Слайд 2
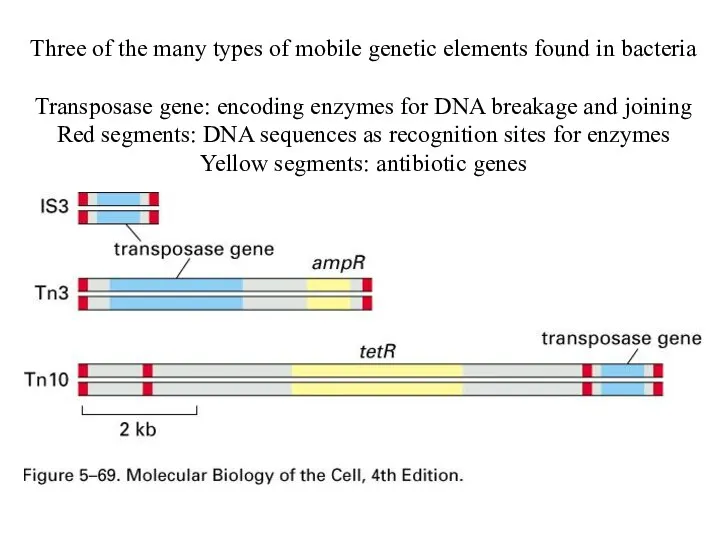
Three of the many types of mobile genetic elements found in
bacteria
Transposase gene: encoding enzymes for DNA breakage and joining
Red segments: DNA sequences as recognition sites for enzymes
Yellow segments: antibiotic genes
Слайд 3
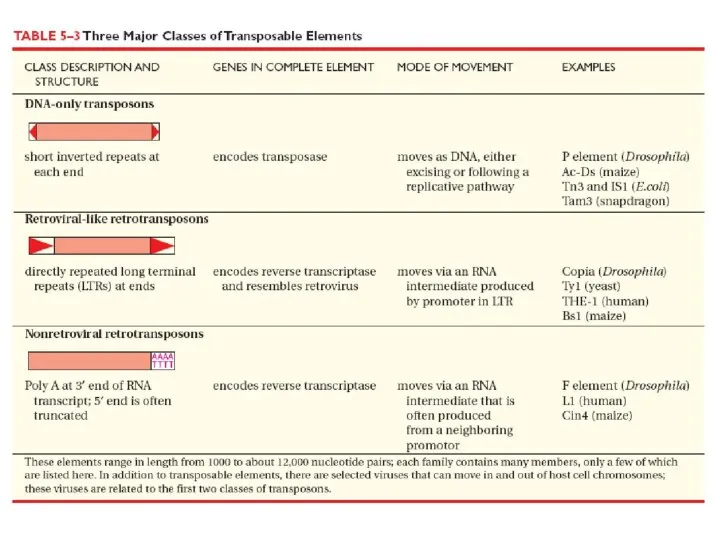
Слайд 4
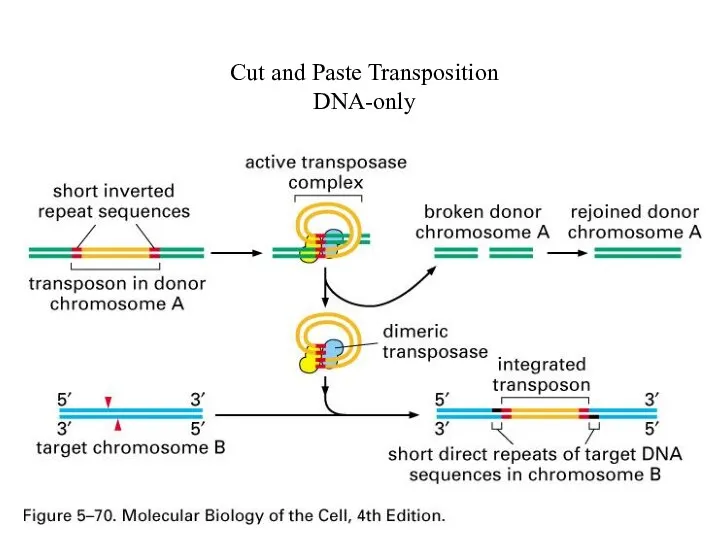
Cut and Paste Transposition
DNA-only
Слайд 5
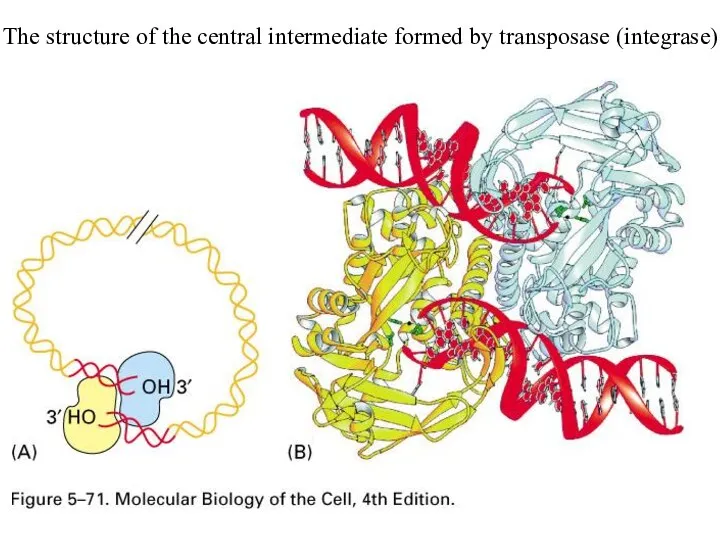
The structure of the central intermediate formed by transposase (integrase)
Слайд 6
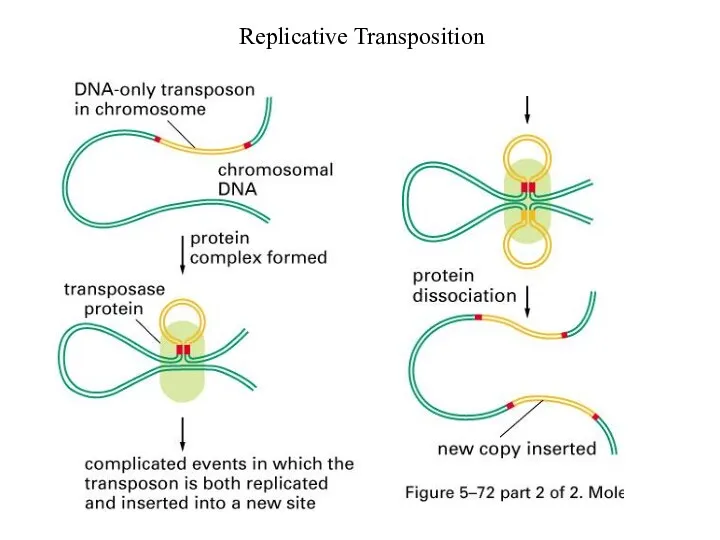
Replicative Transposition
Слайд 7
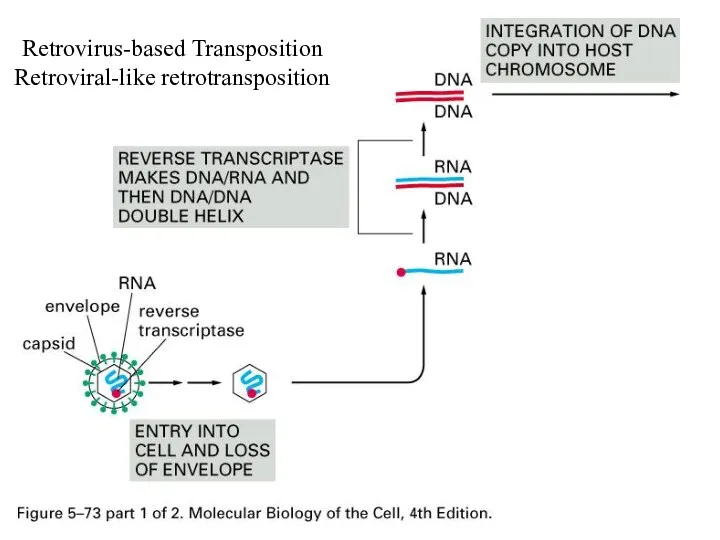
Retrovirus-based Transposition
Retroviral-like retrotransposition
Слайд 8
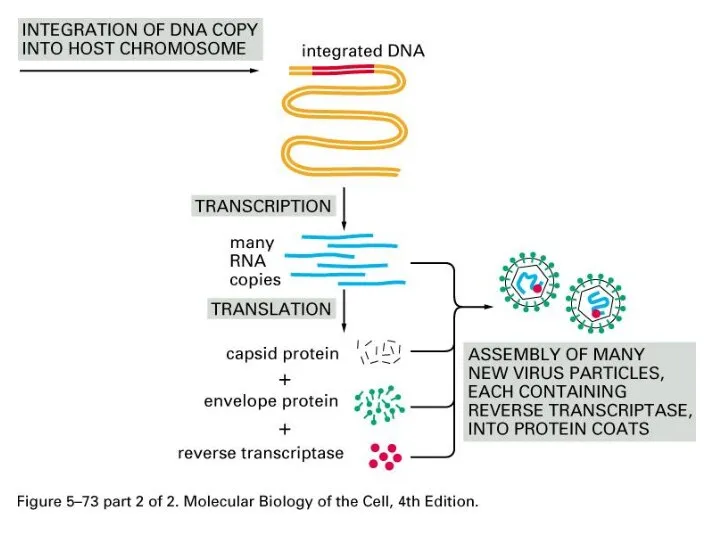
Слайд 9
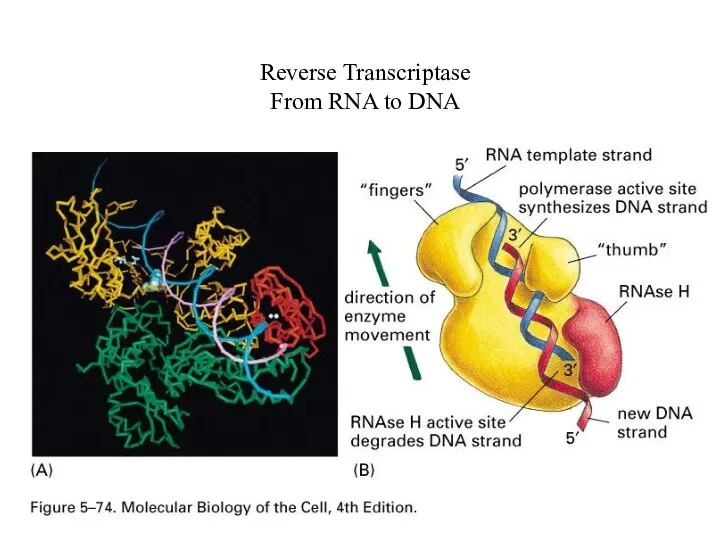
Reverse Transcriptase
From RNA to DNA
Слайд 10
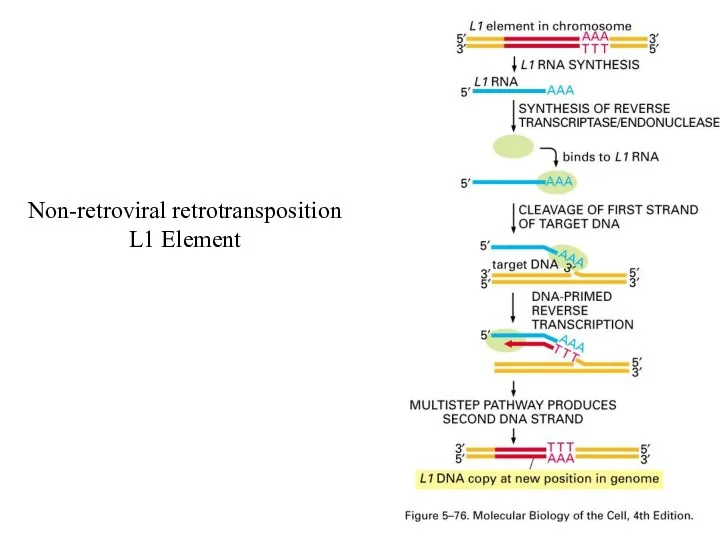
Non-retroviral retrotransposition
L1 Element
Слайд 11
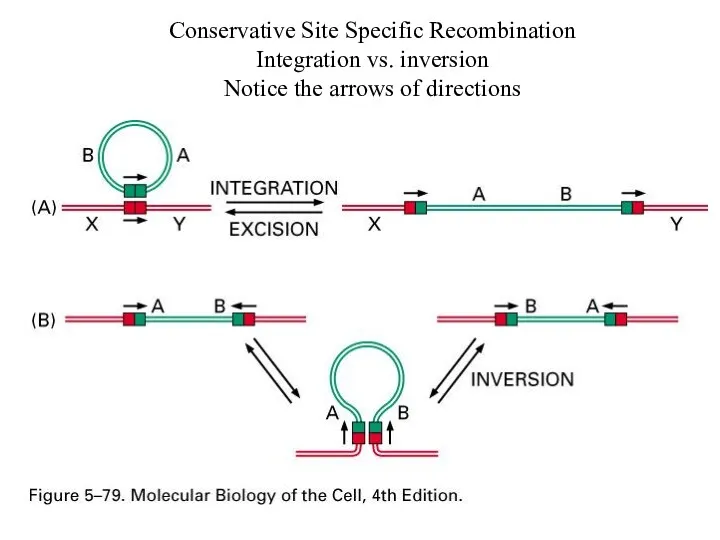
Conservative Site Specific Recombination
Integration vs. inversion
Notice the arrows of directions
Слайд 12
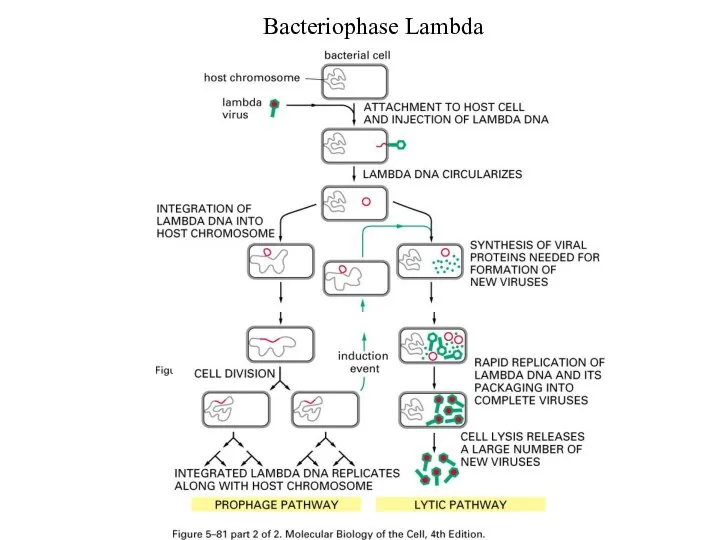
Слайд 13
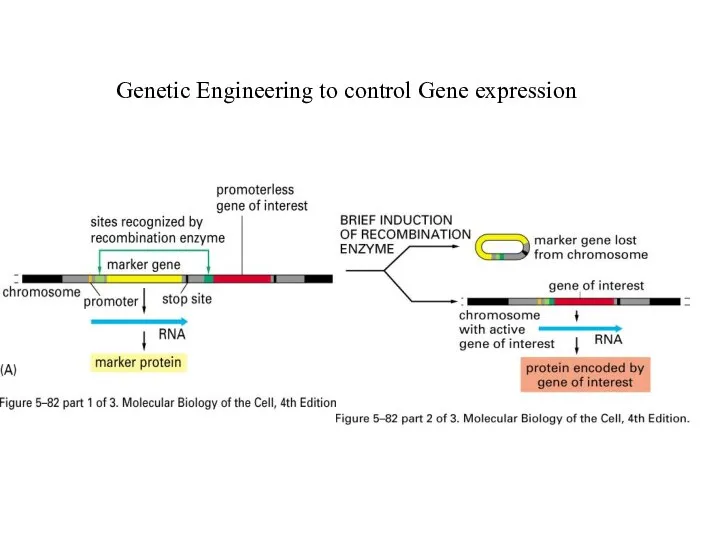
Genetic Engineering to control Gene expression
Слайд 14
Summary
DNA site-specific recombination
transpositional; conservative
Transposons: mobile genetic elements
Transpositional: DNA only transposons, retroviral-like
retrotransposons, nonretroviral retrotransposons
Слайд 15

Слайд 16
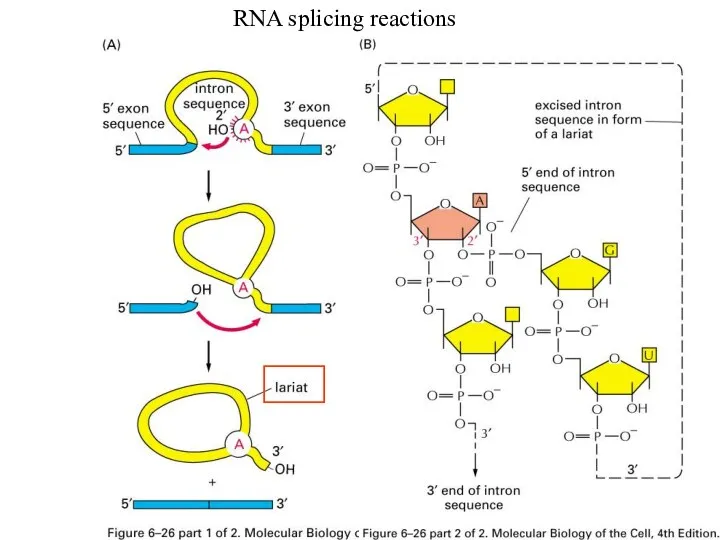
Слайд 17
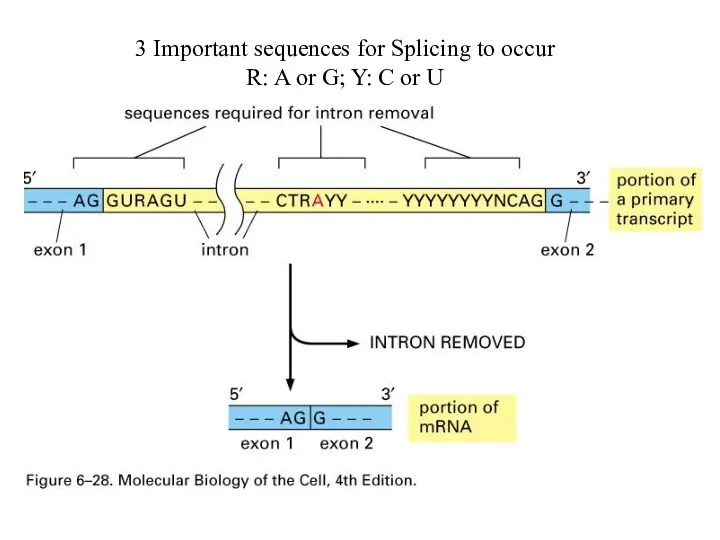
3 Important sequences for Splicing to occur
R: A or G; Y:
C or U
Слайд 18
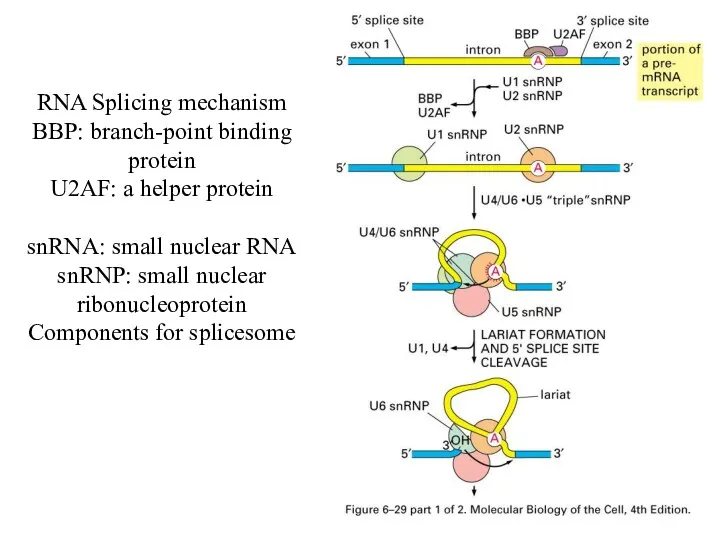
RNA Splicing mechanism
BBP: branch-point binding protein
U2AF: a helper protein
snRNA: small nuclear
RNA
snRNP: small nuclear ribonucleoprotein
Components for splicesome
Слайд 19
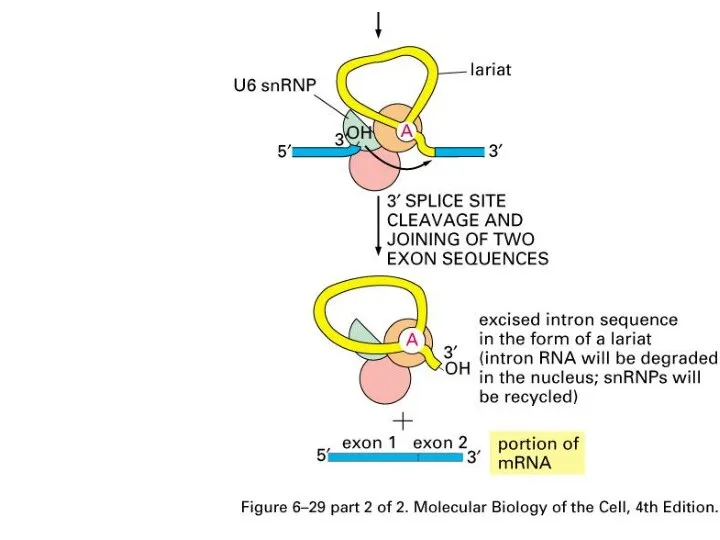
Слайд 20
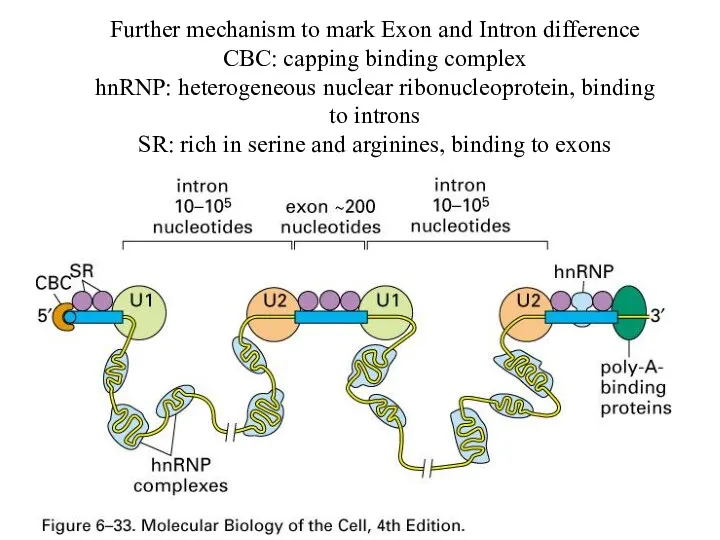
Further mechanism to mark Exon and Intron difference
CBC: capping binding complex
hnRNP:
heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein, binding to introns
SR: rich in serine and arginines, binding to exons
Слайд 21
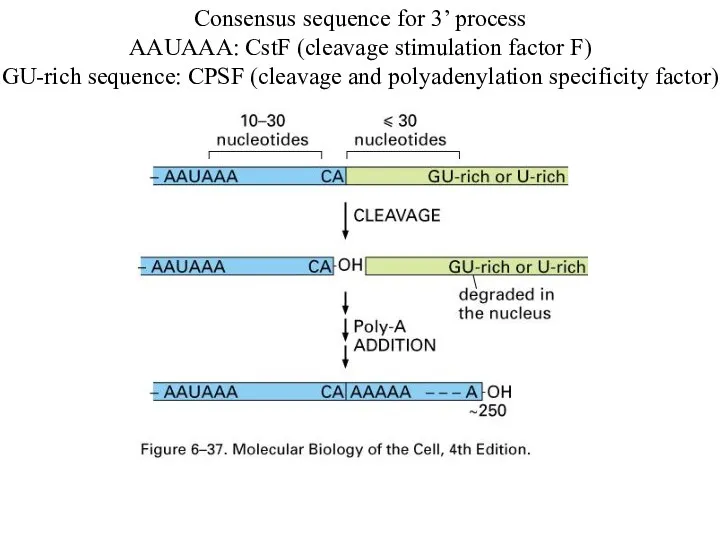
Consensus sequence for 3’ process
AAUAAA: CstF (cleavage stimulation factor F)
GU-rich sequence:
CPSF (cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor)
Слайд 22

Слайд 23
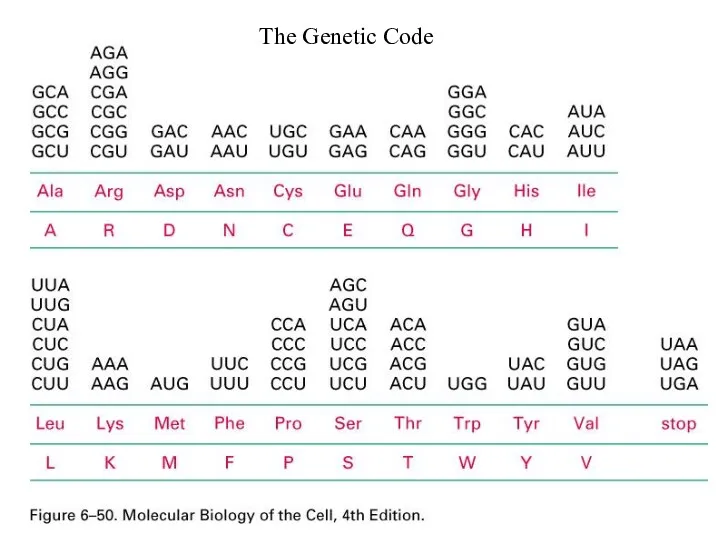
Слайд 24
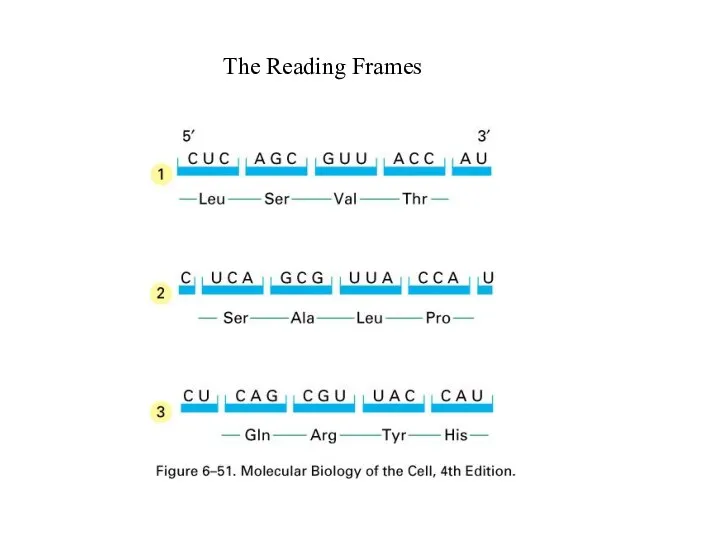
Слайд 25
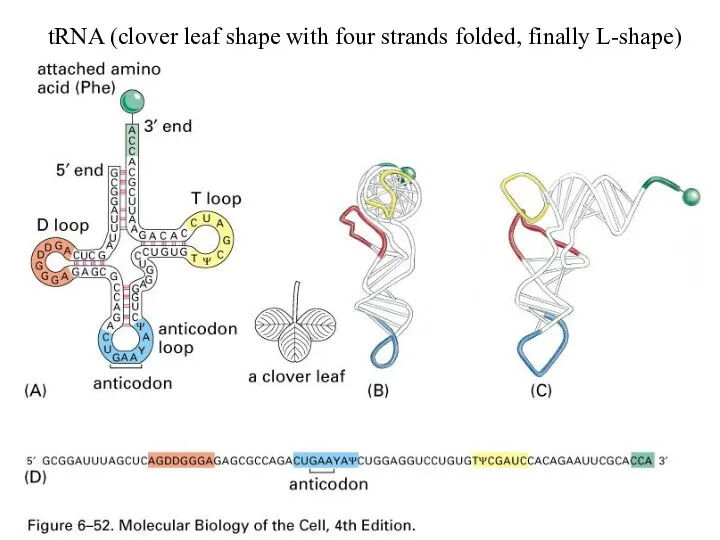
tRNA (clover leaf shape with four strands folded, finally L-shape)
























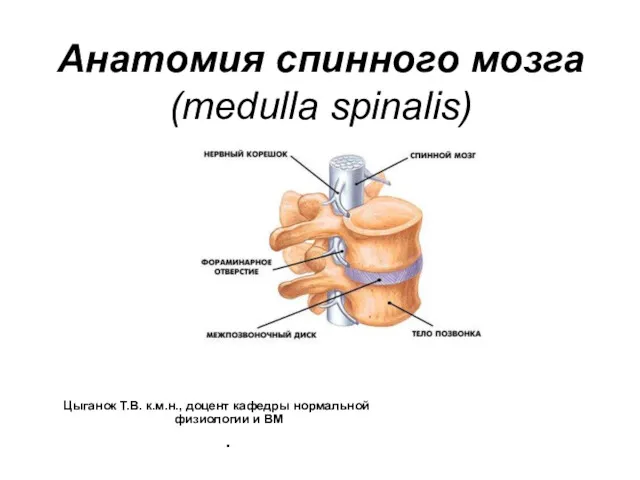 Анатомия спинного мозга (medulla spinalis)
Анатомия спинного мозга (medulla spinalis) Устройство увеличительных приборов. 5 класс
Устройство увеличительных приборов. 5 класс Видоизменение побегов. Клубень
Видоизменение побегов. Клубень Редко встречающиеся виды краснокнижных растений
Редко встречающиеся виды краснокнижных растений Зимующие птицы
Зимующие птицы Растительный мир Алтайского края
Растительный мир Алтайского края Муравьи: семейство формицидов
Муравьи: семейство формицидов Птицы Рязанской области. Знакомство с уникальными видами птиц
Птицы Рязанской области. Знакомство с уникальными видами птиц Почему нужно есть много овощей и фруктов
Почему нужно есть много овощей и фруктов Единый государственный экзамен по биологии. Содержательные блоки курса биология
Единый государственный экзамен по биологии. Содержательные блоки курса биология Нейрон. Рефлекс. Рефлекторна дуга. Будова нервової системи. Нервова тканина
Нейрон. Рефлекс. Рефлекторна дуга. Будова нервової системи. Нервова тканина Особливості годівлі хутрових звірів
Особливості годівлі хутрових звірів Генетика микроорганизмов
Генетика микроорганизмов История развития анатомии, физиологии и медицины
История развития анатомии, физиологии и медицины Презентация, Обобщающий урок по теме скелет.
Презентация, Обобщающий урок по теме скелет. Презентация к КВН Зеленые друзья 6 класс
Презентация к КВН Зеленые друзья 6 класс Культивирование клеток. Лекция 3
Культивирование клеток. Лекция 3 Wild and domestic animals
Wild and domestic animals Проверочная работа по теме Органоиды клетки.
Проверочная работа по теме Органоиды клетки. Отряды насекомых
Отряды насекомых Факторы, лимитирующие первичную продукцию в наземных и водных сообществах
Факторы, лимитирующие первичную продукцию в наземных и водных сообществах Самоочищение водоема
Самоочищение водоема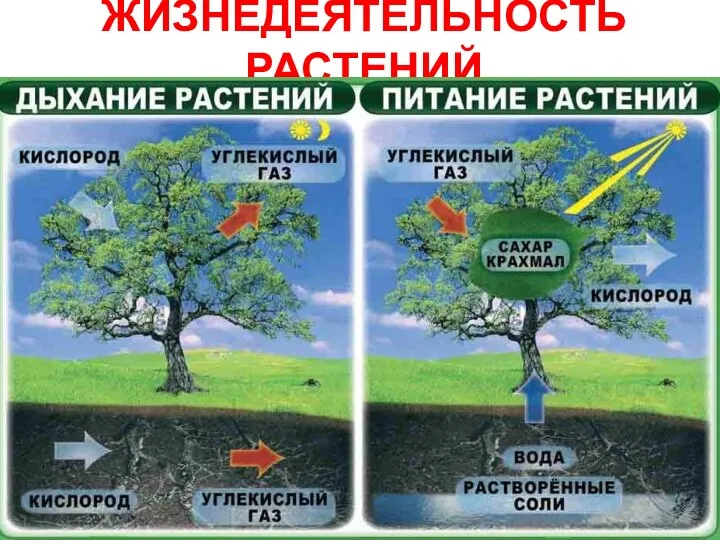 Жизнедеятельность растений
Жизнедеятельность растений Органи рослин
Органи рослин Ботаникалық сипаттамасы
Ботаникалық сипаттамасы Тип Хордовые. Подтип Бесчерепные. Подтип Черепные (Позвоночные)
Тип Хордовые. Подтип Бесчерепные. Подтип Черепные (Позвоночные) Первые современные люди - неоантропы
Первые современные люди - неоантропы Виявлення пристосувань до способу життя птахів. Практична робота 3
Виявлення пристосувань до способу життя птахів. Практична робота 3