Слайд 2

Lecture’s topics
What is organisation structure?
What are the basic elements of organisation
structure?
What are the basic types of organisation structure?
Слайд 3

Organisation Structure
Organisation structure describes the way work is
divided, supervised and
coordinated.
Слайд 4

Organisation Charts
Organisation structure is often represented by an
organisation chart –
i.e. a chart showing the main
departments and work positions in the organisation
and the reporting relations between them.
Слайд 5
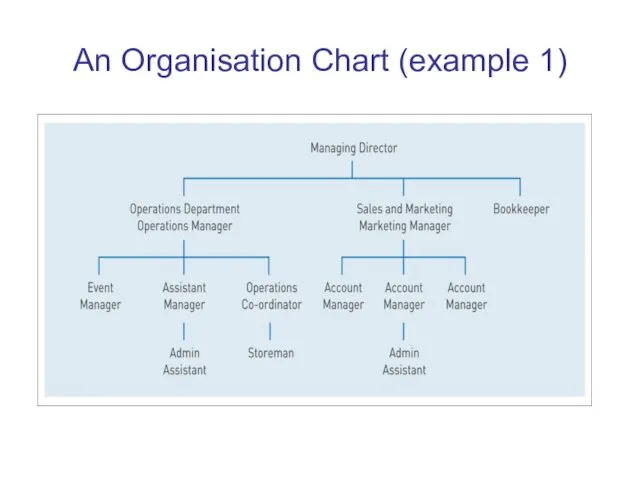
An Organisation Chart (example 1)
Слайд 6
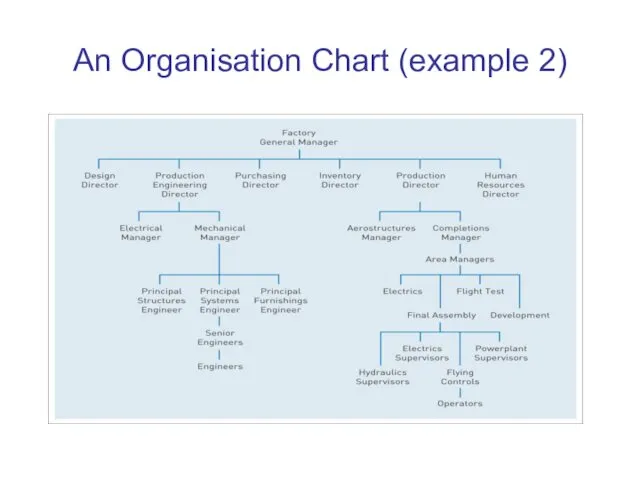
An Organisation Chart (example 2)
Слайд 7

Types of structure
Formal structure:
The official structure of the organisation.
The official guidelines,
documents or procedures setting out how the organisation’s activities are divided, supervised and coordinated.
Слайд 8

Types of structure
Informal structure:
The unofficial, but often critical, working relationships between
organisational members.
If this could be drawn, it would show who talks to and interacts regularly with whom regardless of their formal titles and relationships.
Слайд 9

The Basic Elements of Structure
1. Work specialisation
2. Chain of command
3. Span
of control
4. Centralisation vs Decentralisation
5. Departmentalisation
Слайд 10

Work Specialisation
a job is broken down into a number of steps
and each step is completed by a separate individual
different employees have different skills
need to make efficient use of the diversity of skills that employees have
Слайд 11

Negative results of work specialisation
Слайд 12

Chain of Command
The continuous chain of authority that extends
from the
highest levels in an organisation to the
lowest levels and clarifies who reports to whom.
Слайд 13

Chain of Command
Early management writers believed that each
employee should report
to only one manager –
a term called unity of command.
Слайд 14

Chain of Command
Some concepts closely related to chain of command:
Authority
Responsibility
Accountability
Delegation
Слайд 15

Authority
The right that a person in a specified role has to
make
decisions, allocate resources or give instructions.
If managers attempt to give instructions beyond their
area of formal authority, they are likely to meet
resistance.
Слайд 16

Responsibility
An employee’s duty to perform assigned activities
and to meet the
expectations associated with a
task.
Слайд 17

Accountability
Employees with formal authority over an area are
required to report
on their work to those above
them in the chain of command.
Слайд 18

Delegation
Managers giving people who are below them in
the chain of
command the authority to undertake
specific activities or decisions.
Слайд 19
Authority vs Power
Authority
Power
Слайд 20

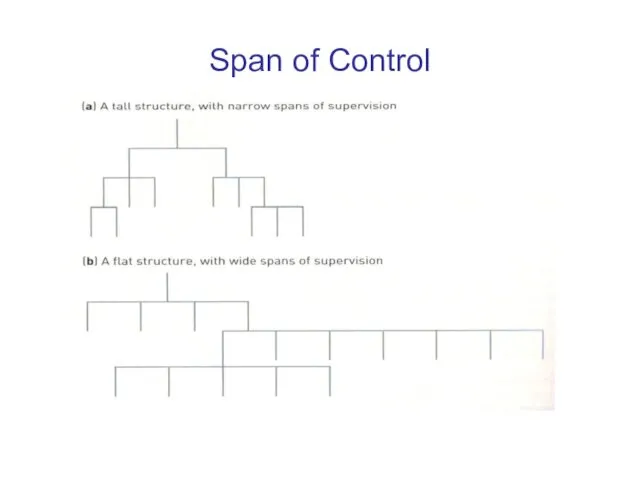
Span of Control
The number of persons (subordinates) directly
reporting to a
manager.
The right number must be found in order for these people to be managed effectively and efficiently.
Слайд 21

Span of Control
The level of direct supervision an employee needs
decreases
with the level of experience they have and
training they receive.
Слайд 22
Слайд 23

Centralisation vs Decentralisation
Centralised organisations: decisions are made
by a few people
at the centre of the organisation.
Decentralised organisations: decisions are pushed
down to the level closest to where the problem is.
Слайд 24

Departmentalisation
refers to how the various activities of the organisation are grouped
together into units
a manager is in charge of each unit
Слайд 25
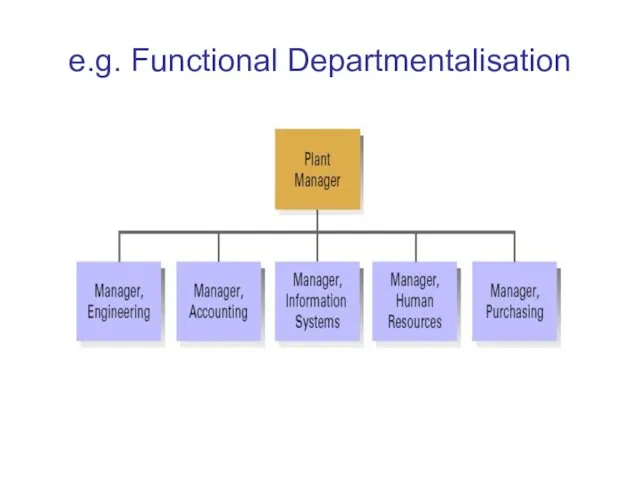
e.g. Functional Departmentalisation
Слайд 26
Types of Structure
Mechanistic structure
Organic structure
(Burns & Stalker, 1961)
Слайд 27

Mechanistic Structure
High in specialisation.
High in centralisation.
High in formalisation (i.e. the practice
of using written documents to direct and control employees).
Communication is vertical.
Слайд 28

Organic Structure
Knowledge is widely spread.
There are few prescriptive job descriptions and
rules and regulations are kept to a minimum.
Cross-functional team work is encouraged.
Communication is horizontal.
Слайд 29
Types of structure
One of the these two types of structure is
frequently
called a ‘bureaucracy’. Which one is it?
Слайд 30
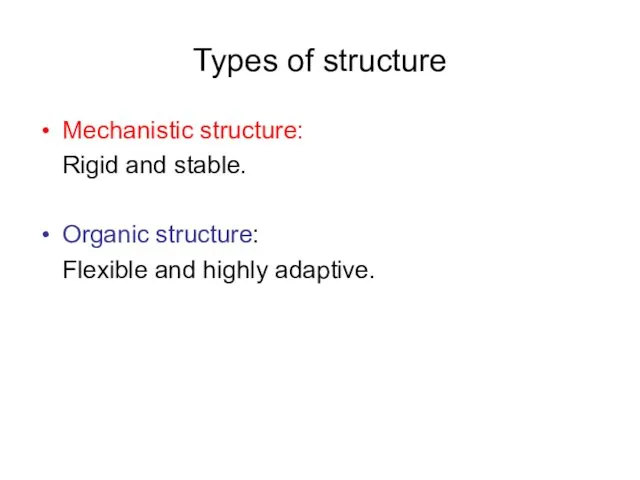
Types of structure
Mechanistic structure:
Rigid and stable.
Organic structure:
Flexible and highly adaptive.
Слайд 31
Types of structure
Mechanistic structure:
Best at simple and repetitive tasks.
Organic structure:
More effective
at complex and unique tasks.
Слайд 32
Types of structure
Mechanistic structures are most effective in stable
environments.
Organic structures
are most effective in dynamic
and uncertain environments.
Слайд 33
Types of structure
Organisations could use a combination of the
two types.
e.g.
finance department – mechanistic
advertising department – organic
































 Поняття, сутність та задачі бізнес-плану
Поняття, сутність та задачі бізнес-плану Ethno Shop
Ethno Shop Бизнес жоспар. Бурабай қонақ үйі
Бизнес жоспар. Бурабай қонақ үйі Бизнес-жоспар: Сібе бестігі туристік корпорациясын құру
Бизнес-жоспар: Сібе бестігі туристік корпорациясын құру Презентация бизнес-плана реализации инвестиционного проекта строительства агропромышленного комплекса площадью 180 га
Презентация бизнес-плана реализации инвестиционного проекта строительства агропромышленного комплекса площадью 180 га Бизнес Орифлэйм
Бизнес Орифлэйм Бизнес – проект Diva
Бизнес – проект Diva Қор биржасының пайда болу тарихы
Қор биржасының пайда болу тарихы Бізнес-план ЗАТ Софія
Бізнес-план ЗАТ Софія Фонд по содействию кредитованию субъектов малого и среднего предпринимательства Республики
Фонд по содействию кредитованию субъектов малого и среднего предпринимательства Республики Мобильная сухая автомойка
Мобильная сухая автомойка Школа практических знаний. Бизнес-план
Школа практических знаний. Бизнес-план Соціальне підприємництво
Соціальне підприємництво Бізнес-план. Відкриття магазина одягу Des KIRIF
Бізнес-план. Відкриття магазина одягу Des KIRIF Маркетинг-план - 2020. Легкий старт успешного бизнеса
Маркетинг-план - 2020. Легкий старт успешного бизнеса Сущность предпринимательства и его основы
Сущность предпринимательства и его основы Знакомство с командой (запуски)
Знакомство с командой (запуски) Бизнес-план производства мягкой мебели. Фирма VISTA
Бизнес-план производства мягкой мебели. Фирма VISTA Предпринимательство
Предпринимательство Наша визитная карточка. Интерфакс
Наша визитная карточка. Интерфакс L’Oreal Paris history: worldwide success
L’Oreal Paris history: worldwide success Программа Ты - предприниматель
Программа Ты - предприниматель Бизнес-план мебельной фирмы Вторая жизнь
Бизнес-план мебельной фирмы Вторая жизнь Копирайтинг 3.0. День 4
Копирайтинг 3.0. День 4 Бизнес и предпринимательство. Формы организации бизнеса
Бизнес и предпринимательство. Формы организации бизнеса Бизнес-план компании ООО Ареал: Агротехническая промышленность в Ялуторовском районе
Бизнес-план компании ООО Ареал: Агротехническая промышленность в Ялуторовском районе Қазақстандағы шағын және орта бизнеске талдау
Қазақстандағы шағын және орта бизнеске талдау Бизнес-план Компьютерный клуб
Бизнес-план Компьютерный клуб