Содержание
- 2. Human genetics Determines how hereditary information is passed and observes these traits in individuals Studies the
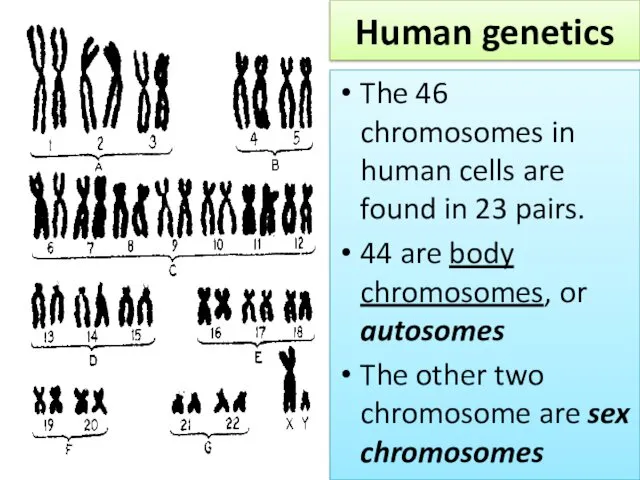
- 3. Human genetics The 46 chromosomes in human cells are found in 23 pairs. 44 are body
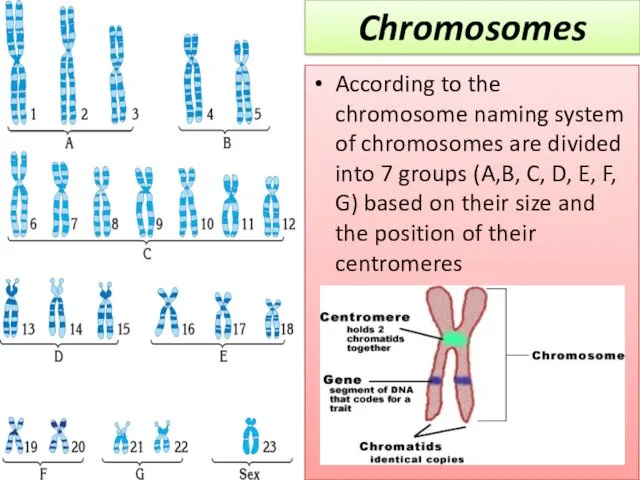
- 4. According to the chromosome naming system of chromosomes are divided into 7 groups (A,B, C, D,
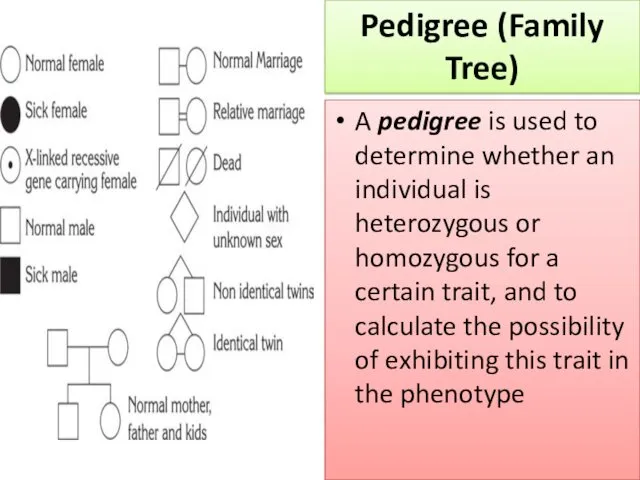
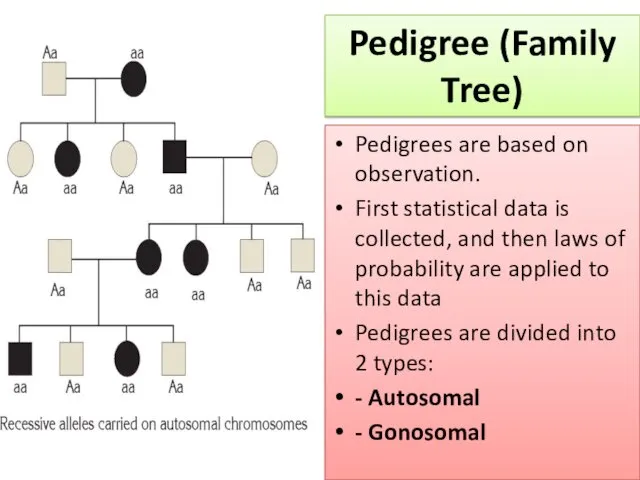
- 5. A pedigree is used to determine whether an individual is heterozygous or homozygous for a certain
- 6. Pedigrees are based on observation. First statistical data is collected, and then laws of probability are
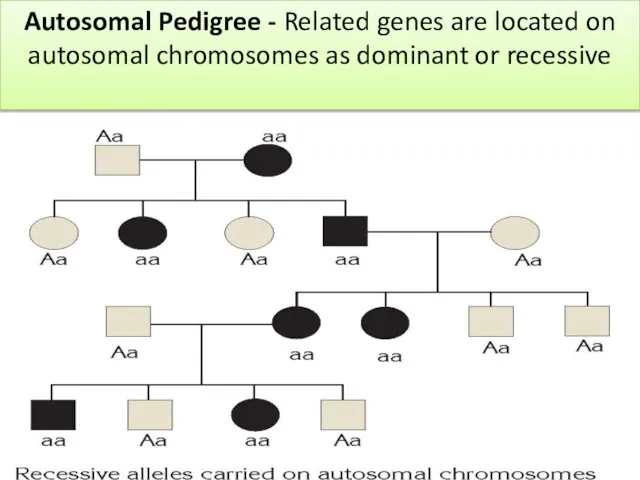
- 7. Autosomal Pedigree - Related genes are located on autosomal chromosomes as dominant or recessive
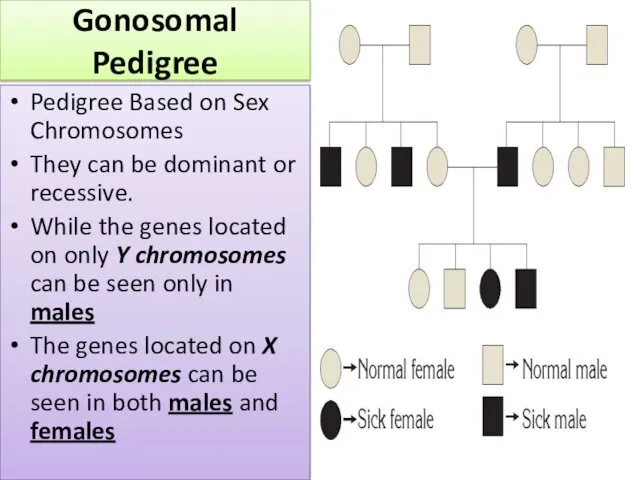
- 8. Gonosomal Pedigree Pedigree Based on Sex Chromosomes They can be dominant or recessive. While the genes
- 9. A man with a Y-linked disorder has three sons and three daughters by the same mother.
- 10. A man with a X-linked disorder has son and three daughters (2 of them are normal,
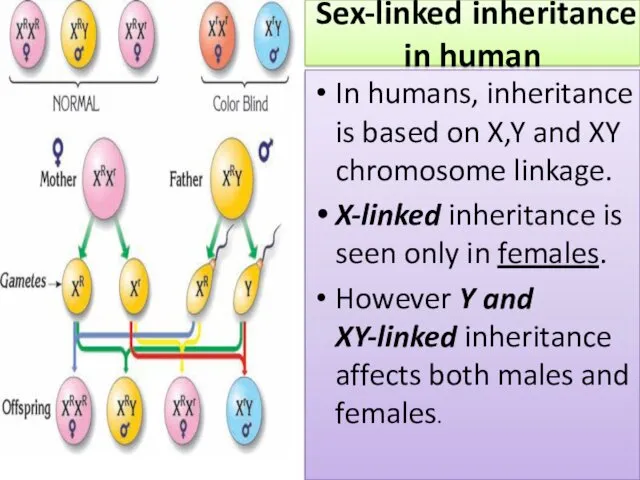
- 11. Sex-linked inheritance in human In humans, inheritance is based on X,Y and XY chromosome linkage. X-linked
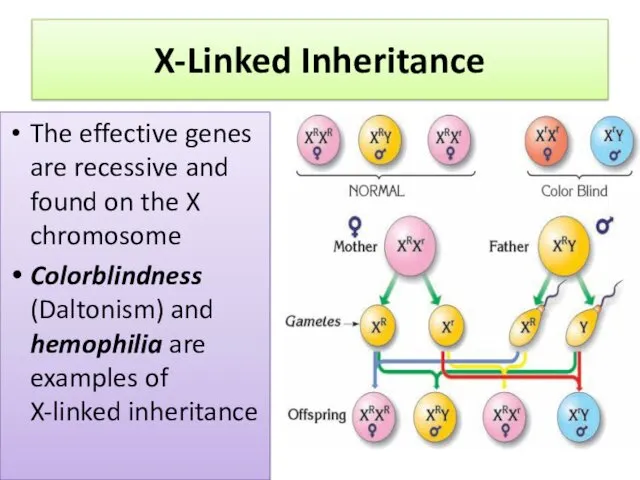
- 12. X-Linked Inheritance The effective genes are recessive and found on the X chromosome Colorblindness (Daltonism) and
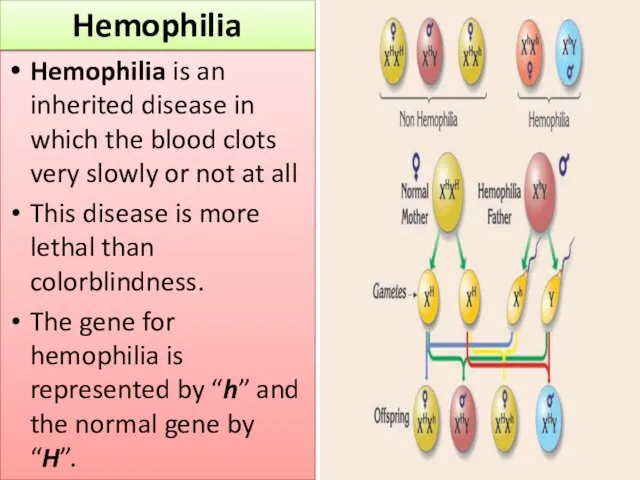
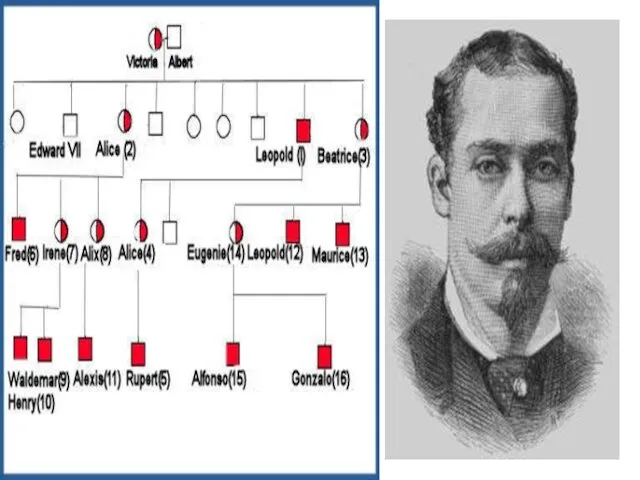
- 13. Hemophilia is an inherited disease in which the blood clots very slowly or not at all
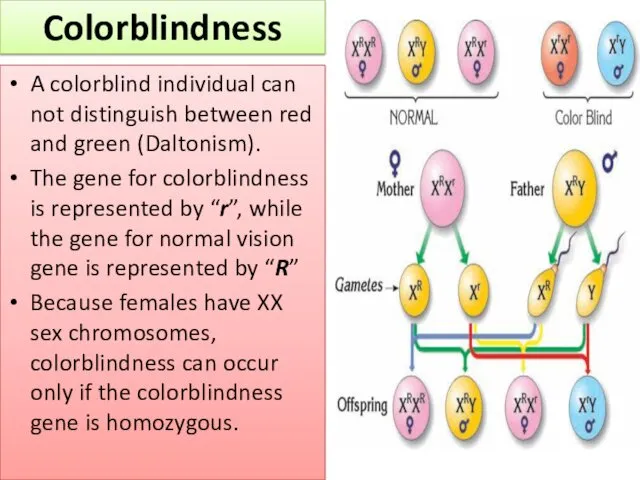
- 15. A colorblind individual can not distinguish between red and green (Daltonism). The gene for colorblindness is
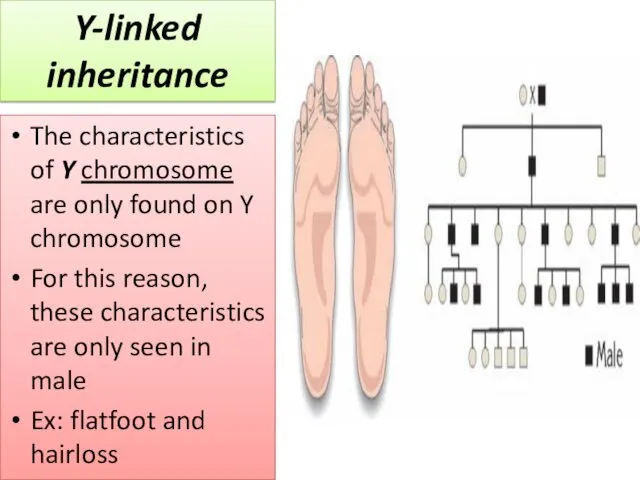
- 16. The characteristics of Y chromosome are only found on Y chromosome For this reason, these characteristics
- 17. Problem 1 A human female "carrier" who is heterozygous for the recessive, sex-linked trait causing red-green
- 18. Problem 2 A human female "carrier" who is heterozygous for the recessive, sex-linked trait red color
- 19. Problem 3 A human female "carrier" who is heterozygous for the recessive, sex-linked trait red color
- 20. Problem 4 Hypophosphatemia (vitamin D-resistant rickets) is inherited as an X-linked dominant. An unaffected woman mates
- 21. Problem 5 Hypophosphatemia (vitamin D-resistant rickets) is inherited as an X-linked dominant. A woman without hypophosphatemia
- 22. Problem 6 A human female "carrier" who is heterozygous for the recessive, sex-linked trait red color
- 24. Скачать презентацию








 Иммунитет.
Иммунитет. Симптоми харчового отруєння. Отруйні рослини і гриби. Профілактика харчових отруєнь. 8 клас
Симптоми харчового отруєння. Отруйні рослини і гриби. Профілактика харчових отруєнь. 8 клас Биосфера және жердегі тіршілік
Биосфера және жердегі тіршілік Плоды и семена
Плоды и семена Физиология продолговатого и среднего мозга. (Лекция 8)
Физиология продолговатого и среднего мозга. (Лекция 8) 15 порід собак
15 порід собак Агрохимия почв
Агрохимия почв Генетика пола человека
Генетика пола человека Углеводы и липиды. Строение и функции
Углеводы и липиды. Строение и функции Общая гистология. Эпителиальные ткани
Общая гистология. Эпителиальные ткани Животные Ярославской области, занесенные в Красную книгу
Животные Ярославской области, занесенные в Красную книгу Презентация Влияние среды на строение листа
Презентация Влияние среды на строение листа Строение нейрона. Синапс
Строение нейрона. Синапс Ядра основания головного мозга (базальные ядра). Внутренняя капсула
Ядра основания головного мозга (базальные ядра). Внутренняя капсула Методы выделения чистой культуры анаэробов
Методы выделения чистой культуры анаэробов Імунітет людини
Імунітет людини Транспортные системы организма
Транспортные системы организма Урок Витамины ПризПродукты питания богатые витамином В12
Урок Витамины ПризПродукты питания богатые витамином В12 Майстерність маскування
Майстерність маскування Техника пикировки растений
Техника пикировки растений Собака – верный друг
Собака – верный друг Макроэволюция. Основные направления эволюции
Макроэволюция. Основные направления эволюции Фитоценоздағы өсімдіктердің ярустық жіктелуі
Фитоценоздағы өсімдіктердің ярустық жіктелуі Класс млекопитающие (звери)
Класс млекопитающие (звери) Химический состав клетки. Органические соединения. Углеводы. Липиды (10 класс)
Химический состав клетки. Органические соединения. Углеводы. Липиды (10 класс) Царство грибы
Царство грибы Отряды млекопитающих
Отряды млекопитающих Безопасные ягоды и грибы
Безопасные ягоды и грибы