Слайд 2

The Stages of IR
The First Industrial Revolution (1770-s -1850/70-s )
- on
steam, water, iron and shift from agriculture;
The Second Industrial Revolution (1870-s to 1914)
- new technologies of electricity, development of petrol engine, oil, and greater use of cheap steel.
Слайд 3

The reasons for IR
Growth in global trade;
Agricultural revolution;
new techniques (crop rotation,
selective breeding, etc.);
new crops (corn and potatoes);
Enclosure Movement in Britain;
Слайд 4

Agricultural Inventions
Jethro Tull's Seed drill
Bakewell’s quick-fattening sheep for mutton
Слайд 5

The reasons for IR
Increased speed of transportation;
Слайд 6

The reasons for IR
Application of steam engines.
Слайд 7

Why in Britain?
Increased Food Production;
Population Growth;
Financial Innovations:
central banks, stock markets,
joint stock companies
The Enlightenment and the Scientific Revolution
Слайд 8

Why in Britain?
Coal and Iron deposits;
Navigable Rivers and Canals;
Government Policies;
World Trade
The Cottage Industry
Слайд 9

Social Changes
New family and class structures emerged;
New classes: the working
class and the middle class (bourgeoisie)
Population migration from rural areas to urban areas.
Слайд 10

Working Class
Introduced mechanisms of labour supervision;
schools set up in collaboration
with the church to inculcate values;
the specialization of work;
Слайд 11

The Middle Class
- entrepreneurs and professional-lawyers, notaries, physicians and teachers.
Wealthy
bourgeoisie – the bankers, factory & mine owners and merchants;
Less rich professionals-lawyers, shopkeepers etc.
Слайд 12

The Family
The 18th century family (pre-industrial):
(a) kin members like widows, siblings,
step children
(b) non-kin members like servants, tutors etc.
All family members engaged in domestic production (family economy).
In the 19th century - ‘family wage economy’
only kin members living under one roof;
the private sphere - handled by wives/mothers;
the public sphere of work, commerce and politics -men.
Слайд 13

The Working Class Family
women contributed wages to the family fund, managed
the house, bore and cared for children;
married women were not working - the concept of a ‘male bread winner’ emerged;
children and specially daughters were an important economic recourse
Слайд 14

The Middle Class Family
Children and wives usually didn't work;
The mother’s role
as chief organizer of the house was valued;
private bedrooms became distanced from common spaces like the kitchen and parlour;
family activities (playing the piano after dinner) and family holidays developed.
Слайд 15
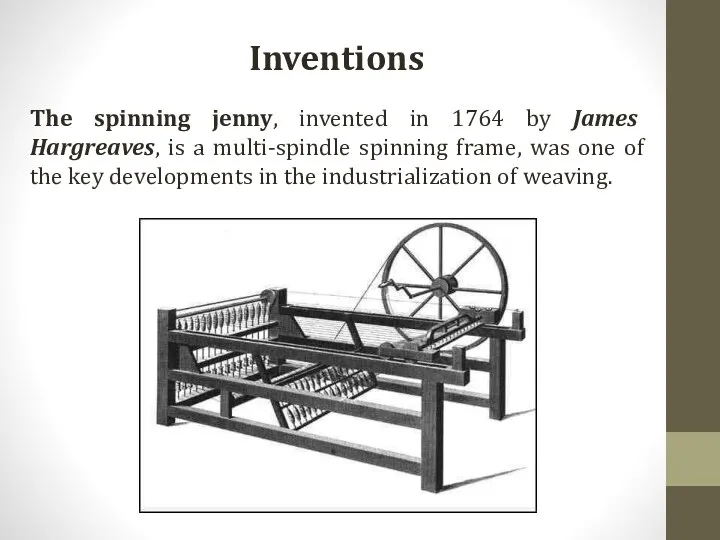
Inventions
The spinning jenny, invented in 1764 by James Hargreaves, is a
multi-spindle spinning frame, was one of the key developments in the industrialization of weaving.
Слайд 16
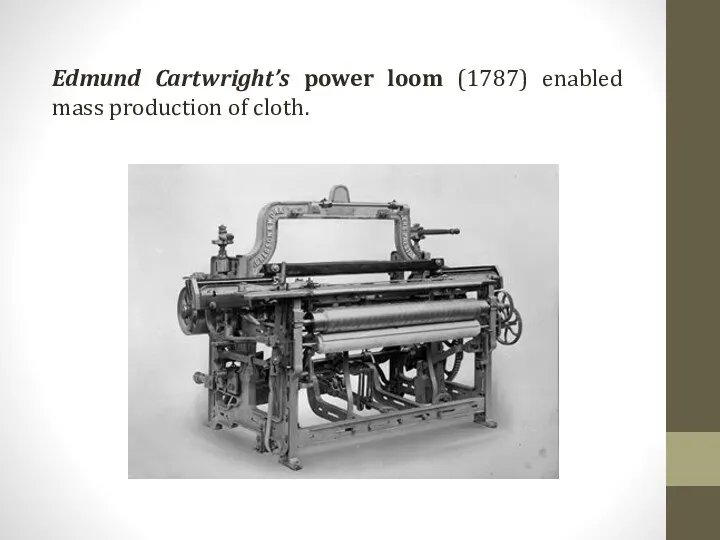
Edmund Cartwright’s power loom (1787) enabled mass production of cloth.
Слайд 17
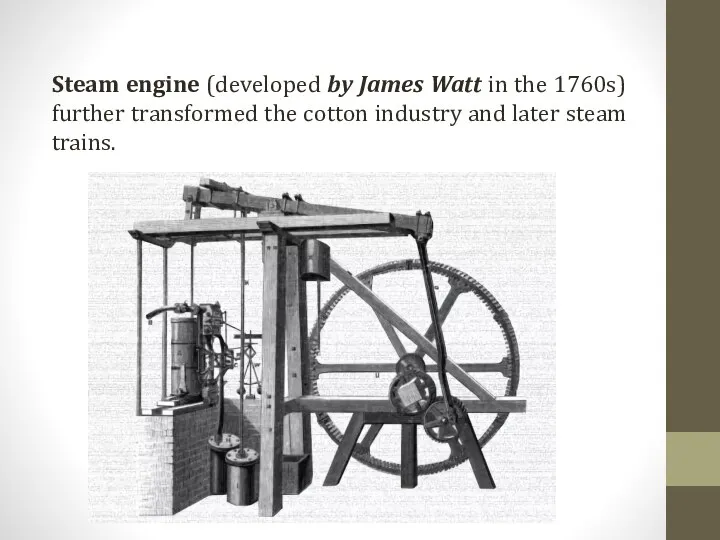
Steam engine (developed by James Watt in the 1760s) further transformed
the cotton industry and later steam trains.
Слайд 18

Smelting iron, pig iron. A new method of producing iron, developed
by Abraham Darby (1678-1717).
Слайд 19
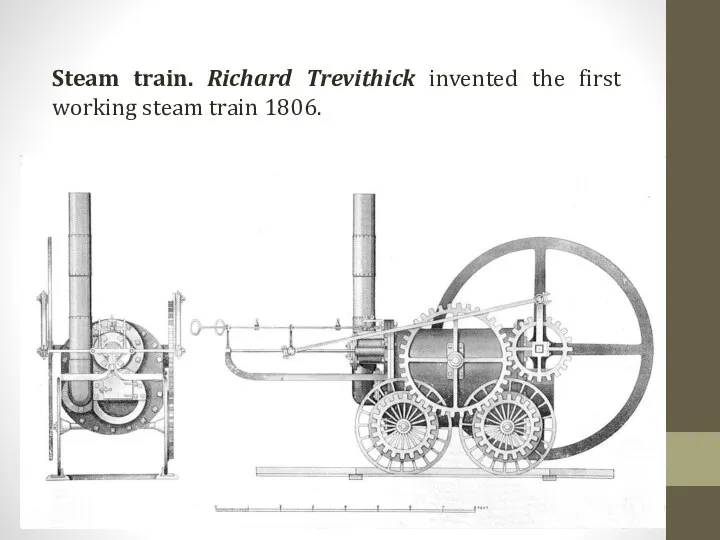
Steam train. Richard Trevithick invented the first working steam train 1806.
Слайд 20

Other countries
Belgium
The IR was brought by William and John Cockerill by
developing machine shops at Liège;
centred in iron, coal, and textiles.
Switzerland
the lack of raw materials was compensated specialising in niche products (silk weaving, cotton processing and engineering, clock-making)
Слайд 21

France
The second industrial power (by the mid 19th);
concentrated on finished
products (luxury goods like woven silk, china and leather goods).
Germany
was outproducing Britain in steel;
the world leader in the chemical industries;
Japan
The inauguration of a new Western-based education system;
Government initiative dominated manufacturing;
Private enterprise was involved in the economy, especially in textiles.
Слайд 22

In the USA occurred the Second Industrial Revolution. (mid-18th).
After the Civil
War;
built on the advancements made in Britain;
the build out of railroads;
large-scale iron and steel production;
widespread use of machinery in manufacturing;
use of the telegraph;
use of petroleum.
Слайд 23

Problems of the IR
Great pollution
The West Midlands became known as the
‘Black Country’.
Слайд 24

Lower worker class lifespan;
Child labour;
poor sanitation;
The slave trade
Слайд 25

Benefits of the IR
Higher real wages;
Life expectancy rose;
First government regulations;
Education and
health care;
Movement of people;
Wealth led to philanthropy.
Слайд 26
![Bibliographical References Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / New Word Encyclopedia.](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/338160/slide-25.jpg)
Bibliographical References
Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / New Word Encyclopedia. – Режим
доступа: http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Industrial_Revolution#History_of_the_name, свободный.
Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] /www.referatele.com. – Режим доступа: http://www.referatele.com/referate/engleza/online21/Industrial-Revolution---Reasons-why-the-Industrial-Revolution-began-Agrarian-Revolution-Social-condi.php, свободный.
Facts about the Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / Biography Online. – Режим доступа: https://www.biographyonline.net/facts-about-the-industrial-revolution/, свободный.
Слайд 27
![The Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / myglobal2009.wikispaces.com. – Режим доступа:](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/338160/slide-26.jpg)
The Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / myglobal2009.wikispaces.com. – Режим доступа: https://docviewer.yandex.ru/view/156256976/?*,
свободный.
The Industrial Revolution Begins in England (1760-1850) [Электронный ресурс] /Modern World History. – Режим доступа: http://webs.bcp.org/sites/vcleary/modernworldhistorytextbook/industrialrevolution/IRbegins.html, свободный.
Collingwood R.G. Social impact of industrial revolution // Idea of History [Электронный ресурс] / R. G. Collingwood. – Режим доступа: http://idea-of-history.blogspot.ru/2012/12/social-impact-of-industrial-revolution.html, свободный.
The Industrial Revolution in Europe [Электронный ресурс] / European Route of Industrial Heritage. – Режим доступа: http://www.erih.net/how-it-started/the-industrial-revolution-in-europe/, свободный.
Слайд 28
![Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / Encyclopedia Britannica. – Режим доступа:](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/338160/slide-27.jpg)
Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / Encyclopedia Britannica. – Режим доступа: https://www.britannica.com/event/Industrial-Revolution,
свободный.
The Industrial Revolution in Europe, Russia, and Japan [Электронный ресурс] / Prezi. – Режим доступа: https://prezi.com/nohdiij0rdiu/the-industrial-revolution-in-europe-russia-and-japan/, свободный.
Industrialization of Japan [Электронный ресурс] / Weatern Civilization II Guides. – Режим доступа: http://westerncivguides.umwblogs.org/2012/05/03/industrialization-of-japan/, свободный.
Child Labor during the British Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] /EH.net. – Режим доступа: http://eh.net/encyclopedia/child-labor-during-the-british-industrial-revolution/, свободный.
























![Bibliographical References Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / New Word Encyclopedia.](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/338160/slide-25.jpg)
![The Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / myglobal2009.wikispaces.com. – Режим доступа:](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/338160/slide-26.jpg)
![Industrial Revolution [Электронный ресурс] / Encyclopedia Britannica. – Режим доступа:](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/338160/slide-27.jpg)
 Экономические теории товара и денег
Экономические теории товара и денег Государство в системе макроэкономической регуляции
Государство в системе макроэкономической регуляции Создание проекта сайта по трудоустройству студентов
Создание проекта сайта по трудоустройству студентов Конкурентоспособность продукции и факторы ее определяющие
Конкурентоспособность продукции и факторы ее определяющие Народосбережение. Демографическая ситуация, основные причины сложившегося положения дел, задачи народосбережения
Народосбережение. Демографическая ситуация, основные причины сложившегося положения дел, задачи народосбережения Инфляцияның түрлері, типтері және инфляцияға қарсы саясат
Инфляцияның түрлері, типтері және инфляцияға қарсы саясат Понятие экономика
Понятие экономика Макроэкономические показатели и качество жизни_ 10 кл
Макроэкономические показатели и качество жизни_ 10 кл Меры поддержки для участников проекта
Меры поддержки для участников проекта Классические модели стратегического анализа и планирования: модель Хофера-Шенделя
Классические модели стратегического анализа и планирования: модель Хофера-Шенделя Экономическая оценка инвестиций в сферу природопользования
Экономическая оценка инвестиций в сферу природопользования Оценка эффективности инноваций
Оценка эффективности инноваций Подсистемы антикризисного управления на предприятии. (Тема 6)
Подсистемы антикризисного управления на предприятии. (Тема 6) Рыбалкин М.Д. ОБ16-1 Внешнеэкономическая деятельность, сущность, основные формы, механизм реализации
Рыбалкин М.Д. ОБ16-1 Внешнеэкономическая деятельность, сущность, основные формы, механизм реализации Пропозиція та її чинники
Пропозиція та її чинники Человек на рынке труда
Человек на рынке труда Стратегическое планирование и развитие крупнейших городов. (Тема 6)
Стратегическое планирование и развитие крупнейших городов. (Тема 6) Понятие рыночной власти
Понятие рыночной власти Экономический рост
Экономический рост Германия на пути к единству
Германия на пути к единству Роль государства в экономике
Роль государства в экономике Роль государства в экономике
Роль государства в экономике Ежегодный отчёт главы Новомихайловского городского поселения Туапсинского района о результатах деятельности за 2017 год
Ежегодный отчёт главы Новомихайловского городского поселения Туапсинского района о результатах деятельности за 2017 год Трудовая миграция. Франция
Трудовая миграция. Франция Держава та суспільне виробництво
Держава та суспільне виробництво Экономическая сущность и эффективность использования основных производственных фондов
Экономическая сущность и эффективность использования основных производственных фондов Вертикальные ограничивающие контракты. Тема 9
Вертикальные ограничивающие контракты. Тема 9 История экономической мысли
История экономической мысли