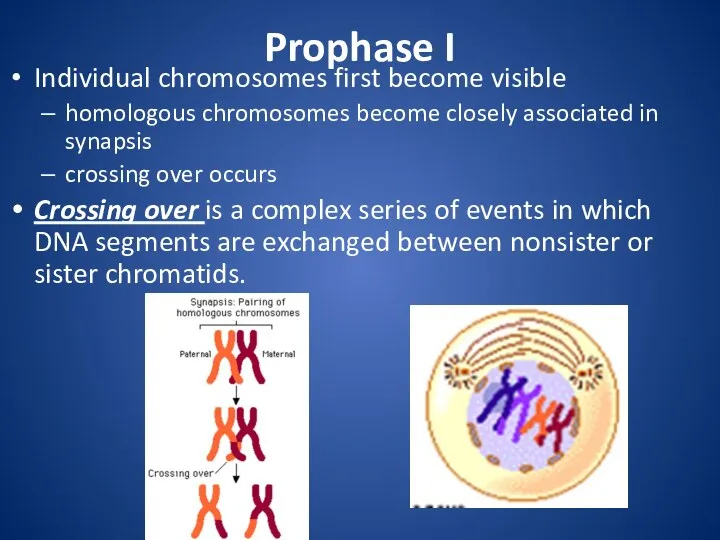
Prophase I
Individual chromosomes first become visible
homologous chromosomes become closely associated
in synapsis
crossing over occurs
Crossing over is a complex series of events in which DNA segments are exchanged between nonsister or sister chromatids.
Слайд 10
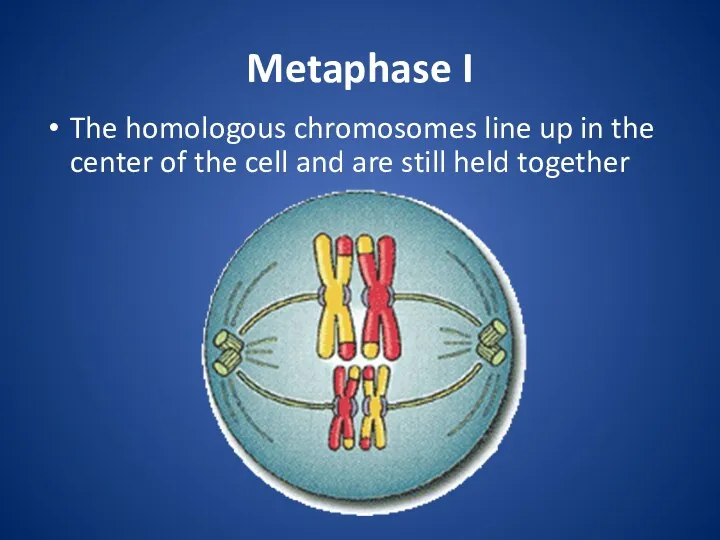
Metaphase I
The homologous chromosomes line up in the center of the
cell and are still held together
Слайд 11

Anaphase I
Spindle fibers shorten
The homologous chromosomes are separated (the sister chromatids
are still paired)
Слайд 12

Telophase I
The nuclear membrane reforms around each daughter nucleus
Each new cell
now contains two sister chromatids that are NOT identical due to crossing over
Слайд 13
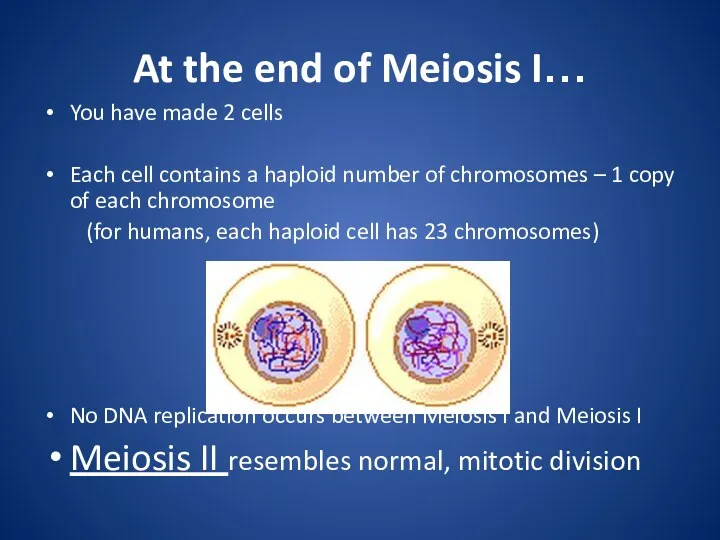
At the end of Meiosis I…
You have made 2 cells
Each cell
contains a haploid number of chromosomes – 1 copy of each chromosome
(for humans, each haploid cell has 23 chromosomes)
No DNA replication occurs between Meiosis I and Meiosis I
Meiosis II resembles normal, mitotic division
Слайд 14
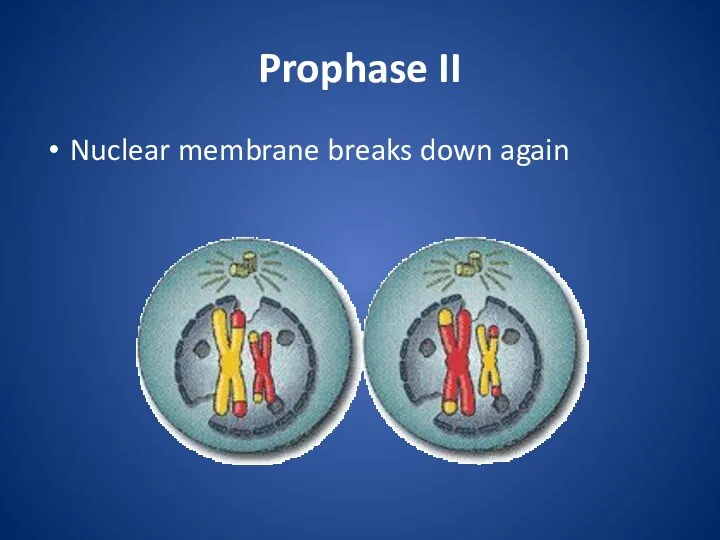
Prophase II
Nuclear membrane breaks down again
Слайд 15
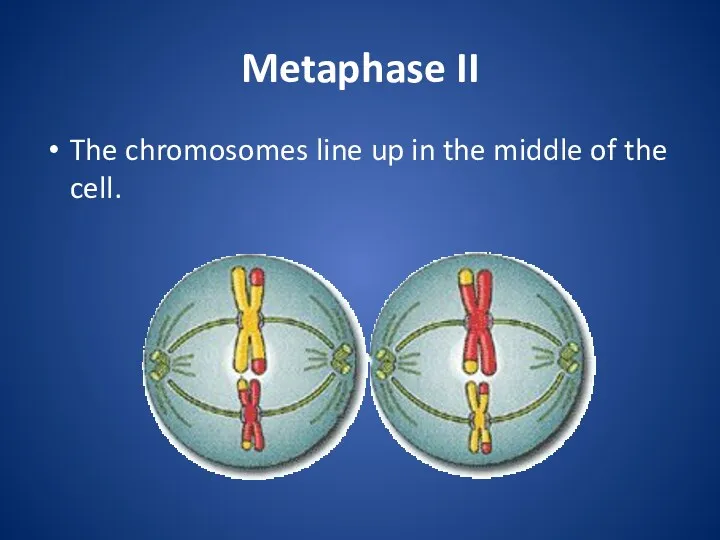
Metaphase II
The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
Слайд 16
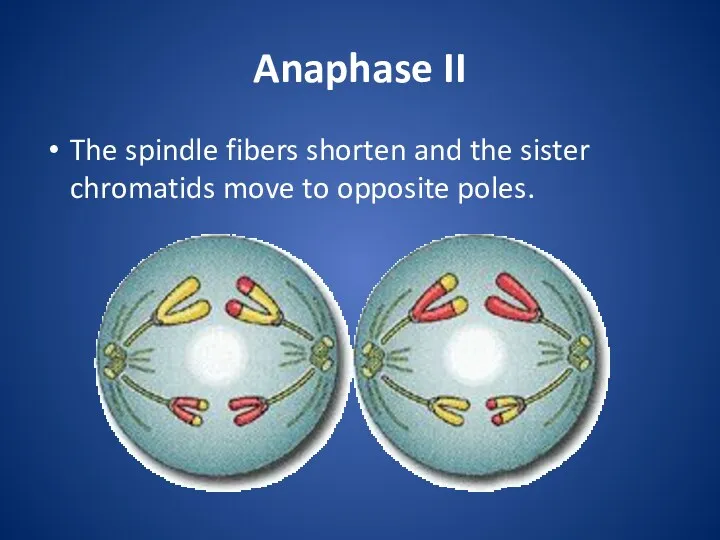
Anaphase II
The spindle fibers shorten and the sister chromatids move to
opposite poles.
Слайд 17
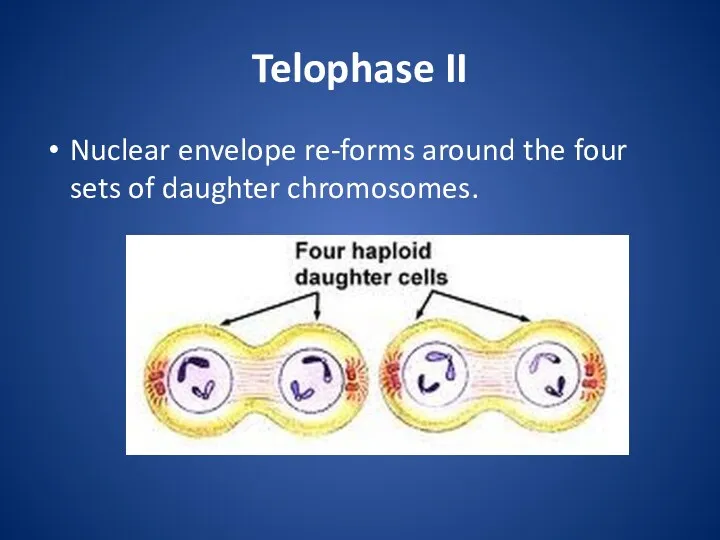
Telophase II
Nuclear envelope re-forms around the four sets of daughter chromosomes.
















 Ощущение и восприятие. Нейрофизиологические механизмы восприятия
Ощущение и восприятие. Нейрофизиологические механизмы восприятия Анатомо-физиологические особенности системы органов дыхания
Анатомо-физиологические особенности системы органов дыхания Сцепленное наследование признаков
Сцепленное наследование признаков Тип Nemathelminthes. Класс Gаstrotricha
Тип Nemathelminthes. Класс Gаstrotricha Сердечно-сосудистая система
Сердечно-сосудистая система Клеточный цикл. Деление клетки
Клеточный цикл. Деление клетки Связи между показателями строения древостоев по высоте и формой насаждения
Связи между показателями строения древостоев по высоте и формой насаждения Генетические алгоритмы
Генетические алгоритмы Класс Млекопитающие (Звери)
Класс Млекопитающие (Звери) Общие закономерности ВНД у человека и животных
Общие закономерности ВНД у человека и животных Породы лошадей
Породы лошадей Водоросли
Водоросли Обмен веществ в организме человека
Обмен веществ в организме человека Дикие животные леса. Игра для детей старшего дошкольного возраста
Дикие животные леса. Игра для детей старшего дошкольного возраста Состав и структура сообщества
Состав и структура сообщества Изучение многообразия животных по следам их жизнедеятельности (по объектам природной части краеведческого музея)
Изучение многообразия животных по следам их жизнедеятельности (по объектам природной части краеведческого музея) Выдающиеся биологи России
Выдающиеся биологи России Физиология дыхательной системы
Физиология дыхательной системы Зәр шығару жүйесі
Зәр шығару жүйесі Систематика живого мира
Систематика живого мира Жизнь в океане
Жизнь в океане Беспозвоночные. Особенности строения и экологии представителей некоторых систематических групп
Беспозвоночные. Особенности строения и экологии представителей некоторых систематических групп Биосинтез белка
Биосинтез белка Анализ типичных ошибок участников ЕГЭ по биологии 2019 года
Анализ типичных ошибок участников ЕГЭ по биологии 2019 года Домашние питомцы
Домашние питомцы Антропозоонозы. Гигиена труда при обслуживании больных животных
Антропозоонозы. Гигиена труда при обслуживании больных животных Викторина по биологии
Викторина по биологии Ракообразные (лат. Crustacea)
Ракообразные (лат. Crustacea)