Содержание
- 2. At the end of the lesson you will be able to describe oscillatory motion explain the
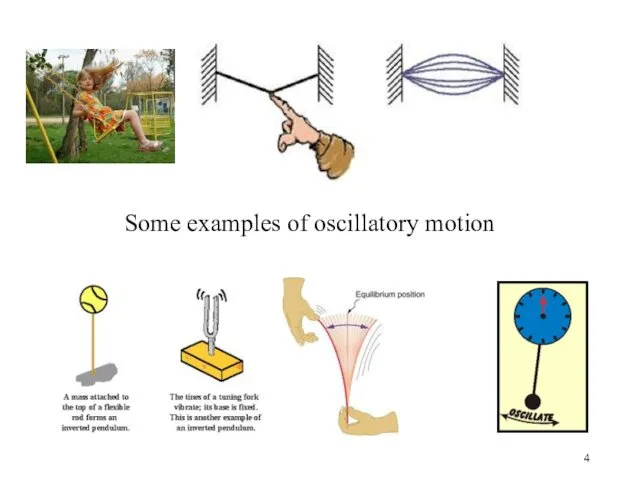
- 4. Some examples of oscillatory motion
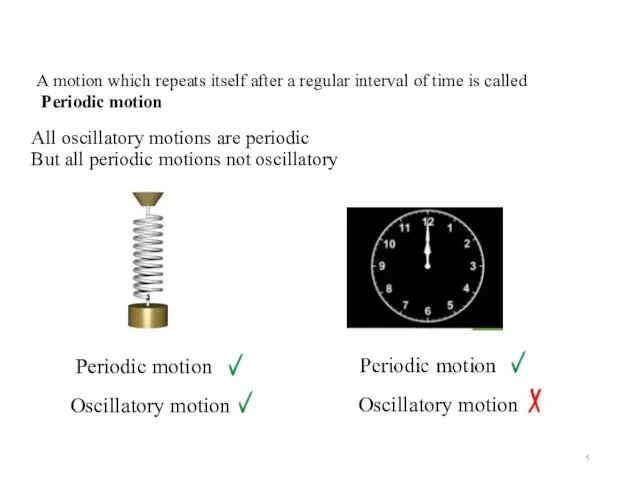
- 5. All oscillatory motions are periodic But all periodic motions not oscillatory A motion which repeats itself
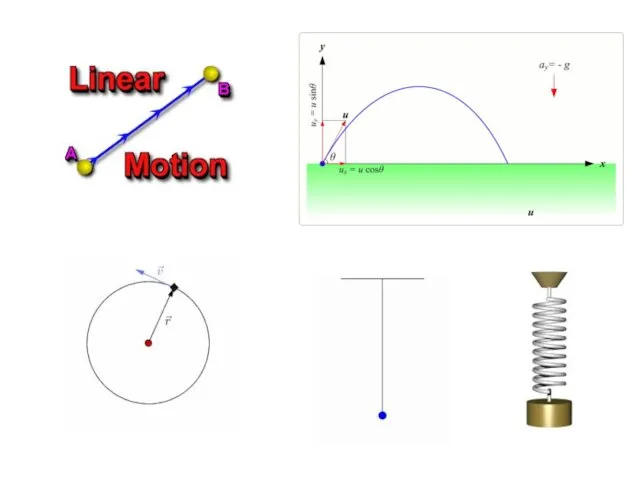
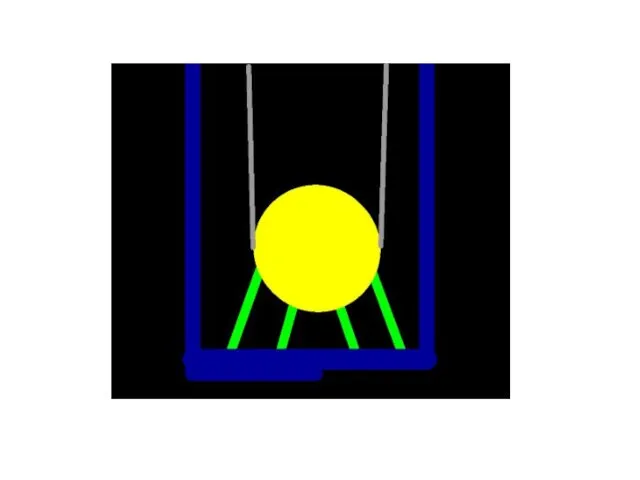
- 6. An oscillation is a repetitive back and-forth motion. One complete oscillation is called a cycle. Parameters
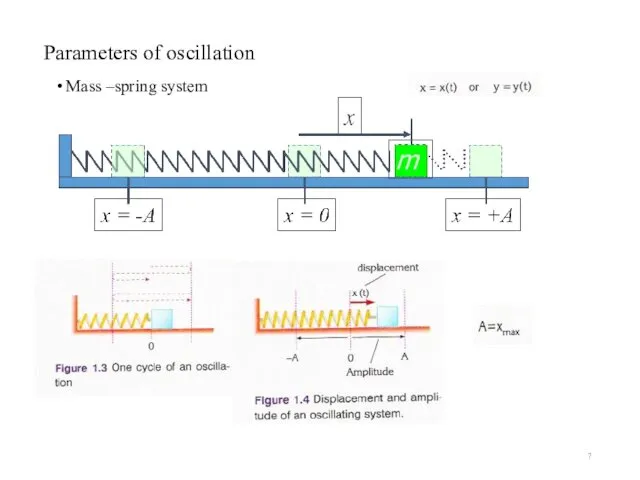
- 7. Parameters of oscillation Mass –spring system
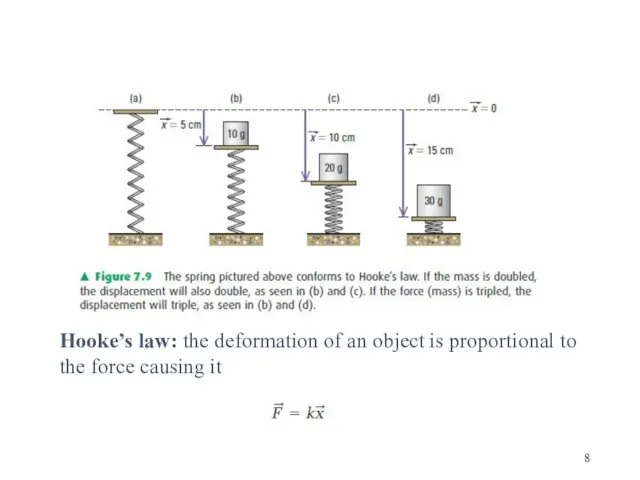
- 8. Hooke’s law: the deformation of an object is proportional to the force causing it
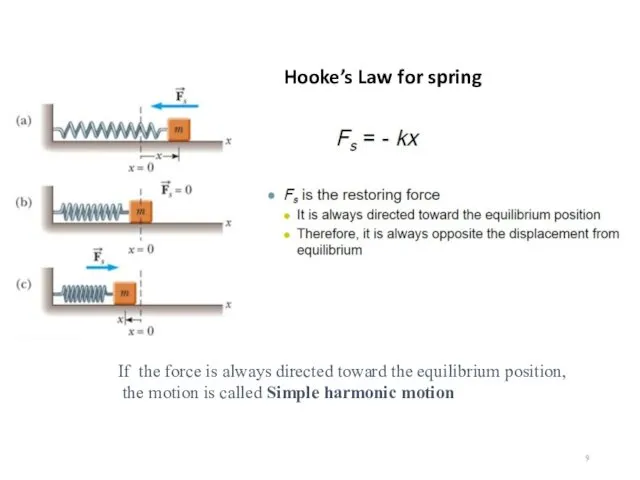
- 9. Hooke’s Law for spring If the force is always directed toward the equilibrium position, the motion
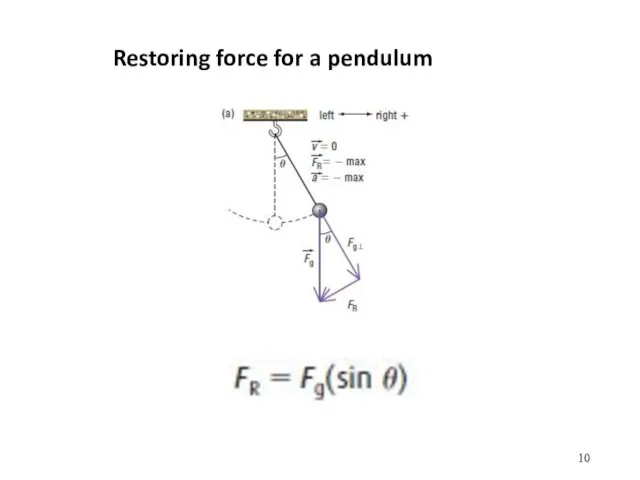
- 10. Restoring force for a pendulum
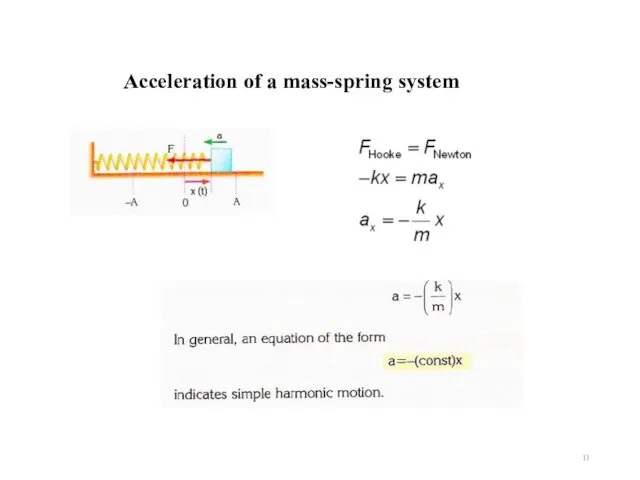
- 11. Acceleration of a mass-spring system
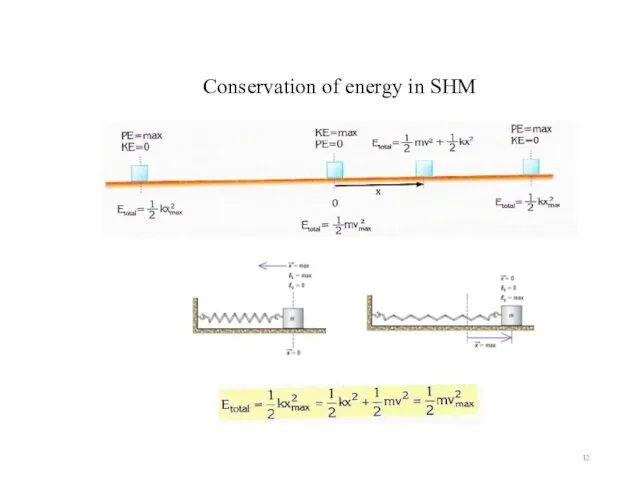
- 12. Conservation of energy in SHM
- 13. Maximum speed of mass-spring system
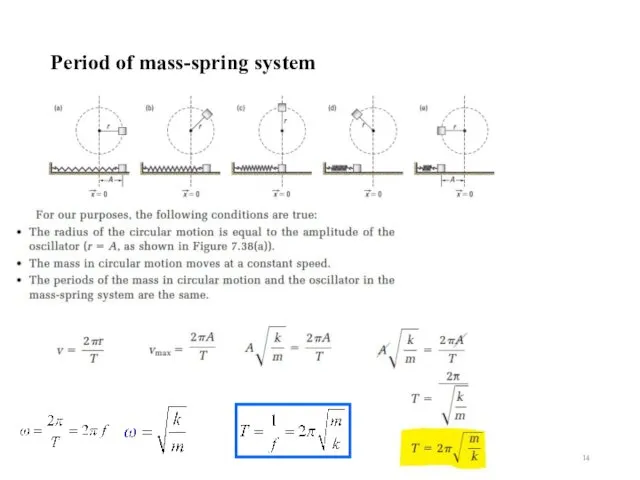
- 14. Period of mass-spring system
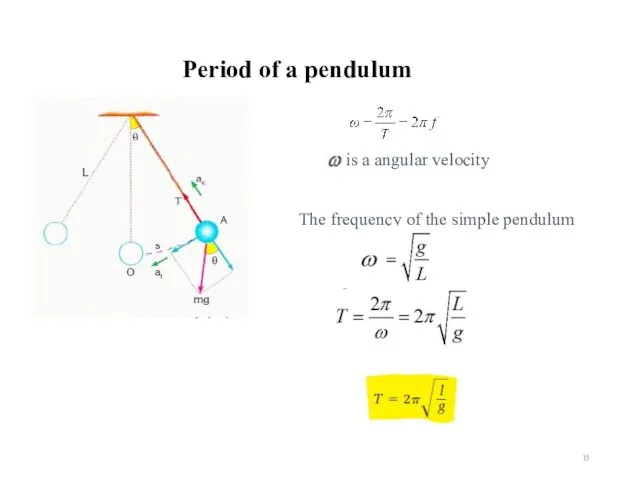
- 15. Period of a pendulum is a angular velocity The frequency of the simple pendulum
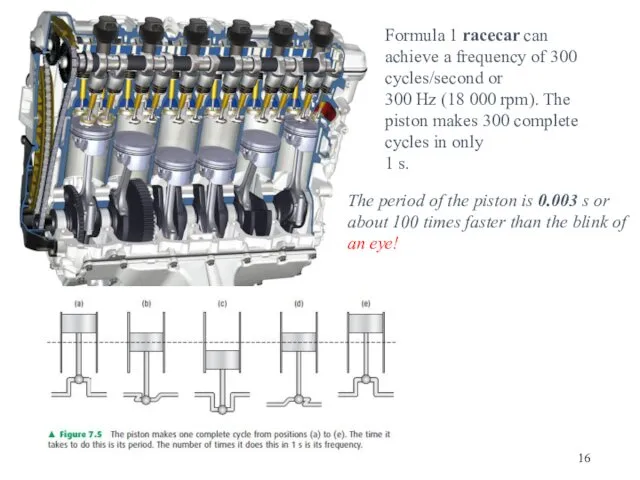
- 16. Formula 1 racecar can achieve a frequency of 300 cycles/second or 300 Hz (18 000 rpm).
- 17. Practice problems
- 18. Check and reflect 1. What conditions describe oscillatory motion? 2. Which unit is equivalent to cycles/s?
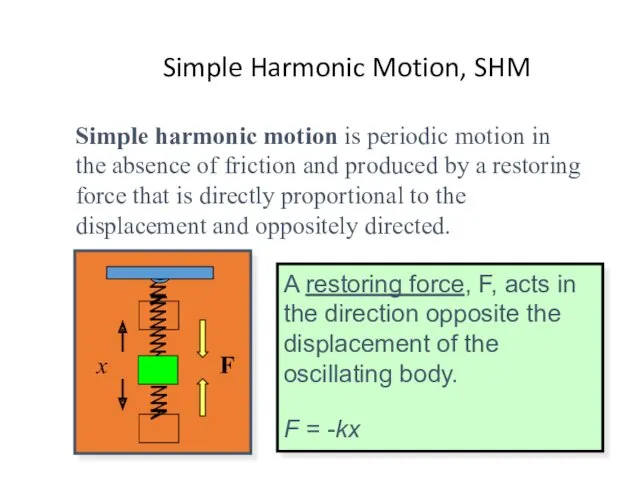
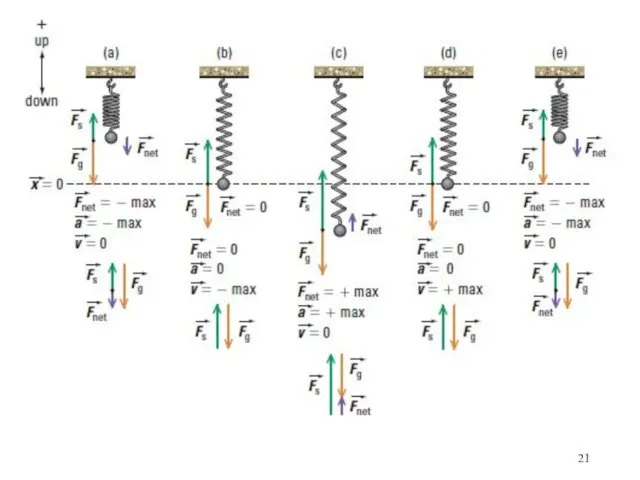
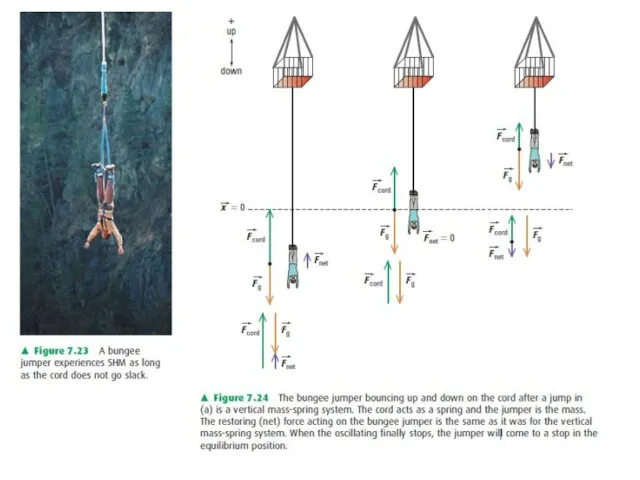
- 20. Simple Harmonic Motion, SHM Simple harmonic motion is periodic motion in the absence of friction and
- 25. Conclusion SHM is repetitive and predictable, so we can state the following: • The restoring force
- 26. Applications of Simple Harmonic Motion
- 27. Resonant frequency- is a natural frequency of vibration determined by the physical parameters of the vibrating
- 28. Mechanical resonance – is the increase in amplitude of oscillation of a system, when the frequency
- 31. Resonant frequency of a quarts crystal
- 33. QUIZ An astronaut who has just landed on Pluto wants to determine the gravitational field strength.
- 35. Скачать презентацию














 Изгиб с кручением круглых стержней в конструкциях различных механизмов
Изгиб с кручением круглых стержней в конструкциях различных механизмов Гальванометр. Виды и применение
Гальванометр. Виды и применение Сборка изделий из тонколистового металла, проволоки и искусственных материалов. 5 класс
Сборка изделий из тонколистового металла, проволоки и искусственных материалов. 5 класс Адаптация обучающихся в учебном пространстве предмета - физика
Адаптация обучающихся в учебном пространстве предмета - физика Прибор для демонстрации графиков электромагнитных колебаний
Прибор для демонстрации графиков электромагнитных колебаний Работа лопастной машины на сеть. Напорная характеристика сети
Работа лопастной машины на сеть. Напорная характеристика сети Сила Архимеда
Сила Архимеда Атмосферное давление
Атмосферное давление Види самостійних газових розрядів
Види самостійних газових розрядів Механикалық қозғалыс. Траектория. Жол. Орын ауыстыру
Механикалық қозғалыс. Траектория. Жол. Орын ауыстыру Электрообогрев лобового стекла автомобиля
Электрообогрев лобового стекла автомобиля Презентация к уроку по физике 10 класс Применение законов Ньютона
Презентация к уроку по физике 10 класс Применение законов Ньютона Lektsia_4
Lektsia_4 Ремонт КШМ двигателя Д-240
Ремонт КШМ двигателя Д-240 Резерфорд тәжірбесі. Атомның планетарлық моделі
Резерфорд тәжірбесі. Атомның планетарлық моделі Управління потоками реактивної енергії
Управління потоками реактивної енергії Работа и мощность электрического тока
Работа и мощность электрического тока Блок - разновидность простого механизма
Блок - разновидность простого механизма Радиоактивность, модели атомов
Радиоактивность, модели атомов Лекция 5. Динамика материальной системы. Динамика тела переменной массы
Лекция 5. Динамика материальной системы. Динамика тела переменной массы ТРИЗ Электричество
ТРИЗ Электричество Электрические измерения в системах электроснабжения
Электрические измерения в системах электроснабжения Системы безопасности эксплуатации автомобилей
Системы безопасности эксплуатации автомобилей Допуски и посадки подшипников качения
Допуски и посадки подшипников качения Твердые тела и их свойства
Твердые тела и их свойства Конустық қосылыстардың өзара алмасымдылығы, әдістері және кұралдары
Конустық қосылыстардың өзара алмасымдылығы, әдістері және кұралдары Теплопередача или теплообмен
Теплопередача или теплообмен Фрезерование. Лекция №14
Фрезерование. Лекция №14