Содержание
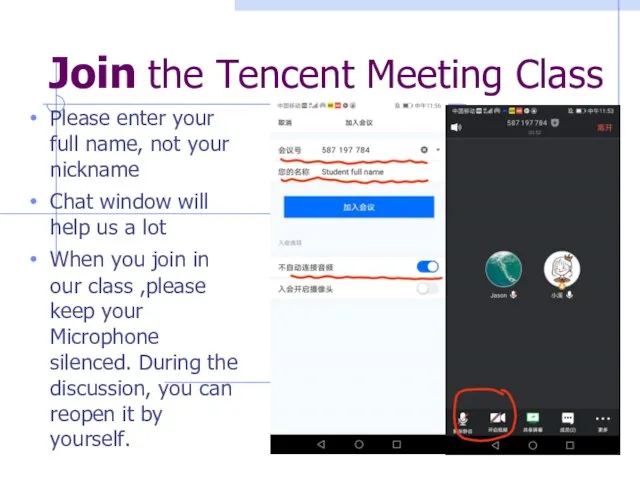
- 2. Join the Tencent Meeting Class Please enter your full name, not your nickname Chat window will
- 3. Materials of the Course Textbook: Horngren’s Accounting, Pearson, 10th Global edition Learning Objectives, Chapter Summary handout
- 4. Materials of the Course (cont’d) Textbook:Noble, L.Tracie; Mattison, L. Brenda & Matsumura Mae Ella, Horngren’s Accounting,
- 5. Materials of the Course (cont’d) Accounting
- 6. Study Guide Part 1: Introduction of accounting Accounting and Business Environment Financial Accounting vs. Managerial Accounting
- 7. Study Guide Part 2: Prepare Financial Statement Adjusting process Closing process The Accounting cycle Common Accounting
- 8. Unit Assessment Task In class practice 15% multiple choices, ‘try it’ Q, practices in class Mid-term
- 9. Tips for success in the course Experience of Learning Accounting Spend more time on the beginning
- 10. Chapter 1: Learning Objectives Introduction Importance of Accounting Governing Organizations and Guidelines Basic Accounting assumptions Accounting
- 11. Introduction of Accounting What Is Accounting? Accounting is an information process, which is related with collecting
- 12. Users of Accounting Information External Users Creditors Shareholders Tax Authorities Outside Investors External Auditors Customers Bankers
- 13. Multiple Choices 2mins Which of the following are external users of a business’s financial information? A.
- 14. True or False Questions 5mins Shareholders primarily use accounting information for decision-making purposes. Local, state, and
- 15. Importance of Accounting For individual Saving and Managing money Statement of Financial Performance (oversea student) Accounting
- 16. Importance of Accounting accounting positions for the careers External auditors, BIG 4 Accounting Firms Internal auditors,
- 17. BIG 4 Auditors - How Big ? leading firms: Account for ¾ auditing markets, Company’s Income
- 18. Importance of Accounting for Business Firms All the businesses and organizations need accountants. Financial Annual Reports—public
- 19. How to govern accounting? I. Governing Organizations SEC FASB in USA IASB in UK II. Guidelines
- 20. I. Governing Organizations Governing organizations are: Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
- 21. I. Governing Organizations Securities and Exchange Commission SEC is an U.S. governmental agency that oversees the
- 22. I. Governing Organizations FASB in USA the Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB) is a private organazation.
- 23. II. Guidelines for accounting information Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) It is the main US accounting
- 24. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) Issued by the FASB. Establishes the rules for recording transactions and
- 25. II. Guidelines for accounting information International Financial Report Standards (IFRS) A set of global accounting guidelines
- 26. Multiple Choice The guidelines for accounting information are called: Globally Accepted and Accurate Policies. Global Accommodation
- 27. III. Basic Accounting Assumption and Principle 1. Economic Entity Assumption 2. Goning Concern Assumption 3. Monetary
- 28. 1. Economic Entity Assumption Proprietorship (sole trader) means one person or a family owns the firm
- 30. 2. Going Concern Assumption Financial statements are prepared under the assumption that the entity will continue
- 31. 3. Monetary Unit Assumptiom The assumption that requires the items on the financial statements to be
- 32. 4. The Cost Principle assets should be recorded at their actual cost (historical cost) on the
- 33. Accounting Assumptions Accounting Economic Entity Assumption Cost Principle Going Concern Assumption Monetary Unit Assumption
- 34. Multiple Choices 2mins The formation of a partnership firm requires a minimum of: A) four partners.
- 35. Multiple Choices 2mins According to which of the following accounting concepts should the acquired assets be
- 36. TRY IT!
- 37. Accounting Fields Financial Accounting Managerial Accounting Auditing Public Sector Accounting – governments Accounting
- 38. Accounting Fields Managerial Accounting Financial Accounting Public Sector Accounting Auditing
- 39. Two basic branches of accounting Management accounting(MA) special requirement for the purposes to make better decisions
- 40. Comparison of FA and MA
- 41. Comparison of FA and MA
- 42. Users of Financial Information 1- ©2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 43. Multiple Choices 2mins Managerial accounting information is used by: taxing authorities. auditors. lenders. internal decision makers.
- 44. Relationship between MA and FA Both of them are parts of the accounting information system. Management
- 46. Скачать презентацию










































 Автобусный тур по окрестностям Франкфурта-на-майне (Германия)
Автобусный тур по окрестностям Франкфурта-на-майне (Германия) Популярные бизнес-модели
Популярные бизнес-модели Первый отель-комьюнити в Нижнем Новгороде
Первый отель-комьюнити в Нижнем Новгороде Коммерческое предложение по поставке систем альтернативной энергетики для электротранспорта. Группа компаний Экомоторс
Коммерческое предложение по поставке систем альтернативной энергетики для электротранспорта. Группа компаний Экомоторс Экономический потенциал малого и среднего бизнеса
Экономический потенциал малого и среднего бизнеса Модели рынка. Конкуренция и типы рыночных структур
Модели рынка. Конкуренция и типы рыночных структур Деятельность индивидуальных предпринимателей в Беларуси
Деятельность индивидуальных предпринимателей в Беларуси Шаблон заявки проекта в Visa’s Everywhere Initiative
Шаблон заявки проекта в Visa’s Everywhere Initiative Бизнес-план. Таксопарк
Бизнес-план. Таксопарк Основные этапы бизнес -планирования предприятия
Основные этапы бизнес -планирования предприятия Бизнес в школе (бизнес план)
Бизнес в школе (бизнес план) ЖК Спортивная деревня. Недвижимость
ЖК Спортивная деревня. Недвижимость Инновационная экономика и технологическое предпринимательство
Инновационная экономика и технологическое предпринимательство Проект открытия фитнес-клуба Verso
Проект открытия фитнес-клуба Verso Виды и формы бизнеса
Виды и формы бизнеса Комплексная юридическая поддержка бизнеса на расстоянии звонка
Комплексная юридическая поддержка бизнеса на расстоянии звонка Бизнес-жоспар Пластикалық терезелерді өндіру жөніндегі цехты құру
Бизнес-жоспар Пластикалық терезелерді өндіру жөніндегі цехты құру Шаблон презентации
Шаблон презентации Поддержка молодежного инновационного предпринимательства
Поддержка молодежного инновационного предпринимательства Кирово-Чепецкий район. Анализ рынка недвижимости
Кирово-Чепецкий район. Анализ рынка недвижимости Развитие туризма в России
Развитие туризма в России Пошаговое построение высокоприбыльного отдела продаж в агентстве недвижимости
Пошаговое построение высокоприбыльного отдела продаж в агентстве недвижимости Курсовой проект. Ресторан на 200 посадочных мест
Курсовой проект. Ресторан на 200 посадочных мест Tez Tour по Белоруси. Описание концепции
Tez Tour по Белоруси. Описание концепции Предлагаем идеи для бизнеса
Предлагаем идеи для бизнеса Бизнес-жоспар кофехана “Французский круассан”
Бизнес-жоспар кофехана “Французский круассан” Типологическая характеристика и оборудование гостиниц
Типологическая характеристика и оборудование гостиниц Предпринимательская деятельность
Предпринимательская деятельность