Содержание
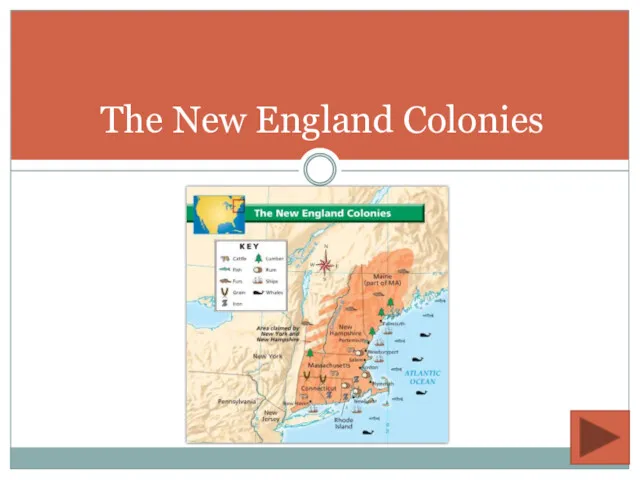
- 2. The New England Colonies
- 3. Geography Location New Hampshire, Vermont, Maine, Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Rhode Island Terrain Hills and low mountains,
- 4. Establishment Chartered by the Puritans Wanted to reform the Church of England Persecuted by King Charles
- 5. Growth and Change New England colonists earned their livelihoods in several different ways Leather goods, fishing,
- 6. New England Colonies – Comprehension Check Question 1: Why were the New England Colonies founded? A.
- 7. New England Colonies – Comprehension Check Question 2: How did most New England colonists make their
- 8. The Middle Colonies
- 9. Geography Location New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware Terrain Mostly lowland Weather and Resources Warmer
- 10. Establishment New York began as the Dutch colony of New Netherland Was an economic success (farming
- 11. Growth and Change Wheat was the top cash crop in this area, produced by small farms
- 12. Middle Colonies – Comprehension Check Question 1: Where did most of the colonists in the Middle
- 13. Middle Colonies – Comprehension Check Question 2: What is the main cash crop in the Middle
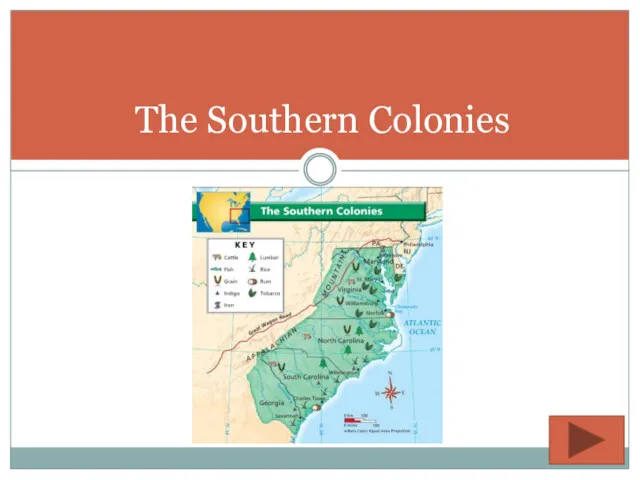
- 14. The Southern Colonies
- 15. Geography Location South of the Mason-Dixon Line Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia Terrain
- 16. Establishment In 1632 King Charles I granted charter for a colony in Maryland Chartered by the
- 17. Growth and Change Two distinct ways of life The Tidewater region Plantations – crops of cotton,
- 18. Southern Colonies – Comprehension Check Question 1: What is the climate in the Southern Colonies? A.
- 19. Southern Colonies – Comprehension Check Question 2: What are the two distinct ways of life in
- 21. Скачать презентацию















 Гидрологический расчет параметров речного стока
Гидрологический расчет параметров речного стока Суворовский район в Тульской области России
Суворовский район в Тульской области России Водные богатства Земли
Водные богатства Земли Своя игра. Водные объекты Земли
Своя игра. Водные объекты Земли Водный режим водохранилищ. Их влияние на речной сток и окружающую среду
Водный режим водохранилищ. Их влияние на речной сток и окружающую среду Геологическая деятельность
Геологическая деятельность Туризм в Казахстане
Туризм в Казахстане Путешествие в Закавказье. Иберия - Колхида
Путешествие в Закавказье. Иберия - Колхида Состав и функции биосферы
Состав и функции биосферы Степная зона России
Степная зона России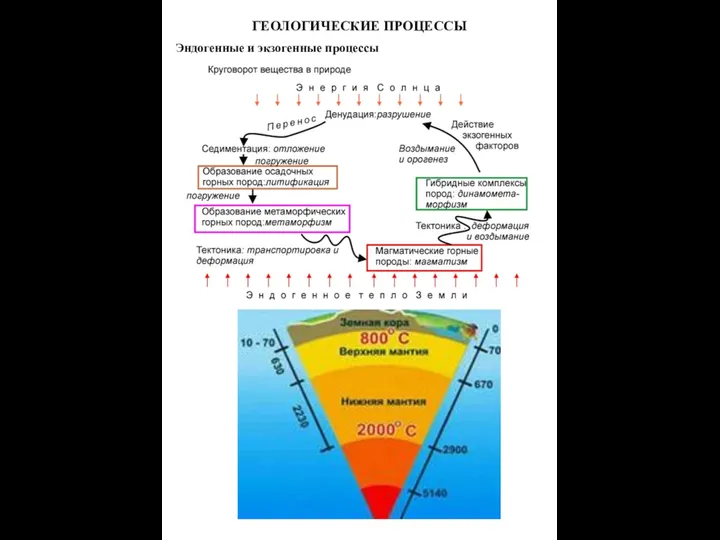 Геологические процессы. Эндогенные и экзогенные процессы
Геологические процессы. Эндогенные и экзогенные процессы Восточная Сибирь
Восточная Сибирь Физико-географическая характеристика районов проведения спортивных туров
Физико-географическая характеристика районов проведения спортивных туров География России в денежных знаках
География России в денежных знаках Фотофиксация. Лекция №8
Фотофиксация. Лекция №8 Виды туризма и их география
Виды туризма и их география Природные районы Дальнего Востока
Природные районы Дальнего Востока ЭГП Дальний Восток
ЭГП Дальний Восток Интересные факты про Беларусь
Интересные факты про Беларусь Трактовки понятия ландшафт. Типологическая классификация ландшафтов. Ландшафтное картографирование
Трактовки понятия ландшафт. Типологическая классификация ландшафтов. Ландшафтное картографирование Разнообразие природных комплексов России
Разнообразие природных комплексов России кл_Животные Северной Америки
кл_Животные Северной Америки Азербайджан. Старое и новое
Азербайджан. Старое и новое Волга
Волга Монако
Монако Geography Rulers and politics
Geography Rulers and politics Южная Америка: образ материка
Южная Америка: образ материка Масштаб и его виды
Масштаб и его виды