Содержание
- 2. Mineral And Rock Resources “If it can’t be grown, it must be mined.” Mineral – naturally
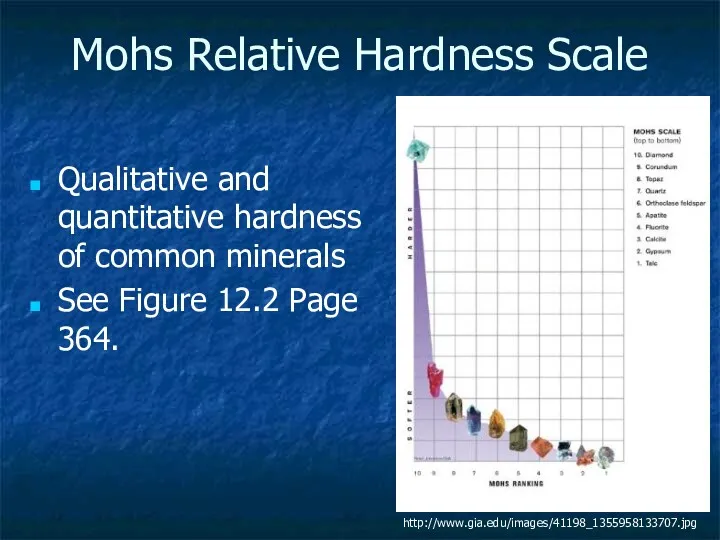
- 3. Mohs Relative Hardness Scale Qualitative and quantitative hardness of common minerals See Figure 12.2 Page 364.
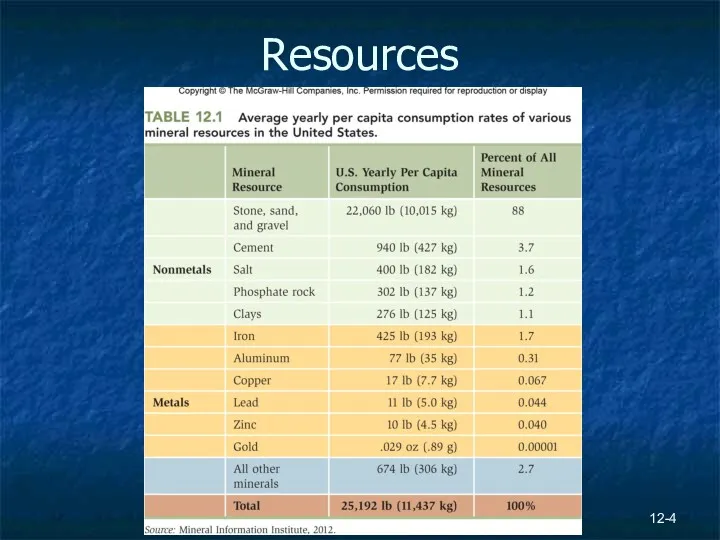
- 4. 12- Resources
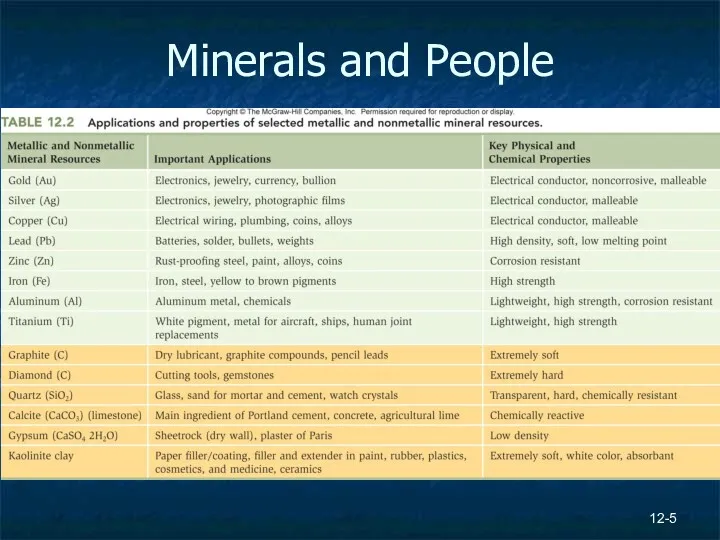
- 5. 12- Minerals and People
- 6. 12- Economic Mineral Deposits Enrichment factor – degree to which mineral is concentrated above its average
- 7. 12- Geology of Mineral Resources Igneous Processes Diamond pipes – associated with unusual type of igneous
- 8. Intrusive Deposits 12-
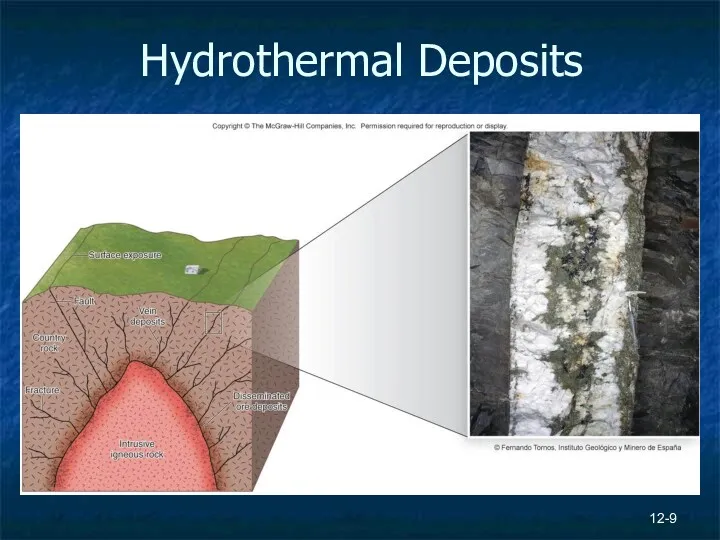
- 9. Hydrothermal Deposits 12-
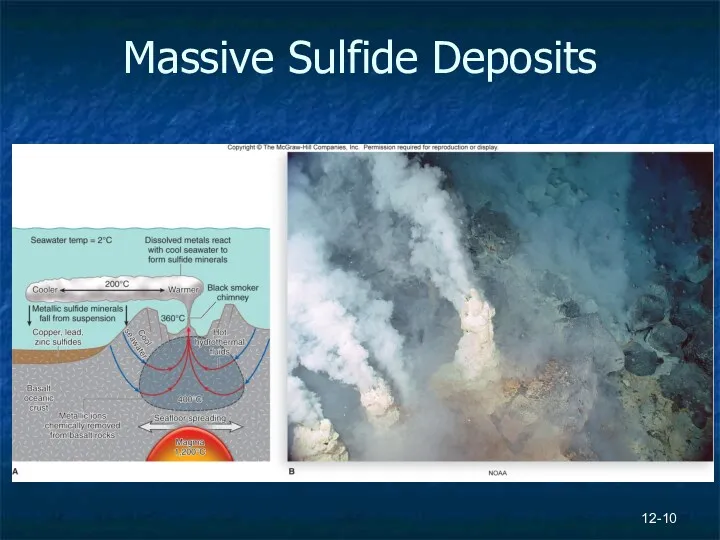
- 10. Massive Sulfide Deposits 12-
- 11. 12- Geology of Mineral Resources Metamorphic processes – deep subsurface physical and chemical changes Regional metamorphism
- 12. Contact Metamorphism 12-
- 13. 12- Geology of Mineral Resources Sedimentary processes – tend to concentrate certain types of minerals Placer
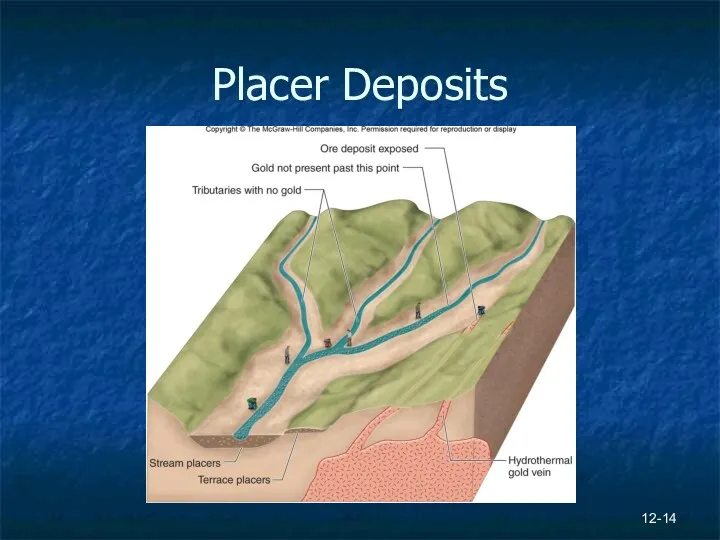
- 14. Placer Deposits 12-
- 15. More Sedimentary Processes Residual weathering products – secondary weathering products results in release of ions. Bauxite
- 16. Banded Iron Deposits Iron used in making steel for use in making machines, trucks, trains, ships,
- 17. Two Types of Evaporites Marine – minerals reflect chemical composition of seawater (Cl and Na ions)
- 18. Phosphorites Phosphorus important plant nutrient Result from chemical weathering of rocks then transported to water bodies
- 19. 12- Mining & Processing of Minerals Mining Techniques Surface mining Open pit – terraced down slope
- 20. Open Pit Mining 12-
- 21. Underground Mining 12-
- 22. 12- Mining & Processing of Minerals Mineral processing Physical separation – crushing and using screens or
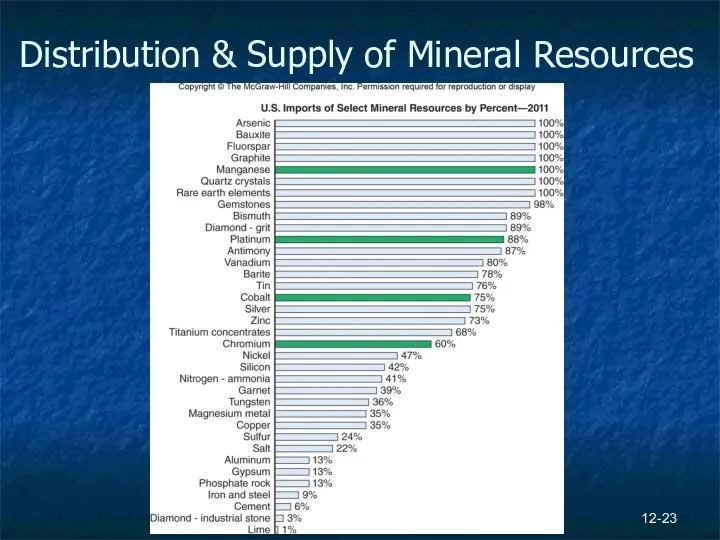
- 23. 12- Distribution & Supply of Mineral Resources
- 24. 12- Supply of Mineral Resources Not evenly distributed Strategic minerals – critical, large amounts imported in
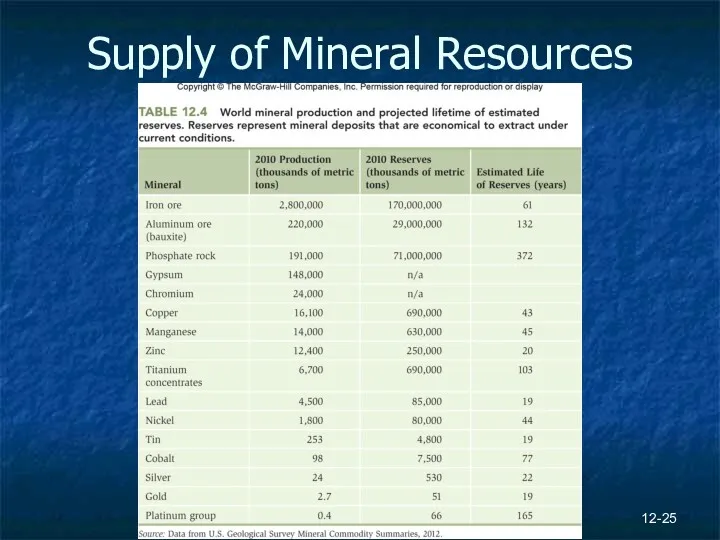
- 25. 12- Supply of Mineral Resources
- 26. 12- Supply of Mineral Resources
- 27. 12- Environmental Impacts & Mitigation General Mining Act 1872 – “1872 Mining Law.” Governs mining of
- 28. 12- Environmental Impacts & Mitigation Toxic heavy metals and acid drainage Increases acidity
- 29. 12- Environmental Impacts & Mitigation Processing of ores – can release toxins into environment; impermeable layers
- 30. Environmental Impacts & Mitigation Constructed wetlands to treat acid mine waters Superfund – Government trust fund
- 32. Скачать презентацию





















 Виды изображений земной поверхности. План местности (6 класс)
Виды изображений земной поверхности. План местности (6 класс) Средняя Сибирь. Рельеф и геологическое строение
Средняя Сибирь. Рельеф и геологическое строение Размещение населения
Размещение населения Технологические вопросы создания тематических карт в ГИС
Технологические вопросы создания тематических карт в ГИС Часовые пояса
Часовые пояса Геологическая деятельность атмосферы
Геологическая деятельность атмосферы Основи суспільно-географічного районування
Основи суспільно-географічного районування Новгородская область
Новгородская область Рельеф России, геологическое строение и полезные ископаемые
Рельеф России, геологическое строение и полезные ископаемые Текстуры и отдельность магматических пород
Текстуры и отдельность магматических пород районирование РФ
районирование РФ Религиозный состав России. Тест 9 класс
Религиозный состав России. Тест 9 класс География отраслей мирового хозяйства
География отраслей мирового хозяйства Туған жердің қадірін, шетте жүрсең білесің
Туған жердің қадірін, шетте жүрсең білесің Оңтүстік Қазақстан шипажайлары
Оңтүстік Қазақстан шипажайлары Рельеф и полезные ископаемые Африки
Рельеф и полезные ископаемые Африки Погода в графиках
Погода в графиках Урал. Природные богатства Урала
Урал. Природные богатства Урала Магматизм. Типы вулканов
Магматизм. Типы вулканов История географии как наука. География античности
История географии как наука. География античности Минералы и горные породы
Минералы и горные породы Половозрастной состав населения России
Половозрастной состав населения России Городское и сельское население. Урбанизация как всемирный процесс
Городское и сельское население. Урбанизация как всемирный процесс Нижегородская область в РФ
Нижегородская область в РФ About Berlin, Germany
About Berlin, Germany Самарская Лука
Самарская Лука Землетрясения
Землетрясения Место географии в системе наук
Место географии в системе наук