Содержание
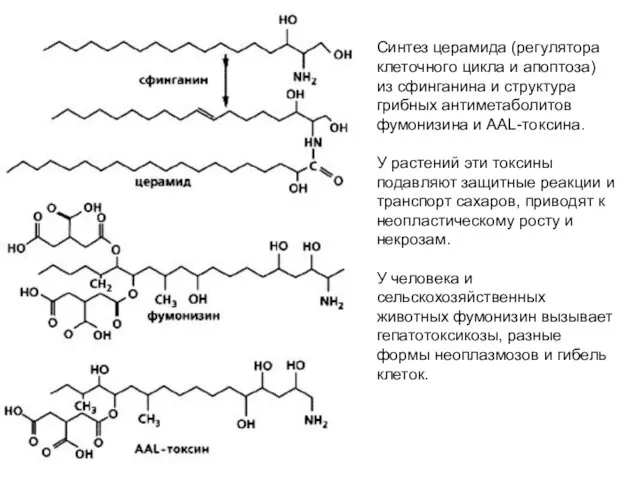
- 2. Синтез церамида (регулятора клеточного цикла и апоптоза) из сфинганина и структура грибных антиметаболитов фумонизина и AAL-токсина.
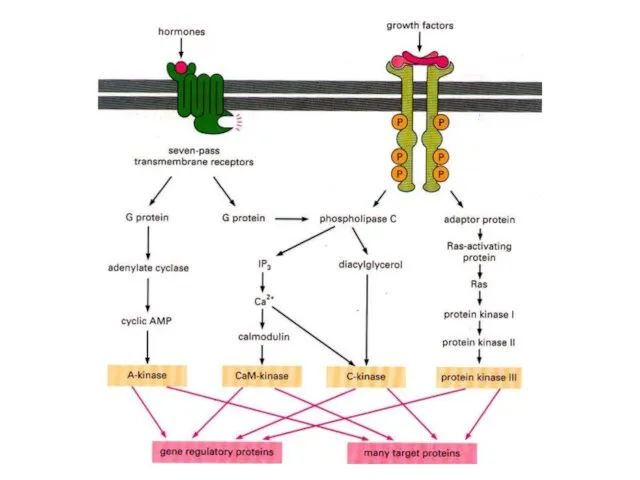
- 3. Сигнальные системы передачи сигнала для возбуждения экспрессии защитных генов: циклоаденилатная, MAP-киназная (mitogen-activated protein-kinase), фосфатидокислотная, кальциевая, липоксигеназная,
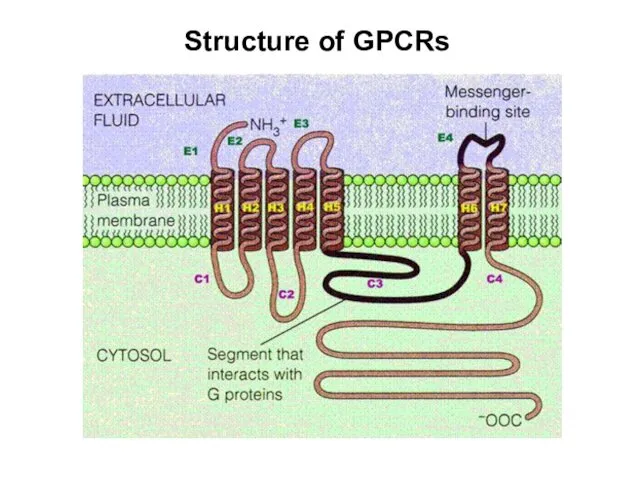
- 4. Structure of GPCRs
- 5. Classification of GPCRs: Class A (1) (Rhodopsin-like) Class B (2) (Secretin receptor family) Class C (3)
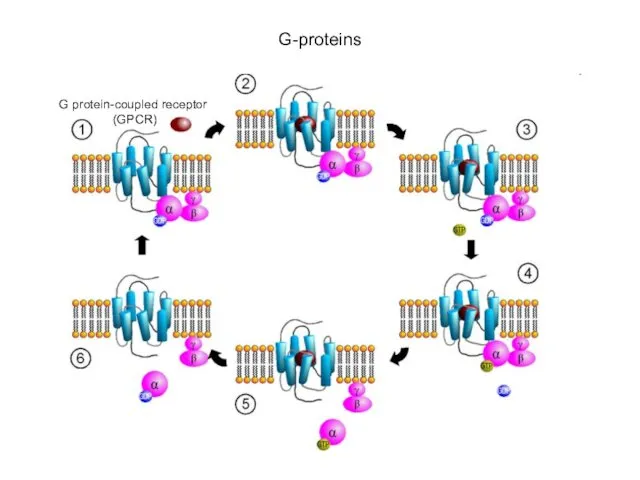
- 6. G-proteins G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)
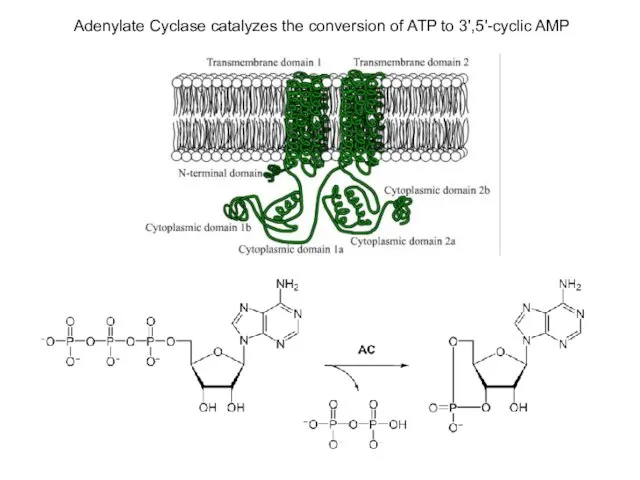
- 7. Adenylate Cyclase catalyzes the conversion of ATP to 3',5'-cyclic AMP
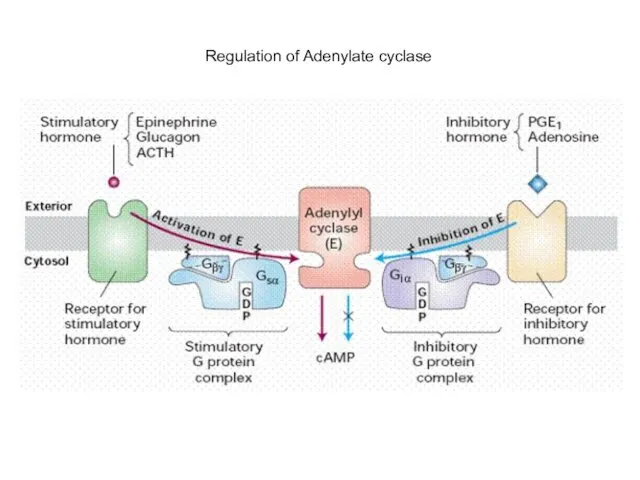
- 8. Regulation of Adenylate cyclase
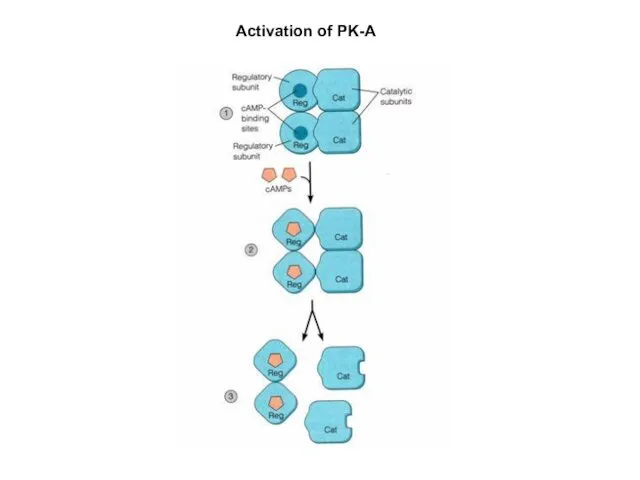
- 9. Activation of PK-A
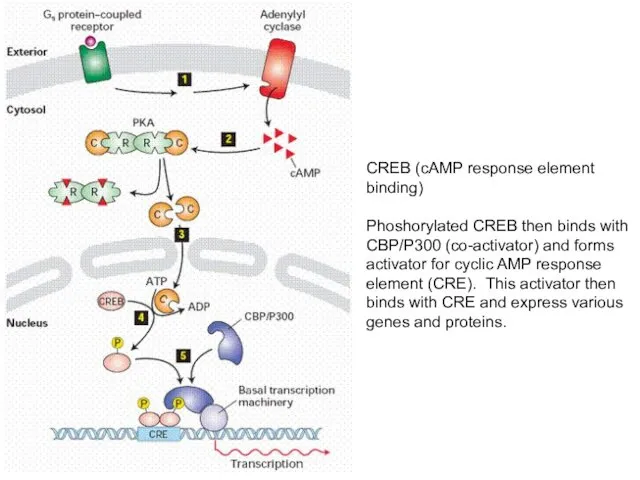
- 10. CREB (cAMP response element binding) Phoshorylated CREB then binds with CBP/P300 (co-activator) and forms activator for
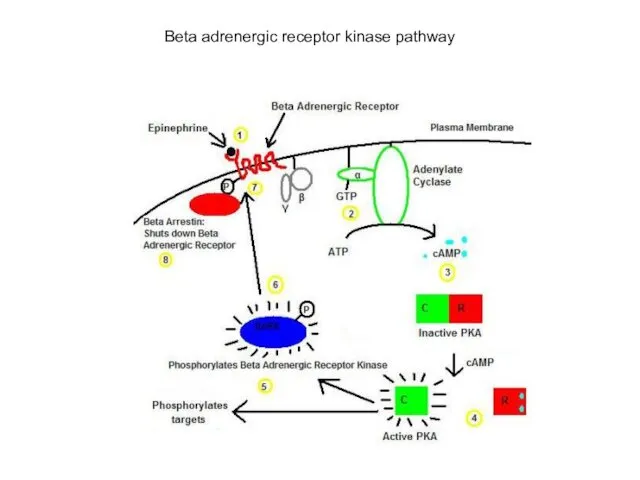
- 11. Beta adrenergic receptor kinase pathway
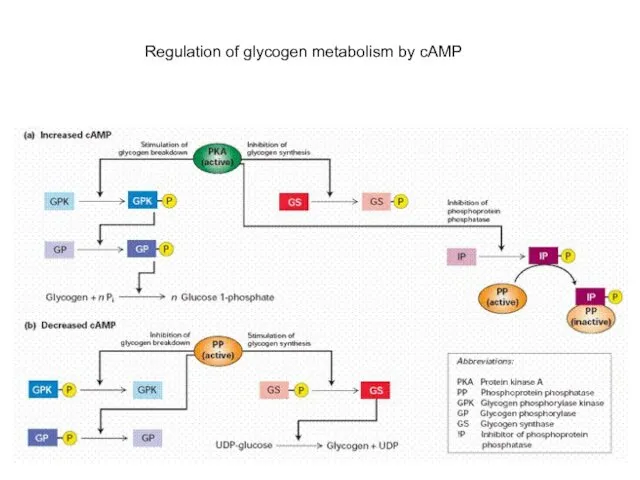
- 12. Regulation of glycogen metabolism by cAMP
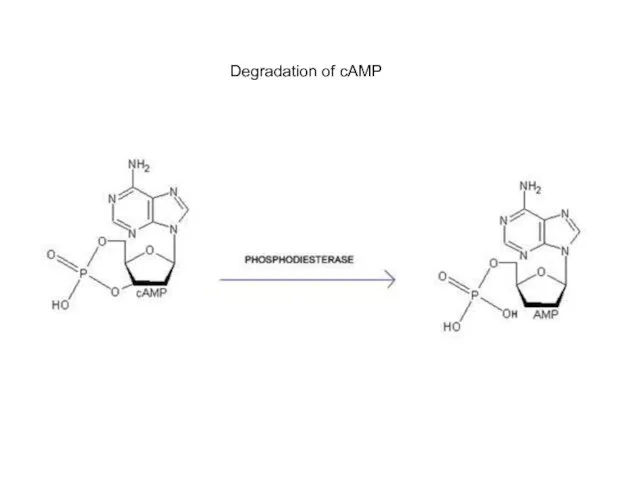
- 13. Degradation of cAMP
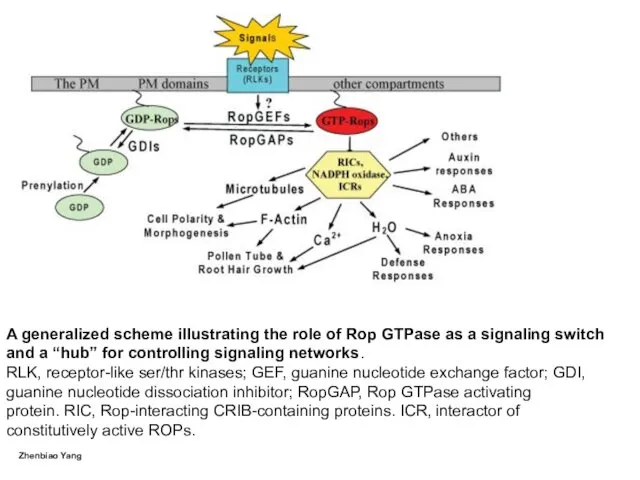
- 14. A generalized scheme illustrating the role of Rop GTPase as a signaling switch and a “hub”
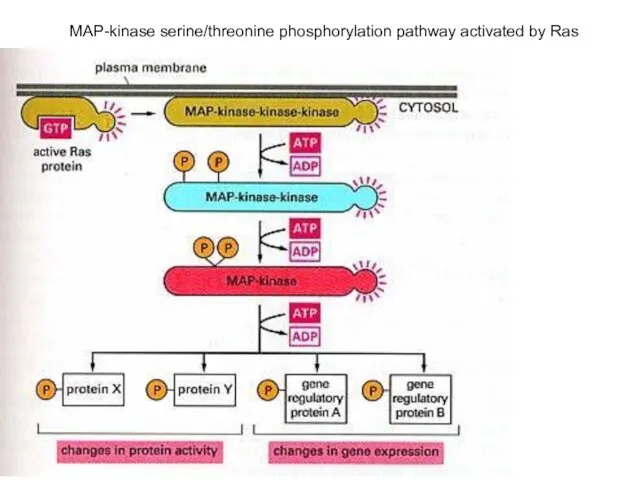
- 15. MAP-kinase serine/threonine phosphorylation pathway activated by Ras
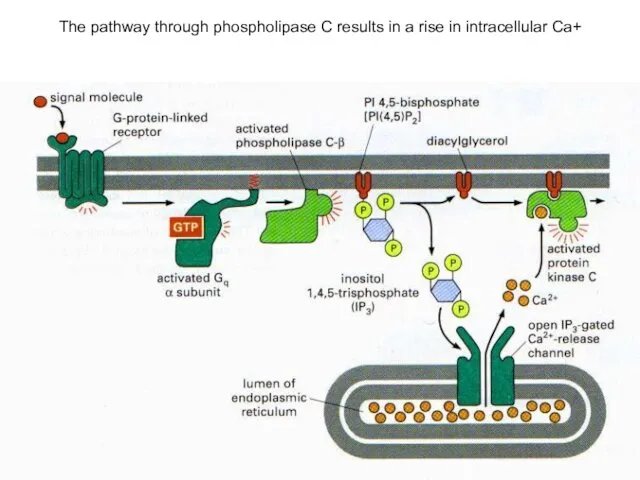
- 16. The pathway through phospholipase C results in a rise in intracellular Ca+
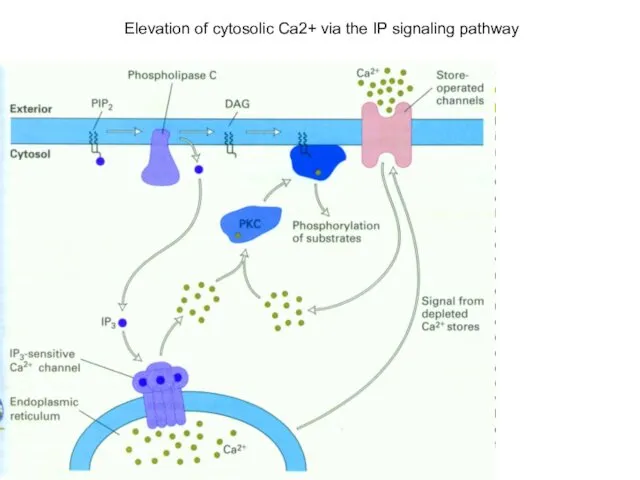
- 17. Elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ via the IP signaling pathway
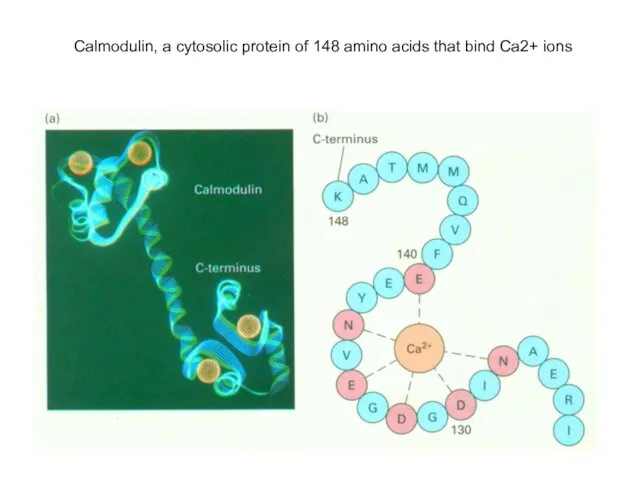
- 18. Calmodulin, a cytosolic protein of 148 amino acids that bind Ca2+ ions
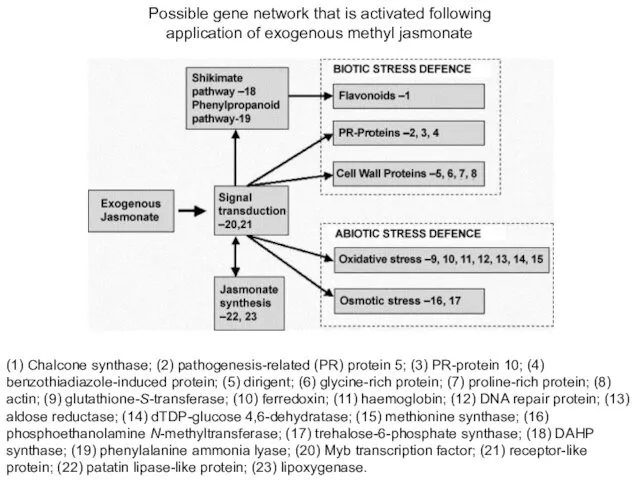
- 21. (1) Chalcone synthase; (2) pathogenesis-related (PR) protein 5; (3) PR-protein 10; (4) benzothiadiazole-induced protein; (5) dirigent;
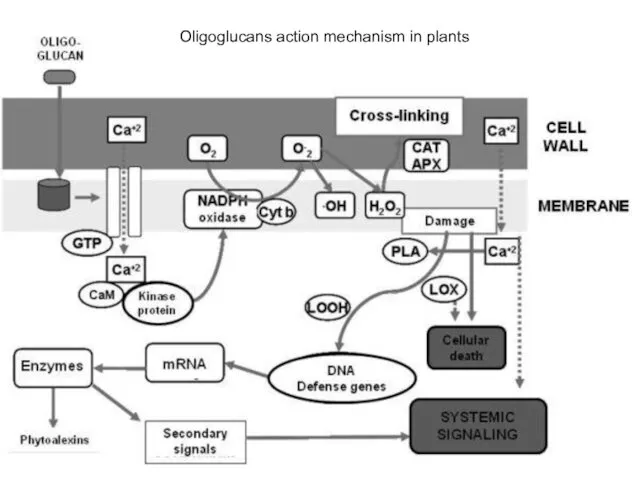
- 22. Oligoglucans action mechanism in plants
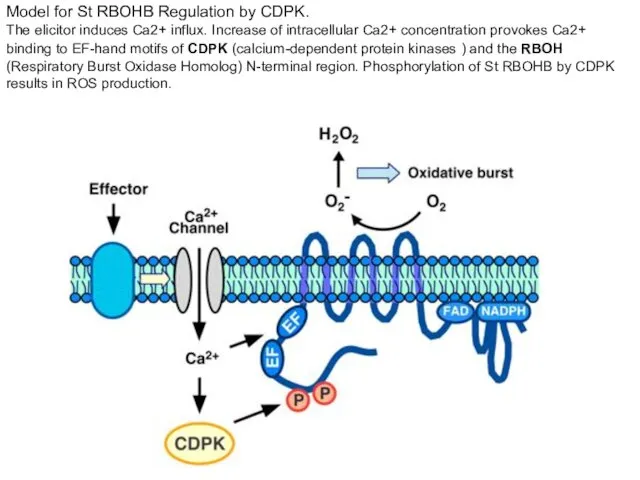
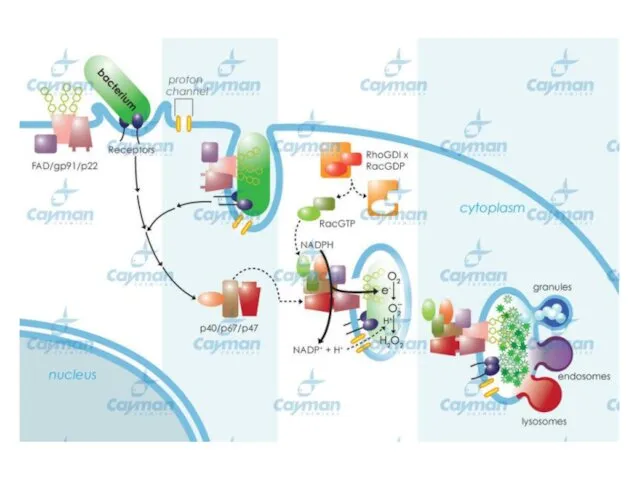
- 23. Model for St RBOHB Regulation by CDPK. The elicitor induces Ca2+ influx. Increase of intracellular Ca2+
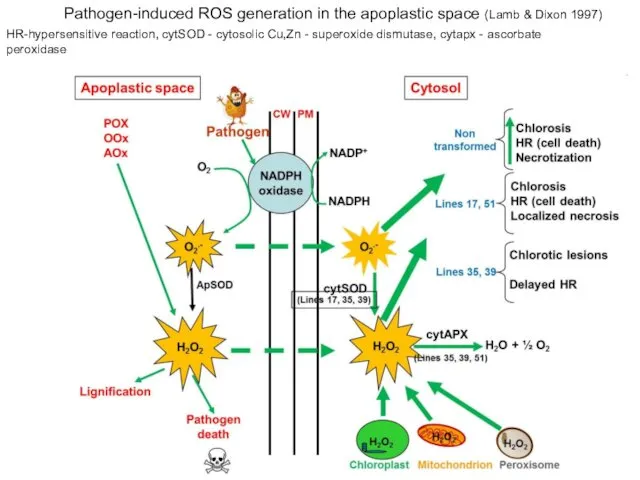
- 25. Pathogen-induced ROS generation in the apoplastic space (Lamb & Dixon 1997) HR-hypersensitive reaction, cytSOD - cytosolic
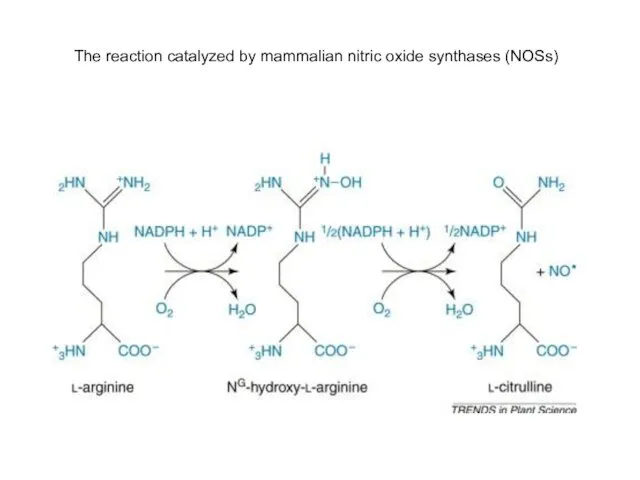
- 26. The reaction catalyzed by mammalian nitric oxide synthases (NOSs)
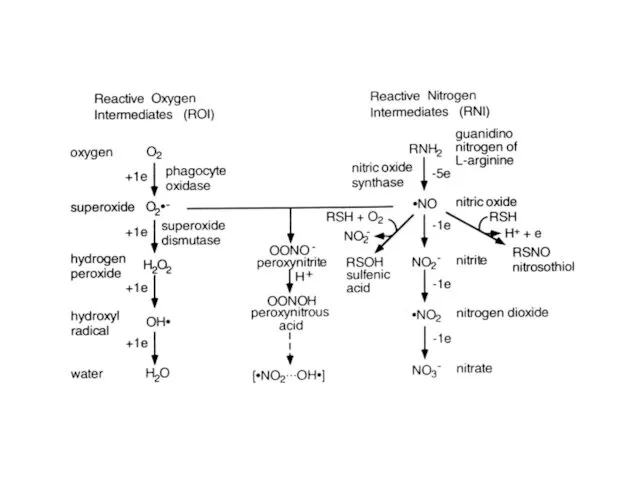
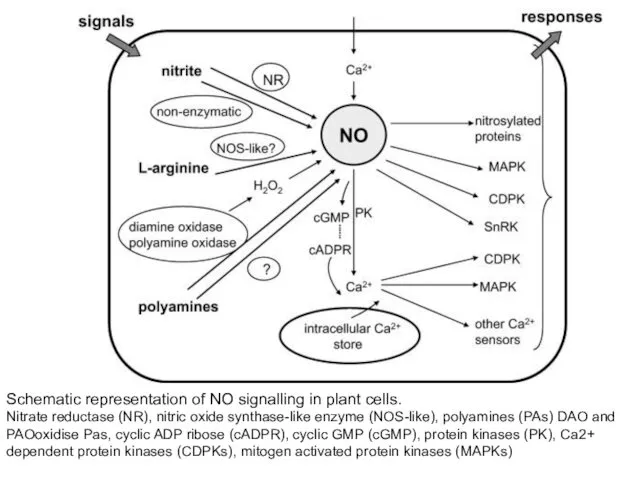
- 28. Schematic representation of NO signalling in plant cells. Nitrate reductase (NR), nitric oxide synthase-like enzyme (NOS-like),
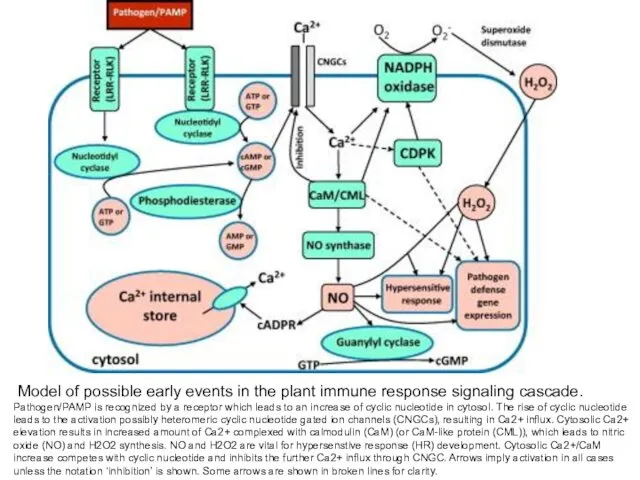
- 29. Model of possible early events in the plant immune response signaling cascade. Pathogen/PAMP is recognized by
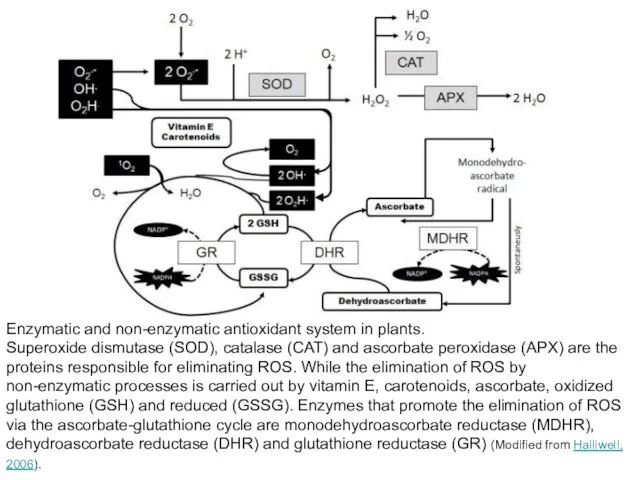
- 35. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant system in plants. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and ascorbate peroxidase (APX)
- 37. Скачать презентацию






 Дыхание растений
Дыхание растений презентация к теме Эволюционное учение
презентация к теме Эволюционное учение Рецепция
Рецепция Классификацая органического мира
Классификацая органического мира Шеміршекті балықтар: акулалар және скаттар. Бекіре балықтар маңызы және оларды қалпына келтіру шаралары. Қостынысты балықтар
Шеміршекті балықтар: акулалар және скаттар. Бекіре балықтар маңызы және оларды қалпына келтіру шаралары. Қостынысты балықтар Мышцы шеи
Мышцы шеи Ноосфера. Вернадский В. И
Ноосфера. Вернадский В. И Школьная клумба
Школьная клумба Функциональная анатомия промежуточного мозга
Функциональная анатомия промежуточного мозга Гербарий КГПУ им. В.П. Астафьева
Гербарий КГПУ им. В.П. Астафьева Гаструляция. Дробление и гаструляция в кишечнодышащих
Гаструляция. Дробление и гаструляция в кишечнодышащих Тесты по биологии
Тесты по биологии Нутриенты для попугаев, при содержании в искусственных условиях
Нутриенты для попугаев, при содержании в искусственных условиях Өсімдіктердің стресс механизмдері
Өсімдіктердің стресс механизмдері ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ДЛЯ ИНТЕРАКТИВНОЙ ДОСКИ. Многобразие Простейших 5-7 класс.
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ДЛЯ ИНТЕРАКТИВНОЙ ДОСКИ. Многобразие Простейших 5-7 класс. Тірі ағзалардың көптүрлілігі
Тірі ағзалардың көптүрлілігі Растение в интерьере жилого дома
Растение в интерьере жилого дома Химический состав бактериальной клетки
Химический состав бактериальной клетки Хемосинтез (автотрофное питание)
Хемосинтез (автотрофное питание) Строение и функции стебля
Строение и функции стебля Оживление грибов дрожжей
Оживление грибов дрожжей Аграрний сервіс майбутнього
Аграрний сервіс майбутнього Квантовые методы в медицине. Ядерный магнитный резонанс. Электронный парамагнитный резонанс. (Лекция 14)
Квантовые методы в медицине. Ядерный магнитный резонанс. Электронный парамагнитный резонанс. (Лекция 14) Презентация по биологии для учащихся 8 класса на тему: Гигиена пищеарения
Презентация по биологии для учащихся 8 класса на тему: Гигиена пищеарения Органы пищеварения
Органы пищеварения Своя игра Общие сведения о мире животных
Своя игра Общие сведения о мире животных Класс Пресмыкающиеся, или рептилии
Класс Пресмыкающиеся, или рептилии Липиды.
Липиды.