Содержание
- 2. Week 1 1. Fertilization – is the fusion of the sperm and ovum (male and female
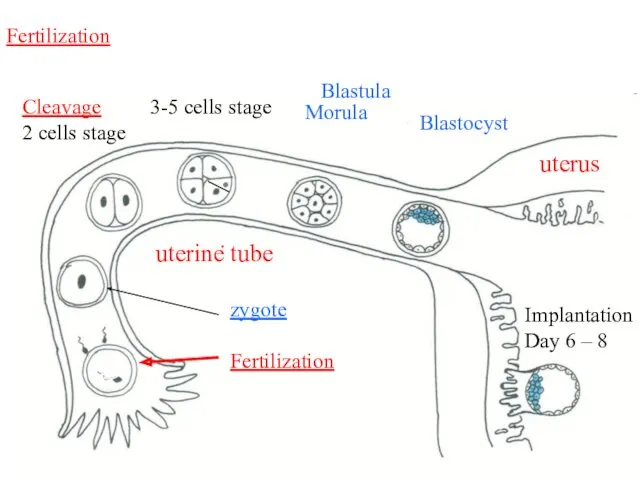
- 3. Week 1 Zygote – 1 cell embryo – starts to divide: 2. Cleavage – is the
- 4. zygote Fertilization zygote Fertilization Cleavage 2 cells stage 3-5 cells stage Morula Blastocyst Implantation Day 6
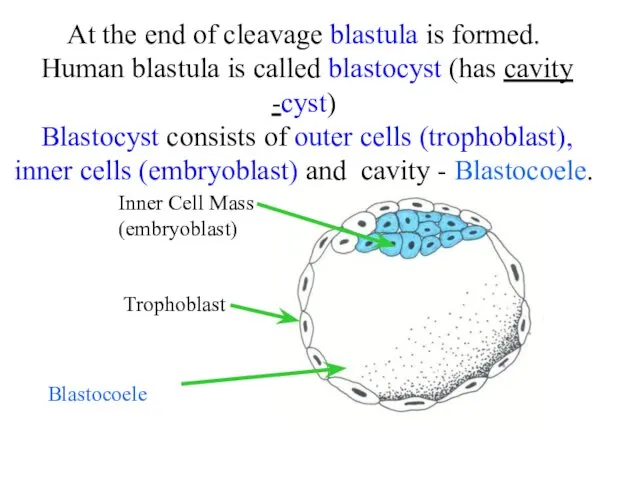
- 5. At the end of cleavage blastula is formed. Human blastula is called blastocyst (has cavity -cyst)
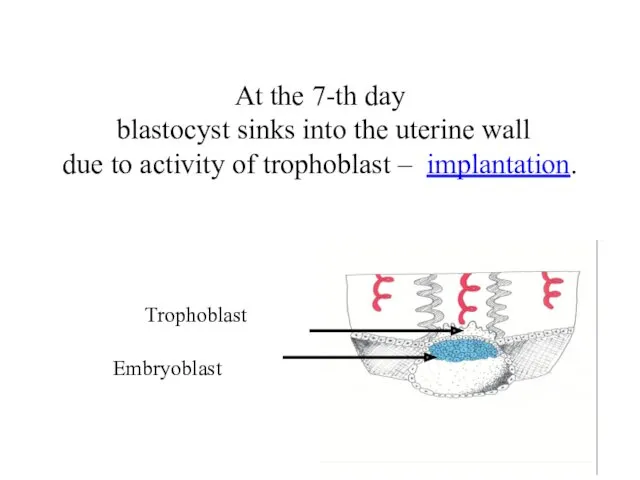
- 6. Embryoblast At the 7-th day blastocyst sinks into the uterine wall due to activity of trophoblast
- 7. Week 2: Beginning of 3. Gastrulation – formation of 3 germ layers Early Gastrulation take place
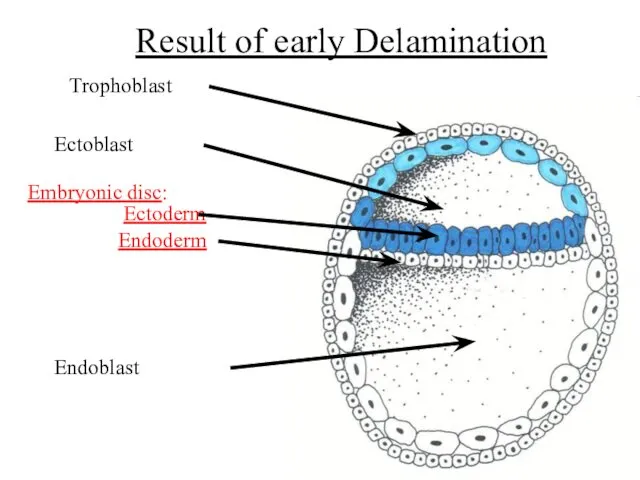
- 8. Result of early Delamination Embryonic disc:
- 9. Late gastrulation – formation of mesoderm – 3-d germ layer – take place by cell migration:
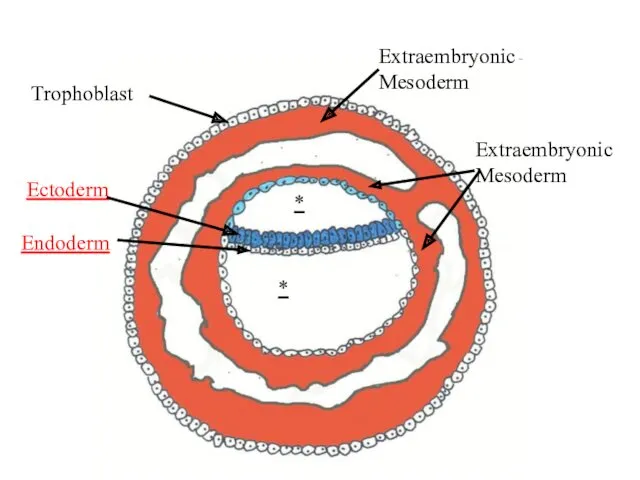
- 10. 1-st appear extraembryonic mesoderm: it surrounds upper and lower sacs, and underly trophoblast
- 11. Trophoblast Extraembryonic Mesoderm * Ectoderm Endoderm Extraembryonic Mesoderm *
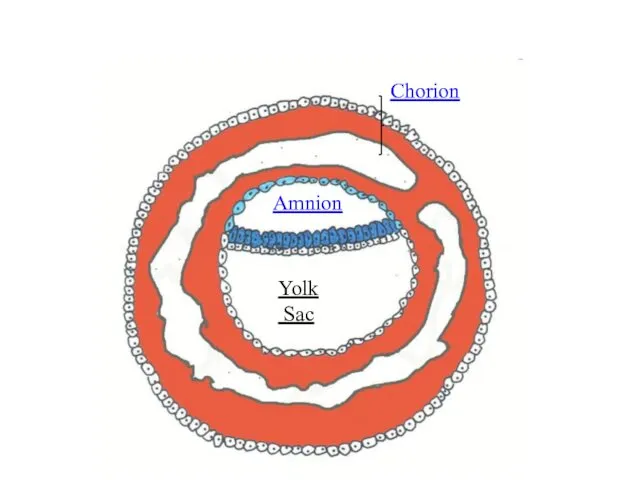
- 12. As a result appear so-called extraembryonic organs - amnion, yolk sac and chorion
- 13. Chorion Amnion Yolk Sac
- 14. Migration of cells within the embryonic disc leads to formation of the embryonic mesoderm and axial
- 15. Migration of cells within embryonic disc leads to formation of temporal cellular assemblage between ectoderm and
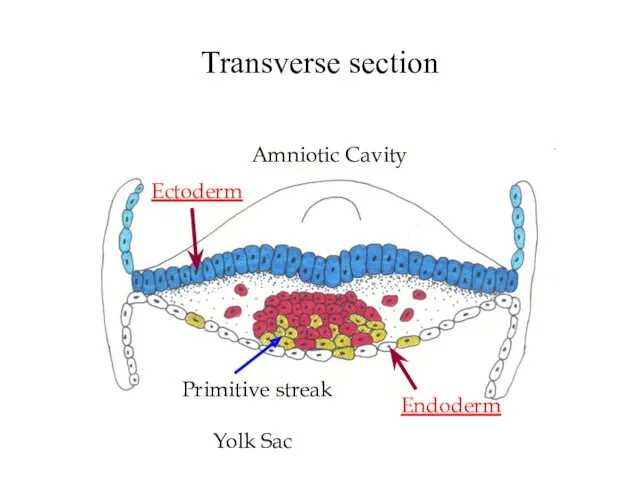
- 16. Transverse section Ectoderm Endoderm Amniotic Cavity Primitive streak Yolk Sac
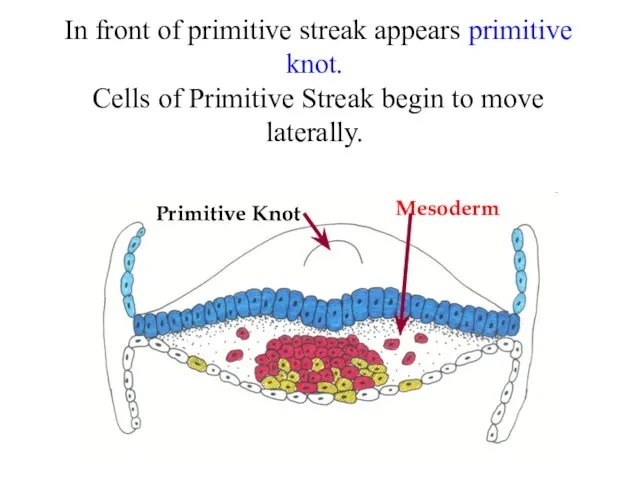
- 17. In front of primitive streak appears primitive knot. Cells of Primitive Streak begin to move laterally.
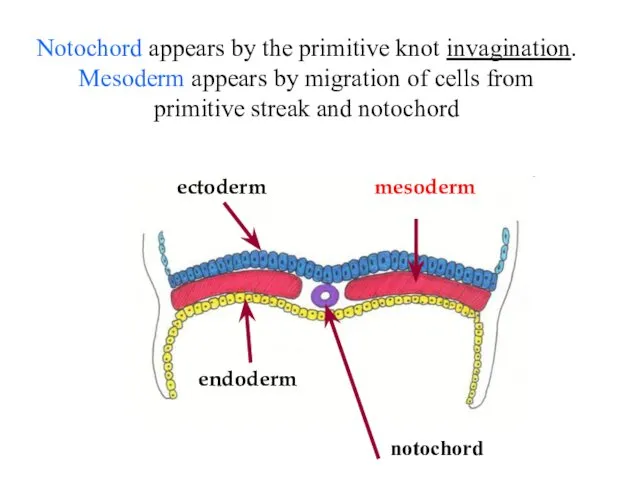
- 18. ectoderm endoderm mesoderm Notochord appears by the primitive knot invagination. Mesoderm appears by migration of cells
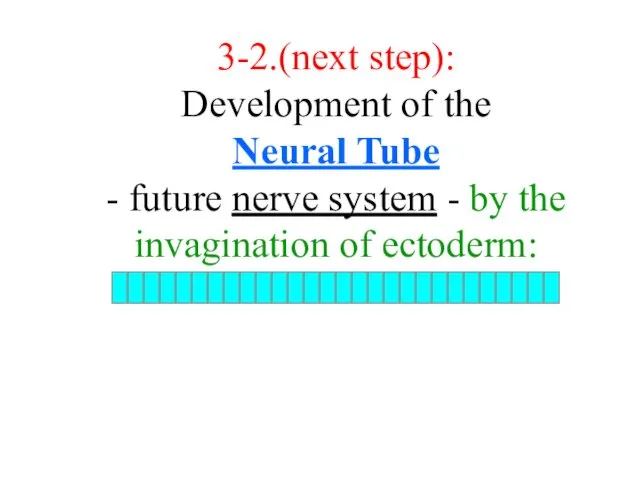
- 19. 3-2.(next step): Development of the Neural Tube - future nerve system - by the invagination of
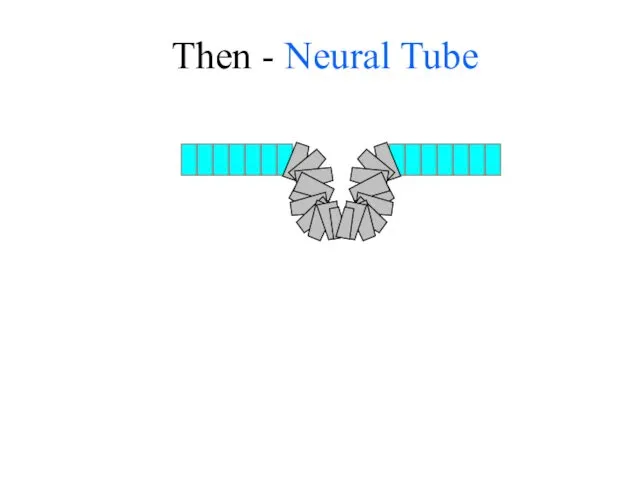
- 20. Neural plate in Surface Ectoderm forms Neural groove
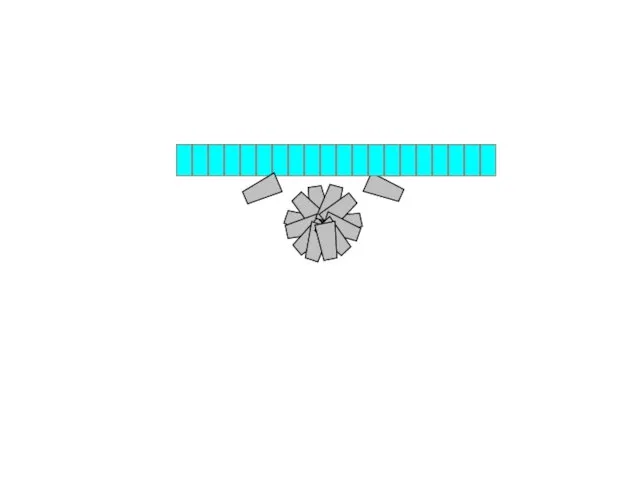
- 21. Then - Neural Tube
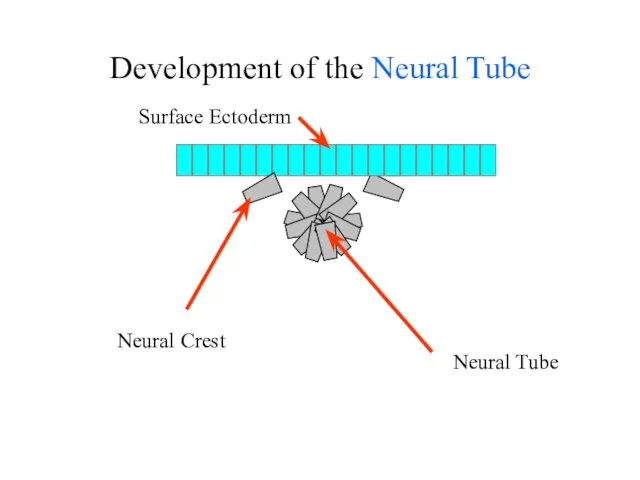
- 23. Development of the Neural Tube Surface Ectoderm Neural Crest Neural Tube
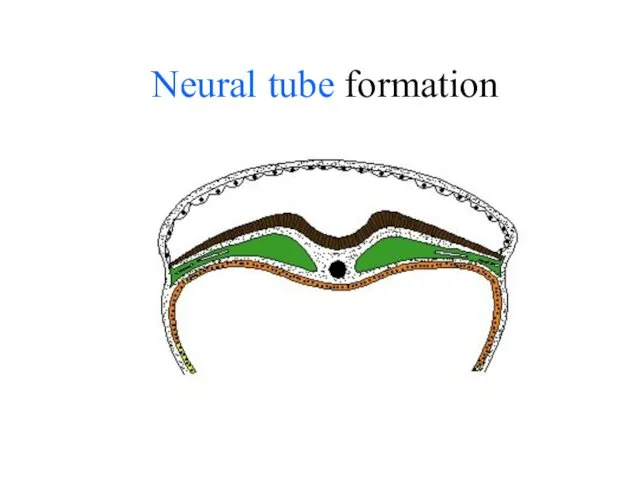
- 24. Neural tube formation
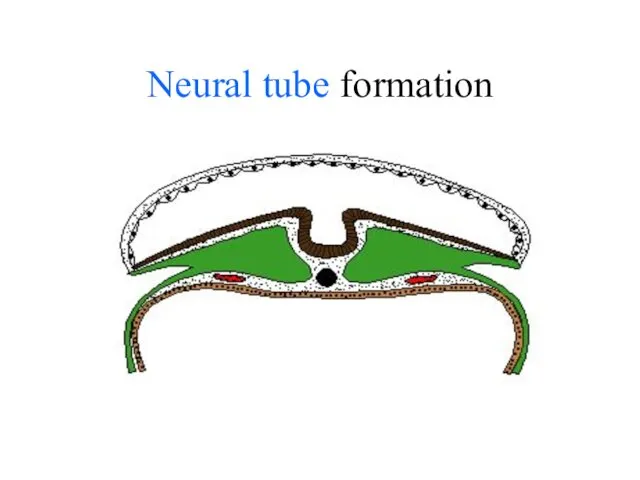
- 25. Neural tube formation
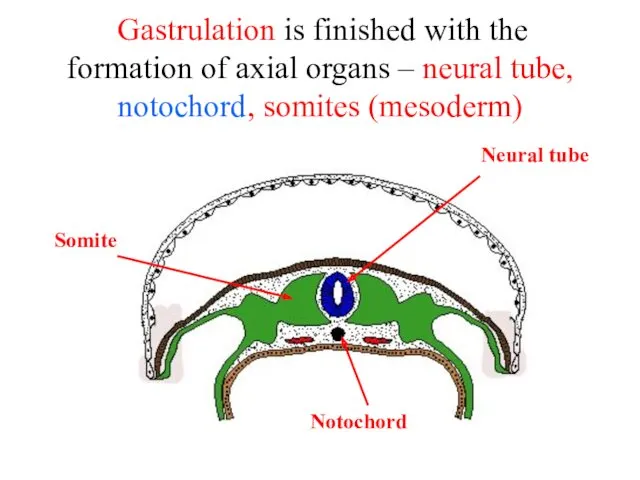
- 26. Gastrulation is finished with the formation of axial organs – neural tube, notochord, somites (mesoderm) Somite
- 27. 4. Formation of the embryo body (20-th day) by: - body flexion, - head and tail
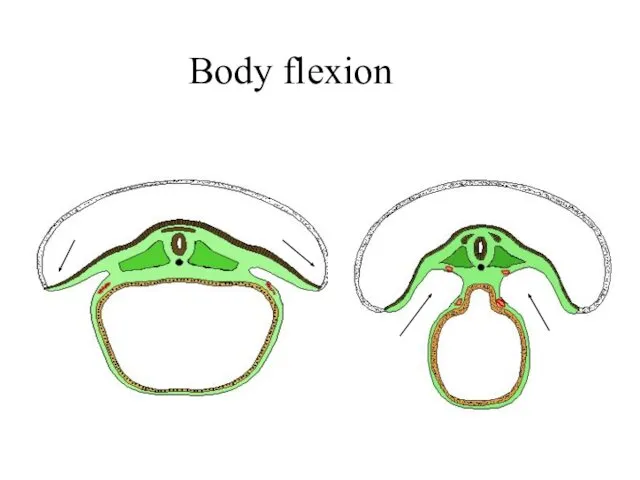
- 28. Body flexion
- 29. Differentiation of GERM LAYERS: 1. Differentiation of Ectoderm A. Surface Ectoderm B. Neural Tube 2. Differentiation
- 30. Surface Ectoderm differentiates to epithelium of skin, and its derivatives, oral cavity epithelium, rectal epithelium, outer
- 31. Neural tube (neuroectoderm) --- brain, spinal cord, and the retina Neural crests --- Peripheral Nervous system,
- 32. Endoderm differentiates to epithelium of stomach, intestine, liver, pancreas, respiratory system
- 33. Mesoderm Notochord Endoderm Ectoderm Yolk Sac Amniotic Cavity Somite Intermediate mesoderm (nephrotome) Lateral plate mesoderm (somatopleuric,
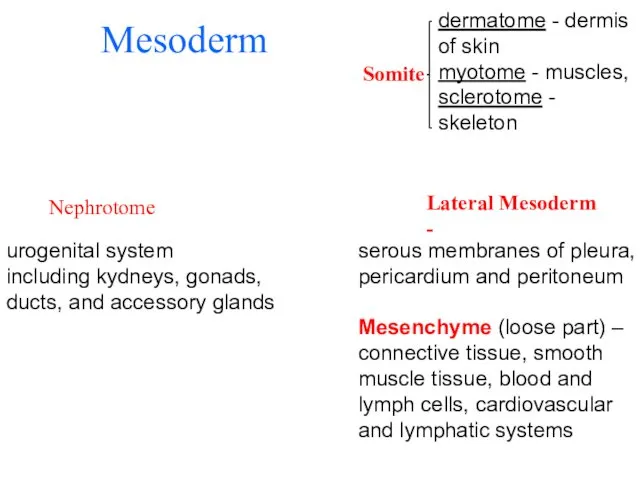
- 34. Mesoderm Nephrotome urogenital system including kydneys, gonads, ducts, and accessory glands Somite dermatome - dermis of
- 35. Late embryonic stages Histogenesis Organogenesis
- 37. Скачать презентацию
















 Этические проблемы использования животных
Этические проблемы использования животных Пищеварение 1.1
Пищеварение 1.1 Общие признаки животных. 5 класс
Общие признаки животных. 5 класс Ретикулярная формация. Лимбическая система. Оболочки мозга
Ретикулярная формация. Лимбическая система. Оболочки мозга Хемосинтез. Хемосинтезирующие организмы
Хемосинтез. Хемосинтезирующие организмы Визначення типу шкіри на різних ділянках обличчя та складання правил догляду за власною шкірою
Визначення типу шкіри на різних ділянках обличчя та складання правил догляду за власною шкірою Прокариоты на службе по защите почвенной среды жизни от тяжёлых металлов
Прокариоты на службе по защите почвенной среды жизни от тяжёлых металлов Прісноводна гідра
Прісноводна гідра Zebra is a striped member of the horse family
Zebra is a striped member of the horse family Голоса птиц
Голоса птиц Імунітет рослин до інфекційних хвороб
Імунітет рослин до інфекційних хвороб Морфологическое описание растения
Морфологическое описание растения Презентация по биологии для учащихся 9 класса по теме Клеточная мембрана
Презентация по биологии для учащихся 9 класса по теме Клеточная мембрана Про кошек
Про кошек Презентация к уроку биологии в 7 классе Отряд Жесткокрылые, или Жуки
Презентация к уроку биологии в 7 классе Отряд Жесткокрылые, или Жуки Транскрипция и трансляция. Генетическая трансформация
Транскрипция и трансляция. Генетическая трансформация Китообразные и ластоногие
Китообразные и ластоногие Породы кошек
Породы кошек Классификация и характеристика рыб
Классификация и характеристика рыб Строение клеток прокариот и эукариот
Строение клеток прокариот и эукариот Органы и системы органов
Органы и системы органов Мед - пчелиная заслуга
Мед - пчелиная заслуга Микробиология - наука о микроорганизмах
Микробиология - наука о микроорганизмах Карл Линней - основоположник биологической систематики
Карл Линней - основоположник биологической систематики Движение крови в организме. Органы кровообращения
Движение крови в организме. Органы кровообращения Приглашение на семинар по управлению инкубаторием компании Пас Реформ
Приглашение на семинар по управлению инкубаторием компании Пас Реформ Витамины красоты
Витамины красоты Внеклассное мероприятие Красная книга Оренбургской области
Внеклассное мероприятие Красная книга Оренбургской области