Содержание
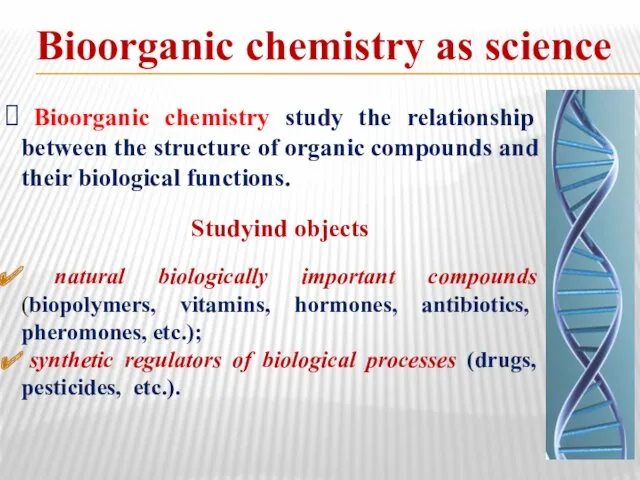
- 2. Bioorganic chemistry as science Bioorganic chemistry study the relationship between the structure of organic compounds and
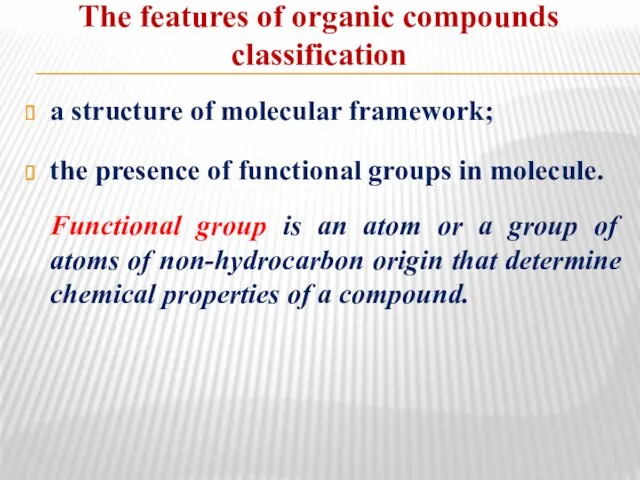
- 3. The features of organic compounds classification a structure of molecular framework; the presence of functional groups
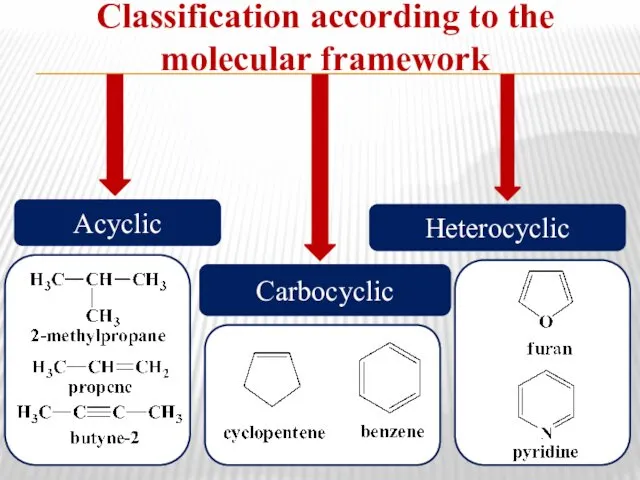
- 4. Classification according to the molecular framework Acyclic Heterocyclic Carbocyclic
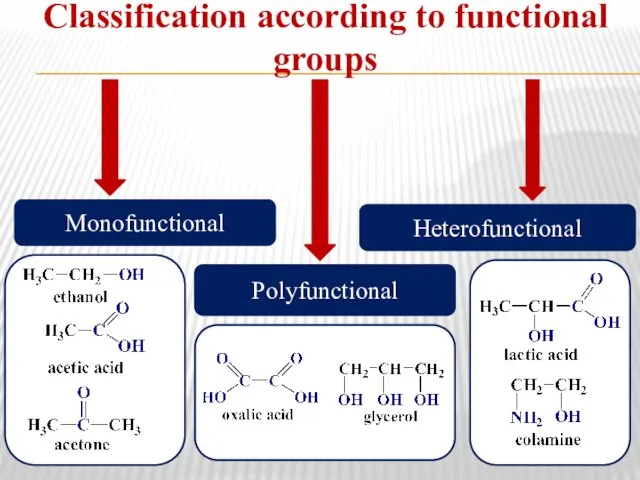
- 5. Classification according to functional groups Monofunctional Heterofunctional Polyfunctional
- 6. Nomenclature of organic compounds Nomenclature is an arrangement of terms that describes complete structure of organic
- 7. Basic terms Parent name – a part of the name used for the formation of a
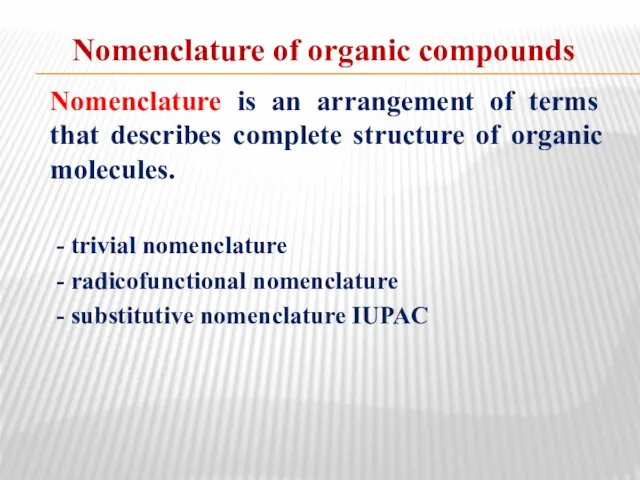
- 8. IUPAC nomenclature rules Step 1 Determine the kind of characteristic group for use as principal group,
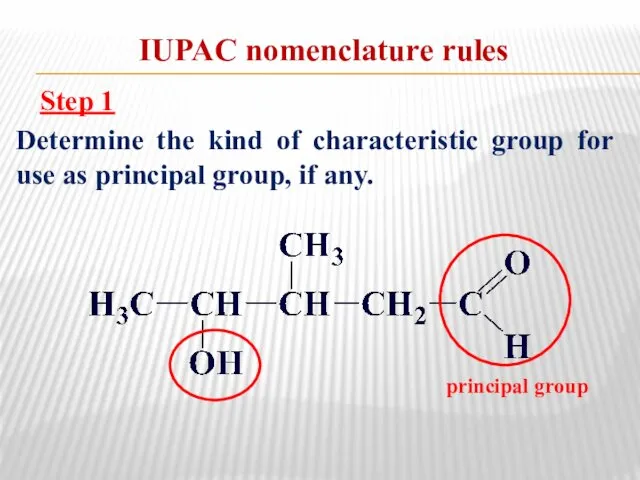
- 9. IUPAC nomenclature rules Step 2 Determine the parent structure (principal chain or parent ring system).
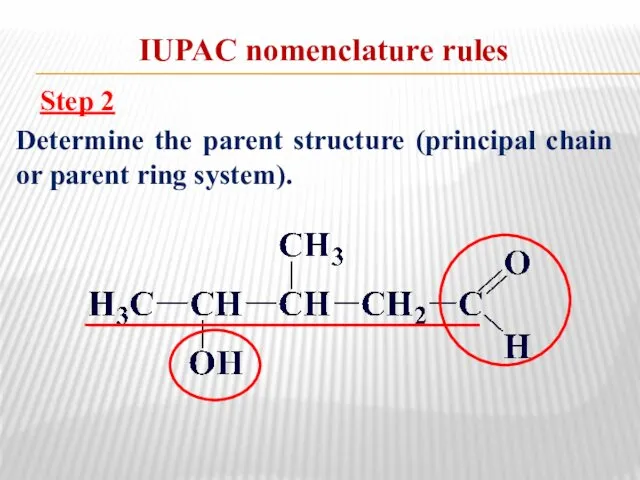
- 10. IUPAC nomenclature rules Step 3 Name the parent structure and the principal group(s). pentane al
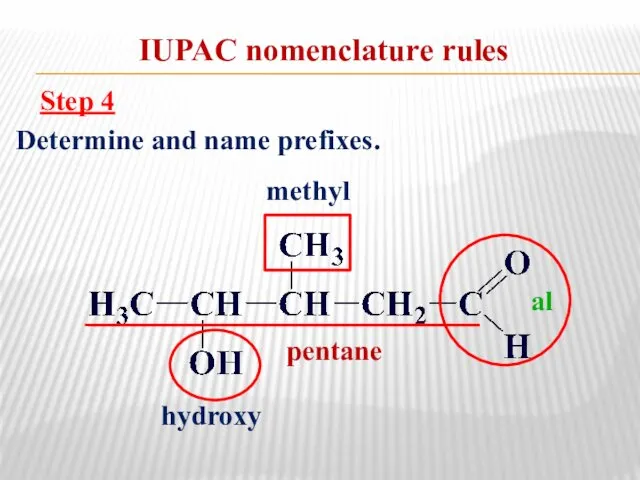
- 11. IUPAC nomenclature rules Step 4 Determine and name prefixes. pentane methyl al hydroxy
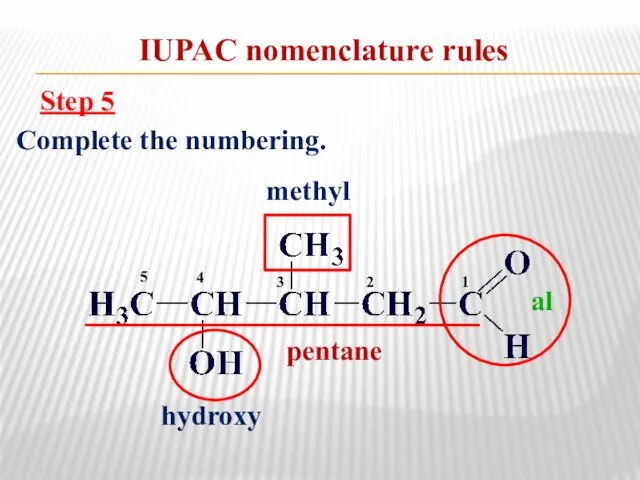
- 12. IUPAC nomenclature rules Step 5 Complete the numbering. pentane methyl al hydroxy 1 2 3 4
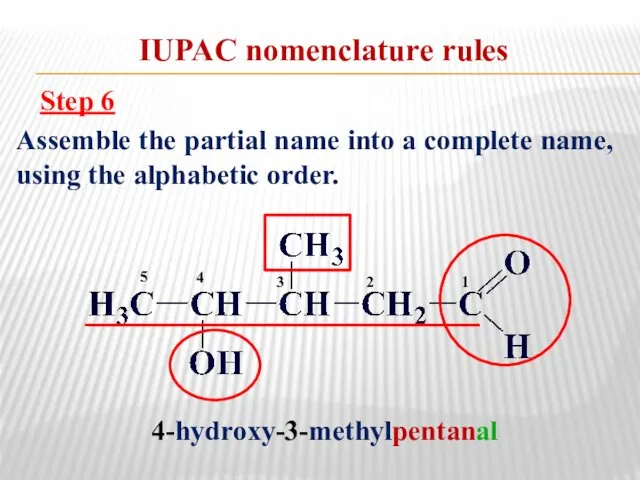
- 13. IUPAC nomenclature rules Step 6 Assemble the partial name into a complete name, using the alphabetic
- 15. Скачать презентацию

 Онтогенез как процесс реализации наследственной информации с эпигенетическими факторами. Принципы клеточной регуляции онтогенеза
Онтогенез как процесс реализации наследственной информации с эпигенетическими факторами. Принципы клеточной регуляции онтогенеза Функциональная межполушарная асимметрия мозга
Функциональная межполушарная асимметрия мозга Характеристика водорослей
Характеристика водорослей Основы разведения животных
Основы разведения животных Еңбектенудің физиологиялық негізі
Еңбектенудің физиологиялық негізі Систематические группы птиц
Систематические группы птиц Зачем животным нужен хвост. 4 класс
Зачем животным нужен хвост. 4 класс Абай ауданы, Шығыс Қазақстан облысы
Абай ауданы, Шығыс Қазақстан облысы Введение в эпизоотологию
Введение в эпизоотологию Простые и сложные соцветия
Простые и сложные соцветия Материалы конкурса Уроки качества
Материалы конкурса Уроки качества Микроорганизмы: эукариоты и прокариоты
Микроорганизмы: эукариоты и прокариоты Строение вирусов. Жизненные циклы вирусов,
Строение вирусов. Жизненные циклы вирусов, Методы изучения природы
Методы изучения природы Будова клітин прокаріот та еукаріот
Будова клітин прокаріот та еукаріот Структура и содержание КИМ - 2023
Структура и содержание КИМ - 2023 Цікаві факти з життя комах
Цікаві факти з життя комах ВПР по биологии 6 класс
ВПР по биологии 6 класс Как видят животные
Как видят животные Общие свойства живых организмов
Общие свойства живых организмов Анамнії та амніоти
Анамнії та амніоти Мероприятия экологической акции Скворушка, проводимые в МКОУ БСОШ №7
Мероприятия экологической акции Скворушка, проводимые в МКОУ БСОШ №7 Ферменты. Биологически активные вещества
Ферменты. Биологически активные вещества Механизмы репродукции клеток
Механизмы репродукции клеток Цветок, его строение и значение
Цветок, его строение и значение Иллюзии зрения
Иллюзии зрения Классификация покрытосеменных растений. Отдел Покрытосеменные. Класс Двудольные. Класс Однодольные
Классификация покрытосеменных растений. Отдел Покрытосеменные. Класс Двудольные. Класс Однодольные Гости из далёких стран
Гости из далёких стран