Содержание
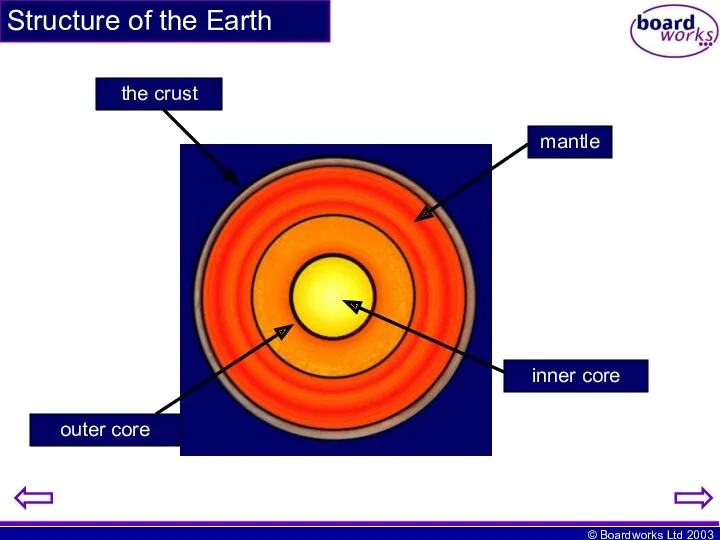
- 2. Structure of the Earth the crust mantle outer core inner core
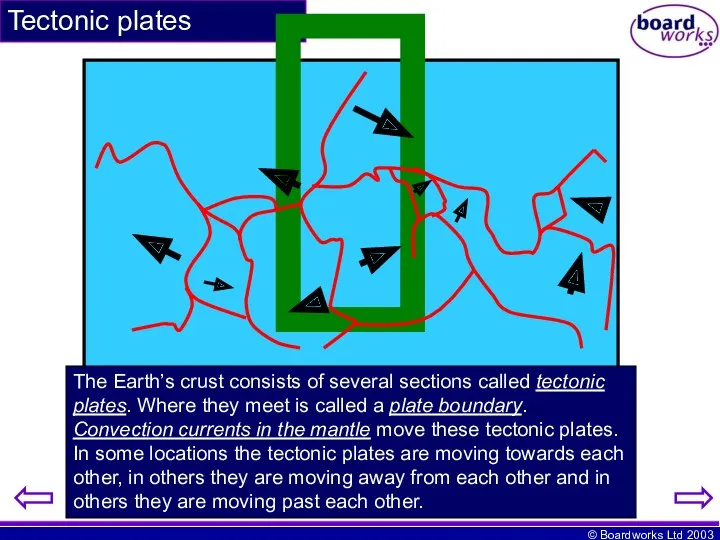
- 3. Tectonic plates The Earth’s crust consists of several sections called tectonic plates. Where they meet
- 4. Plate boundaries 1 When two plates slide past each other, they don’t do it smoothly. The
- 5. Plate boundaries 1
- 6. Why do earthquakes happen?
- 7. Epicentre of an earthquake
- 8. Primary and secondary waves During an earthquake the two types of wave that are released from
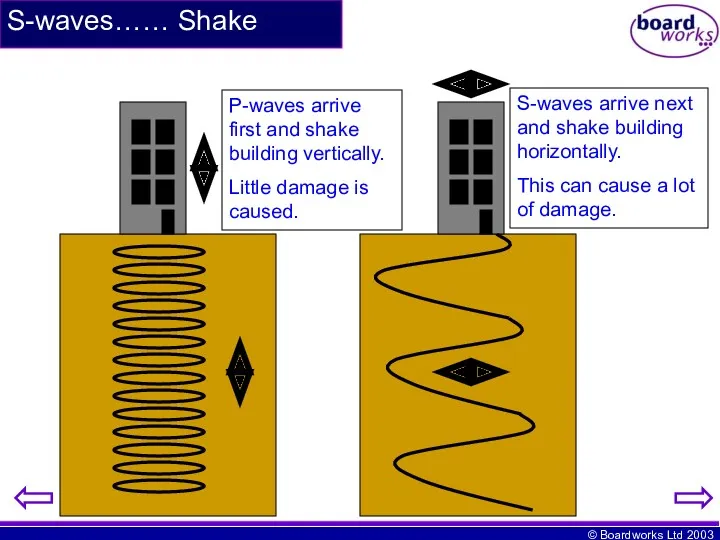
- 9. S-waves…… Shake P-waves arrive first and shake building vertically. Little damage is caused. S-waves arrive next
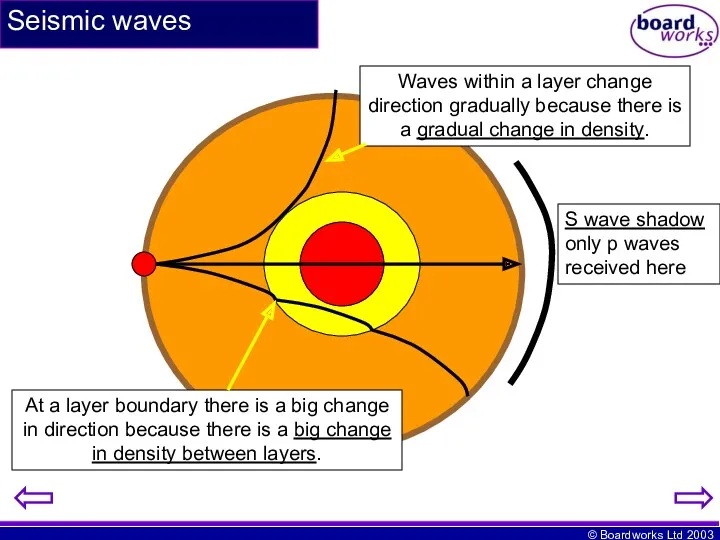
- 10. Seismic waves Waves within a layer change direction gradually because there is a gradual change in
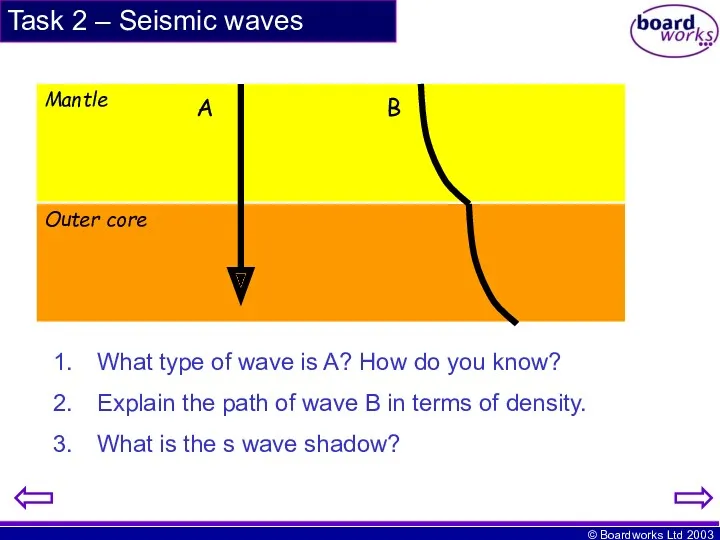
- 11. Task 2 – Seismic waves Outer core Mantle A B What type of wave is A?
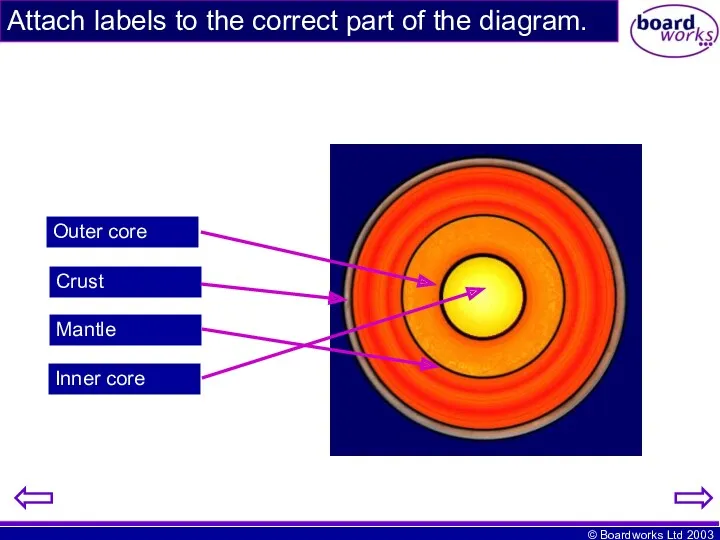
- 12. Outer core Crust Mantle Inner core Attach labels to the correct part of the diagram.
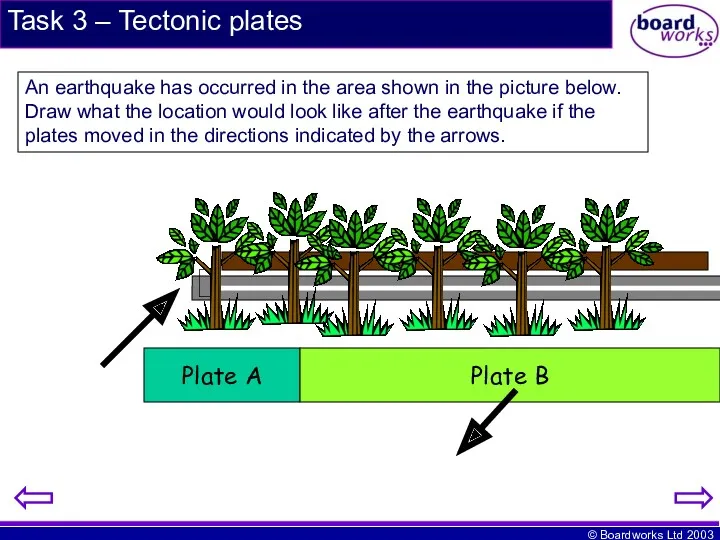
- 13. Task 3 – Tectonic plates Plate A Plate B An earthquake has occurred in the area
- 14. Match the word with the description: Epicentre Primary waves Secondary waves The faster seismic wave, that
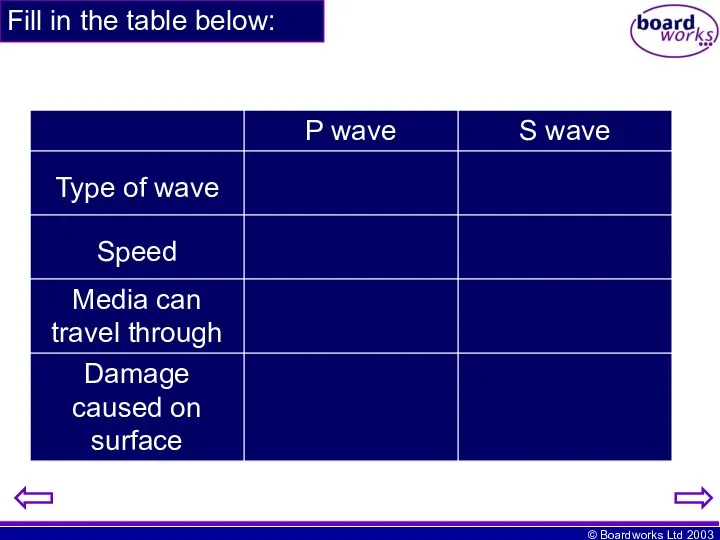
- 15. Fill in the table below:
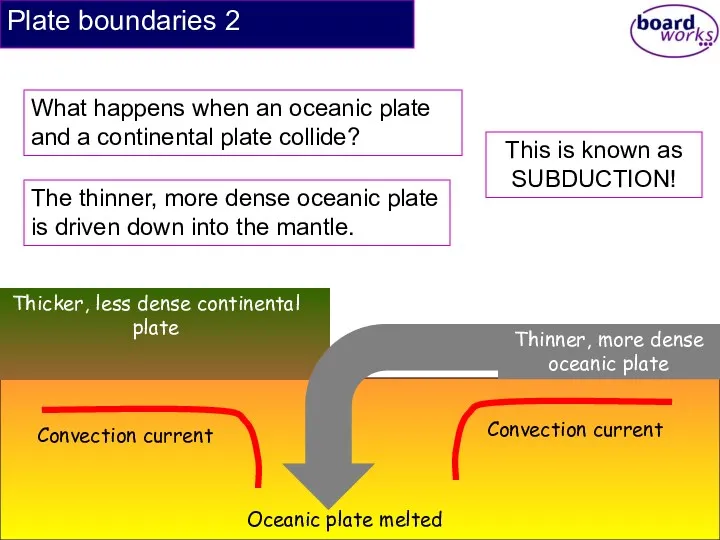
- 16. Plate boundaries 2 What happens when an oceanic plate and a continental plate collide? The thinner,
- 17. Plate boundaries 2
- 18. Convection current Convection current ← Oceanic plate Oceanic plate → What happens when oceanic plates move
- 19. Constructive Plate Boundary Plate boundaries 3
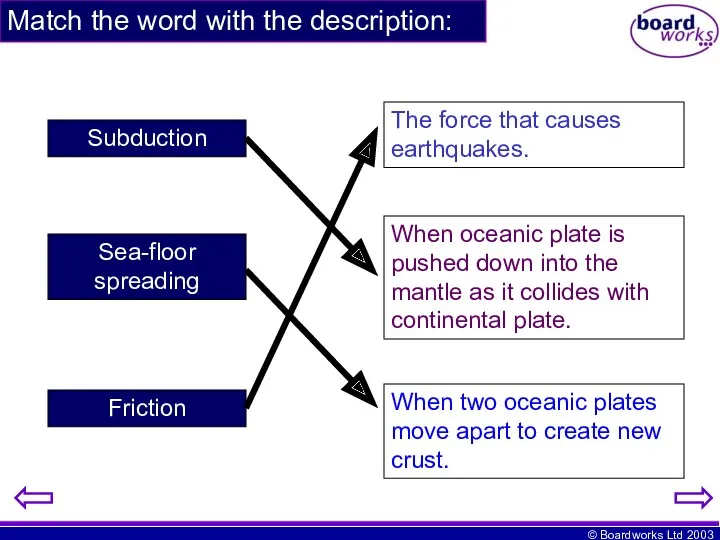
- 20. Match the word with the description: Subduction Sea-floor spreading Friction The force that causes earthquakes. When
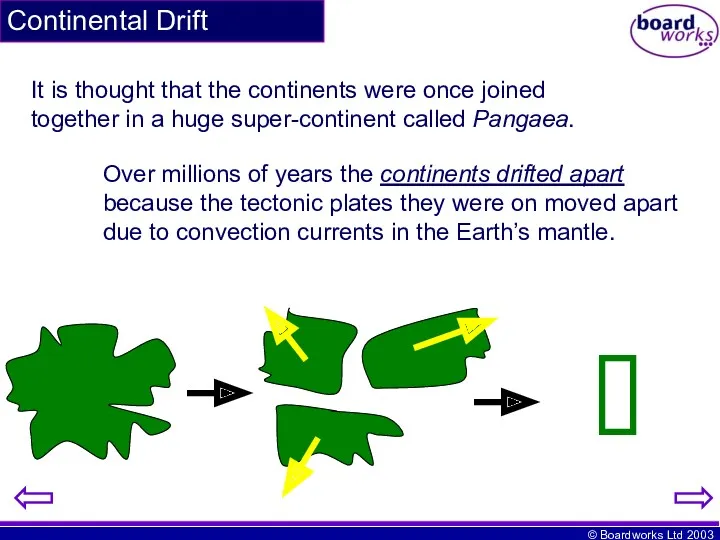
- 21. Continental Drift It is thought that the continents were once joined together in a huge super-continent
- 22. Continental Drift
- 24. Скачать презентацию










 Геоэкологические проблемы и риски: глобальный и региональный аспекты
Геоэкологические проблемы и риски: глобальный и региональный аспекты Әлемдік мұхит өнімділік аймақтарының орналасуы
Әлемдік мұхит өнімділік аймақтарының орналасуы The cities of Ukraine
The cities of Ukraine Гидрометеорологическое обеспечение мореплавания. (Лекция 1)
Гидрометеорологическое обеспечение мореплавания. (Лекция 1) Краснодарскому краю – 75!
Краснодарскому краю – 75! Климат Земли. Климатические пояса, типы климата, климатообразующие факторы
Климат Земли. Климатические пояса, типы климата, климатообразующие факторы Водный голод планеты
Водный голод планеты Кумысная поляна – жемчужина Саратова
Кумысная поляна – жемчужина Саратова Атмосферное давление. Ветер
Атмосферное давление. Ветер Компас своими руками
Компас своими руками Тундра
Тундра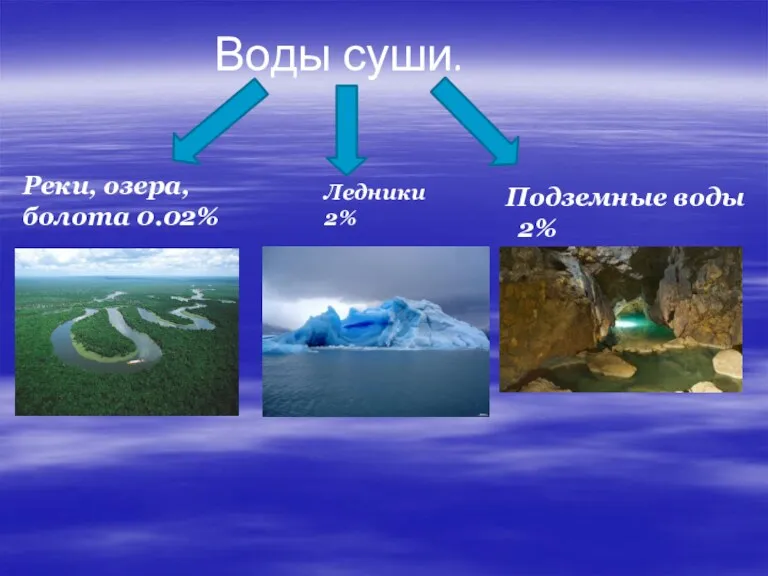 Воды суши. Реки, озера
Воды суши. Реки, озера Весна идет. Романтическое литературное путешествие по Магнитогорску (Ленинский район)
Весна идет. Романтическое литературное путешествие по Магнитогорску (Ленинский район) Климат Пензенской области
Климат Пензенской области Дальний и выездной туризм
Дальний и выездной туризм 8 natural wonders in Russia
8 natural wonders in Russia Линеаменты, естественная делимость верхних горизонтов земной коры
Линеаменты, естественная делимость верхних горизонтов земной коры Население Южной Америки
Население Южной Америки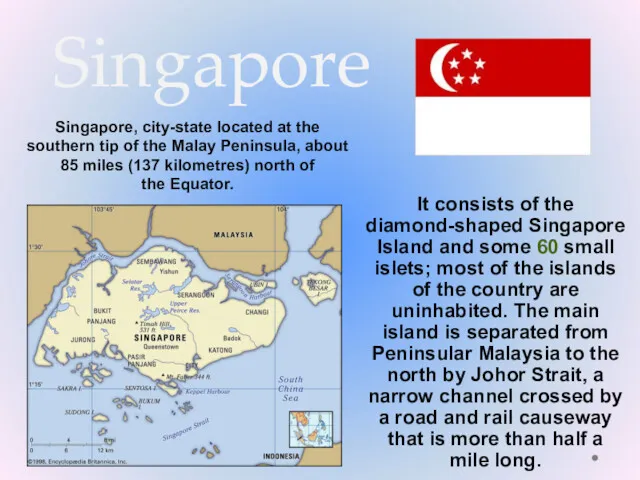 Singapore
Singapore Проблемы использования и воспроизводства природных ресурсов
Проблемы использования и воспроизводства природных ресурсов Австралия
Австралия Процессы в неживой природе
Процессы в неживой природе Северо-запад России. Город Калининград
Северо-запад России. Город Калининград Основные типы вулканокластических пород
Основные типы вулканокластических пород Эндогенные процессы
Эндогенные процессы New South Wales
New South Wales Этнический и религиозный состав населения
Этнический и религиозный состав населения Природное явление засуха
Природное явление засуха