Содержание
- 2. Where? Glycolysis occurs in every cell. In aerobic respiration it is the FIRST stage. In anaerobic
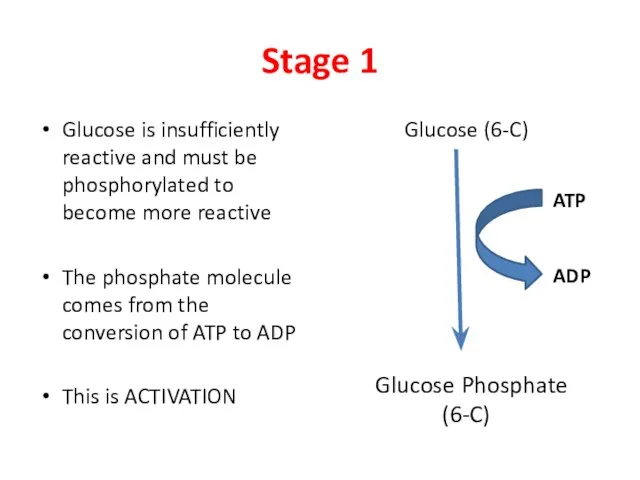
- 3. Stage 1 Glucose is insufficiently reactive and must be phosphorylated to become more reactive The phosphate
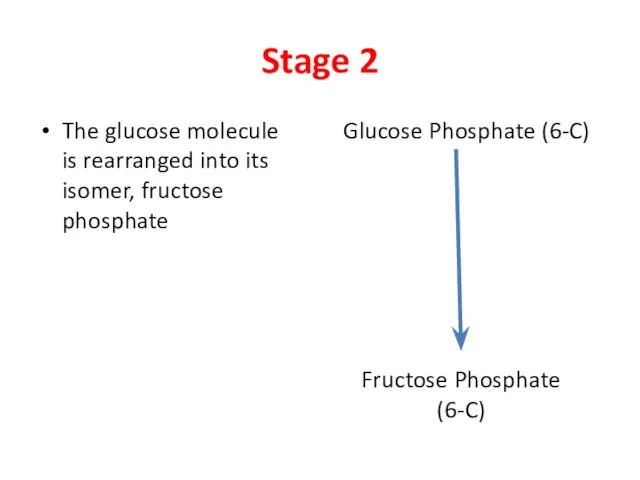
- 4. Stage 2 The glucose molecule is rearranged into its isomer, fructose phosphate Glucose Phosphate (6-C) Fructose
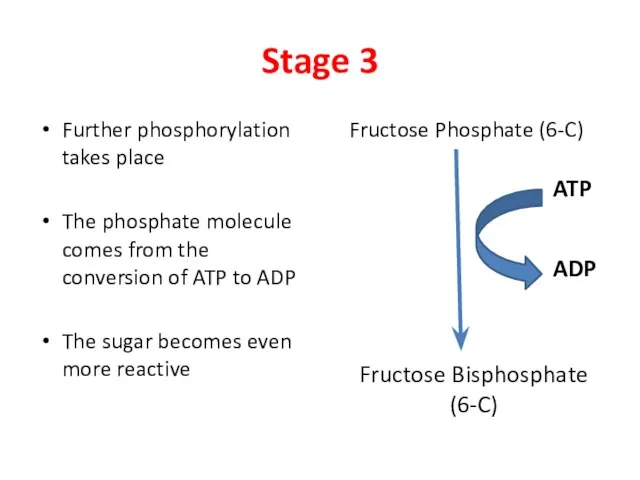
- 5. Stage 3 Further phosphorylation takes place The phosphate molecule comes from the conversion of ATP to
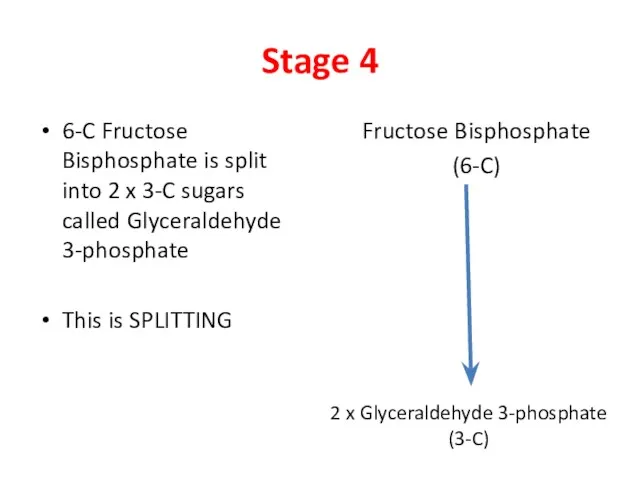
- 6. Stage 4 6-C Fructose Bisphosphate is split into 2 x 3-C sugars called Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate This
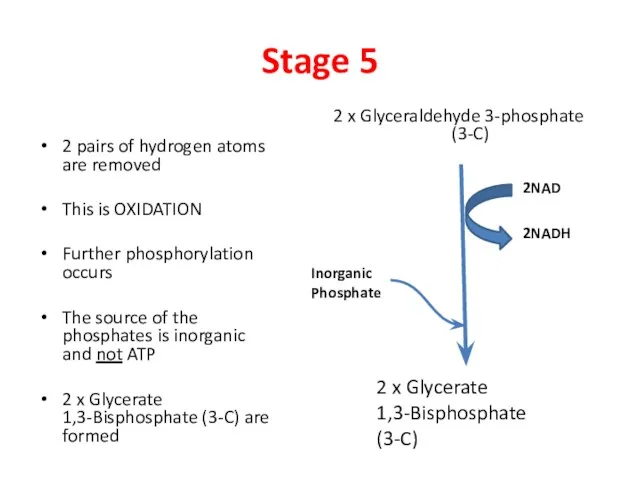
- 7. Stage 5 2 pairs of hydrogen atoms are removed This is OXIDATION Further phosphorylation occurs The
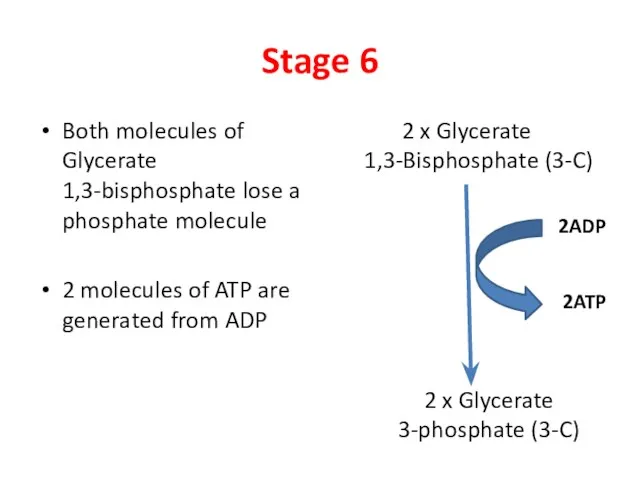
- 8. Stage 6 Both molecules of Glycerate 1,3-bisphosphate lose a phosphate molecule 2 molecules of ATP are
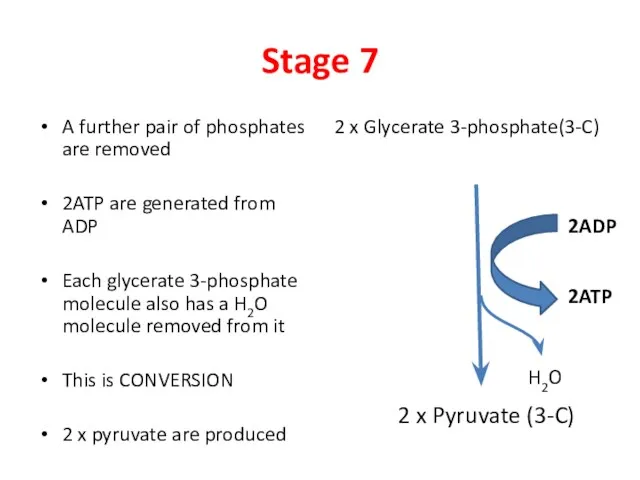
- 9. Stage 7 A further pair of phosphates are removed 2ATP are generated from ADP Each glycerate
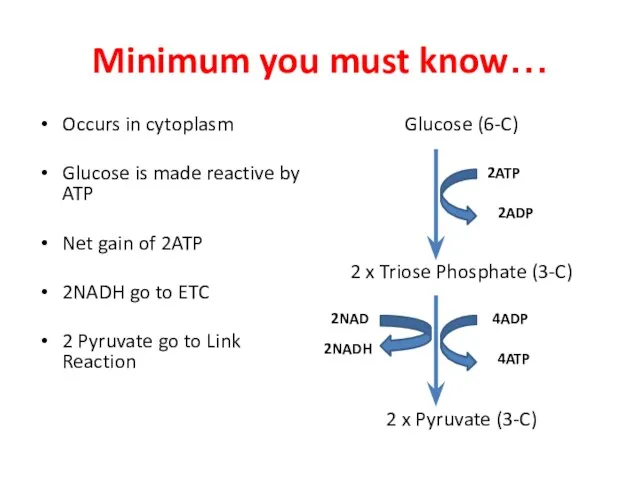
- 10. Minimum you must know… Occurs in cytoplasm Glucose is made reactive by ATP Net gain of
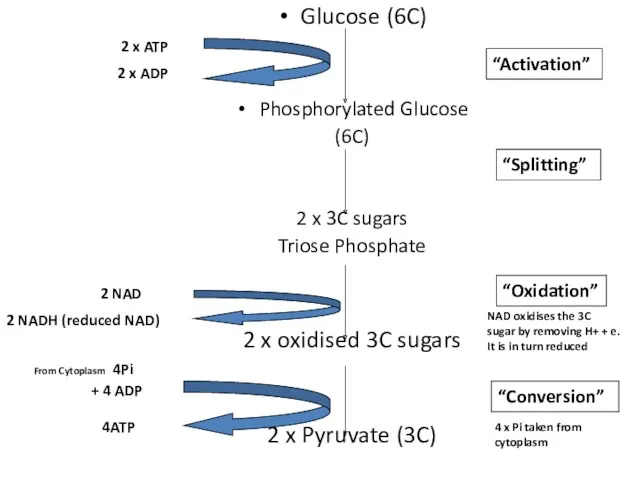
- 11. Glucose (6C) Phosphorylated Glucose (6C) 2 x 3C sugars Triose Phosphate 2 x oxidised 3C sugars
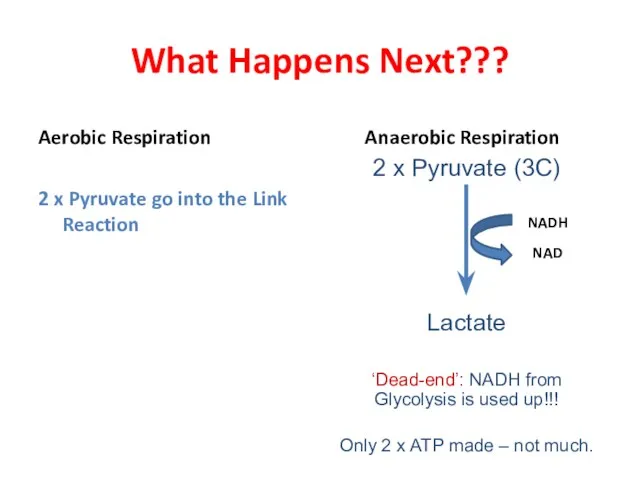
- 12. What Happens Next??? Aerobic Respiration 2 x Pyruvate go into the Link Reaction Anaerobic Respiration 2
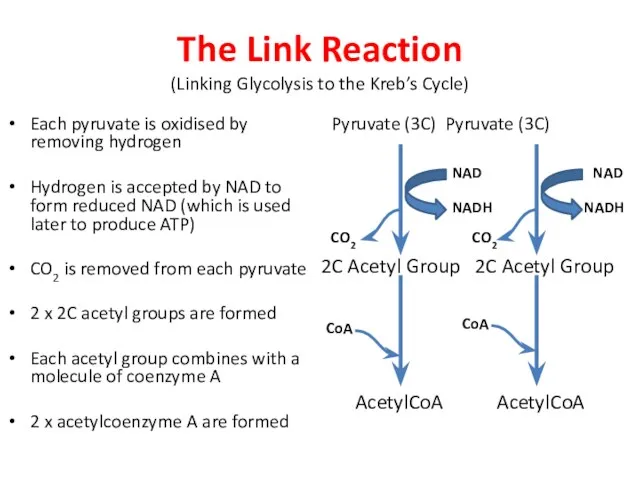
- 13. The Link Reaction (Linking Glycolysis to the Kreb’s Cycle) Each pyruvate is oxidised by removing hydrogen
- 15. Скачать презентацию

 Основные методы селекции
Основные методы селекции Анатомо-физиологические особенности репродуктивной системы человека
Анатомо-физиологические особенности репродуктивной системы человека Размножение. Митоз и мейоз
Размножение. Митоз и мейоз Генная инженерия
Генная инженерия Половое размножение животных. Язык животных в период ухаживания
Половое размножение животных. Язык животных в период ухаживания Материал для подготовки к ГИА
Материал для подготовки к ГИА Микробиологическая лаборатория, оснащение, правила работы
Микробиологическая лаборатория, оснащение, правила работы Поздняя палеозойская эра
Поздняя палеозойская эра Морфология почв. (Лекция 7)
Морфология почв. (Лекция 7) Введение в анатомию. Опорно-двигательный аппарат
Введение в анатомию. Опорно-двигательный аппарат Физиология пищеварения
Физиология пищеварения Дрожжевая подкормка для растений
Дрожжевая подкормка для растений Тип хордовые. Общая характеристика. Подтип бесчерепные. Ланцетник
Тип хордовые. Общая характеристика. Подтип бесчерепные. Ланцетник Растения и животные Красной книги РФ
Растения и животные Красной книги РФ Снижение биоразнообразия на планете
Снижение биоразнообразия на планете Интерактивная игра Пять звезд
Интерактивная игра Пять звезд Моховидные. Строение и размножение мхов
Моховидные. Строение и размножение мхов Общая характеристика типа. Класс Гидроидные
Общая характеристика типа. Класс Гидроидные Антропологиия. Раздел антропогенеза
Антропологиия. Раздел антропогенеза Покрытосеменные, или цветковые
Покрытосеменные, или цветковые Саңырауқұлақтар патшалығы. Оомицеттер, зигомицеттер кластары
Саңырауқұлақтар патшалығы. Оомицеттер, зигомицеттер кластары Желудочно-кишечный тракт (ЖКТ)
Желудочно-кишечный тракт (ЖКТ) Мембрана и органоиды клетки. 9 класс
Мембрана и органоиды клетки. 9 класс Пропорциональные особенности и пластические точки лица человека
Пропорциональные особенности и пластические точки лица человека Цитоплазма. ЭПС
Цитоплазма. ЭПС Особенности строения представителей надкласса Рыбы. 2
Особенности строения представителей надкласса Рыбы. 2 Компетентностноориентированные задания
Компетентностноориентированные задания Розмноження на клітинному рівні
Розмноження на клітинному рівні