Содержание
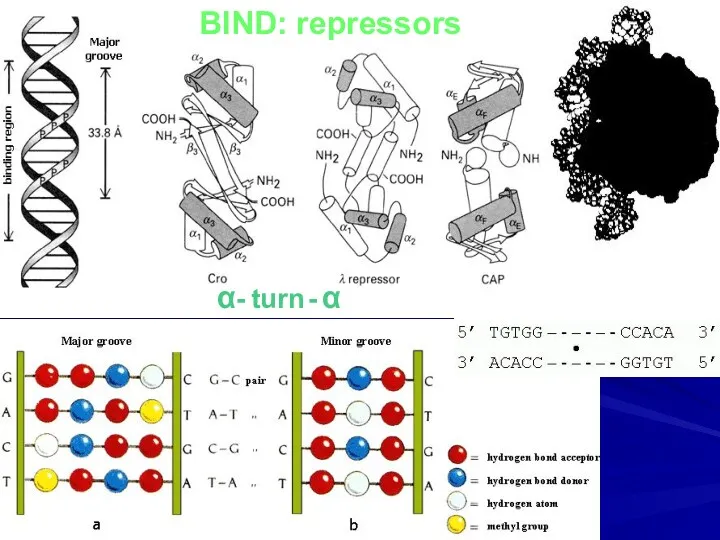
- 2. BIND: repressors α- turn - α
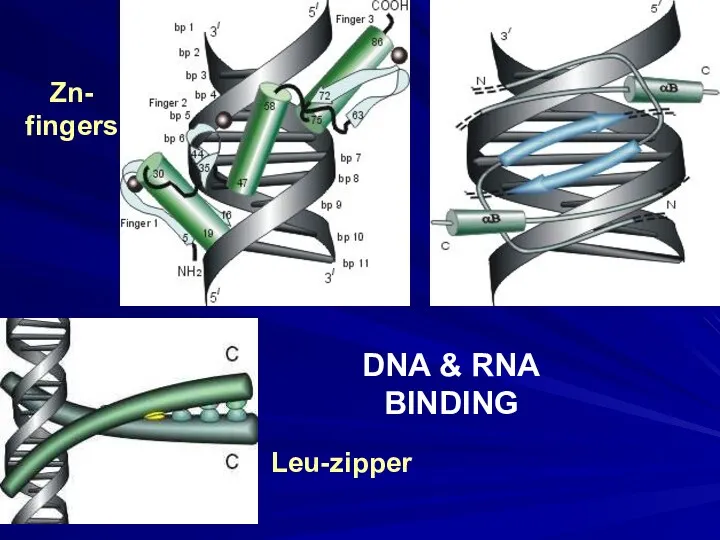
- 3. DNA & RNA BINDING Zn- fingers Leu-zipper
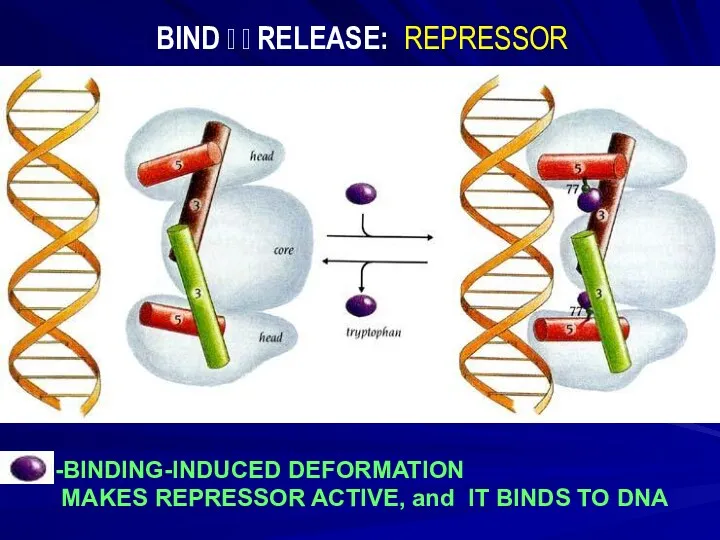
- 4. -BINDING-INDUCED DEFORMATION MAKES REPRESSOR ACTIVE, and IT BINDS TO DNA BIND ? ? RELEASE: REPRESSOR
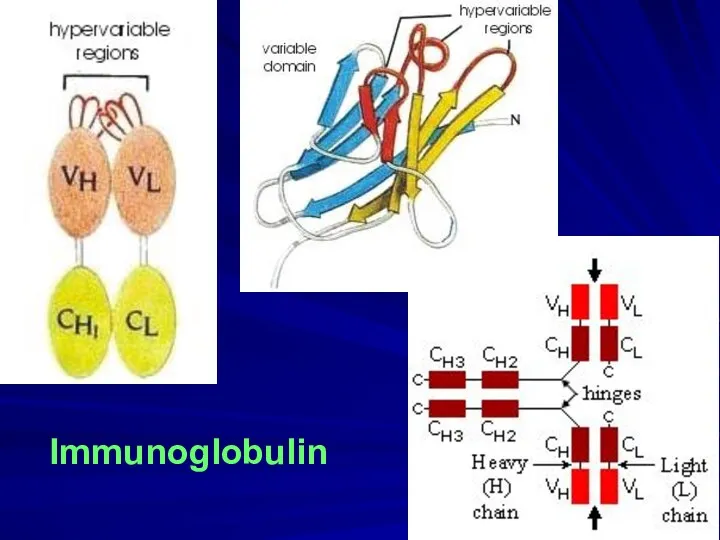
- 5. Immunoglobulin
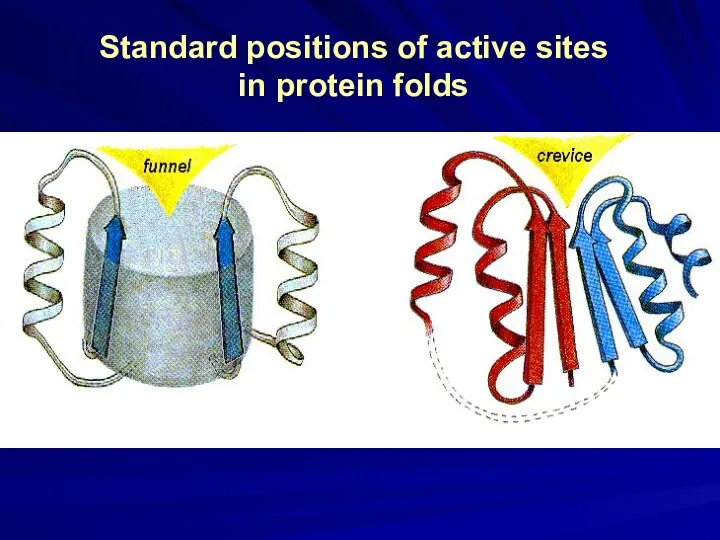
- 6. Standard positions of active sites in protein folds
- 7. There are some with catalytic (Ser-protease) site
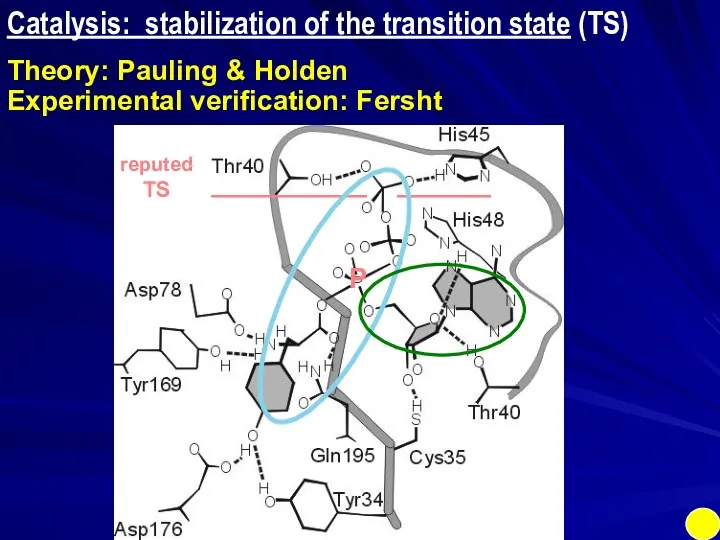
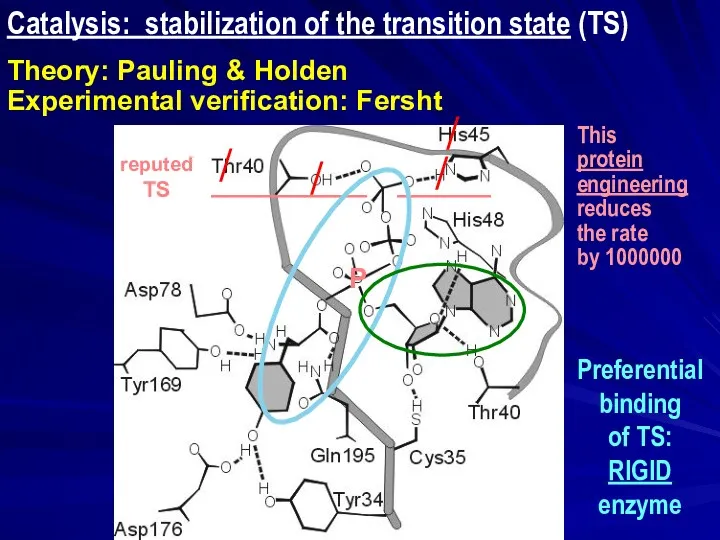
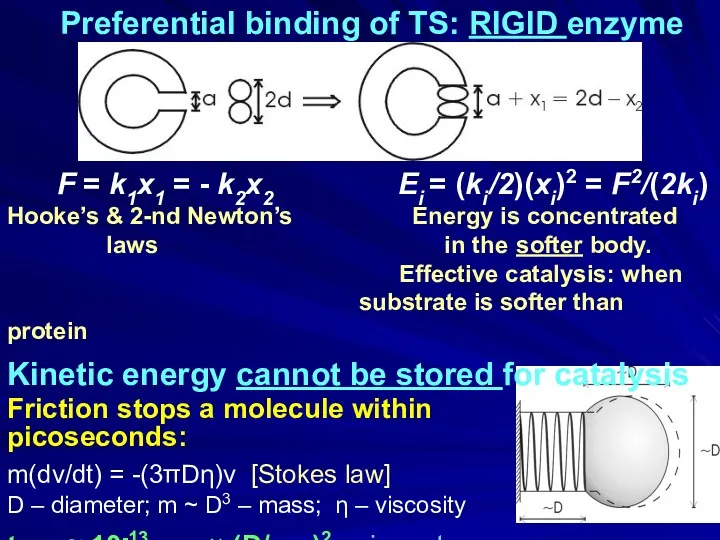
- 8. Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS) Theory: Pauling &
- 9. Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS) Theory: Pauling & Holden Experimental verification: Fersht ______ __________
- 10. Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS) Theory: Pauling & Holden Experimental verification: Fersht ______ __________
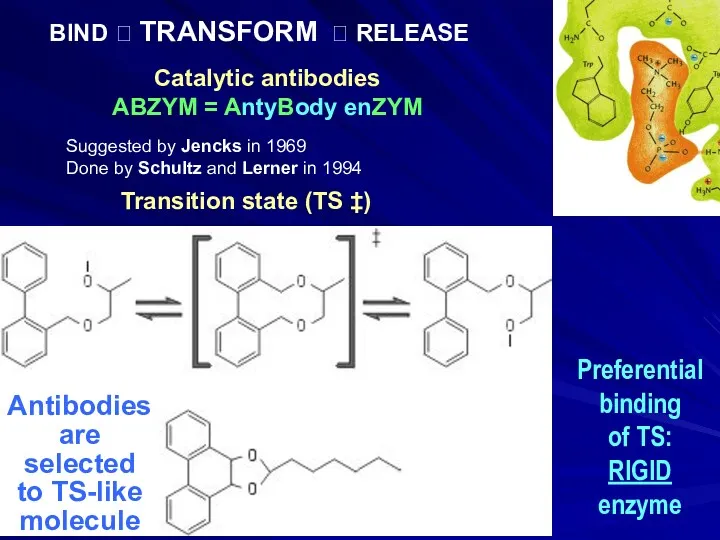
- 11. Catalytic antibodies ABZYM = AntyBody enZYM Antibodies are selected to TS-like molecule Transition state (TS ‡)
- 12. BIND ? TRANSFORM ? RELEASE: ENZYME Note: small active site chymotrypsin
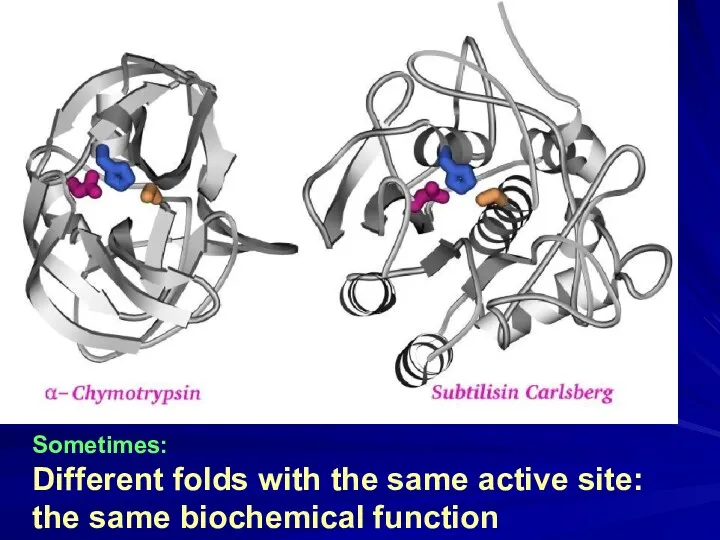
- 13. Sometimes: Different folds with the same active site: the same biochemical function
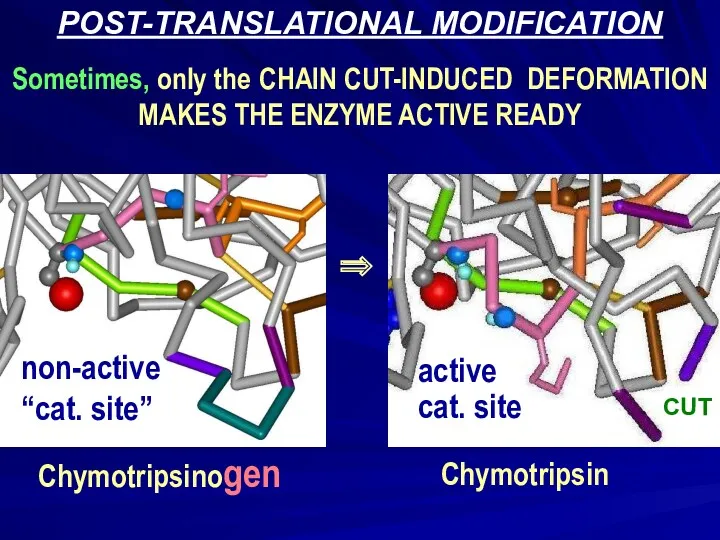
- 14. POST-TRANSLATIONAL MODIFICATION Sometimes, only the CHAIN CUT-INDUCED DEFORMATION MAKES THE ENZYME ACTIVE READY Chymotripsinogen active cat.
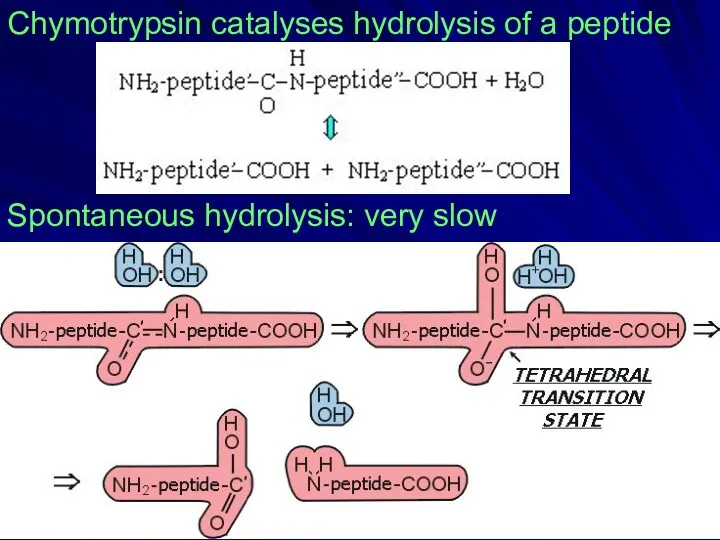
- 15. Chymotrypsin catalyses hydrolysis of a peptide Spontaneous hydrolysis: very slow
- 16. SER-protease: catalysis
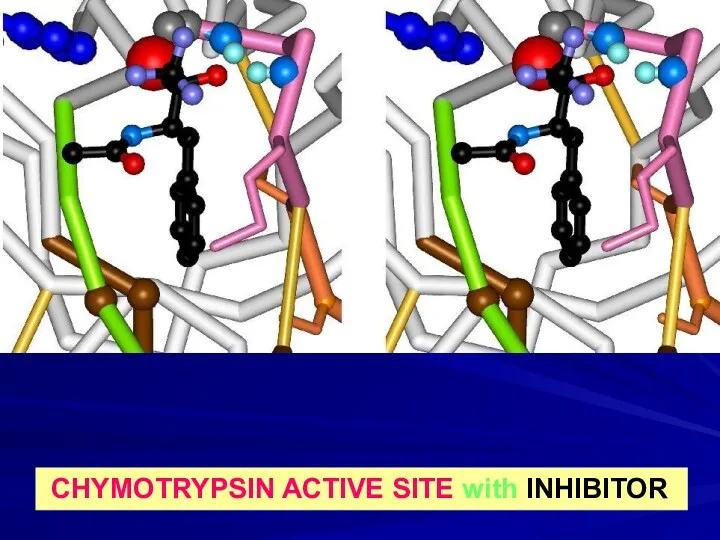
- 17. CHYMOTRYPSIN ACTIVE SITE with INHIBITOR
- 18. Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme F = k1x1 = - k2x2 Ei = (ki /2)(xi)2
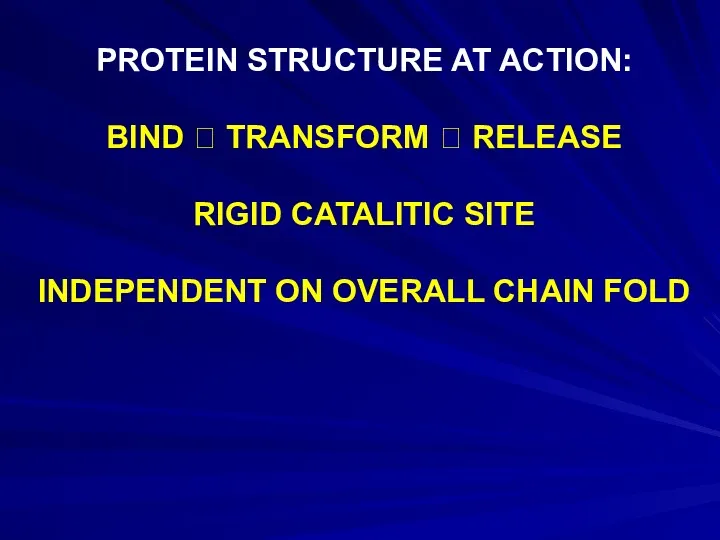
- 19. PROTEIN STRUCTURE AT ACTION: BIND ? TRANSFORM ? RELEASE RIGID CATALITIC SITE INDEPENDENT ON OVERALL CHAIN
- 20. Induced fit model for enzyme catalysis. Daniel Edward Koshland, Jr. (1920 – 2007) Hermann Emil Louis
- 21. MOTIONS
- 22. Double sieve: movement of substrate from one active site to another ⇑ tRNAIle Fersht A.R., Dingwall
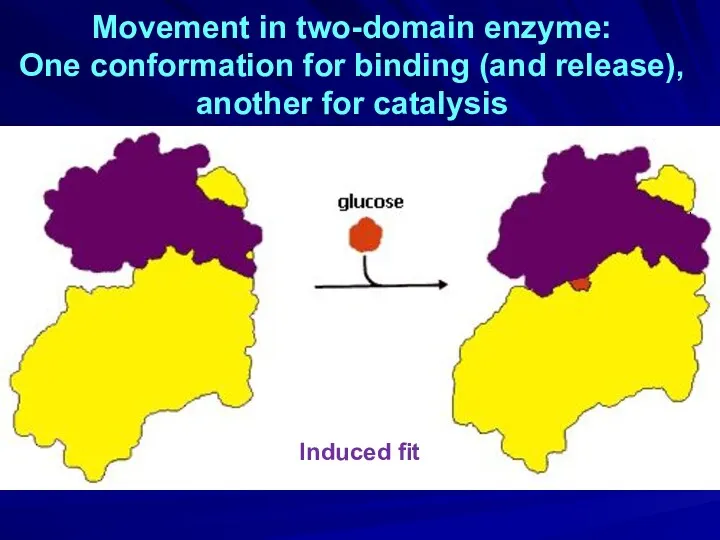
- 23. Movement in two-domain enzyme: One conformation for binding (and release), another for catalysis Induced fit
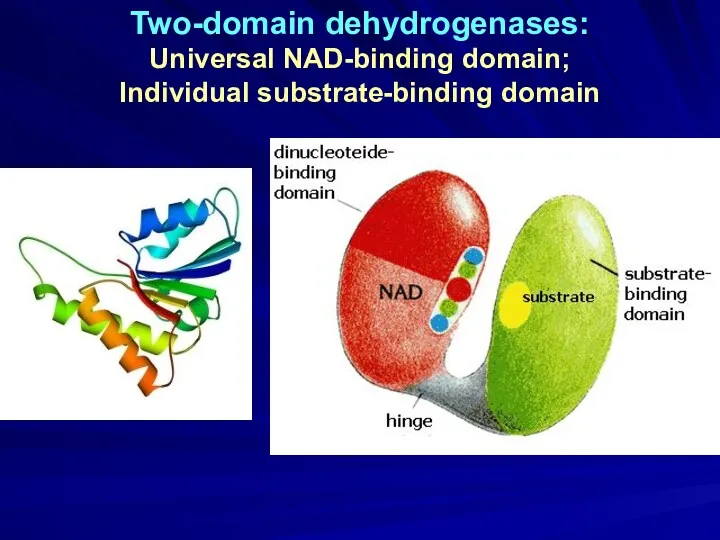
- 24. Two-domain dehydrogenases: Universal NAD-binding domain; Individual substrate-binding domain
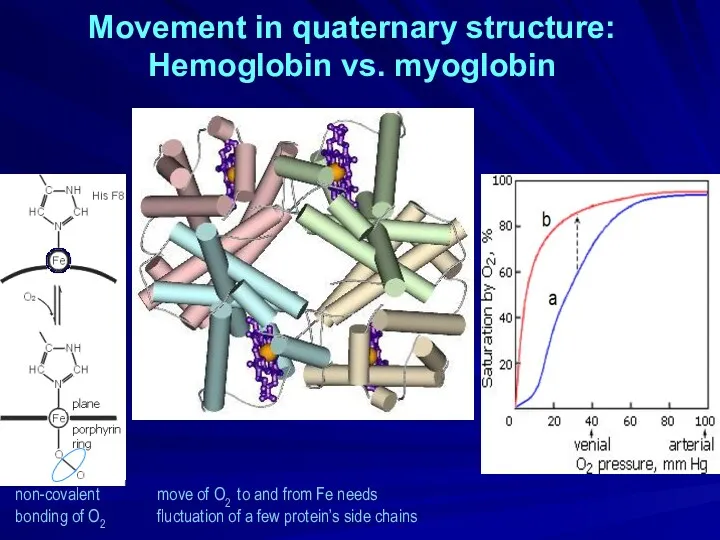
- 25. Movement in quaternary structure: Hemoglobin vs. myoglobin non-covalent bonding of O2 move of O2 to and
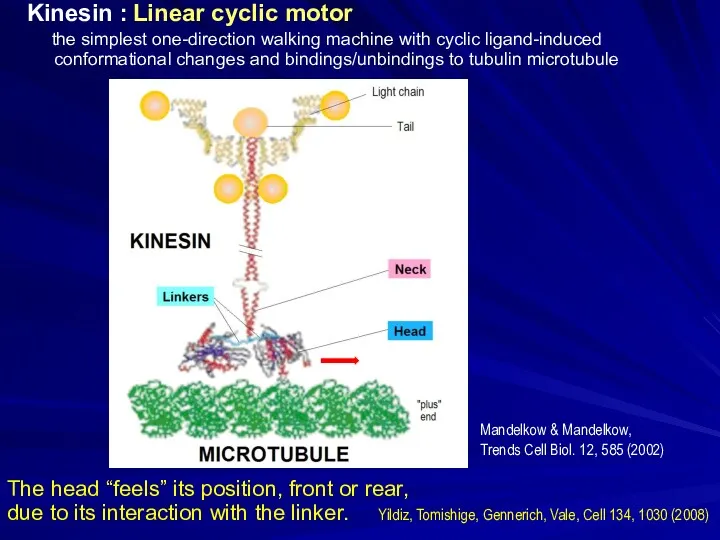
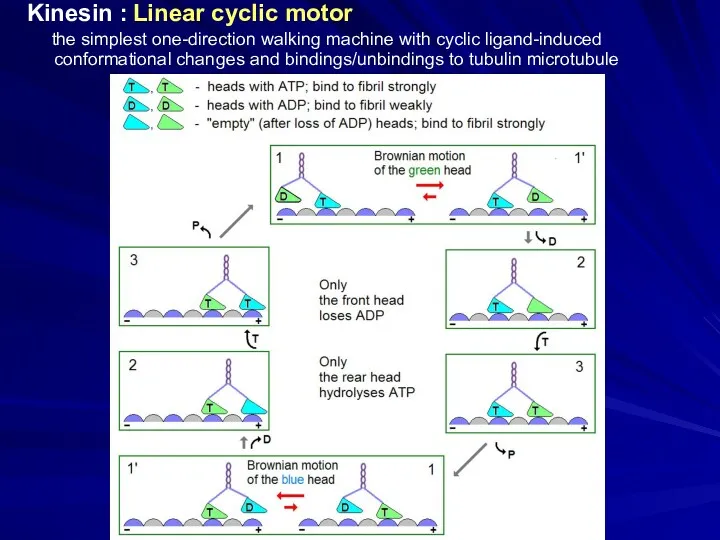
- 26. Kinesin : Linear cyclic motor the simplest one-direction walking machine with cyclic ligand-induced conformational changes and
- 27. Kinesin : Linear cyclic motor the simplest one-direction walking machine with cyclic ligand-induced conformational changes and
- 28. Sir Andrew Fielding Huxley (1917 – 2012) Nobel Prize 1963 Myosin "cross-bridges"
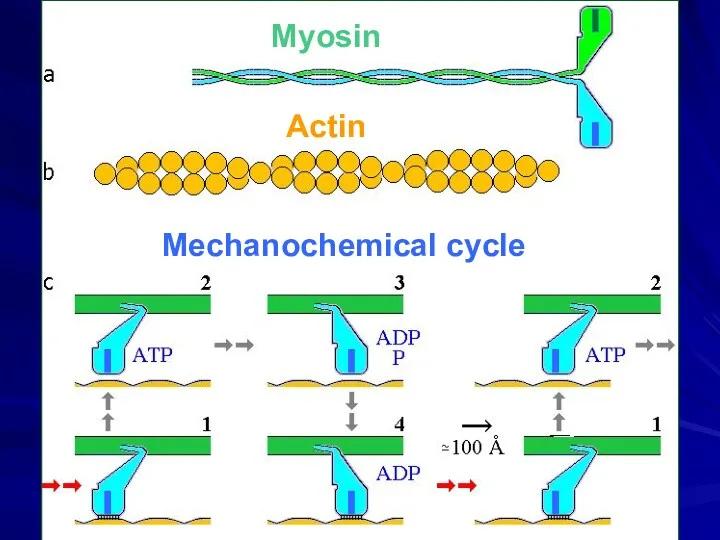
- 29. Механохимический цикл Миозин Актин АТФ → АДФ + Ф 15 ккал/моль в клеточных условиях
- 30. Mechanochemical cycle Myosin Actin
- 31. structure from the X-ray data: Junge, Sielaff, Engelbrecht, Nature, 459, 364 (2009) Rotary motor F0F1-ATP synthase
- 32. Engelbrecht & Junge, FEBS Lett. 414, 485 (1997) Elston, Wang, Oster, Nature, 391, 510 (1998) F0-machine:
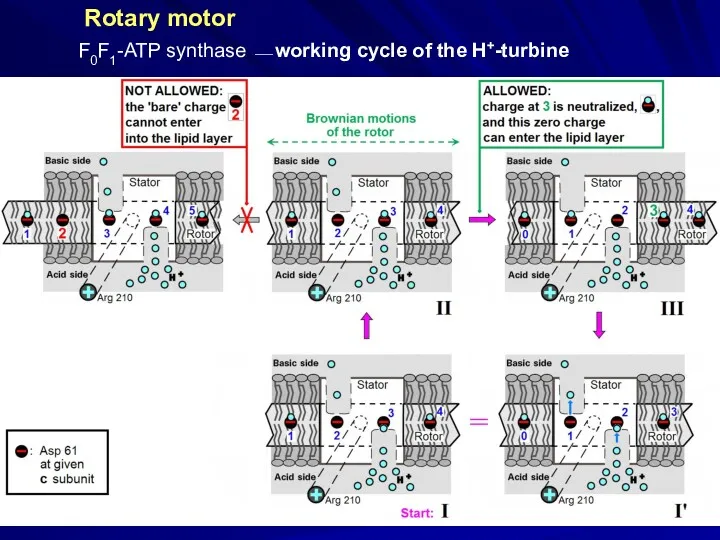
- 33. Rotary motor F0F1-ATP synthase ⎯ working cycle of the H+-turbine
- 34. H3O+ binding in Bacillus pseudofirmus Ion binding to the rotor ring of F0F1-ATP synthase H+ binding
- 35. SUMMARY of the course
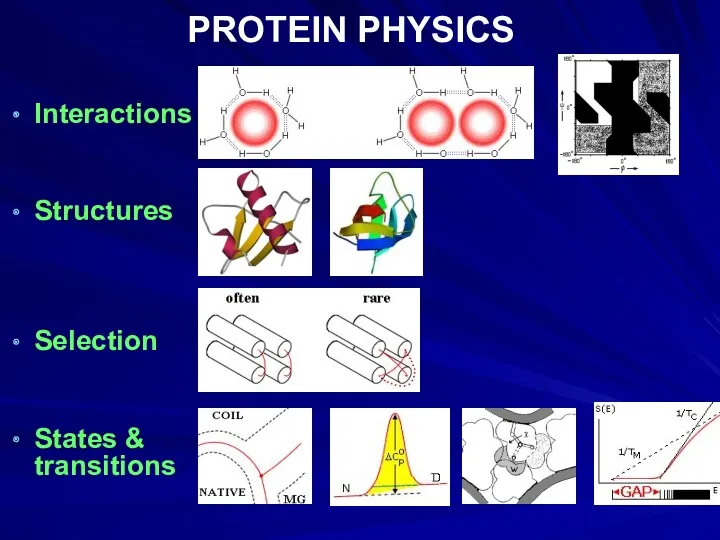
- 36. PROTEIN PHYSICS Interactions Structures Selection States & transitions
- 37. Intermediates & nuclei Structure prediction & bioinformatics Protein engineering & design Functioning
- 38. Благодарю за внимание … товарищи офизевшие биологи!
- 40. Скачать презентацию














 f611e845-2141-4c61-a9b2-34e2049b0658
f611e845-2141-4c61-a9b2-34e2049b0658 Морские свинки
Морские свинки Особенности пищеварения у собак и котов. Питательные и биологически активные вещества
Особенности пищеварения у собак и котов. Питательные и биологически активные вещества Лекция 1. Растениеводство
Лекция 1. Растениеводство Этимология названий лекарственных растений. Мифы и легенды
Этимология названий лекарственных растений. Мифы и легенды Почки растений
Почки растений Турбота про потомство
Турбота про потомство Путешествие в страну Легумия. Систематика покрытосеменных. 6 класс
Путешествие в страну Легумия. Систематика покрытосеменных. 6 класс Нейропрорывы-2017/2018
Нейропрорывы-2017/2018 Презентация по биологии для учащихся 7 класса по теме Класс Пресмыкающиеся
Презентация по биологии для учащихся 7 класса по теме Класс Пресмыкающиеся Вітаміни. Їх роль у життєдіяльності людини
Вітаміни. Їх роль у життєдіяльності людини Размножение - свойство живых организмов
Размножение - свойство живых организмов Підряд Мавпи
Підряд Мавпи Энергетический обмен. Дыхание
Энергетический обмен. Дыхание Цікаві факти про риб
Цікаві факти про риб Талдағыштар физиологиясы. Талдағыштардың жалпы қасиеттері. Көру талдағыштары
Талдағыштар физиологиясы. Талдағыштардың жалпы қасиеттері. Көру талдағыштары Структура и функции клетки
Структура и функции клетки Размножение и развитие человека
Размножение и развитие человека Покрытосеменные, или Цветковые
Покрытосеменные, или Цветковые Самые страшные животные мира
Самые страшные животные мира Рост и развитие растений
Рост и развитие растений Освоение суши растениями
Освоение суши растениями Хромосомная теория наследственностию. Генетика пола
Хромосомная теория наследственностию. Генетика пола Юрский период (195 -137 млн.)
Юрский период (195 -137 млн.) Презентация Великаны и карлики в животном мире
Презентация Великаны и карлики в животном мире Насекомые. Отряд равнокрылые
Насекомые. Отряд равнокрылые Биотические факторы
Биотические факторы Становление наук о человеке. (8 класс)
Становление наук о человеке. (8 класс)