Содержание
- 2. The essence of genetic engineering
- 3. Learning objective explain the essence of genetic engineering
- 4. Success criteria 1.Gives the concept of genetic engineering. 2. Describes the stages of genetic engineering. 3.
- 5. Terminology Restriction enzyme, DNA ligase, DNA polymerase, reverse transcriptase Genetic engineering Recombinant DNA Insulin Vector, plasmid
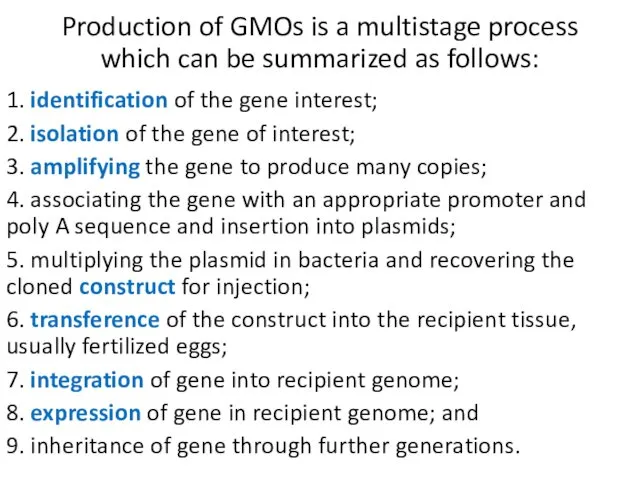
- 6. Production of GMOs is a multistage process which can be summarized as follows: 1. identification of
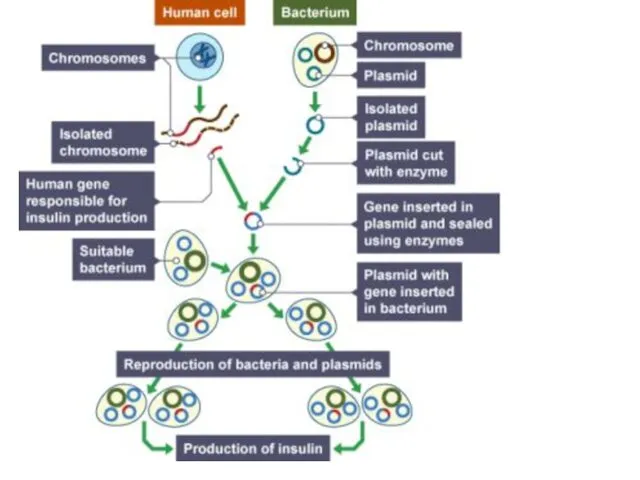
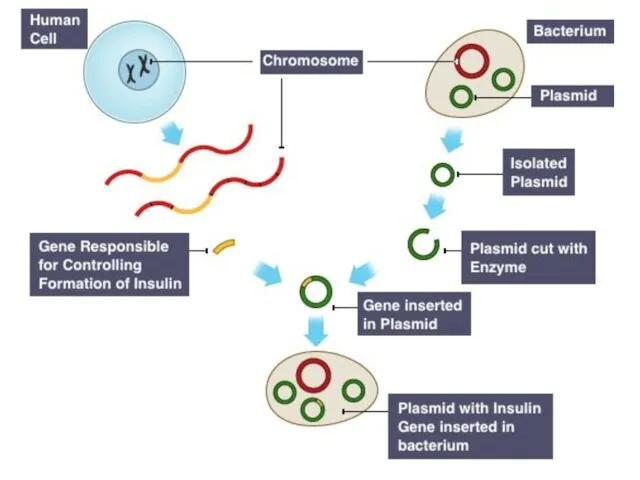
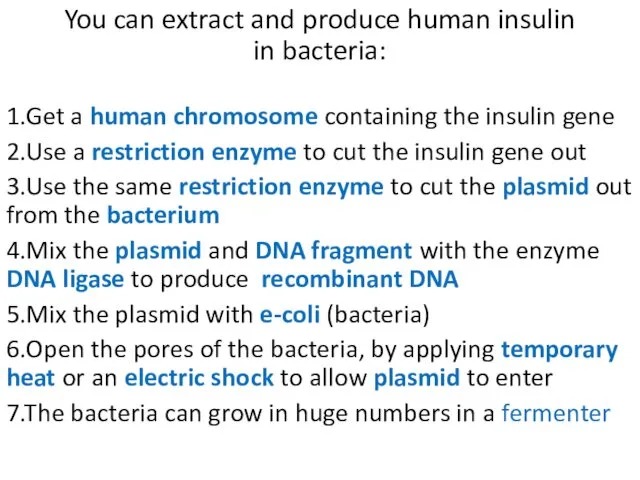
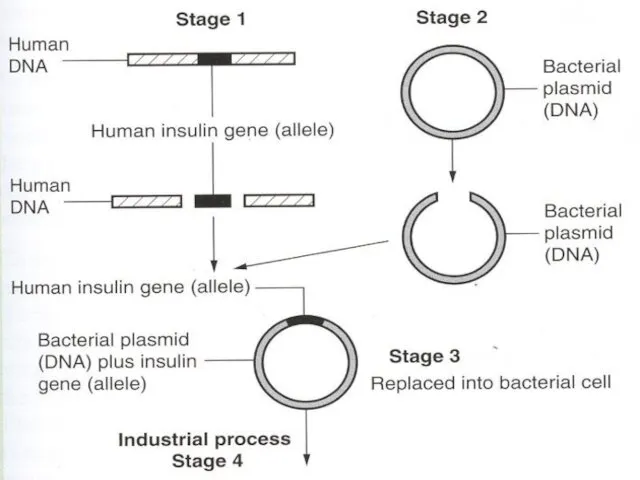
- 9. You can extract and produce human insulin in bacteria: 1.Get a human chromosome containing the insulin
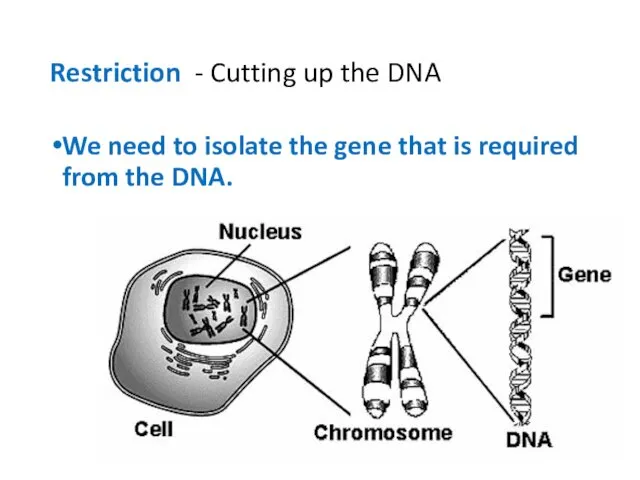
- 10. Restriction - Cutting up the DNA We need to isolate the gene that is required from
- 11. Enzymes can be used that cut the DNA strand isolating the gene. These enzymes are called
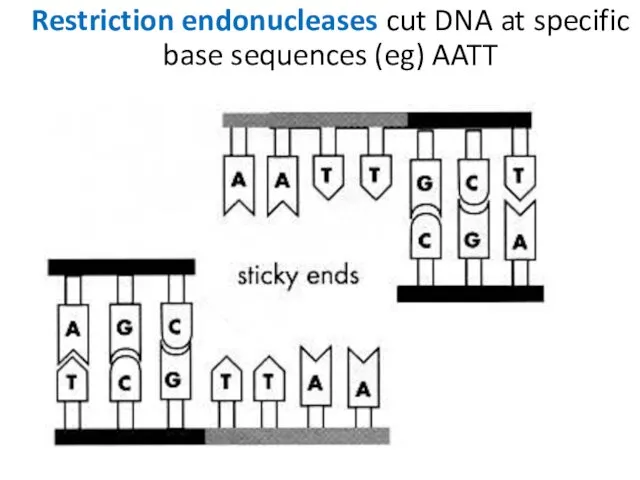
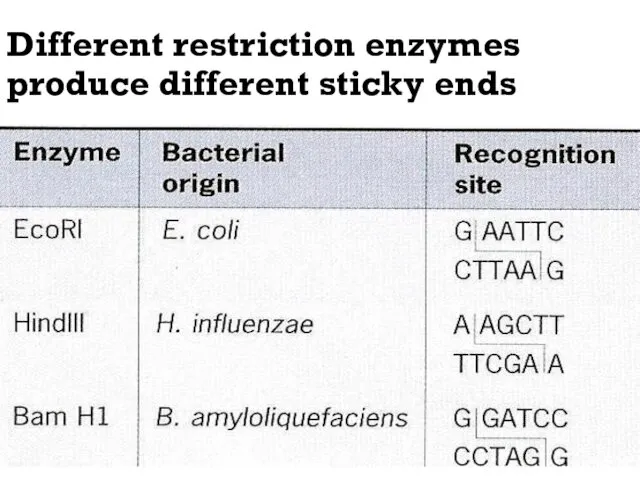
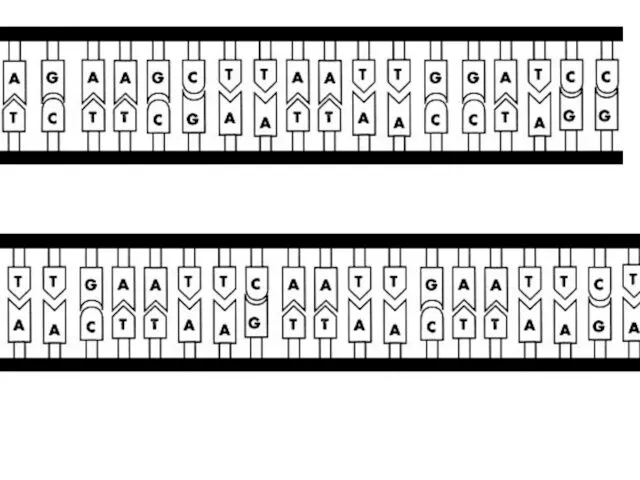
- 12. Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific base sequences (eg) AATT
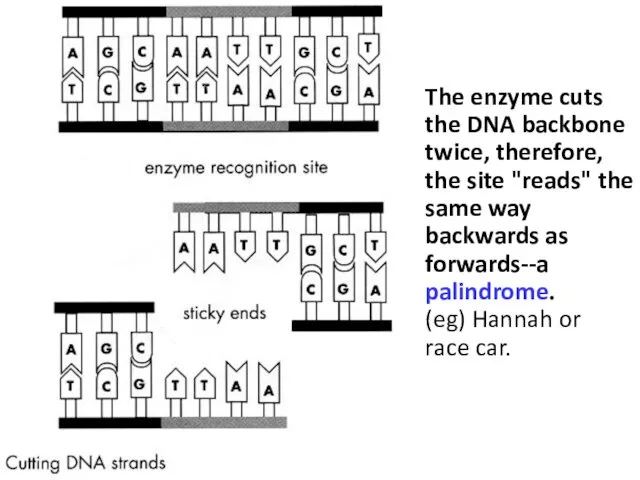
- 13. The enzyme cuts the DNA backbone twice, therefore, the site "reads" the same way backwards as
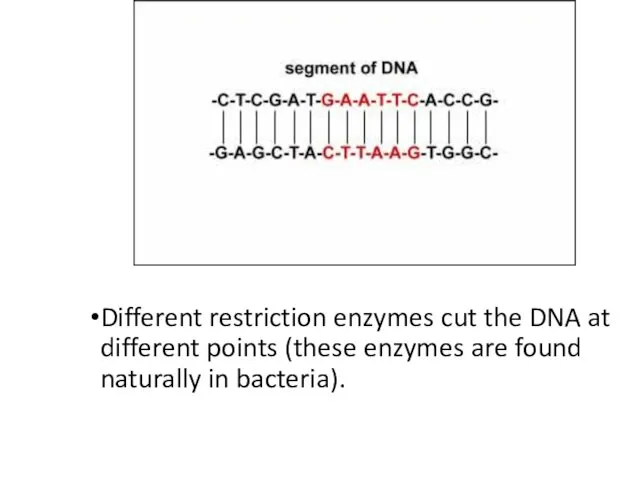
- 14. Different restriction enzymes cut the DNA at different points (these enzymes are found naturally in bacteria).
- 15. Different restriction enzymes produce different sticky ends
- 17. These tails are called sticky ends –easily join with other DNA molecules which have the complimentary
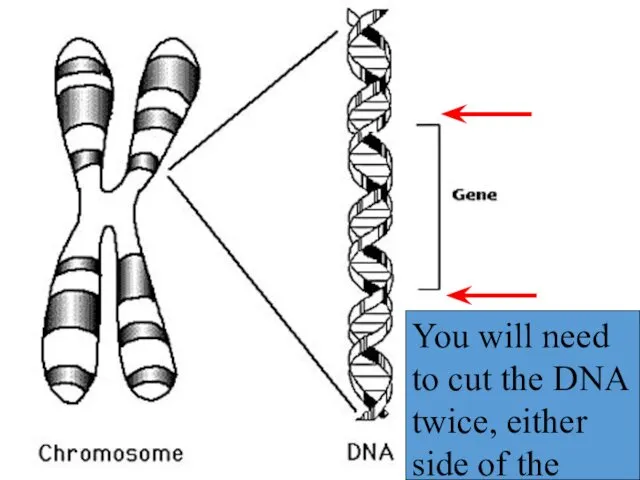
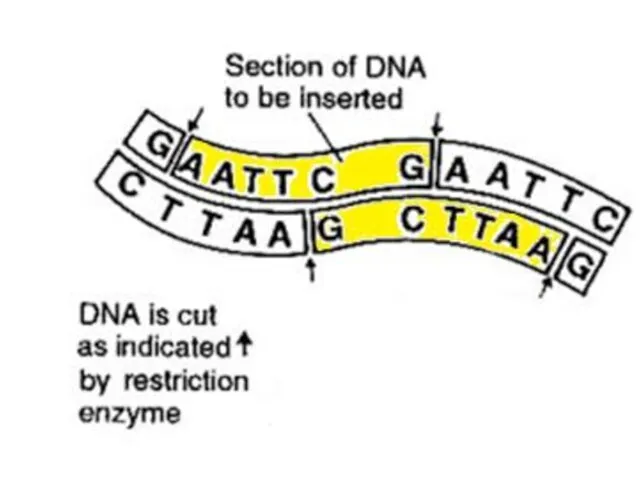
- 18. You will need to cut the DNA twice, either side of the gene.
- 19. Using restriction enzymes you can cut out the gene. But then what are you going to
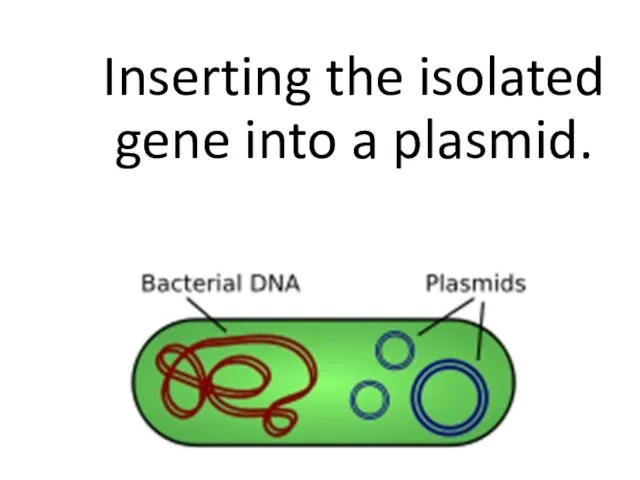
- 20. Inserting the isolated gene into a plasmid.
- 21. Ligation – the gene is inserted into a vector. The isolated gene is inserted into a
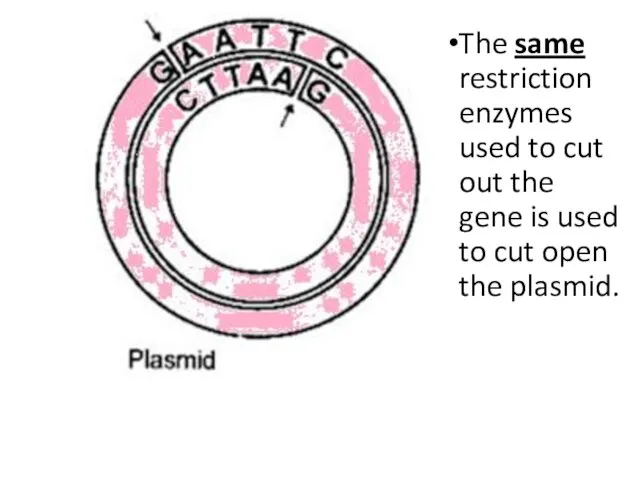
- 23. The same restriction enzymes used to cut out the gene is used to cut open the
- 24. Once DNA and the plasmid have been cut the enzyme is denatured to stop it cutting
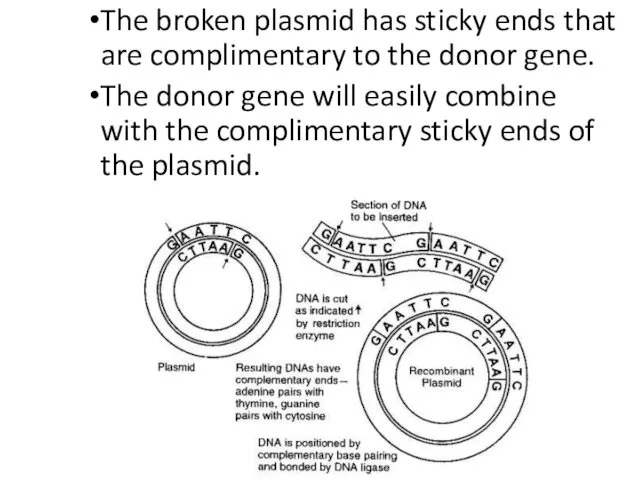
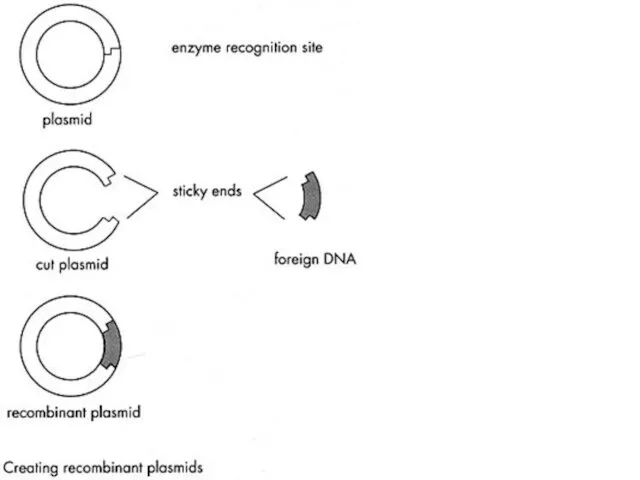
- 25. The broken plasmid has sticky ends that are complimentary to the donor gene. The donor gene
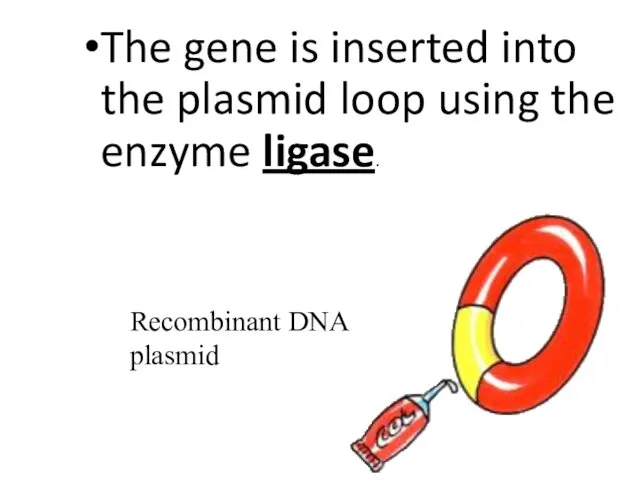
- 26. The gene is inserted into the plasmid loop using the enzyme ligase. Recombinant DNA plasmid
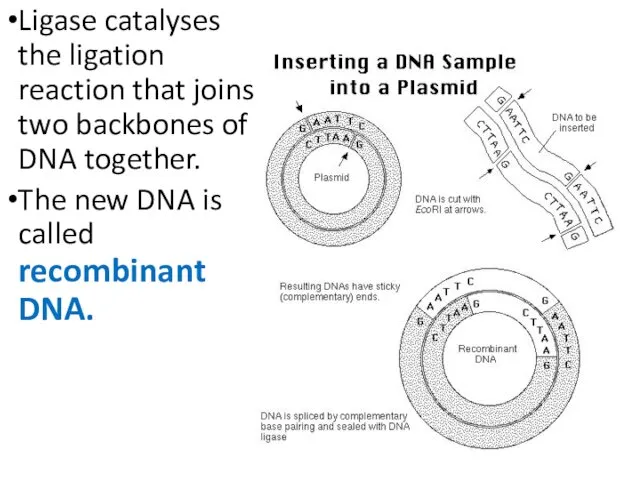
- 27. Ligase catalyses the ligation reaction that joins two backbones of DNA together. The new DNA is
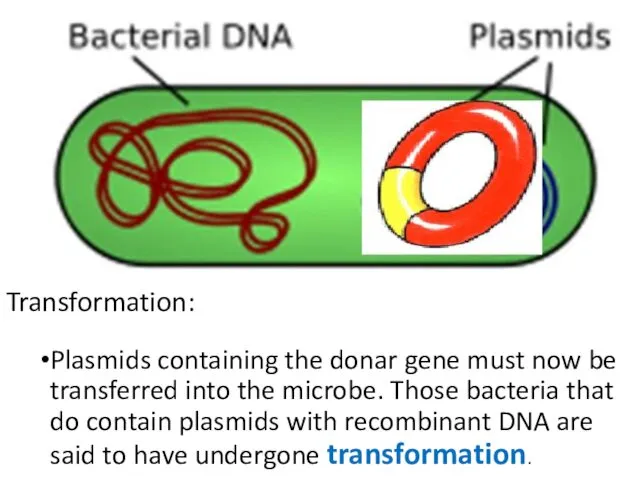
- 30. Transformation: Plasmids containing the donar gene must now be transferred into the microbe. Those bacteria that
- 31. Transformation is not very efficient. You now need to identify and isolate those bacteria that have
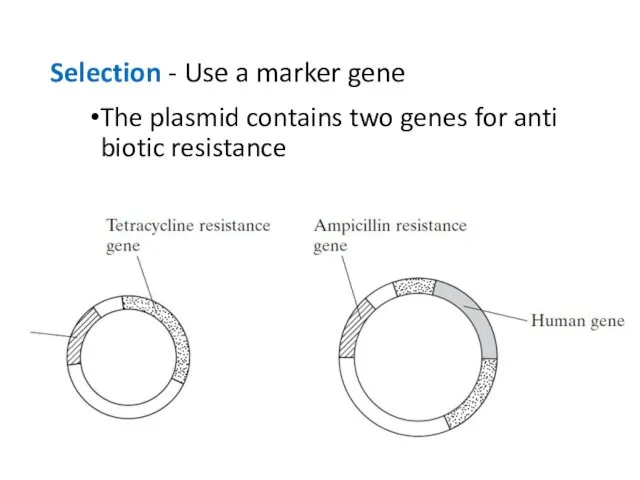
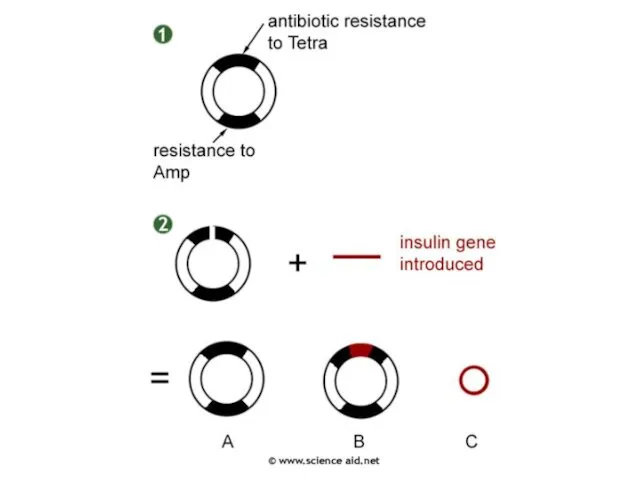
- 32. Selection - Use a marker gene The plasmid contains two genes for anti biotic resistance
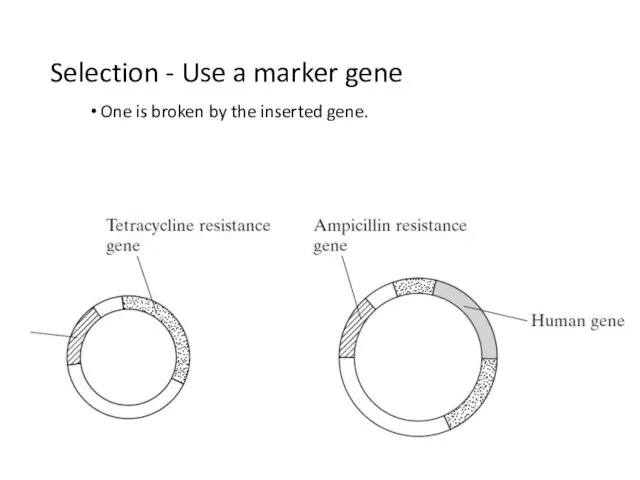
- 33. Selection - Use a marker gene One is broken by the inserted gene.
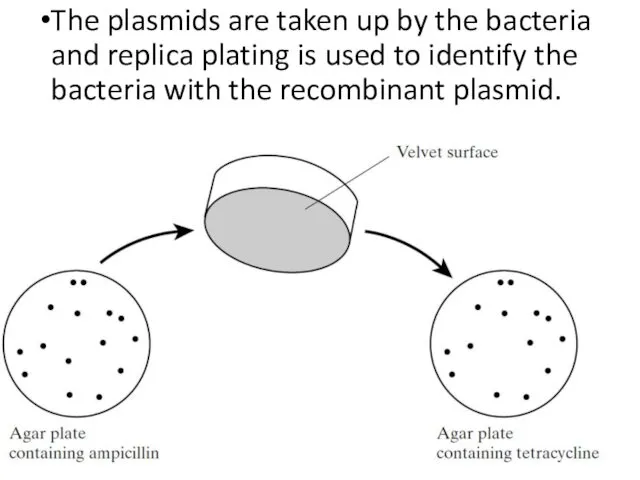
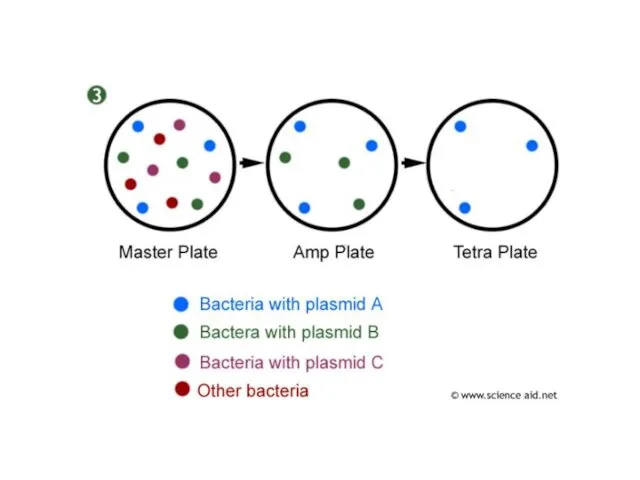
- 34. The plasmids are taken up by the bacteria and replica plating is used to identify the
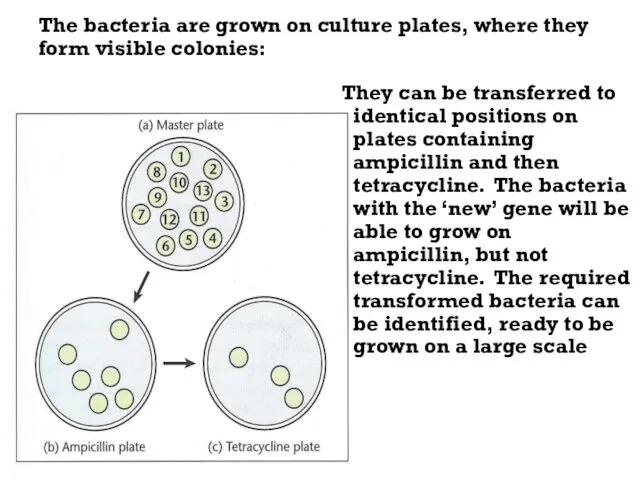
- 37. The bacteria are grown on culture plates, where they form visible colonies: They can be transferred
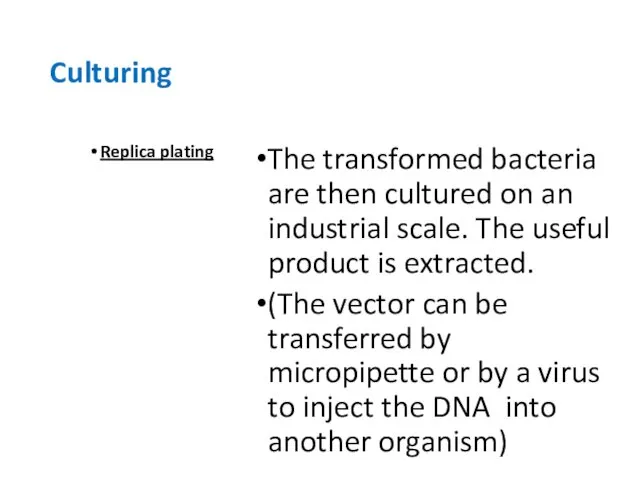
- 38. Culturing Replica plating The transformed bacteria are then cultured on an industrial scale. The useful product
- 39. In vivo gene cloning - These methods of gene cloning are called in vivo as the
- 40. Advantages The production of useful organisms with new features.
- 42. Скачать презентацию












 Как питаются разные животные?
Как питаются разные животные? Торсионные поля
Торсионные поля Хромосомы и стадии их деления. Хромосомные наборы клетки. Функции хромосом
Хромосомы и стадии их деления. Хромосомные наборы клетки. Функции хромосом Динозавры. (Окружающий мир. 1 класс)
Динозавры. (Окружающий мир. 1 класс) Технологии выращивания декоративных растений в защищенном грунте
Технологии выращивания декоративных растений в защищенном грунте Zoológico de Madrid
Zoológico de Madrid История возникновения и развития живого на Земле
История возникновения и развития живого на Земле Лекция5
Лекция5 Внеклассное мероприятие по биологии Наши пернатые друзья
Внеклассное мероприятие по биологии Наши пернатые друзья Биологическая эффективность гербицида Miuris 125 в борьбе с однодольными сорными растениями в посевах сой
Биологическая эффективность гербицида Miuris 125 в борьбе с однодольными сорными растениями в посевах сой Клонування
Клонування Презентация к уроку Анализаторы
Презентация к уроку Анализаторы Овощи в питании человека
Овощи в питании человека Гены, обусловливающие темно-синий окрас глаз
Гены, обусловливающие темно-синий окрас глаз Секреты природы. Грызуны живого уголка
Секреты природы. Грызуны живого уголка Молекулалық генетика негіздері. Ген негіздері. Гендердің интроиды, экзонды орналасуы. Прокориоттардың тұқым қуалауының
Молекулалық генетика негіздері. Ген негіздері. Гендердің интроиды, экзонды орналасуы. Прокориоттардың тұқым қуалауының Гербарий КГПУ им. В.П. Астафьева
Гербарий КГПУ им. В.П. Астафьева Определение пола особи
Определение пола особи Клеточные формы микроорганизмов
Клеточные формы микроорганизмов Презентация педагогического опыта по теме Методологические основы интегрированных уроков
Презентация педагогического опыта по теме Методологические основы интегрированных уроков Тип Моллюски. Класс Головоногие моллюски
Тип Моллюски. Класс Головоногие моллюски Зависимость пролиферации от факторов среды и синхронизация клеток в культуре
Зависимость пролиферации от факторов среды и синхронизация клеток в культуре Структура поведенческого акта. Функциональная система поведенческого акта
Структура поведенческого акта. Функциональная система поведенческого акта Дыхательная система
Дыхательная система Факторы, влияющие на продолжительность жизни человека
Факторы, влияющие на продолжительность жизни человека Ткани животных
Ткани животных Цитологические основы наследственности
Цитологические основы наследственности Николай Семенович Лесков и его сказ Левша
Николай Семенович Лесков и его сказ Левша