Содержание
- 2. Recap PLC Idea generation – bring it to the market
- 3. This week Innovation Ansoff BCG Test Exam 1: Questions 2, 3
- 4. Innovation - ‘New’ product or an improvement. - To be really innovative: fulfil a new function
- 5. New product (service) development (NDP) NPD is a process which is designed to develop, test and
- 6. Types of new products/services New products to the world – innovative products New product lines –
- 7. Types of new products/services * New products to the world – innovative products e.g. ‘apps 1.0’
- 8. Why develop new products/services? To create stars and cash cows for the future To replace declining
- 9. Half of the turnover comes from products which did not exist ten years ago. Return on
- 10. To defeat rivals, maintain/increase market share, keep up with rivals, maintain sustainable competitive advantage - Respond
- 11. New product/service can be used to … Increase/defend market share (by offering more choice or updating
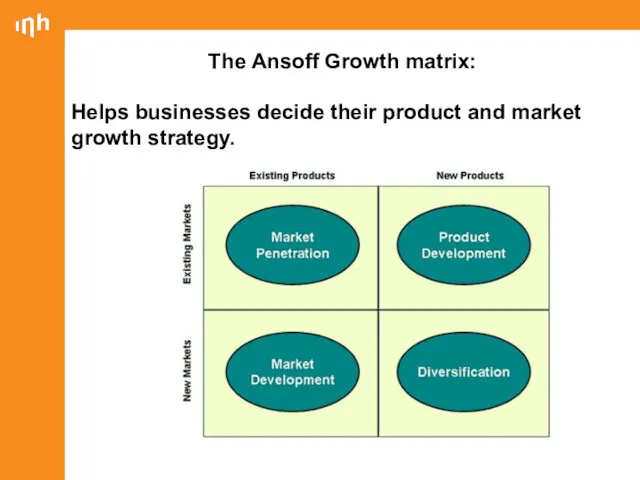
- 12. The Ansoff Growth matrix: Helps businesses decide their product and market growth strategy.
- 13. New product/service planning The firm assesses … Its current product/service portfolio Opportunities and Threats The firm
- 14. Classification of innovations Based on how much effort it takes the customer to accept the product:
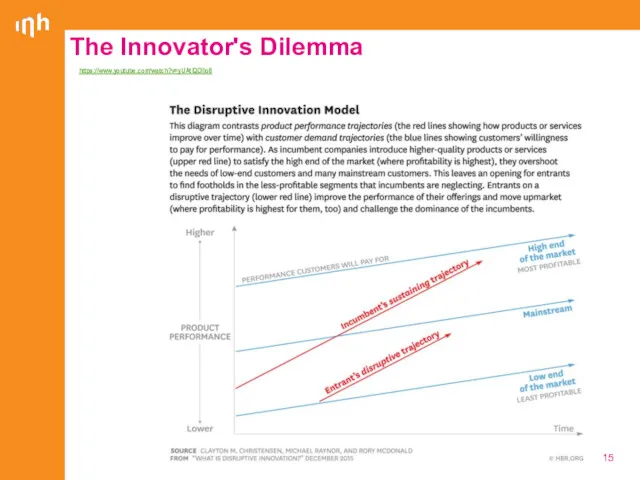
- 15. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yUAtIQDllo8 The Innovator's Dilemma
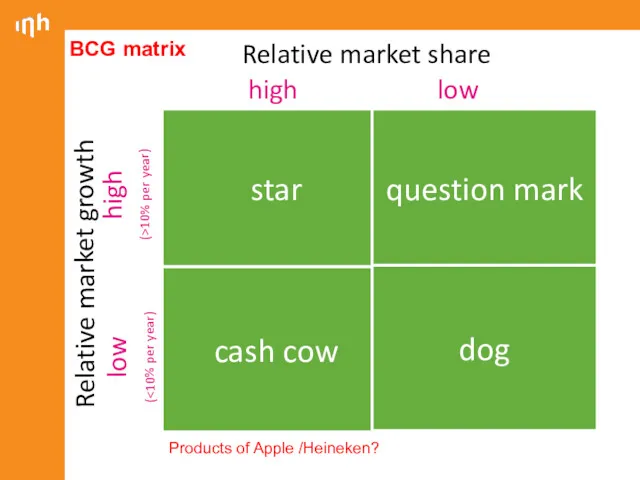
- 16. Boston Consulting Group matrix The business portfolio is the collection of businesses and products that make
- 17. star question mark cash cow dog high low Relative market growth high (>10% per year) low
- 18. BCG matrix Heineken Continents
- 19. Product development process Better results through good planning.
- 20. Strategy development What objective? Perform a SWOT because the external environment affects the innovation. - Proactive
- 21. Make or buy Companies are acquired, merge or go into partnership. Set up own Research &
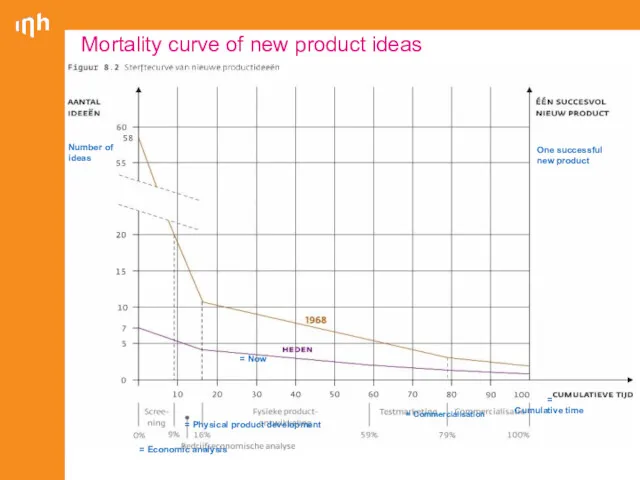
- 22. Mortality curve of new product ideas = Number of ideas = One successful new product =
- 23. Organising product development Venture team: employees from different departments work (temporarily) together on the new product.
- 24. Reasons for success A product responds to needs; sounds logical and is logical, but is often
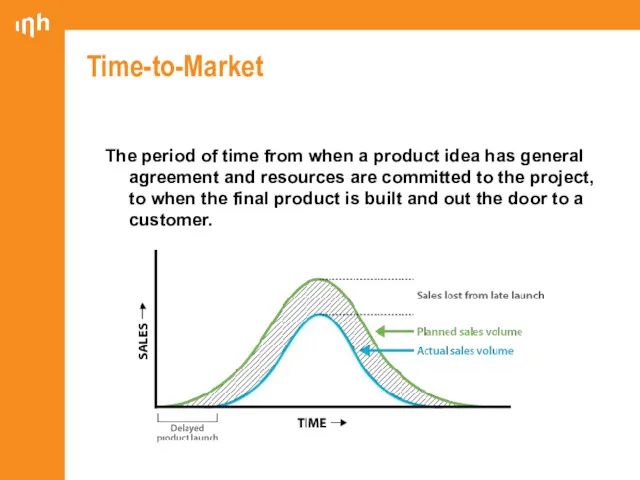
- 25. Time-to-Market The period of time from when a product idea has general agreement and resources are
- 26. Why improve time-to-market? Efficient resource management — Having a reliable timeline will allow you to prepare
- 27. Next week Adoption Proces – Lavige Steiner Adopter categorisation Ratio’s Test exam 1, questions 1, 4,
- 28. QUESTION 2 (25 points) These questions require application of the Abell model to the online fashion
- 29. Answer 2a: Any segments - i.e. groups of (potential) customers within the online fashion market -
- 30. ANSWER 2b: Any need underlying the online fashion market. Segments, individual customers or products are unacceptable
- 31. ANSWER 2c: Any technology underlying the online fashion market. Segments, individual customers or needs are unacceptable
- 32. ANSWER 2d: Business definition: the combination of all Segments-Needs-Technologies which identifies the market in the context
- 33. QUESTION 3 (15 points) Name three different reasons why understanding the Product Life Cycle is useful
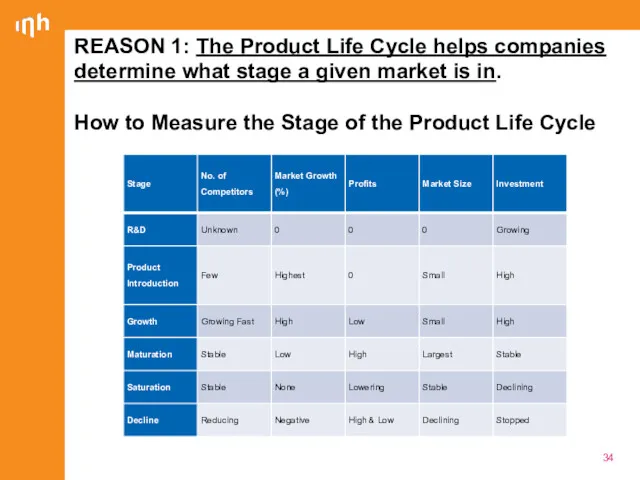
- 34. REASON 1: The Product Life Cycle helps companies determine what stage a given market is in.
- 35. REASON 2: The product life cycle can be used to determine likely competitive trends. Typical levels
- 36. REASON 3: The product life cycle can be used to establish which different marketing strategy will
- 38. Скачать презентацию





























 Автобусный тур по окрестностям Франкфурта-на-майне (Германия)
Автобусный тур по окрестностям Франкфурта-на-майне (Германия) Популярные бизнес-модели
Популярные бизнес-модели Первый отель-комьюнити в Нижнем Новгороде
Первый отель-комьюнити в Нижнем Новгороде Коммерческое предложение по поставке систем альтернативной энергетики для электротранспорта. Группа компаний Экомоторс
Коммерческое предложение по поставке систем альтернативной энергетики для электротранспорта. Группа компаний Экомоторс Экономический потенциал малого и среднего бизнеса
Экономический потенциал малого и среднего бизнеса Модели рынка. Конкуренция и типы рыночных структур
Модели рынка. Конкуренция и типы рыночных структур Деятельность индивидуальных предпринимателей в Беларуси
Деятельность индивидуальных предпринимателей в Беларуси Шаблон заявки проекта в Visa’s Everywhere Initiative
Шаблон заявки проекта в Visa’s Everywhere Initiative Бизнес-план. Таксопарк
Бизнес-план. Таксопарк Основные этапы бизнес -планирования предприятия
Основные этапы бизнес -планирования предприятия Бизнес в школе (бизнес план)
Бизнес в школе (бизнес план) ЖК Спортивная деревня. Недвижимость
ЖК Спортивная деревня. Недвижимость Инновационная экономика и технологическое предпринимательство
Инновационная экономика и технологическое предпринимательство Проект открытия фитнес-клуба Verso
Проект открытия фитнес-клуба Verso Виды и формы бизнеса
Виды и формы бизнеса Комплексная юридическая поддержка бизнеса на расстоянии звонка
Комплексная юридическая поддержка бизнеса на расстоянии звонка Бизнес-жоспар Пластикалық терезелерді өндіру жөніндегі цехты құру
Бизнес-жоспар Пластикалық терезелерді өндіру жөніндегі цехты құру Шаблон презентации
Шаблон презентации Поддержка молодежного инновационного предпринимательства
Поддержка молодежного инновационного предпринимательства Кирово-Чепецкий район. Анализ рынка недвижимости
Кирово-Чепецкий район. Анализ рынка недвижимости Развитие туризма в России
Развитие туризма в России Пошаговое построение высокоприбыльного отдела продаж в агентстве недвижимости
Пошаговое построение высокоприбыльного отдела продаж в агентстве недвижимости Курсовой проект. Ресторан на 200 посадочных мест
Курсовой проект. Ресторан на 200 посадочных мест Tez Tour по Белоруси. Описание концепции
Tez Tour по Белоруси. Описание концепции Предлагаем идеи для бизнеса
Предлагаем идеи для бизнеса Бизнес-жоспар кофехана “Французский круассан”
Бизнес-жоспар кофехана “Французский круассан” Типологическая характеристика и оборудование гостиниц
Типологическая характеристика и оборудование гостиниц Предпринимательская деятельность
Предпринимательская деятельность