Содержание
- 2. Objectives Interstitium Pleural disease Chest wall disease
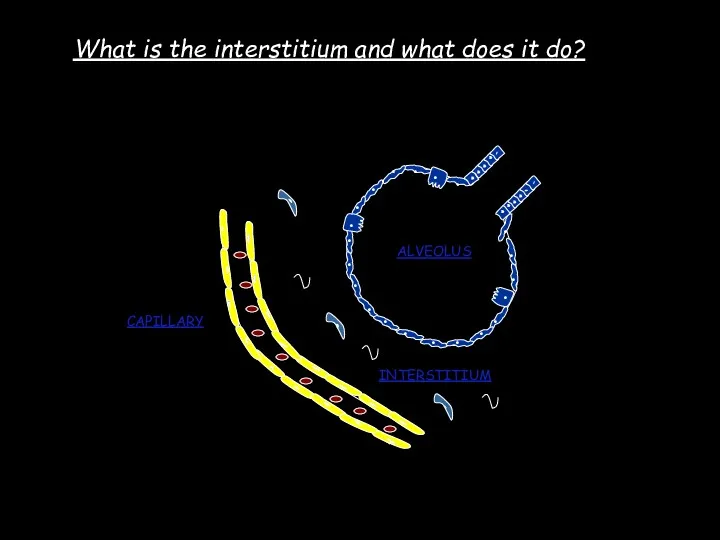
- 3. Interstitial disease What is the interstitium? What does the interstitium do? What are the pathophysiological effects
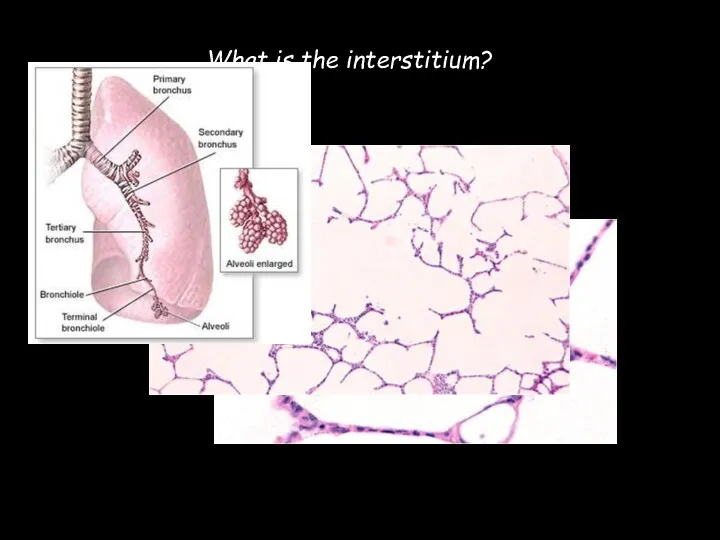
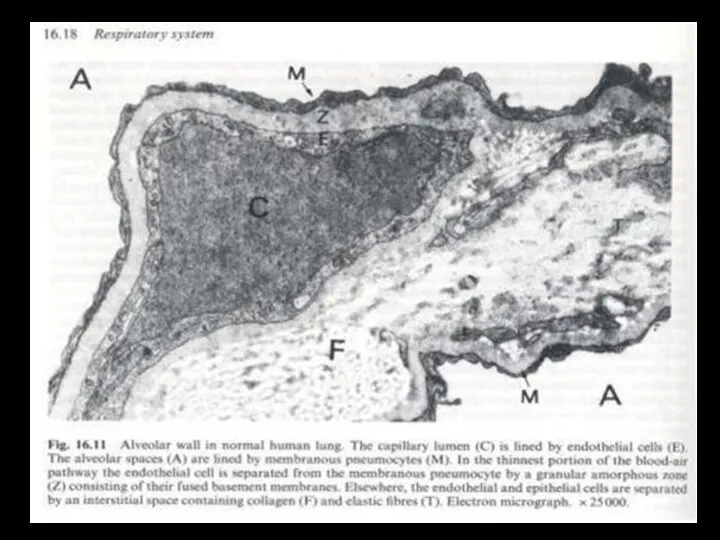
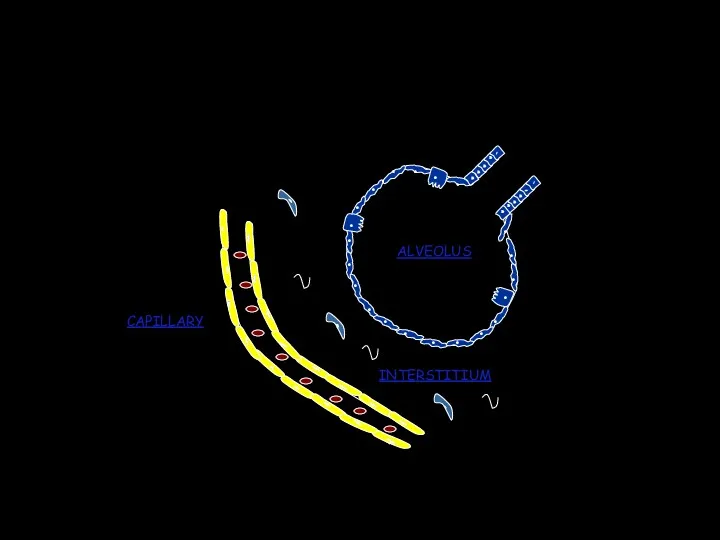
- 4. What is the interstitium?
- 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
- 7. Does interstitial disease effect just the interstitium? NO ! Structures affected: Acini Alveoli lumen Bronchiolar lumen
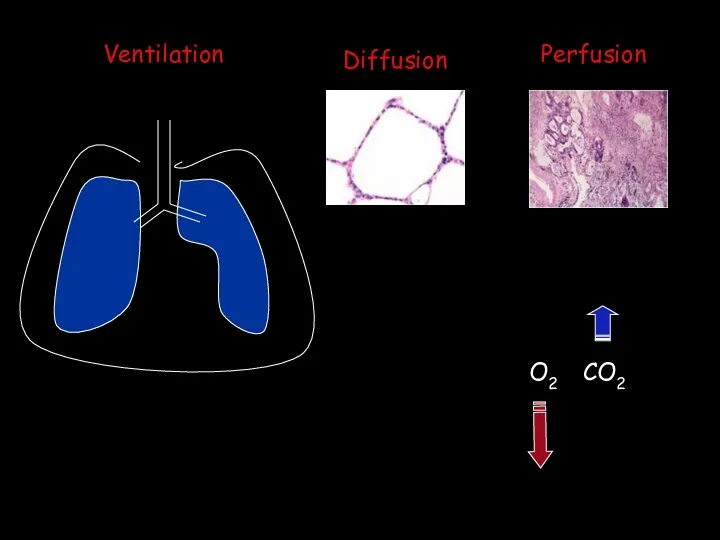
- 8. Ventilation Diffusion Perfusion O2 CO2
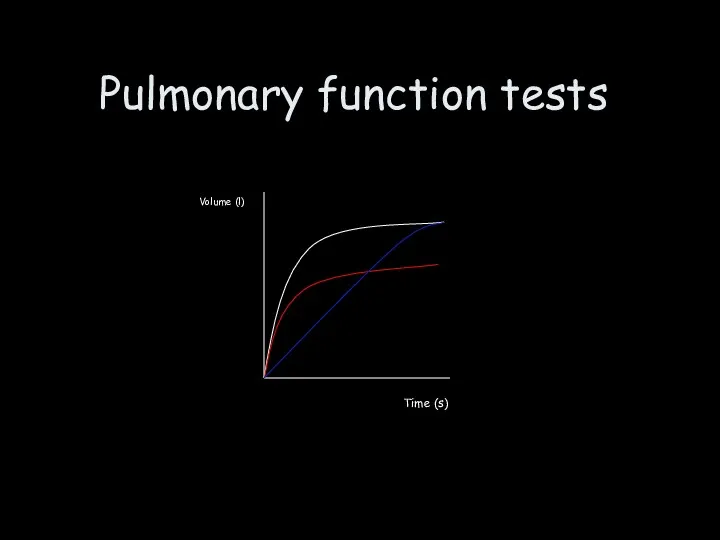
- 9. Pulmonary function tests Volume (l) Time (s)
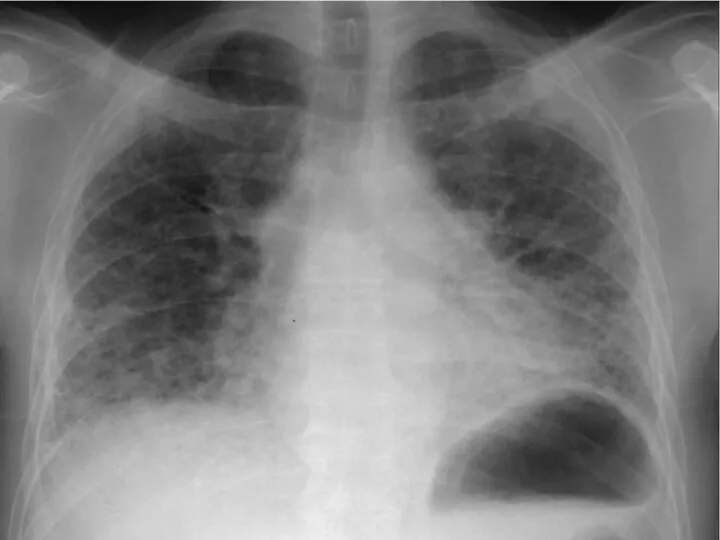
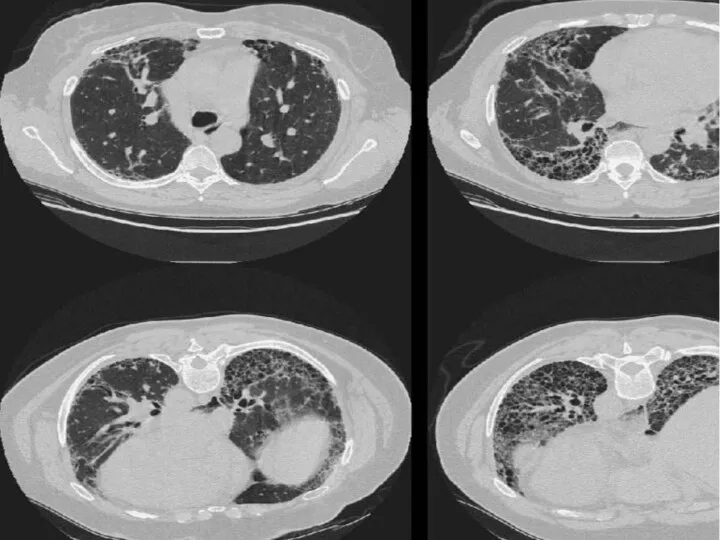
- 10. 59 year old male Shortness of breath & dry cough, increasing 1 year - breathless with
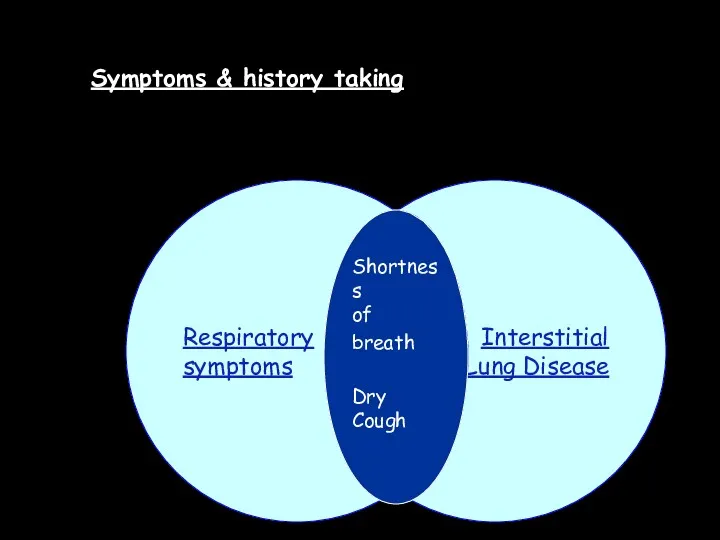
- 13. Symptoms & history taking Interstitial Lung Disease Respiratory symptoms Shortness of breath Dry Cough
- 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
- 15. Common clinical features Symptoms 1-Chronic dry cough 2-Exertional dyspnea Signs 1-Clubbing 2-Basal inspiratory crepitations Laboratory 1-High
- 16. Pulmonary function tests Spirometry 1-Decreased FEV1,FEV (Normal FEV1/FVC) 2-Decreased TLC 3-Mildly Decreased PEF 4-Markedly Decreased DLCO
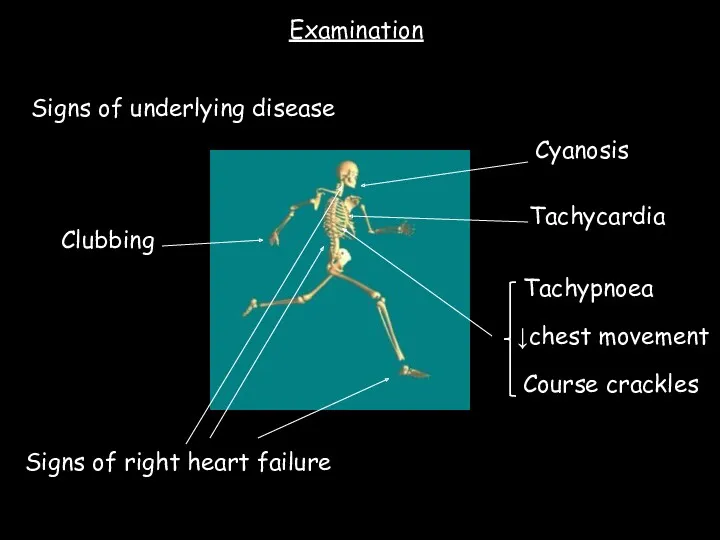
- 17. Clubbing Course crackles Tachypnoea Signs of right heart failure Signs of underlying disease Cyanosis ↓chest movement
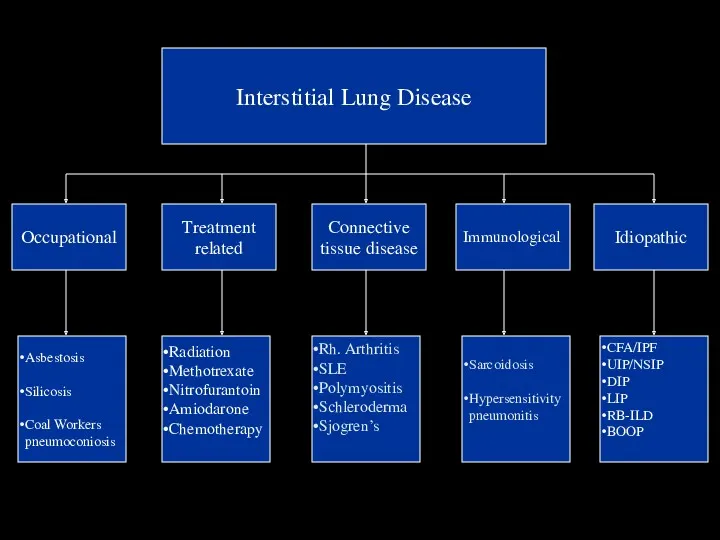
- 18. Blood tests Interstitial Lung Disease Occupational Treatment related Connective tissue disease Idiopathic Asbestosis Silicosis Coal Workers
- 19. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis (IIP) A variety of histological descriptions (UIP,NSIP,DIP,RB-ILD, BOOP) Histological descriptions - high inter
- 20. Asbestos
- 21. Asbestos Asbestos plaques Diffuse pleural thickening Benign asbestos pleural effusions (BAPE) ASBESTOSIS Mesothelioma Bronchogenic lung cancer
- 22. Drug induced ILD Methotrexate Bleomycin Amiodarone Nitrofurantoin Methotrexate Treatment & cause of lung disease Dose &
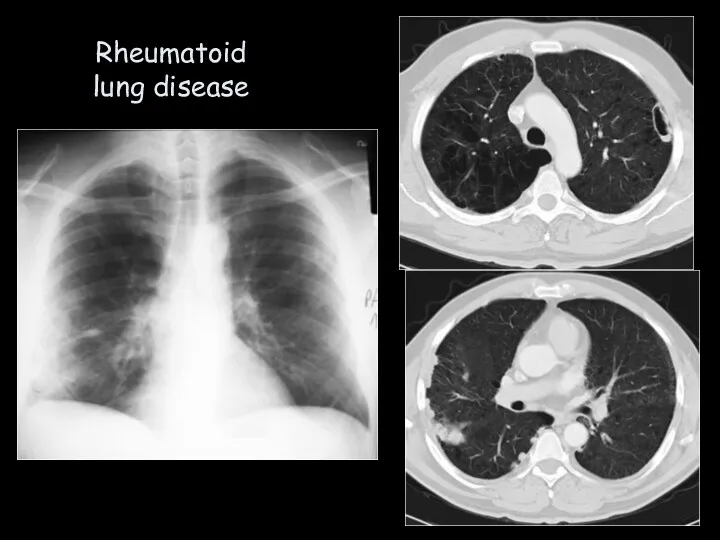
- 23. Rheumatoid lung disease
- 24. Connective tissue disease Dermatomyositis/ Polymyositis Sjogren’s Syndrome Systemic Lupus erythematosis Schleroderma Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid lung disease
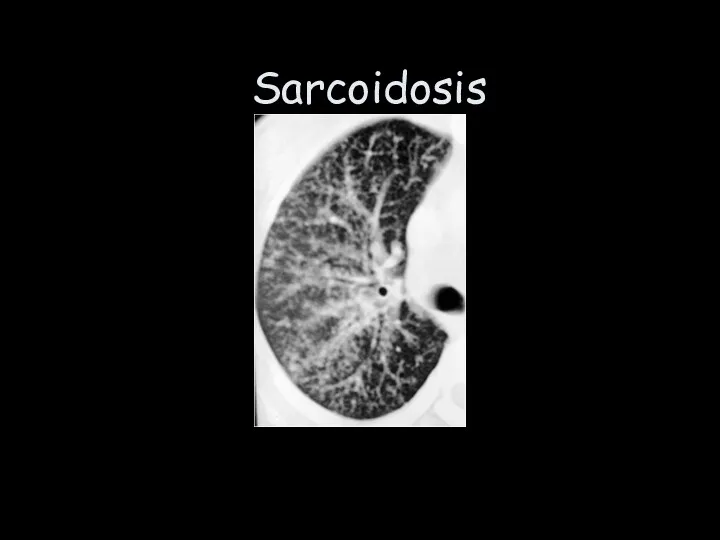
- 25. Sarcoidosis
- 26. Sarcoidosis Often asymptomatic Genetic predisposition Cough & breathlessness Normal chest examination May get better,remain static, worsen…unpredictable
- 27. Interstitial disease What is the interstitium? What does the interstitium do? What are the pathophysiological effects
- 28. Objectives Interstitium Pleural disease Chest wall disease
- 29. Pleural Disease Anatomy Effusions Malignancy
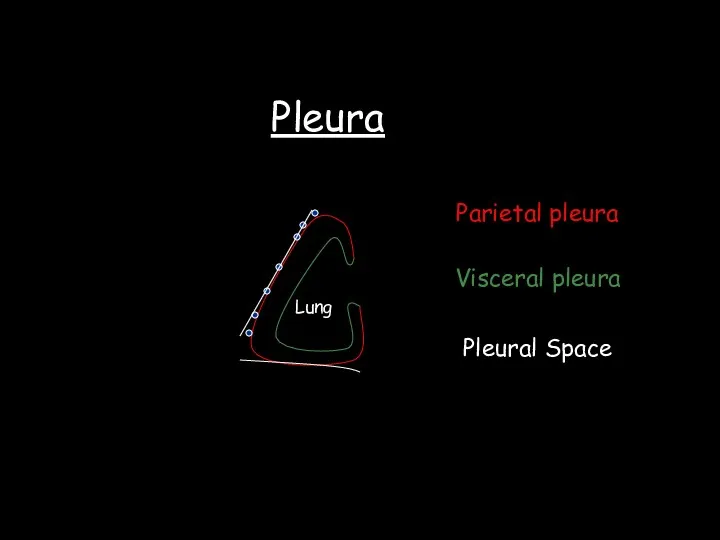
- 30. Pleura Lung Parietal pleura Visceral pleura Pleural Space
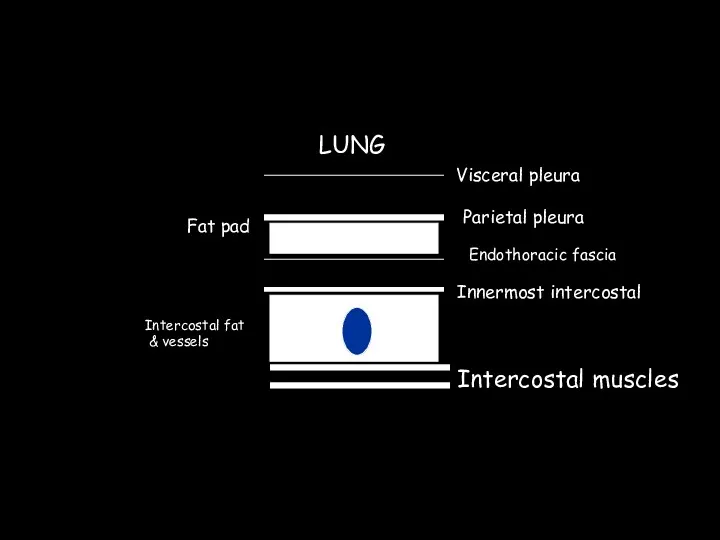
- 31. Visceral pleura Parietal pleura Fat pad Endothoracic fascia Innermost intercostal Intercostal fat & vessels Intercostal muscles
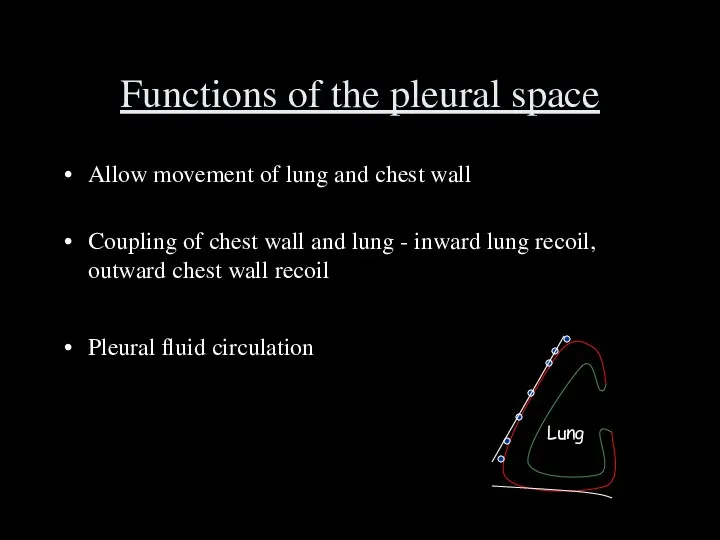
- 32. Functions of the pleural space Allow movement of lung and chest wall Coupling of chest wall
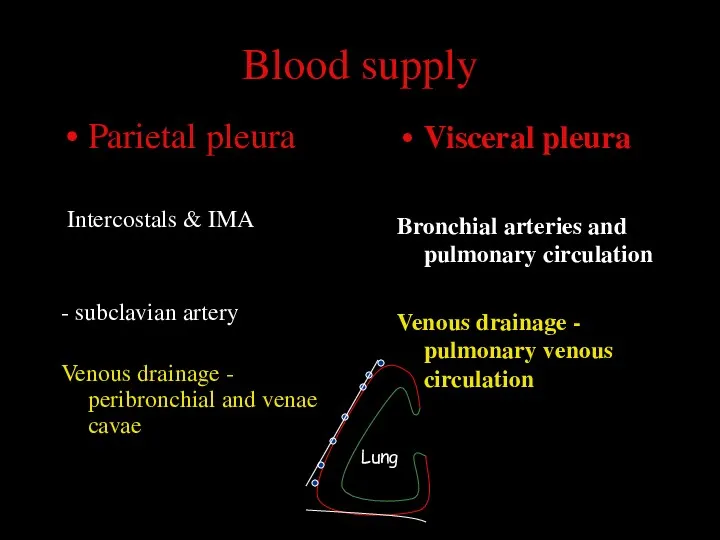
- 33. Blood supply Parietal pleura Intercostals & IMA - subclavian artery Venous drainage - peribronchial and venae
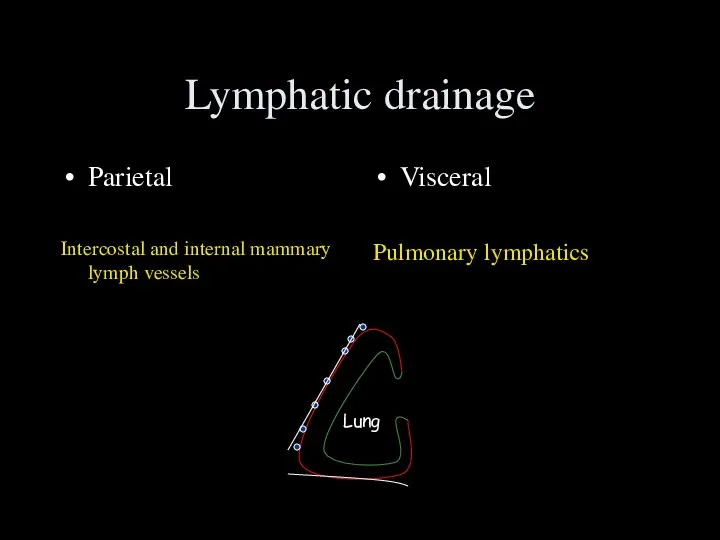
- 34. Lymphatic drainage Parietal Intercostal and internal mammary lymph vessels Visceral Pulmonary lymphatics Lung
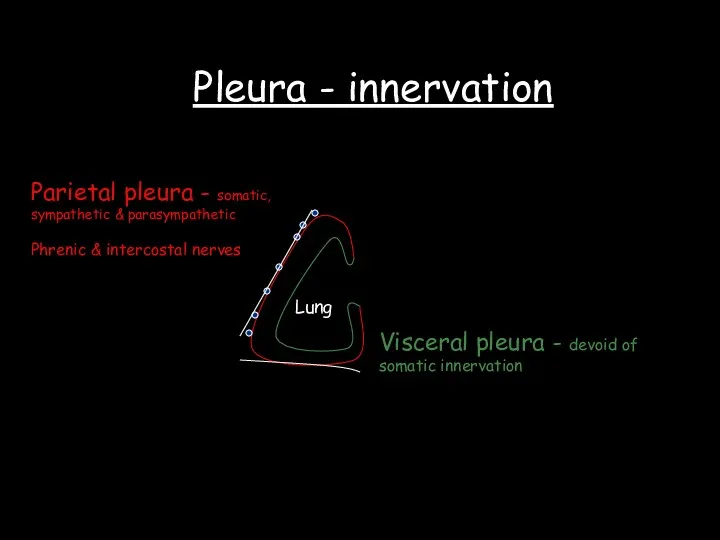
- 35. Pleura - innervation Lung Parietal pleura - somatic, sympathetic & parasympathetic Phrenic & intercostal nerves Visceral
- 36. Pleural fluid turnover 15ml per day ( can increase to 300 ml/day) Production - Capillary filtration(Starling
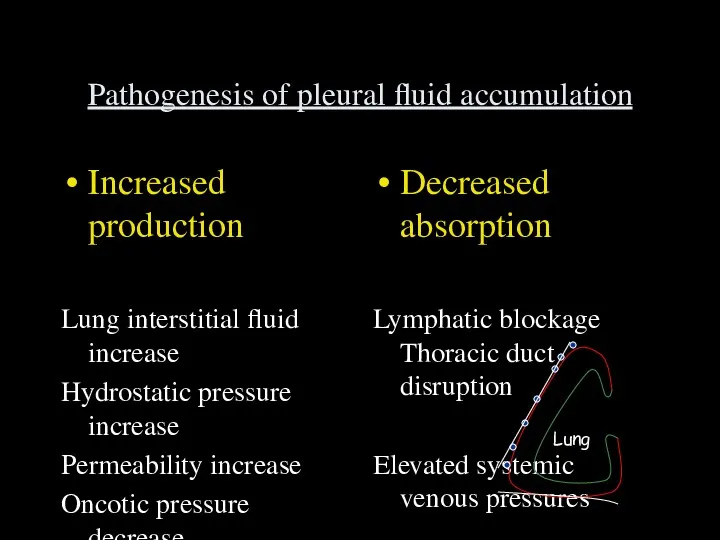
- 37. Pathogenesis of pleural fluid accumulation Increased production Lung interstitial fluid increase Hydrostatic pressure increase Permeability increase
- 38. Pleural effusions Transudate Exudate Hydrothorax Haemothorax Chylothora Empyema Thoracocentesis
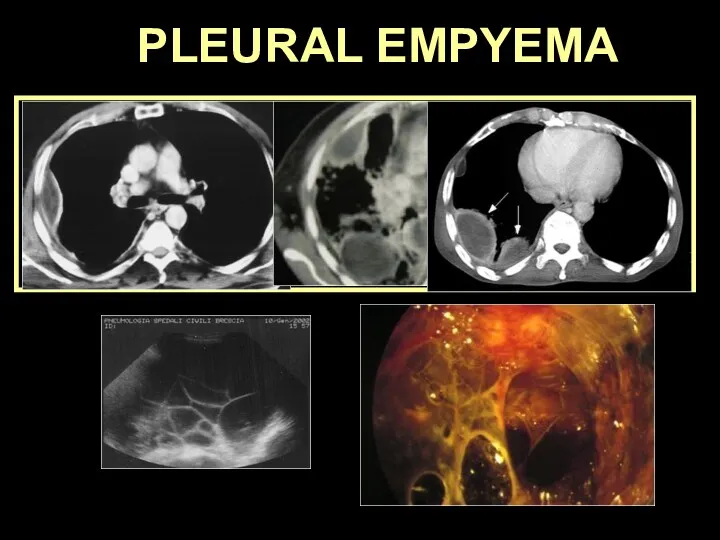
- 39. PLEURAL EMPYEMA
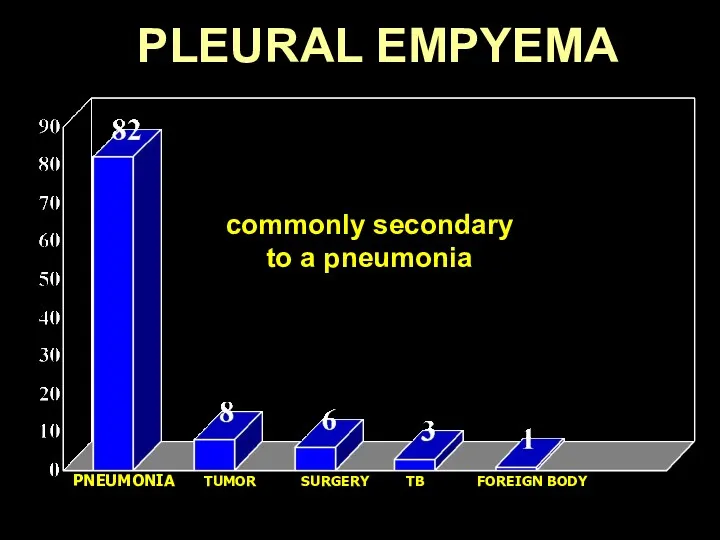
- 40. PLEURAL EMPYEMA PNEUMONIA TUMOR SURGERY TB FOREIGN BODY Collection of pus in the pleural cavity commonly
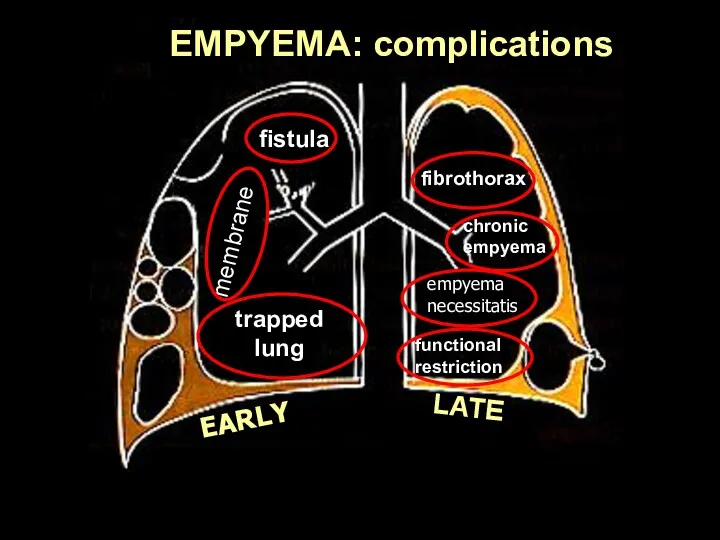
- 41. EARLY LATE fistula trapped lung membranes fibrothorax chronic empyema empyema necessitatis functional restriction EMPYEMA: complications
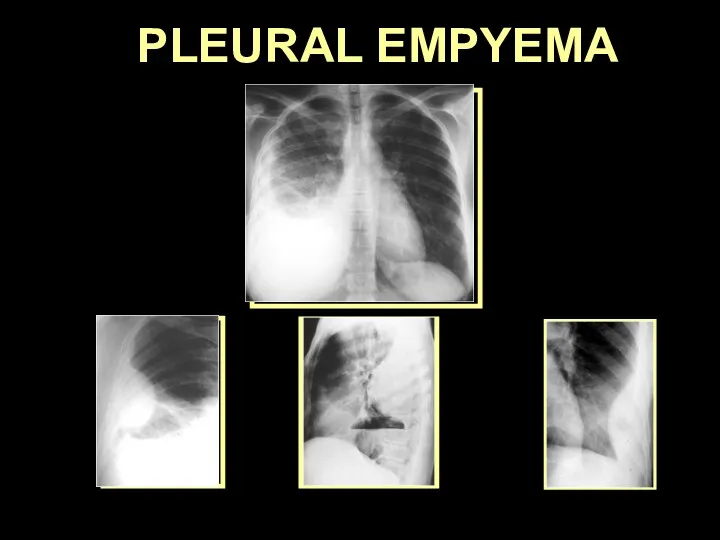
- 42. PLEURAL EMPYEMA
- 43. PLEURAL EMPYEMA
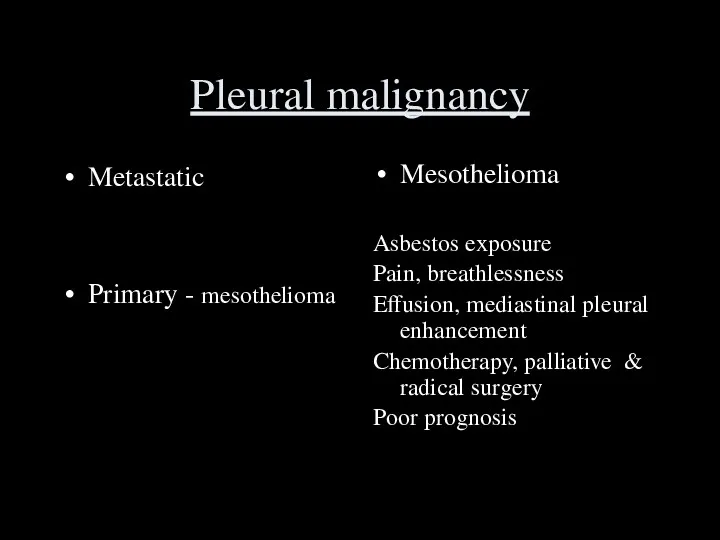
- 44. Pleural malignancy Metastatic Primary - mesothelioma Mesothelioma Asbestos exposure Pain, breathlessness Effusion, mediastinal pleural enhancement Chemotherapy,
- 45. Pleural Disease Anatomy Effusions Malignancy
- 46. Objectives Interstitium Pleural disease Chest wall disease
- 47. Chest wall disease Congenital Pectus deformities Scoliosis Kyphosis Muscular dystrophy Acquired Trauma Iatrogenic Ankylosing spondylitis Motor
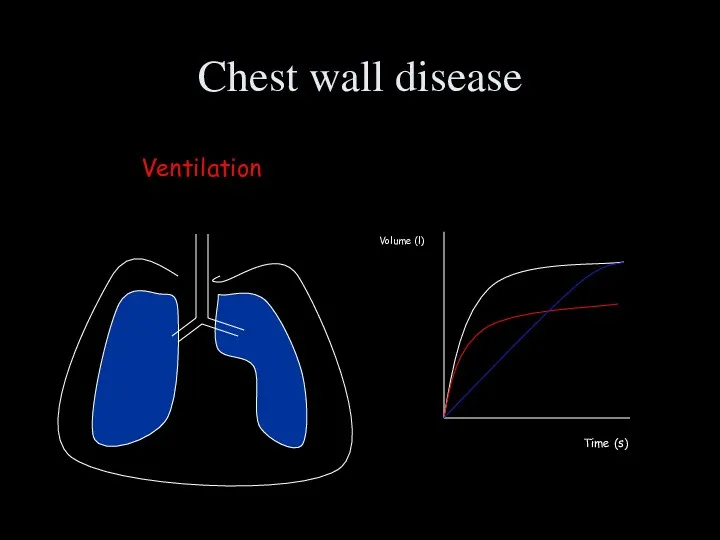
- 48. Chest wall disease Ventilation Volume (l) Time (s)
- 49. Chest wall disease Ventilation Sleep disordered breathing Poor clearance of secretions Atelectasis Pneumonia
- 51. Скачать презентацию




















 Усачи, или дровосеки. Личинки. (Лекция 13)
Усачи, или дровосеки. Личинки. (Лекция 13) Достижения современной селекции
Достижения современной селекции Размножение организмов
Размножение организмов Царство растений. Многообразие растений
Царство растений. Многообразие растений Совы. Виды
Совы. Виды Чудеса селекции. Самые любопытные фрукты и овощи, которые появились на свет благодаря селекции
Чудеса селекции. Самые любопытные фрукты и овощи, которые появились на свет благодаря селекции Забота животных о потомстве
Забота животных о потомстве Красная книга Красноярского края
Красная книга Красноярского края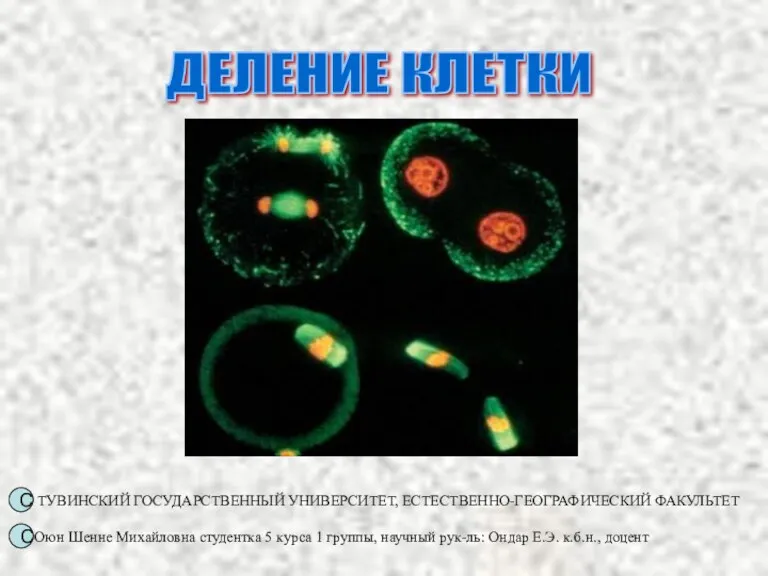 Клеточный цикл
Клеточный цикл Геохронологическая история Земли
Геохронологическая история Земли Чарлз Роберт Дарвин
Чарлз Роберт Дарвин Перелітні птахи
Перелітні птахи Морские свинки
Морские свинки Сердечно-сосудистая система
Сердечно-сосудистая система Отдел Красные водоросли
Отдел Красные водоросли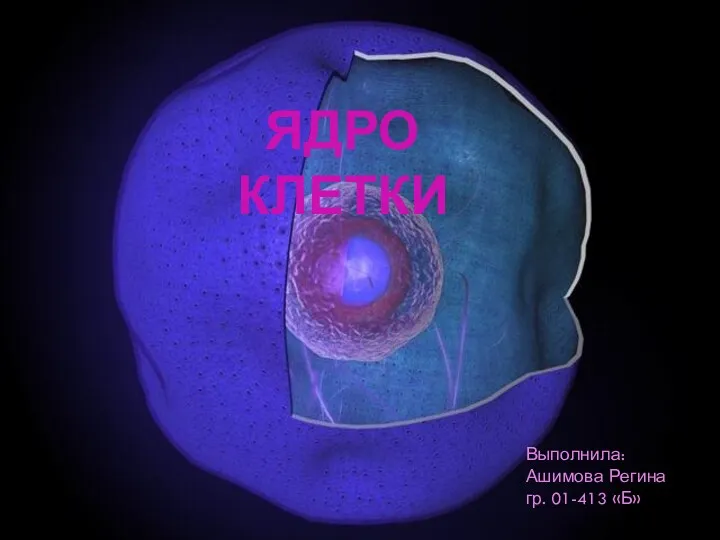 Ядро клетки
Ядро клетки Факторы, лимитирующие первичную продукцию в наземных и водных сообществах
Факторы, лимитирующие первичную продукцию в наземных и водных сообществах СОСТАВ КРОВИ.
СОСТАВ КРОВИ. Многообразие и значение грибов
Многообразие и значение грибов Структурная организация микробной клетки
Структурная организация микробной клетки Оживление грибов дрожжей
Оживление грибов дрожжей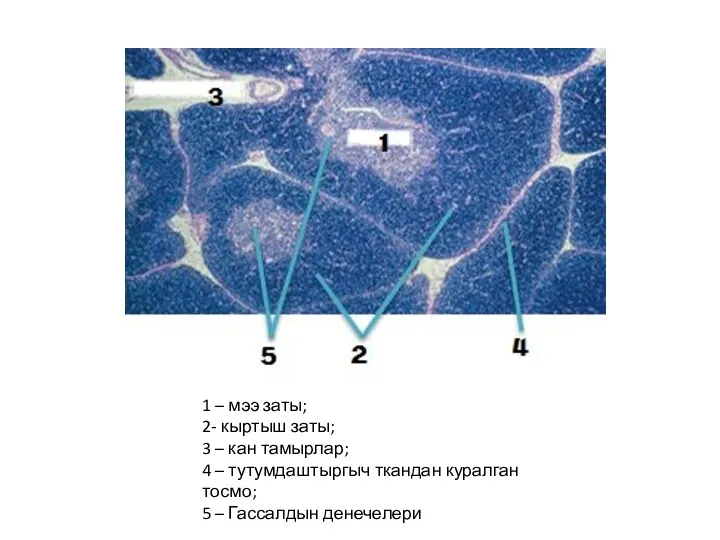 Ткань жана анын мааниси
Ткань жана анын мааниси Открытый урок на тему: Многообразие земноводных.
Открытый урок на тему: Многообразие земноводных. Тренажёр Вода
Тренажёр Вода Биологические задачи. Подготовка к ЕГЭ
Биологические задачи. Подготовка к ЕГЭ Дыхательная система
Дыхательная система Эволюция. Доказательства эволюции (часть 6)
Эволюция. Доказательства эволюции (часть 6) Жизнь организмов в морях и океанах
Жизнь организмов в морях и океанах