Содержание
- 2. Administrative Division Japan is a unitary state Japan is divided into 47 prefectures The central government
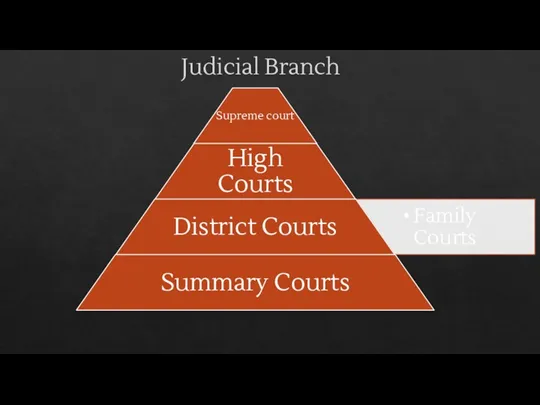
- 3. Judicial Branch
- 4. The Emperor of Japan is the Head of State. His Functions Are: Promulgation of amendments of
- 5. The Cabinet Execution of the law. Conduct of foreign affairs. Conclusion of treaties (with the consent
- 6. The Prime Minister Current Prime Minister is Shinzo Abe To become The Prime Minister you need
- 7. Japanese Parliament (722 Seats)
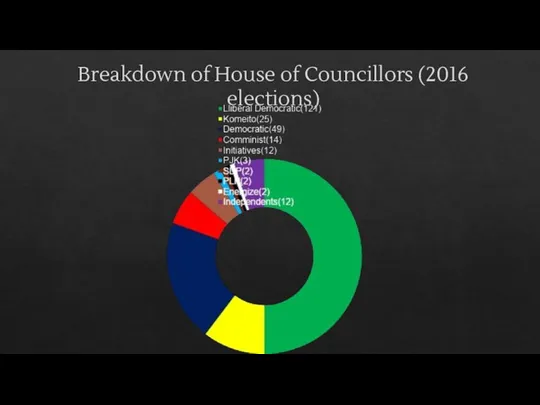
- 8. The House of Councillors Consists of 242 members Cannon be dissolved Members are elected Members need
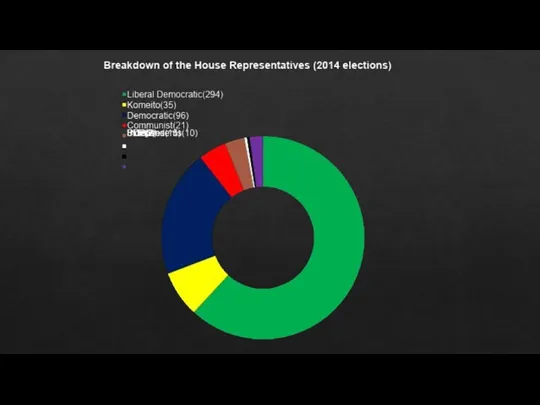
- 9. The House of Representatives Consists of 475 members Can be dissolved by the Prime Minister Members
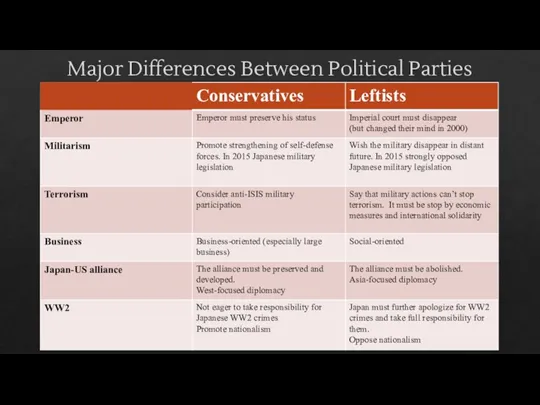
- 10. Political Parties
- 11. “…it has become all but impossible to distinguish the basic policy lines followed by the two
- 12. Major Differences Between Political Parties
- 14. Breakdown of House of Councillors (2016 elections)
- 15. Japanese Self-Defense Forces According to the Article 9 of the Constitution of Japan the country has
- 16. An Army Which Does Not Exist Ranked 7 in the Global Firepower Ranking Active Frontline Personnel:
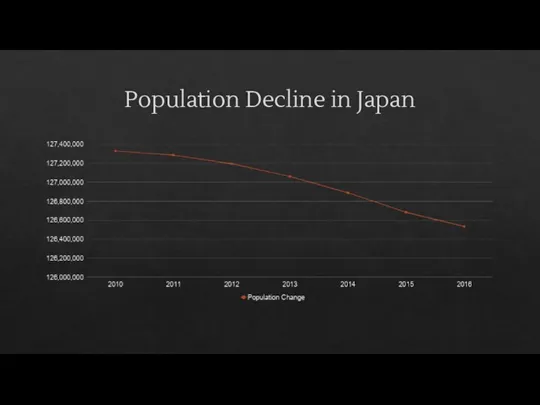
- 17. Population Decline in Japan
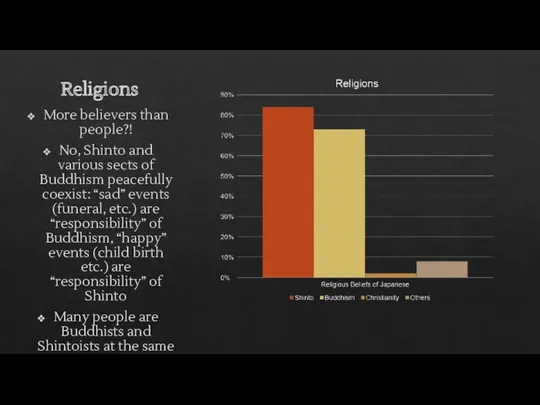
- 18. Religions More believers than people?! No, Shinto and various sects of Buddhism peacefully coexist: “sad” events
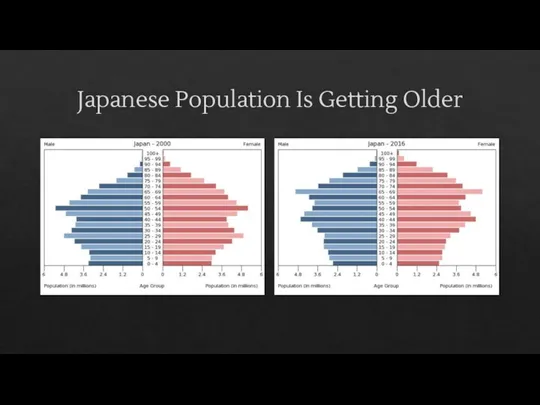
- 19. Japanese Population Is Getting Older
- 20. Japan Is a Monoethnic Country
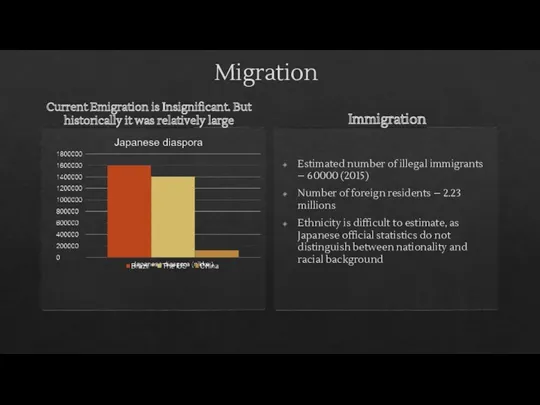
- 21. Migration Current Emigration is Insignificant. But historically it was relatively large Immigration Estimated number of illegal
- 22. Ainu People Indigenous people of Japan Inhabit mainly the island Hokkaido The Ainu have historically suffered
- 23. Burakumin People Causes of discrimination: Religion (they murdered animals and because of that they would never
- 24. Foreign Policy Priorities Strengthening Japan-US alliance Enhancing relations with neighboring countries Solvation of territorial issues Strengthening
- 25. Economic Diplomacy Economic diplomacy is when the government uses full spectrum of economic tools to promote
- 26. Foreign Relations
- 27. Japan-US Relations Despite Japan's defeat and subsequent occupation by Americans, relations with the United States have
- 28. Japanese Relations with Southeast Asia In World War II Japan went to war partly to gain
- 29. Japanese-Korean Relations Japan's harsh colonization of Korea in the early twentieth century has left relations strained
- 30. Relations with China After WWII under U.S. pressure, Japan did not establish relations with the People's
- 31. Relations with Russia Russia. Japan's relations with Russia have been strained throughout the postwar period. In
- 32. Major Export Partners China (131 billion $) The US (128 billion $) South Korea (52 billion
- 33. Membership in International Organizations UN IMF World Bank WTO ADB (Asian Development Bank) G20 IOC
- 35. Скачать презентацию
























 Черная металлургия России. Факторы и география размещения
Черная металлургия России. Факторы и география размещения Ханты-Мансийский Автономный округ. Югра
Ханты-Мансийский Автономный округ. Югра Минеральные ресурсы России
Минеральные ресурсы России Ненцы - самодийский народ в России
Ненцы - самодийский народ в России Население России
Население России Характеристика Индии
Характеристика Индии Географические координаты
Географические координаты Куда текут реки. Урок окружающего мира в 1 классе
Куда текут реки. Урок окружающего мира в 1 классе Профайлинг. Израиль мемлекеті
Профайлинг. Израиль мемлекеті Всероссийская туристско-краеведческая экспедиция Я познаю Россию. Реклама своей деятельности
Всероссийская туристско-краеведческая экспедиция Я познаю Россию. Реклама своей деятельности Южно-Африканская Республика
Южно-Африканская Республика Центральный федеральный округ. Брянская область
Центральный федеральный округ. Брянская область Ліс
Ліс Льодовики та багаторічна мерзлота. Формування льодовиків
Льодовики та багаторічна мерзлота. Формування льодовиків Географическая оболочка Земли
Географическая оболочка Земли Город Магнитогорск
Город Магнитогорск Погода и климат
Погода и климат Герб Саратовской области
Герб Саратовской области Анализ климатограмм
Анализ климатограмм Жемчужина родного края. Саратовская область, село Усовка
Жемчужина родного края. Саратовская область, село Усовка Вулканические взрывы или извержения вулканов
Вулканические взрывы или извержения вулканов Єллоустонський національний парк (Yellowstone National Park)
Єллоустонський національний парк (Yellowstone National Park) Эпоха Великих географических открытий
Эпоха Великих географических открытий Корисні копалини Черкащини
Корисні копалини Черкащини Размещение и миграции населения, их виды
Размещение и миграции населения, их виды Четвертичная геология
Четвертичная геология Реки
Реки Индия (Бхарат)
Индия (Бхарат)