Содержание
- 3. The Cell Membrane
- 5. At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Describe the function of the
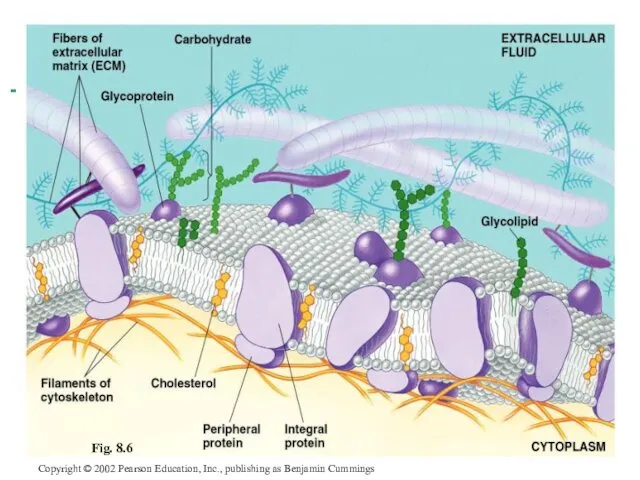
- 6. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Fig. 8.6
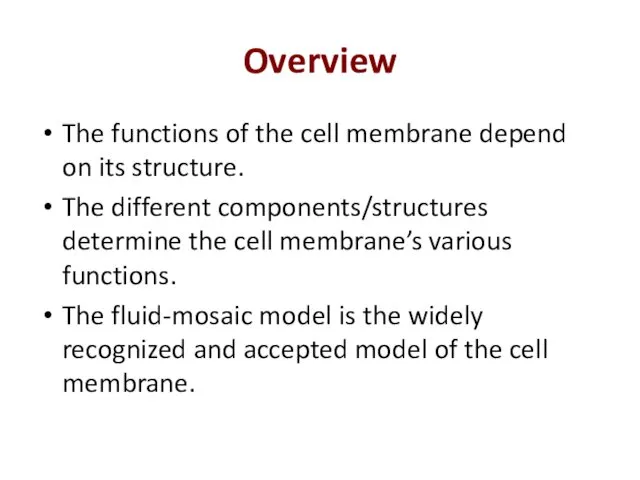
- 7. Overview The functions of the cell membrane depend on its structure. The different components/structures determine the
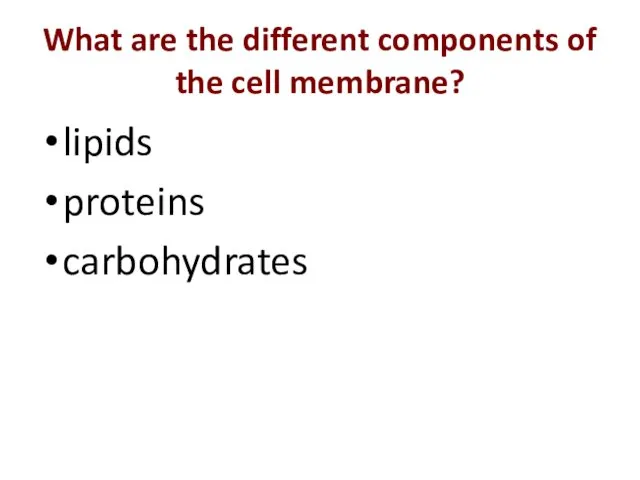
- 8. What’s in it? What are the different components of the cell membrane?
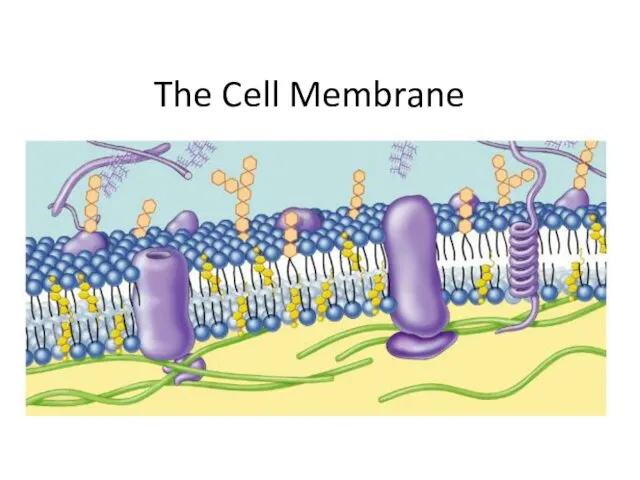
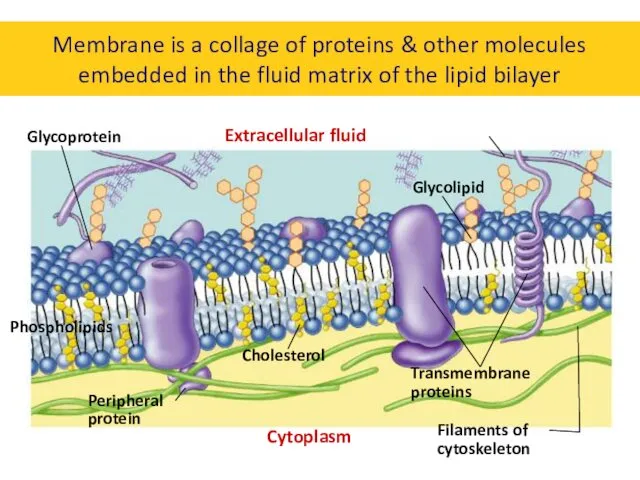
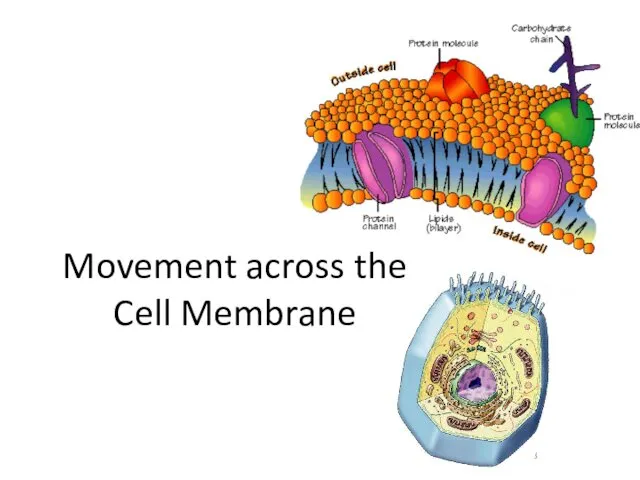
- 9. Membrane is a collage of proteins & other molecules embedded in the fluid matrix of the
- 10. What are the different components of the cell membrane? lipids proteins carbohydrates
- 11. Amphipathic = has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts
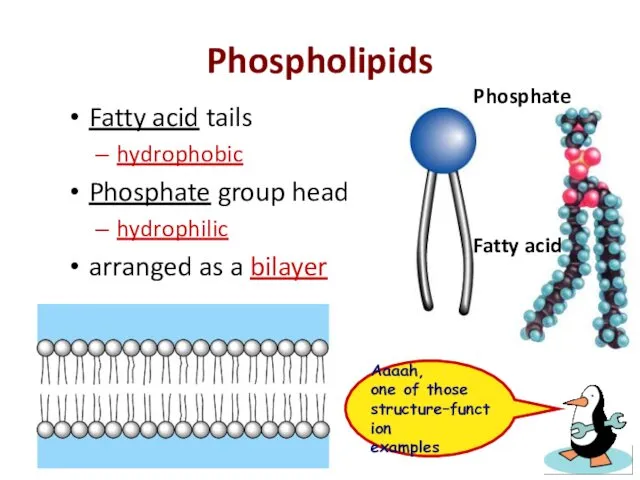
- 12. Phospholipids Fatty acid Phosphate Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Phosphate group head hydrophilic arranged as a bilayer
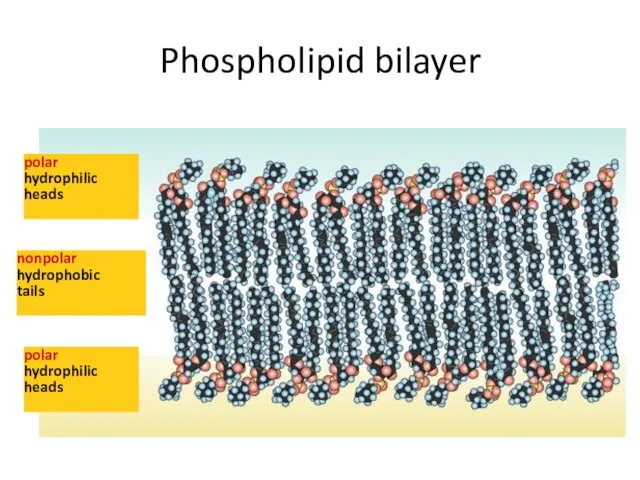
- 13. Phospholipid bilayer polar hydrophilic heads nonpolar hydrophobic tails polar hydrophilic heads
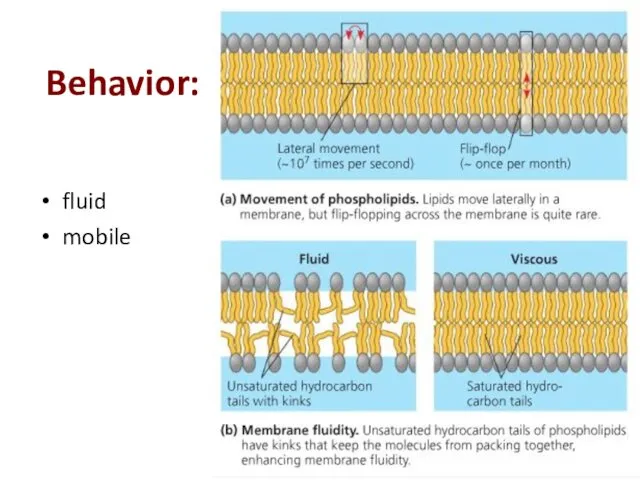
- 14. Behavior: fluid mobile
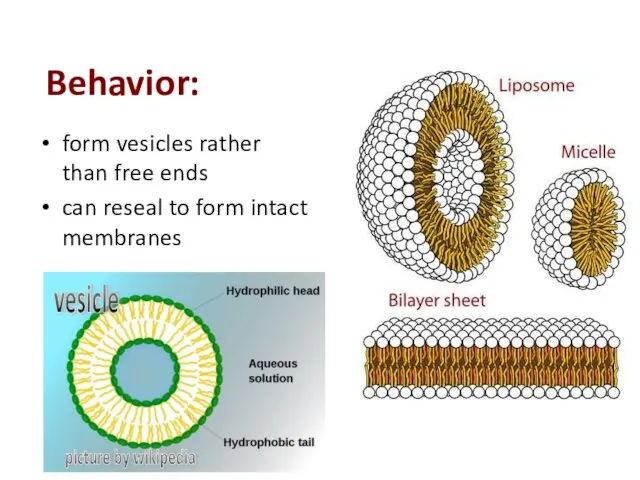
- 15. Behavior: form vesicles rather than free ends can reseal to form intact membranes
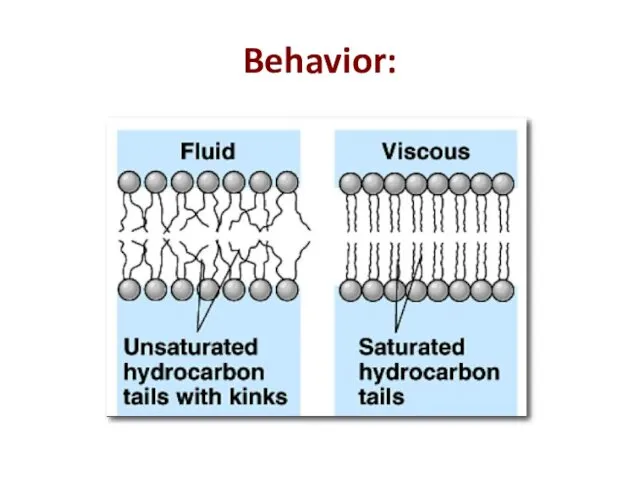
- 16. Behavior:
- 17. Membrane Fat Composition Varies! % unsaturated fatty acids keep the bilipid layer fluid The number of
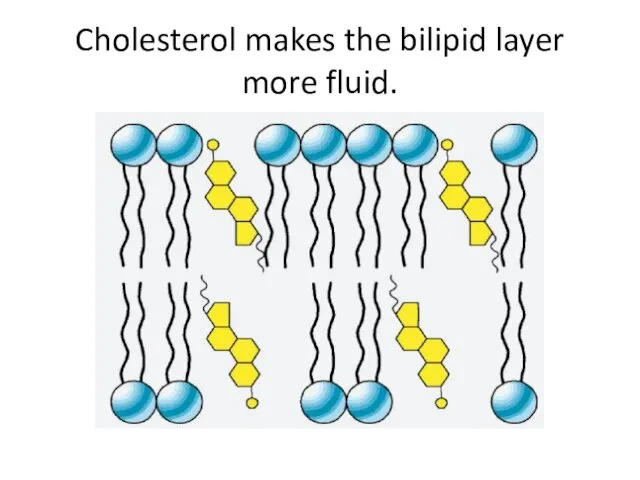
- 18. Cholesterol makes the bilipid layer more fluid.
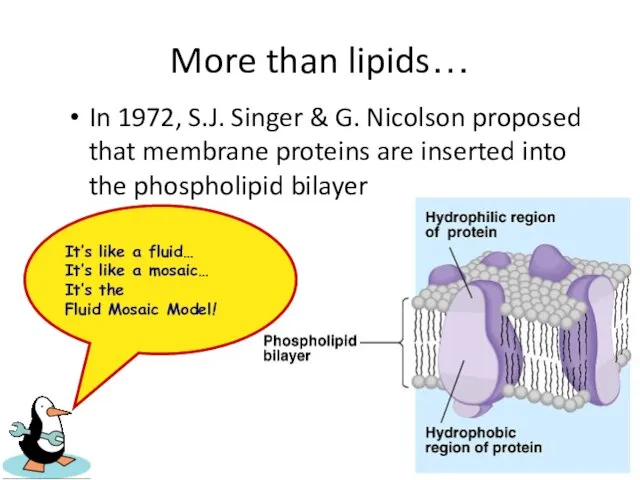
- 19. More than lipids… In 1972, S.J. Singer & G. Nicolson proposed that membrane proteins are inserted
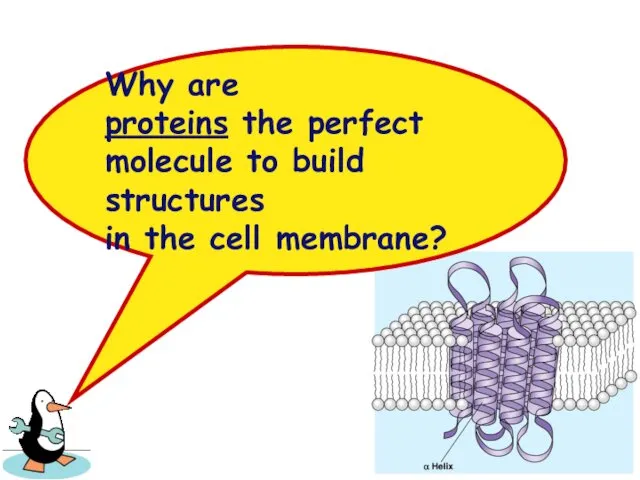
- 20. 2007-2008 Why are proteins the perfect molecule to build structures in the cell membrane?
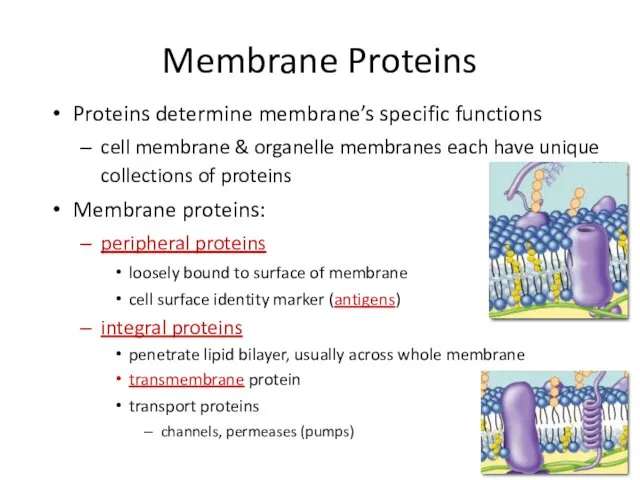
- 21. Membrane Proteins Proteins determine membrane’s specific functions cell membrane & organelle membranes each have unique collections
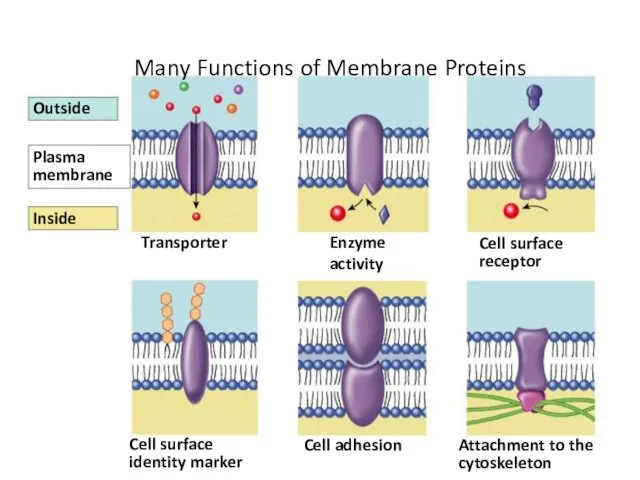
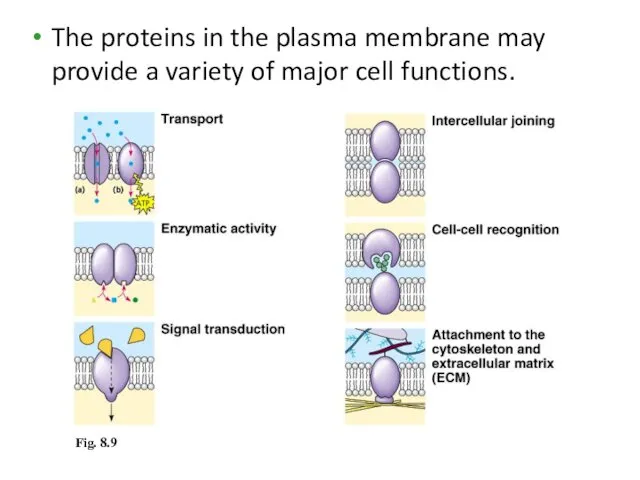
- 22. Many Functions of Membrane Proteins Outside Plasma membrane Inside Transporter Cell surface receptor Enzyme activity Cell
- 23. The proteins in the plasma membrane may provide a variety of major cell functions. Fig. 8.9
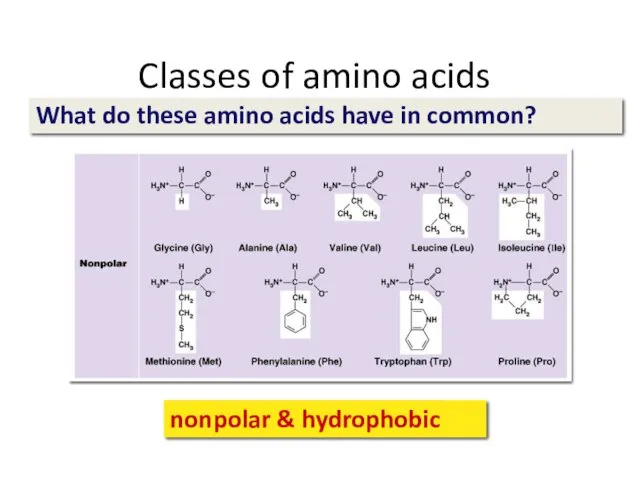
- 24. Classes of amino acids What do these amino acids have in common? nonpolar & hydrophobic
- 25. Classes of amino acids What do these amino acids have in common? polar & hydrophilic I
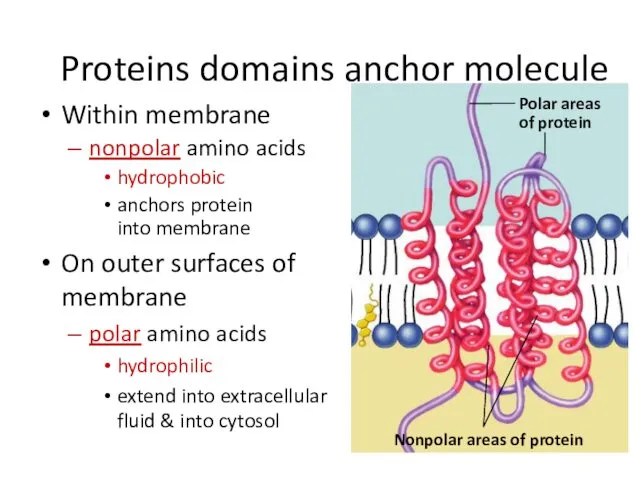
- 26. Proteins domains anchor molecule Within membrane nonpolar amino acids hydrophobic anchors protein into membrane On outer
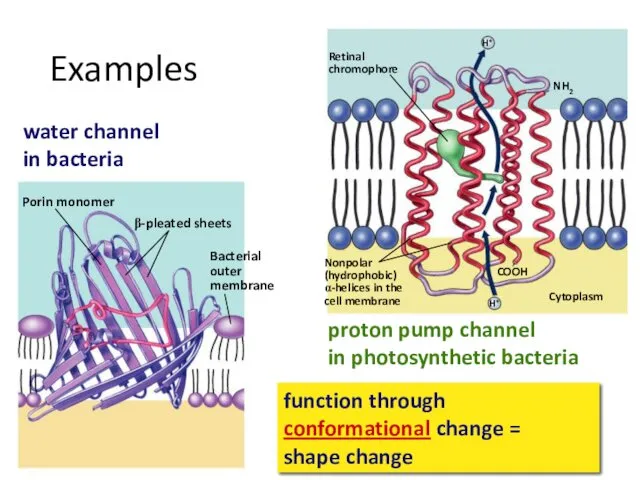
- 27. proton pump channel in photosynthetic bacteria water channel in bacteria function through conformational change = shape
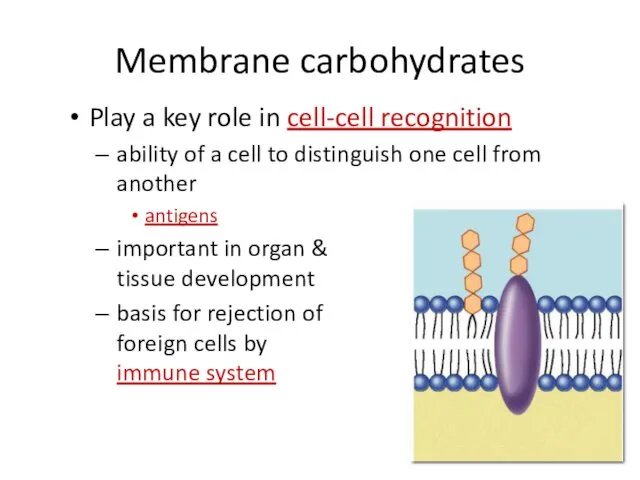
- 28. Membrane carbohydrates Play a key role in cell-cell recognition ability of a cell to distinguish one
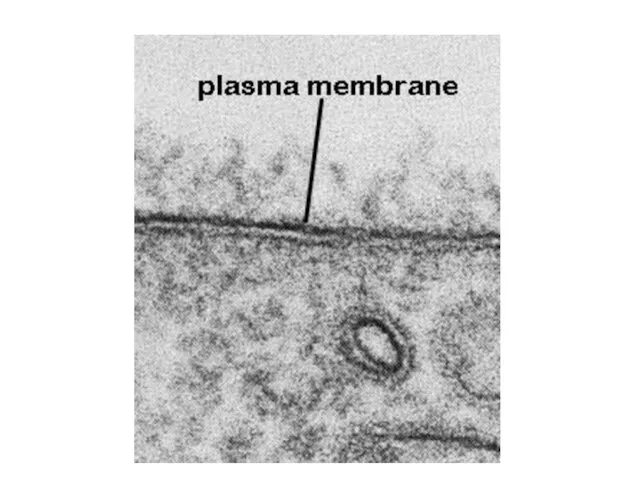
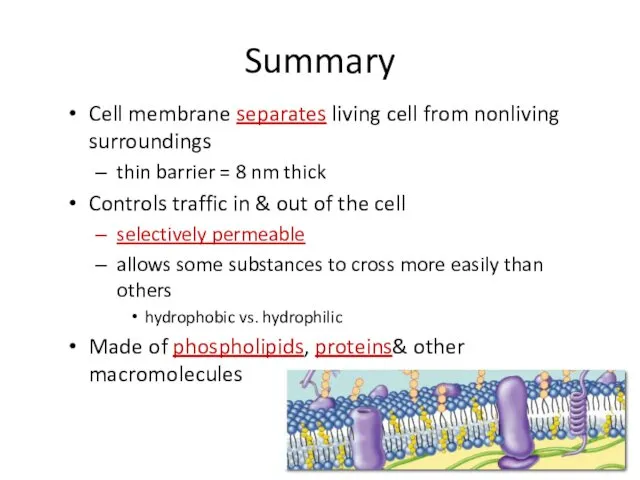
- 29. Summary Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8 nm thick Controls
- 30. Functions of the plasma membrane: acts like the “skin of the cell” separates the intracellular components
- 31. Any Questions??
- 32. 2007-2008 Movement across the Cell Membrane
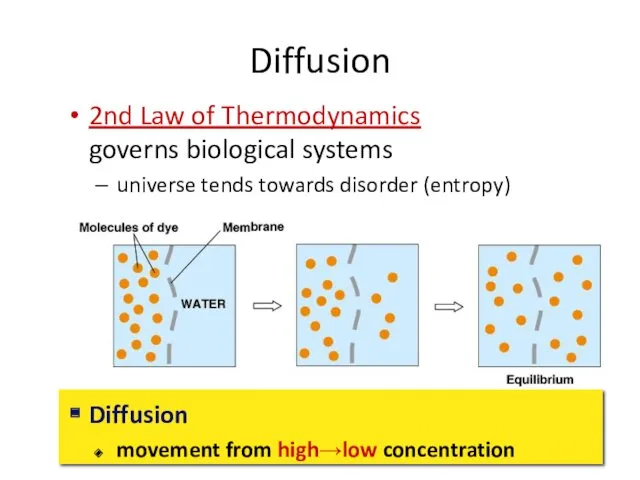
- 33. Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological systems universe tends towards disorder (entropy) Diffusion movement from
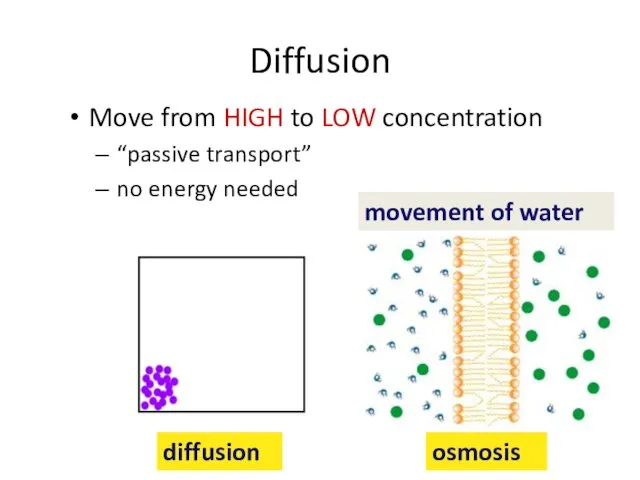
- 34. Diffusion Move from HIGH to LOW concentration “passive transport” no energy needed diffusion osmosis movement of
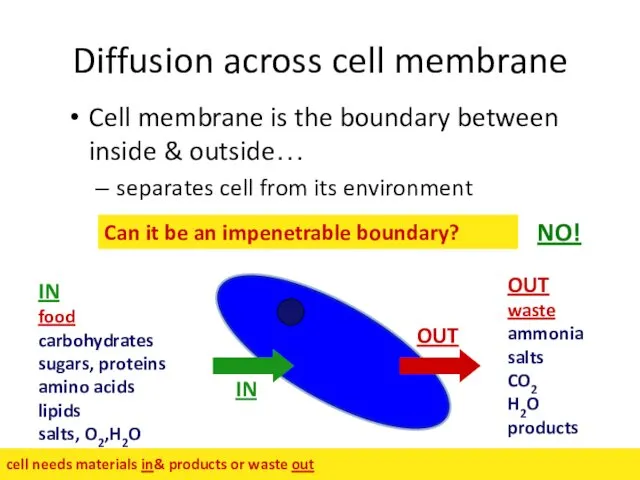
- 35. Diffusion across cell membrane Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside… separates cell from
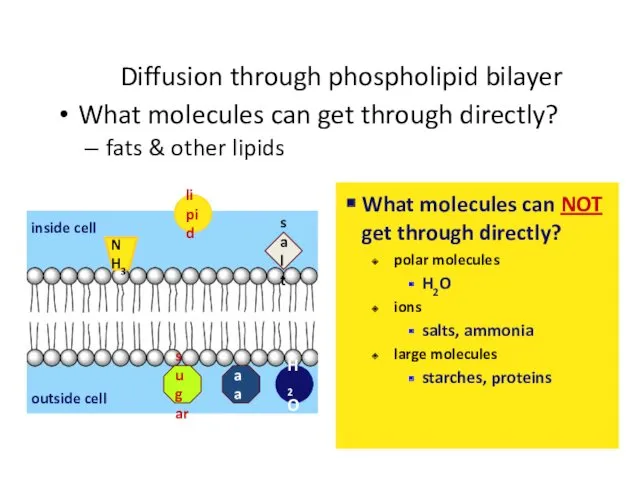
- 36. Diffusion through phospholipid bilayer What molecules can get through directly? fats & other lipids lipid salt
- 37. Channels through cell membrane Membrane becomes semi-permeable with protein channels specific channels allow specific material across
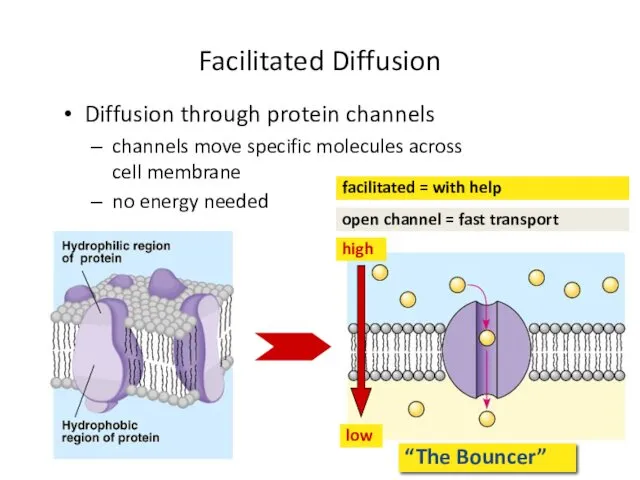
- 38. Facilitated Diffusion Diffusion through protein channels channels move specific molecules across cell membrane no energy needed
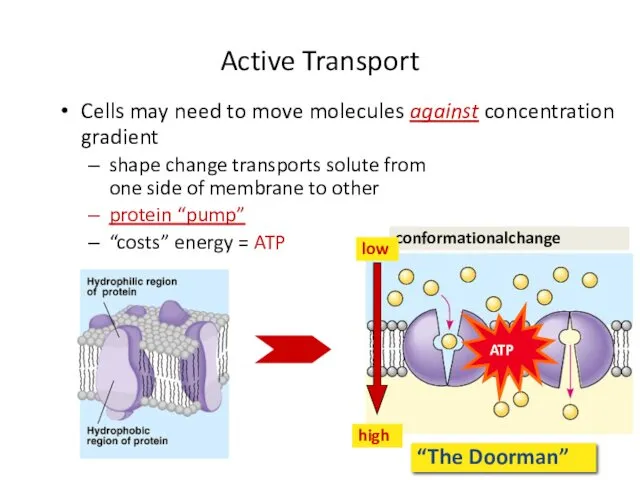
- 39. Active Transport “The Doorman” conformationalchange Cells may need to move molecules against concentration gradient shape change
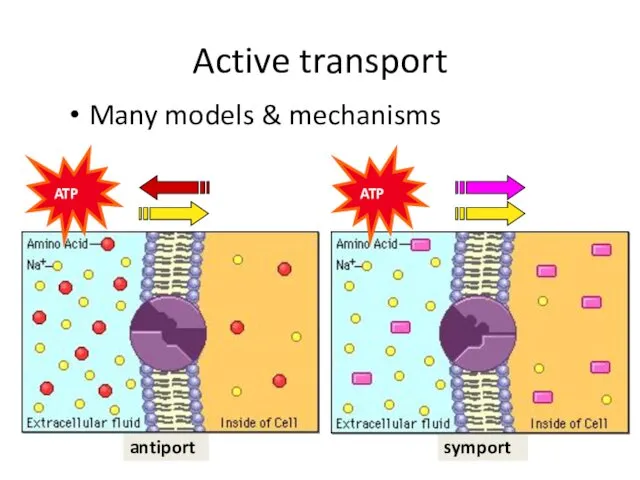
- 40. symport antiport Active transport Many models & mechanisms ATP ATP
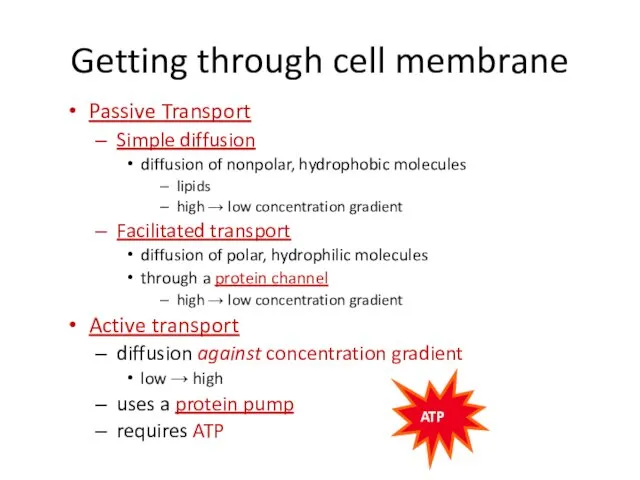
- 41. Getting through cell membrane Passive Transport Simple diffusion diffusion of nonpolar, hydrophobic molecules lipids high →
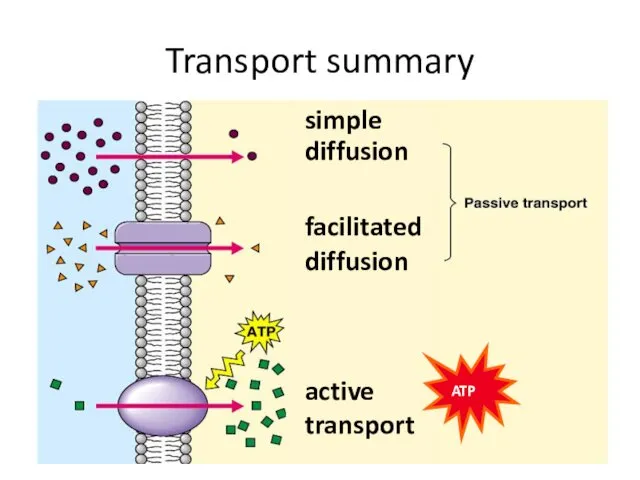
- 42. Transport summary simple diffusion facilitated diffusion active transport ATP
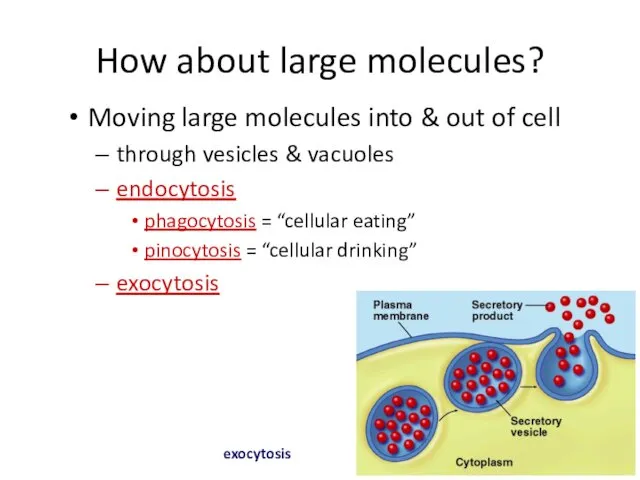
- 43. How about large molecules? Moving large molecules into & out of cell through vesicles & vacuoles
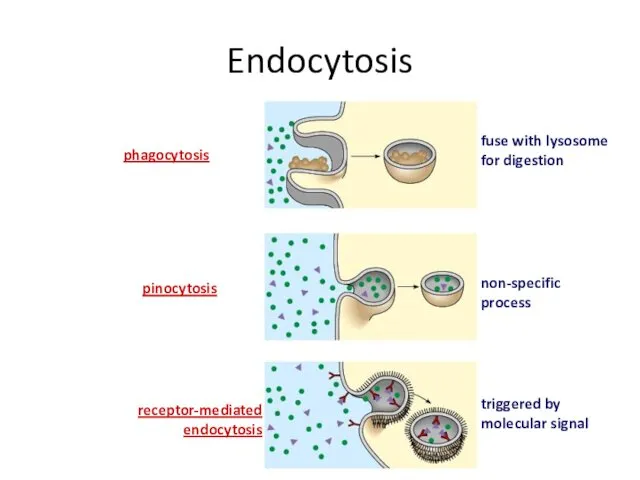
- 45. Endocytosis phagocytosis pinocytosis receptor-mediated endocytosis fuse with lysosome for digestion non-specific process triggered by molecular signal
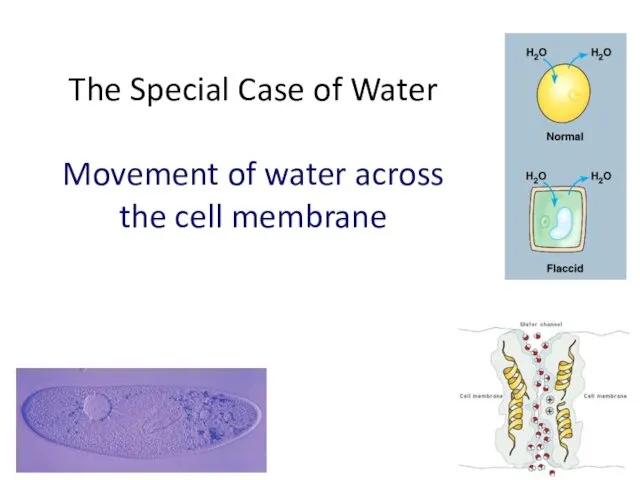
- 46. 2007-2008 The Special Case of Water Movement of water across the cell membrane
- 47. Osmosis is diffusion of water Water is very important to life, so we talk about water
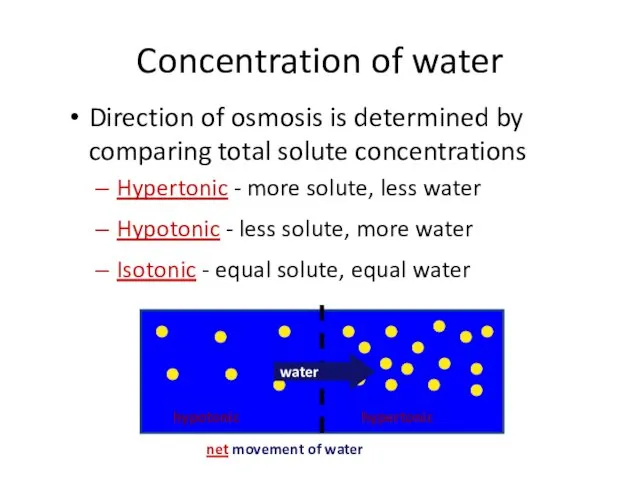
- 48. Concentration of water Direction of osmosis is determined by comparing total solute concentrations Hypertonic - more
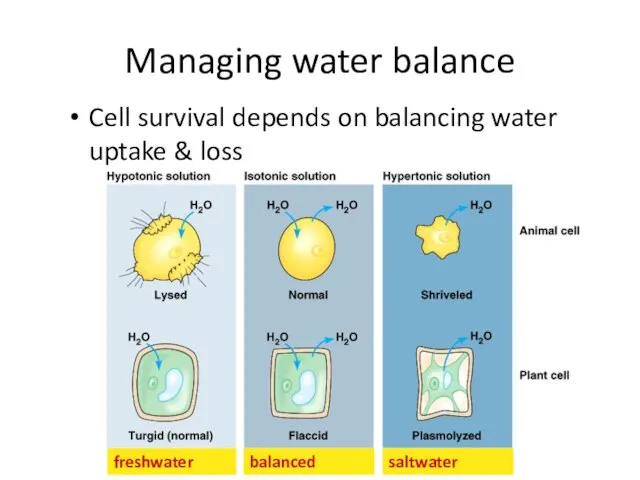
- 49. freshwater balanced saltwater Managing water balance Cell survival depends on balancing water uptake & loss
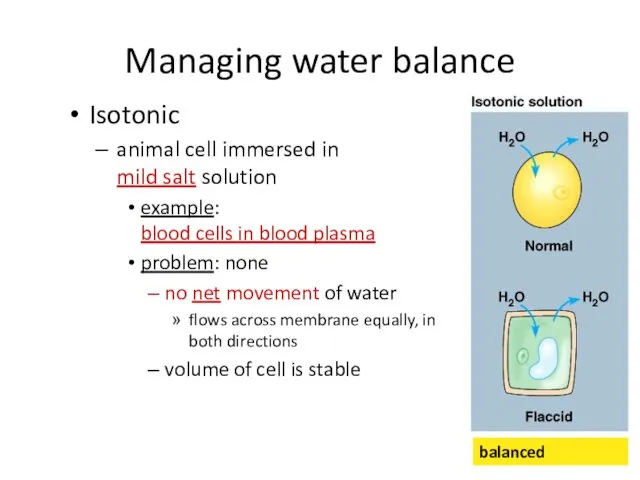
- 50. Managing water balance Isotonic animal cell immersed in mild salt solution example: blood cells in blood
- 51. Managing water balance Hypotonic a cell in fresh water example: Paramecium problem: gains water, swells &
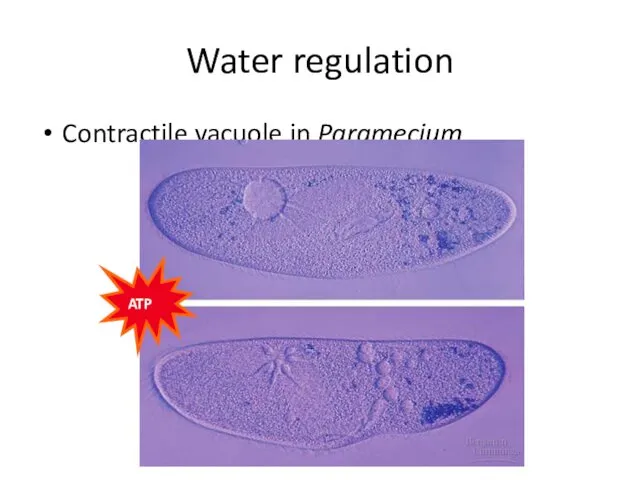
- 52. Water regulation Contractile vacuole in Paramecium ATP
- 53. Managing water balance Hypertonic a cell in salt water example: shellfish problem: lose water & die
- 54. Aquaporins Water moves rapidly into & out of cells evidence that there were water channels 1991
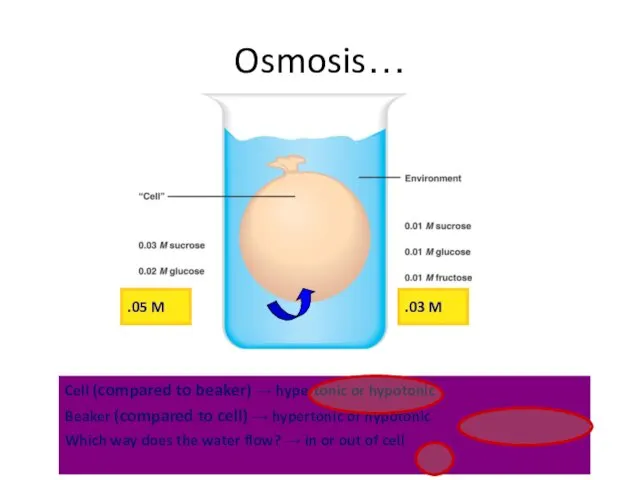
- 55. Cell (compared to beaker) → hypertonic or hypotonic Beaker (compared to cell) → hypertonic or hypotonic
- 57. Скачать презентацию











 Северцов Николай Алексеевич. Биография.
Северцов Николай Алексеевич. Биография. Внутрішня будова птахів
Внутрішня будова птахів Введение в миологию
Введение в миологию Общие представления о жизни. Уровни организации жизни. Организм. Признаки живых организмов
Общие представления о жизни. Уровни организации жизни. Организм. Признаки живых организмов Компоненты центральной нервной системы
Компоненты центральной нервной системы Дыхательная функция крови
Дыхательная функция крови Царство Растения. Высшие семенные растения. Покрытосеменные ( = цветковые)
Царство Растения. Высшие семенные растения. Покрытосеменные ( = цветковые) Породы кошек и собак
Породы кошек и собак Экологический урок: Культура обращения с отходами, раздельный сбор отходов в 2014 году
Экологический урок: Культура обращения с отходами, раздельный сбор отходов в 2014 году Первая помощь при растяжении связок, вывихах суставов, переломах костей
Первая помощь при растяжении связок, вывихах суставов, переломах костей Загадки о животных и растениях (2 класс)
Загадки о животных и растениях (2 класс) Животные Южной Америки
Животные Южной Америки презентация к уроку Голосеменные растения
презентация к уроку Голосеменные растения Введение в высокопроизводительное секвенирование
Введение в высокопроизводительное секвенирование Морфология и ультраструктура бактерий
Морфология и ультраструктура бактерий Анатомия и физиология зрительного анализатора
Анатомия и физиология зрительного анализатора Биотехнология, клеточная и генная инженерия. Клонирование
Биотехнология, клеточная и генная инженерия. Клонирование Мастерская Зелёная лаборатория
Мастерская Зелёная лаборатория Опорно-двигательная система
Опорно-двигательная система Анимированный кроссворд Насекомые
Анимированный кроссворд Насекомые Стадии воспалительной реакции. Скелетные ткани
Стадии воспалительной реакции. Скелетные ткани ГМО в нашей жизни
ГМО в нашей жизни Место человека в системе органического мира
Место человека в системе органического мира Доказательтва животного происхождения человека. Антропология
Доказательтва животного происхождения человека. Антропология Сравнительная характеристика царств живой природы
Сравнительная характеристика царств живой природы Классификация пестицидов. (Лекция 2)
Классификация пестицидов. (Лекция 2) Царство грибы
Царство грибы Основные понятия генетики
Основные понятия генетики