Содержание
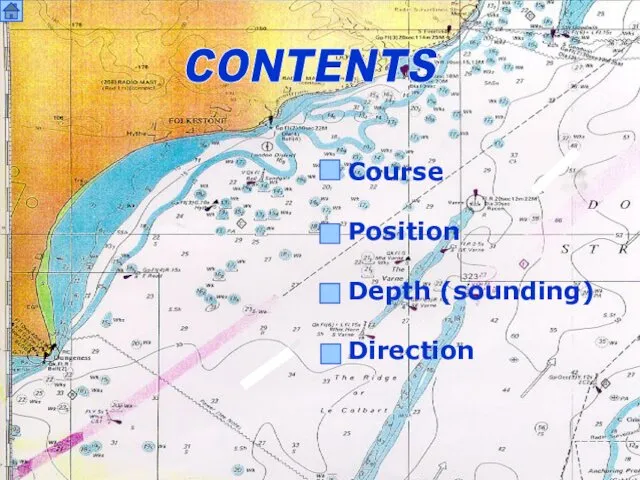
- 2. CONTENTS Course Position Depth (sounding) Direction
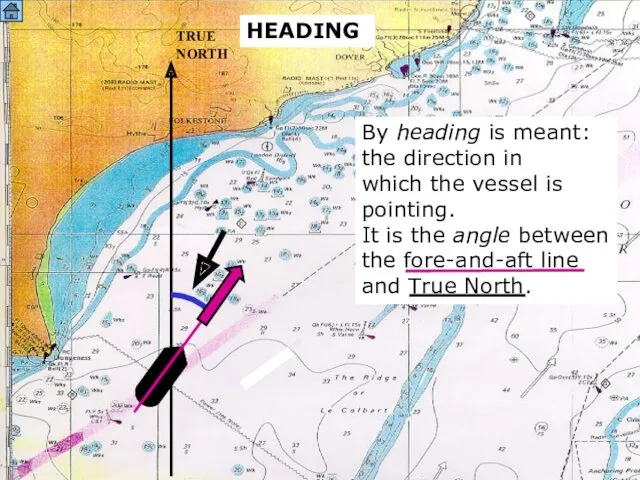
- 3. SOUND HEADING TRUE NORTH By heading is meant: the direction in which the vessel is pointing.
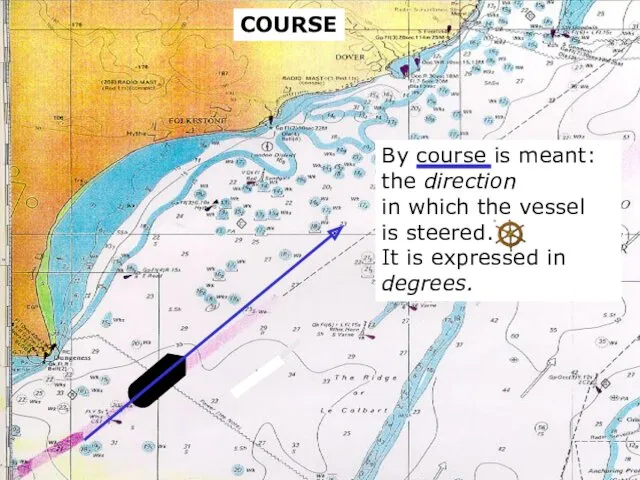
- 4. sound COURSE By course is meant: the direction in which the vessel is steered. It is
- 5. Do not confuse heading and course; HEADING AND COURSE heading constantly changes due to sea- and
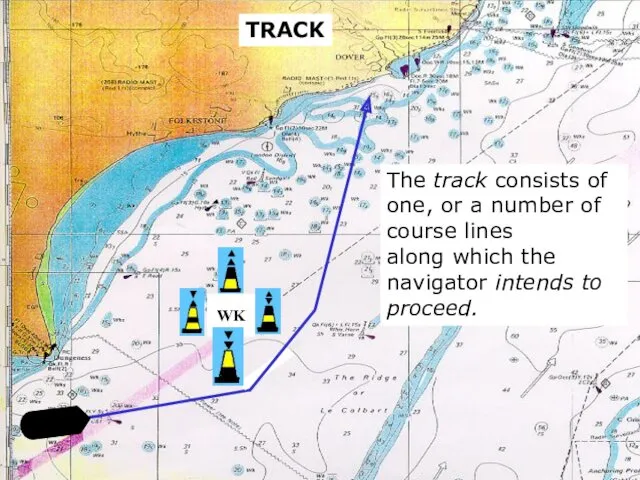
- 6. sound TRACK The track consists of one, or a number of course lines along which the
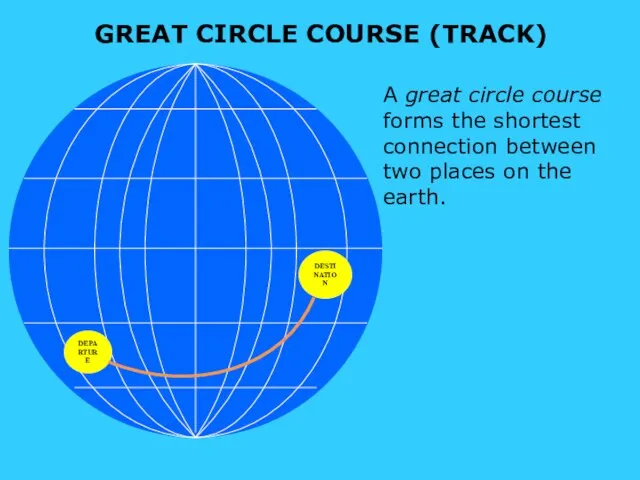
- 7. GREAT CIRCLE COURSE (TRACK) DEPARTURE DESTINATION A great circle course forms the shortest connection between two
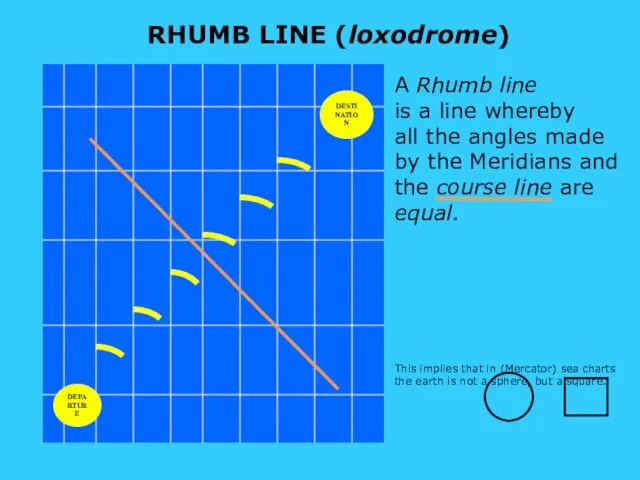
- 8. This implies that in (Mercator) sea charts the earth is not a sphere, but a square.
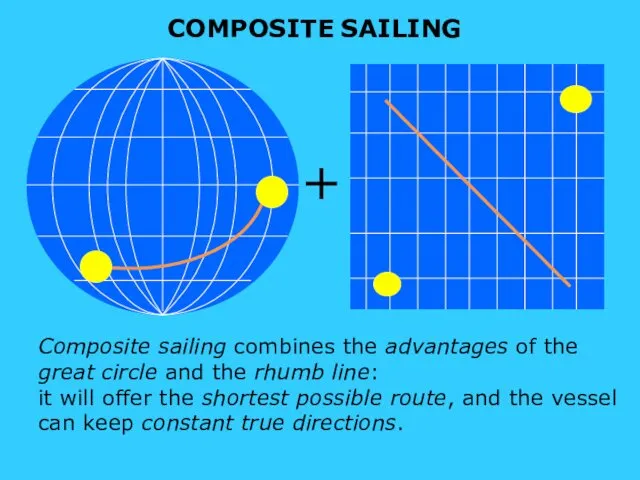
- 9. s sound COMPOSITE SAILING + Composite sailing combines the advantages of the great circle and the
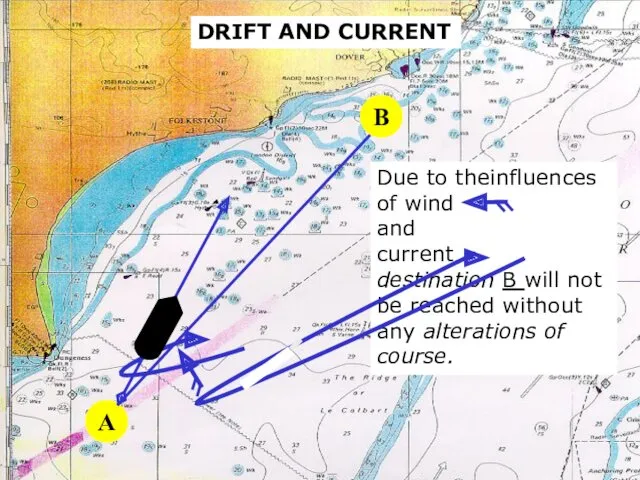
- 10. sound DRIFT AND CURRENT A B Due to theinfluences of wind and current destination B will
- 11. sound A By course made good is understood the course that the ship will follow after
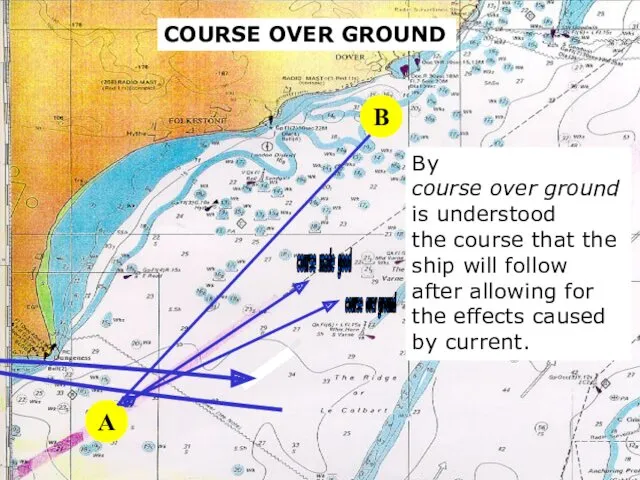
- 12. sound A By course over ground is understood the course that the ship will follow after
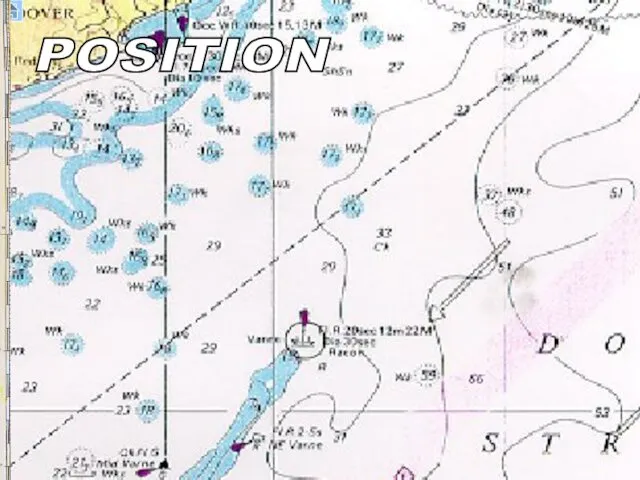
- 13. s POSITION
- 14. Pilotage (coastal navigation) Cross bearing The cocked hat A running fix Dead reckoning Astronomical navigation Satellite
- 15. When sailing along the coast, compass- bearings of conspicuous objects are taken at regular intervals.
- 16. A CONSPICUOUS OBJECT (CONSPIC) is an object on land or at sea, which is mentioned and
- 17. Cross bearings form an intersection of two bearing lines that have been taken of two conspicuous
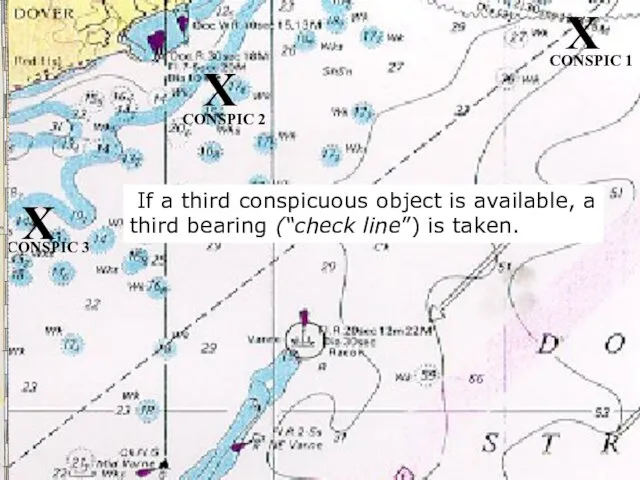
- 18. If a third conspicuous object is available, a third bearing (“check line”) is taken. X X
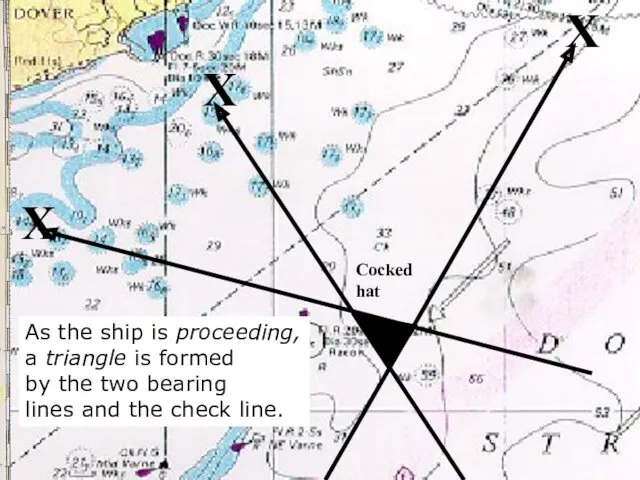
- 19. X X X As the ship is proceeding, a triangle is formed by the two bearing
- 20. When there is only one conspicuous object, a position fix is made by taking two bearings
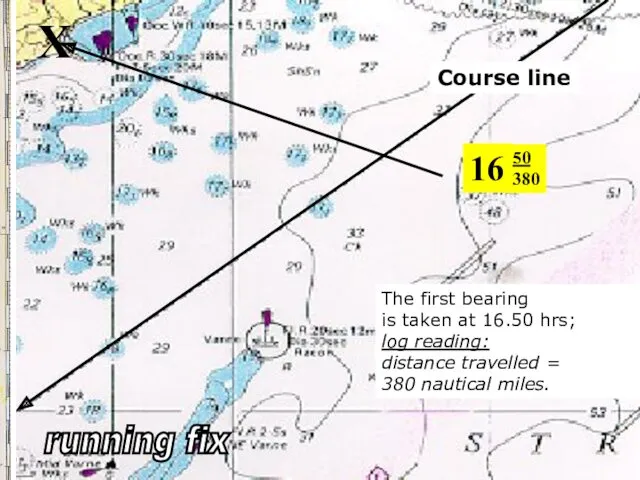
- 21. X Course line 16 50 380 The first bearing is taken at 16.50 hrs; log reading:
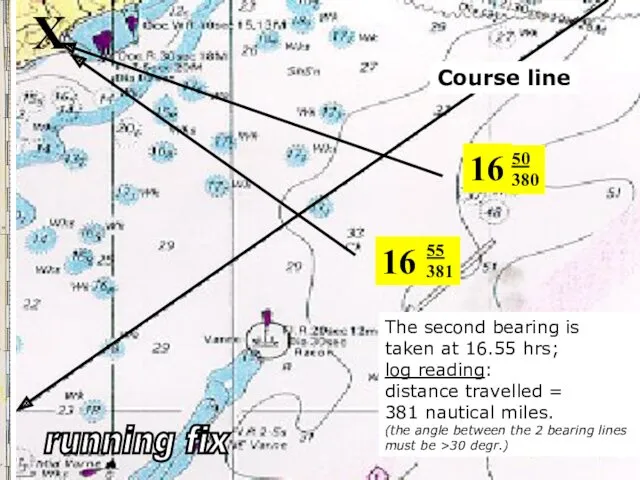
- 22. 16 50 380 X 16 55 381 The second bearing is taken at 16.55 hrs; log
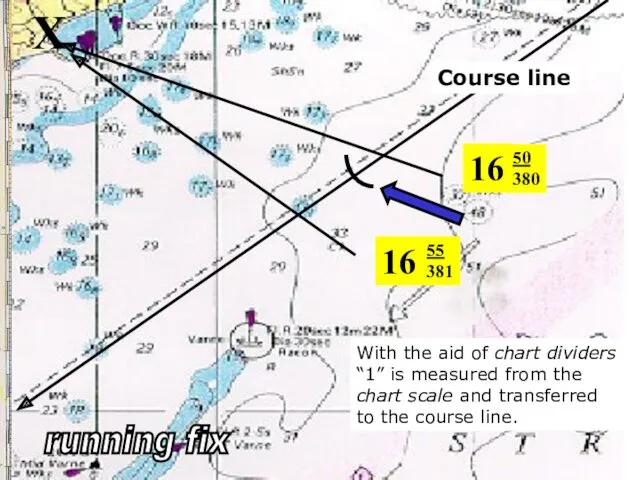
- 23. 16 50 380 X With the aid of chart dividers “1” is measured from the chart
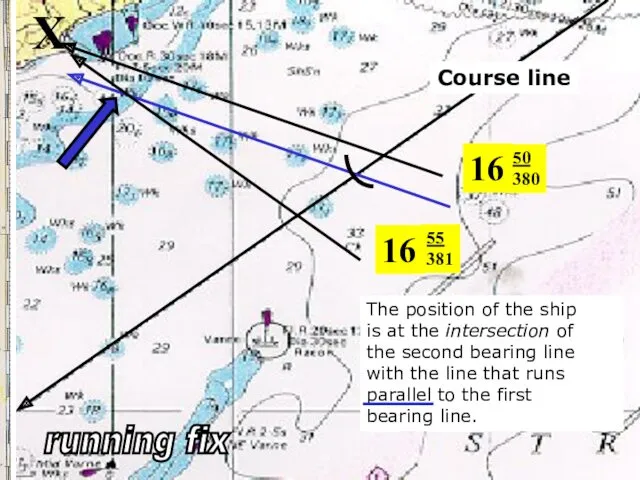
- 24. X 16 50 380 The position of the ship is at the intersection of the second
- 25. sound By “Dead Reckoning” is meant finding one’s position by taking into consideration: . last known
- 26. s ASTRONOMICAL NAVIGATION With astronomical navigation(celestial navigation) observations are taken of the sun, the moon or
- 27. SEXTANT-BEARING The angle between a celestial body and the horizon is measured.
- 28. With the aid of the chronometer and the tables in the nautical almanac the ship’s position
- 29. SATELLITE-BEARING When taking a satellite bearing by means of the Global Positioning System a signal is
- 30. sound s Sounding With the aid of the echo sounder the depth of the water can
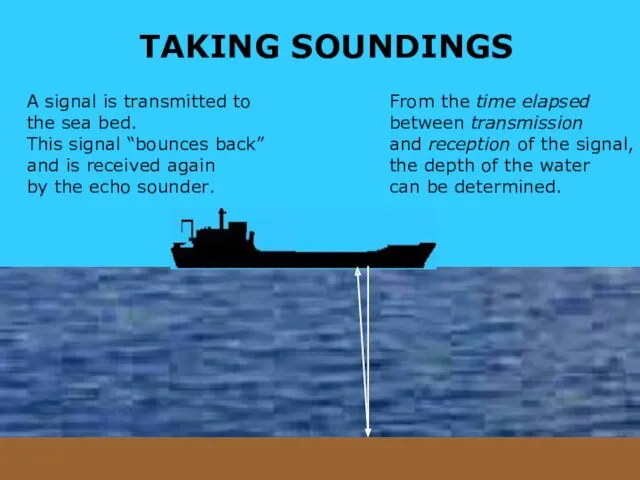
- 31. TAKING SOUNDINGS A signal is transmitted to the sea bed. This signal “bounces back” and is
- 32. TAKING SOUNDINGS With multi-beam echo sounding 3-D images are made of the seabed to determine charted
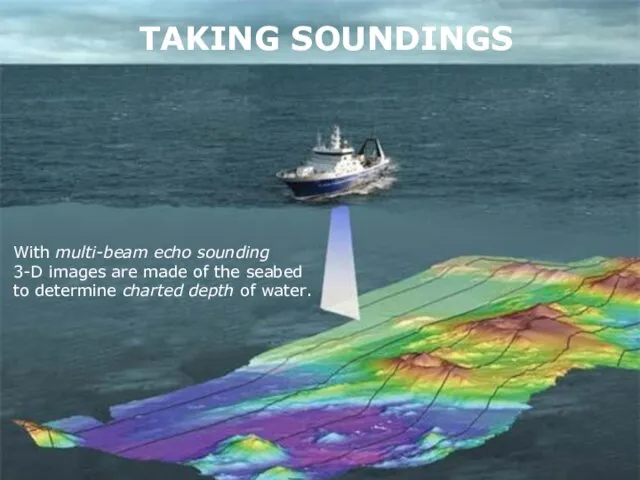
- 33. so WIRE SWEEPING Depth over a protruding obstacle can also be obtained by wire sweeping, whereby
- 34. s Directions
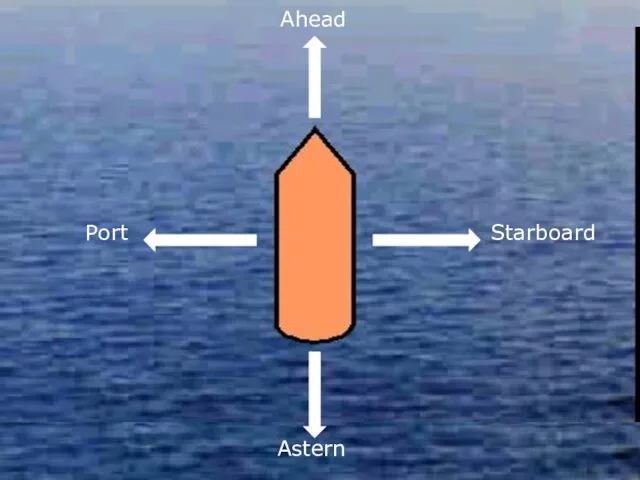
- 35. Ahead Starboard Astern Port
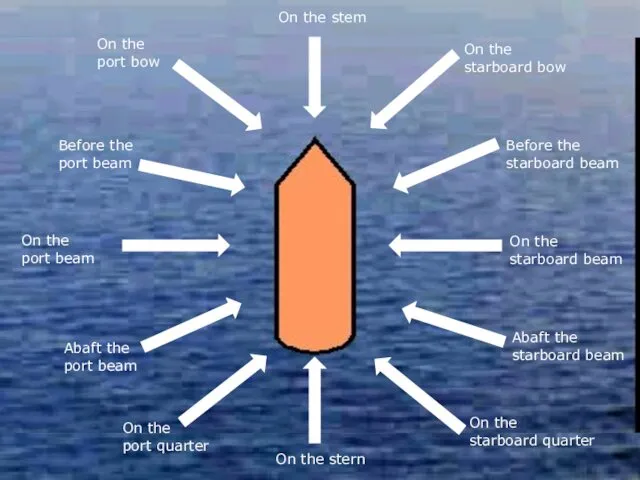
- 36. On the stem On the starboard bow Before the starboard beam On the starboard beam Abaft
- 38. Скачать презентацию















 Еуразия жағалауындағы мұхиттар мен теңіздер. Атлант мұхиты
Еуразия жағалауындағы мұхиттар мен теңіздер. Атлант мұхиты Водоемы. Интерактивный кроссворд
Водоемы. Интерактивный кроссворд Природная зональность. (2 класс)
Природная зональность. (2 класс) The socio-economic, political and cultural achievements of the Republic of Kazakhstan and their role in the world community
The socio-economic, political and cultural achievements of the Republic of Kazakhstan and their role in the world community Урал. Освоение и хозяйство. 2 часть. 9 класс
Урал. Освоение и хозяйство. 2 часть. 9 класс Внесение изменений в генеральный план Находкинского городского округа
Внесение изменений в генеральный план Находкинского городского округа Нововаршавский район
Нововаршавский район Классификация полезных ископаемых
Классификация полезных ископаемых Схема проезда
Схема проезда Объединенные Арабские Эмираты
Объединенные Арабские Эмираты Всемирный День Земли
Всемирный День Земли Моя малая Родина. Город Добрянка
Моя малая Родина. Город Добрянка Озера Кольского края
Озера Кольского края Географические открытия
Географические открытия Современная политическая карта мира
Современная политическая карта мира Восточная Сибирь. Величие и суровость природы
Восточная Сибирь. Величие и суровость природы 20230321_22.02.2023_g_master_klass
20230321_22.02.2023_g_master_klass Поселок Екатериновка Саратовской области
Поселок Екатериновка Саратовской области Хозяйство Северо-Западного экономического района РФ
Хозяйство Северо-Западного экономического района РФ Изображение на плане неровностей земной поверхности
Изображение на плане неровностей земной поверхности Типы климата на территории России
Типы климата на территории России Открытия русских путешественников
Открытия русских путешественников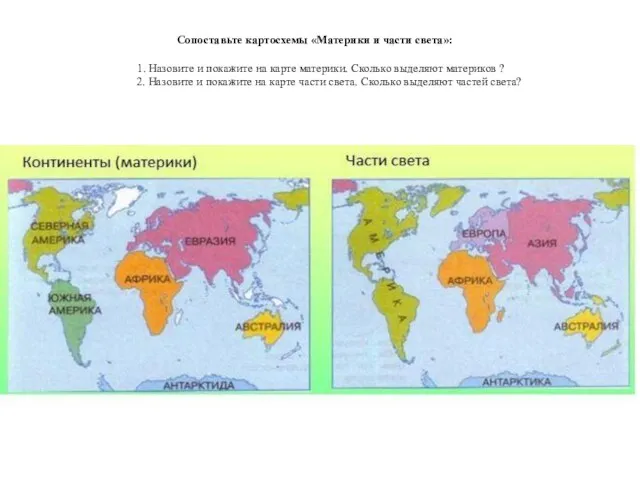 Сопоставьте картосхемы Материки и части света
Сопоставьте картосхемы Материки и части света Природно-хозяйственные зоны России
Природно-хозяйственные зоны России Живу в Беларуси и этим горжусь я
Живу в Беларуси и этим горжусь я Дендрологічний парк Софіївка
Дендрологічний парк Софіївка Основные течения Мирового океана
Основные течения Мирового океана Україна і світ
Україна і світ