Слайд 2

CONTENTS:
General characteristic of the Cluster;
Findings from GLOBE data: Societal
practicies and values;
Findings from Globe data: Outstanding leadership attributes;
Implications for managers;
Personal opinion.
Слайд 3
ARAB WORLD (ARAB NATION)
22 arabic-speaking countries (identity – Arabic language)
Слайд 4
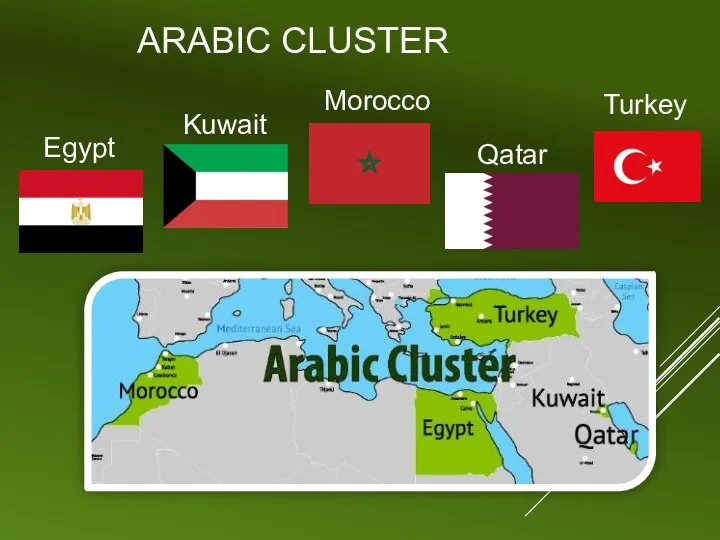
ARABIC CLUSTER
Egypt
Morocco
Kuwait
Turkey
Qatar
Слайд 5
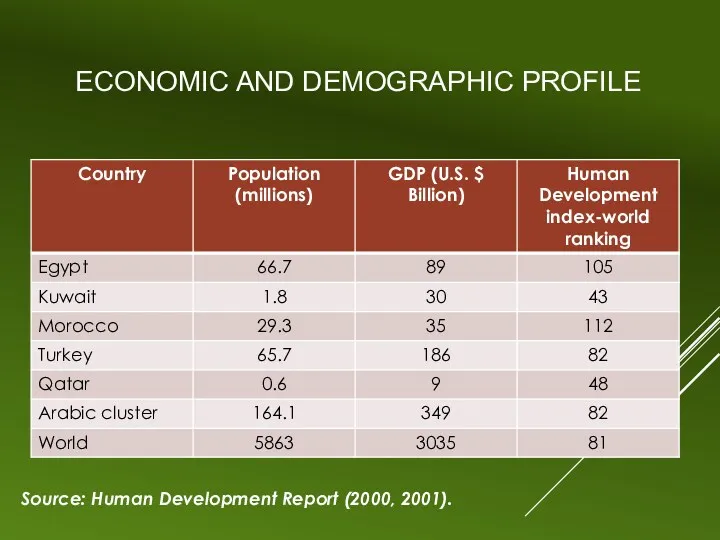
ECONOMIC AND DEMOGRAPHIC PROFILE
Source: Human Development Report (2000, 2001).
Слайд 6

HISTORICAL FOUNDATIONS
The earliest civilizations – Egypt, Anatolia, Morroco.
Egypt and
Morroco were invided by Arabs in the 7th century
Egypt was conquered by Turks (16th century), French invasion (1798-1805), Ottoman province until 1914. Then, under British Protectorate (1914-1952)
Morroco was under Spanish and French protectorates (1912 – 1956)
Kuwait – the terriotory in1500s under Portuguese control, 18th century Anaizia tribe founded Kuwait, 1899-1914 British protectorate
Qatar – 1872-1914 under Ottoman rule, British protectorate (1916-1968)
Turkey – the Ottoman empire (1299-1923), since 1923 – republic
Слайд 7

LEGAL SYSTEMS
Egypt – mix of English common law, Napoleonic codes and
Islamic law
Kuwait – civil legal system (Islamic law is important)
Morocco – mix of Islamic law, French and Spanish civil law
Qatar – Islamic law
Turkey – European civil law
Слайд 8

POLITICAL SYSTEMS
Egypt - Semi-Presidential Republic
Kuwait – Constitutional monarchy
Morocco – Constitutional monarchy
Qatar
– Absolute monarchy
Turkey - Parliamentary Republic
Слайд 9

RELIGION
Egypt – Sunni Muslims (90%) and Coptic Christians (10%);
Kuwait – Sunni
Muslims (70%) and Shi’a Muslims (30%);
Morocco – Muslims (98%);
Turkey – Muslims (99%);
Qatar – Muslims.
Слайд 10

SHARIA
Hygiene and purification laws (the manner of cleansing);
Economic laws (Zakāt, Waqf,
the prohibition on interest or Riba);
Dietary laws;
Theological obligations;
Criminal jurisprudence;
Military jurisprudence (Jihad, offensive and defensive; rules regarding prisoners of war);
Dress code, including hijab;
Other topics include customs and behaviour, slavery and the status of non-Muslims.
Слайд 11

SOCIO-CULTURAL ELEMENTS: LANGUAGE
EGYPT, KUWAIT, MOROCCO, QATAR
Arabic language (Afro-Asiatic family)
TURKEY
Turkish language (Turkic
family)
Слайд 12

ARAB IDENTITY AND ETHNICITY
Arabs are very consious about their Arab identity;
language and common culture creates a feeling of belonging to the Arab world
Defining who is an Arab is based on the following two criteria:
Genealogical: someone who can trace his or her ancestry to the original inhabitants of the Arabian Peninsula and the Syrian Desert (tribes of Arabia).
Linguistic: someone whose first language, and cultural expression is Arabic.
Слайд 13

SOCIO-CULTURAL ELEMENTS: CLOTHING
Слайд 14

SOCIO-CULTURAL ELEMENTS: FOOD
Слайд 15

VALUES
Religion
Family and network of interdependent relations
Equity in personal worth
Honor and respect
Life
Слайд 16
Слайд 17
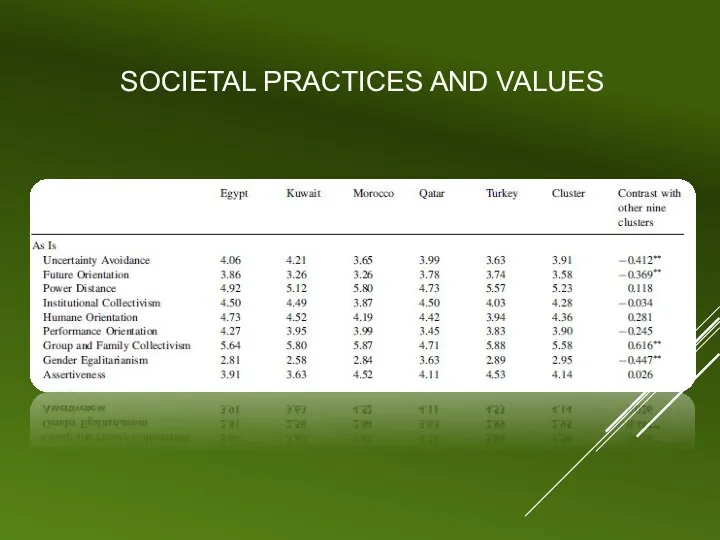
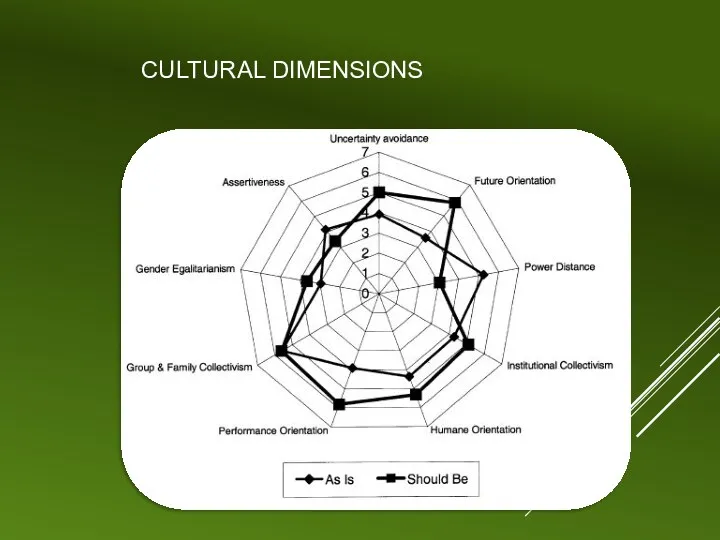
SOCIETAL PRACTICES AND VALUES
Слайд 18
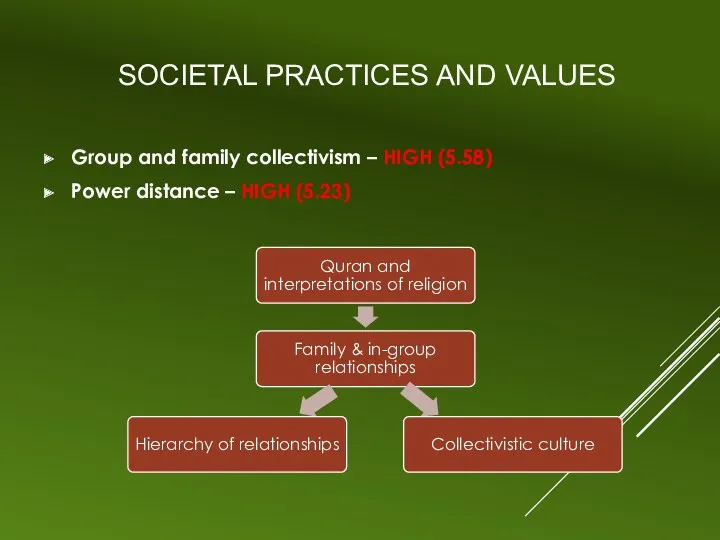
SOCIETAL PRACTICES AND VALUES
Group and family collectivism – HIGH (5.58)
Power distance
– HIGH (5.23)
Слайд 19

SOCIETAL PRACTICES AND VALUES
Future orientation – LOW(3.58)
Concept of “fate”
Low significance of
planning and influencing the future
Gender egalitarianism – LOW (2.95)
Sex role stereotypes and inequalities
Masculine society
Слайд 20

SOCIETAL PRACTICES AND VALUES
Uncertainty avoidance – MEDIUM (3.91)
Institutional collectivism – MEDIUM
(4.28)
Humane orientation – MEDIUM (4.36)
Performance orientation – MEDIUM (3.90)
Assertiveness – MEDIUM (4.14)
Слайд 21

COMPARISON AMONG CLUSTER
Morocco - highest score on power distance.
Turkey and
Morocco - similar results in some cultural dimensions.
Egypt – highest score on humane orientation and future orientation.
Kuwait - highest score on uncertainty avoidance.
Qatar - highest score on gender egalitarianism.
Слайд 22
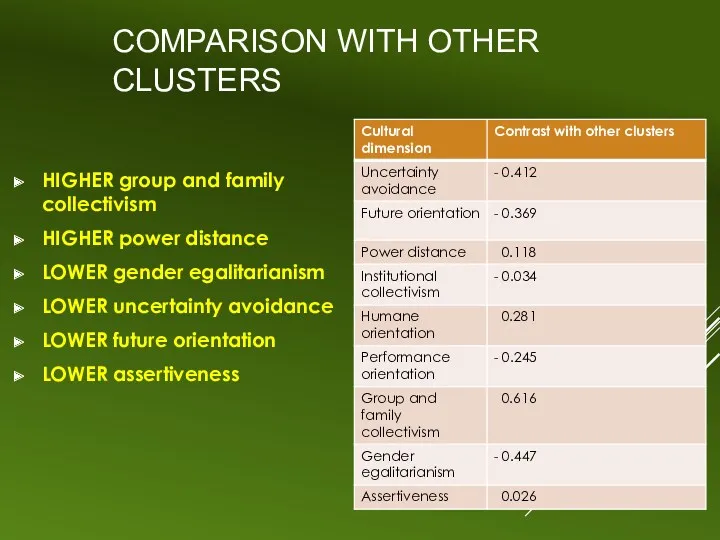
COMPARISON WITH OTHER CLUSTERS
HIGHER group and family collectivism
HIGHER power distance
LOWER gender
egalitarianism
LOWER uncertainty avoidance
LOWER future orientation
LOWER assertiveness
Слайд 23
Слайд 24
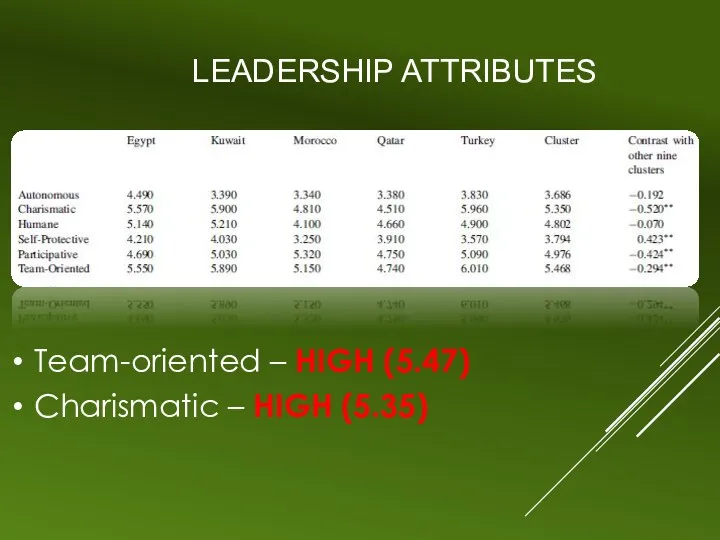
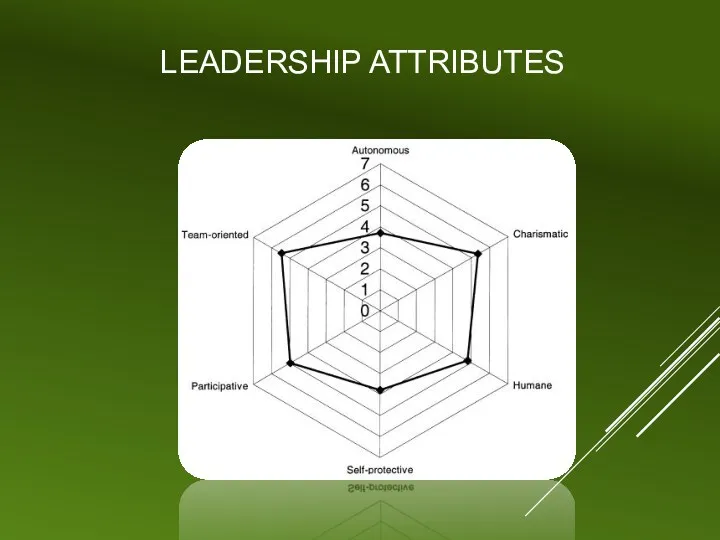
LEADERSHIP ATTRIBUTES
Team-oriented – HIGH (5.47)
Charismatic – HIGH (5.35)
Слайд 25

LEADERSHIP ATTRIBUTES
Team-oriented – HIGH Influence (5.47)
Group-oriented & team-builders
Collaborative, loyal,
consultative
Diplomatic, intra-group conflict avoiders, win-win problem-solvers
Charismatic – HIGH influence (5.35)
Visionary & future oriented
Inspirational, positive, enthusiastic, motivational, confidence builders
Risk takers & self-sacrificial
Decisive, logical
Слайд 26

LEADERSHIP ATTRIBUTES
Participative
Non-autocratic & non-dictatorial manner
Delegate tasks
SLIGHT Influence (4.98)
Humane
Generous
& compassionate in a modest and patient manner
SLIGHT Influence (4.80)
Слайд 27

LEADERSHIP ATTRIBUTES
Self-protective
Self-centered, status conscious, conflict inducer
NEGATIVE Influence (3.79)
Autonomous
Individualistic, independent,
autonomous and unique
NEGATIVE Influence (3.69)
Слайд 28

LEADER
sets a vision and promotes performance-orientation in a collectivistic manner
Initiates change
and improvement by keeping group solidarity and avoiding nepotism
Слайд 29

LEADERSHIP ATTRIBUTES: DIFFERENCES AMONG CLUSTER
Kuwait, Turkey and Egypt – team-oriented and
charismatic
Morocco and Qatar - participative and team-oriented
Слайд 30

COMPARISON WITH OTHER CLUSTERS
Have modest style, not stick out, keep group
solidarity
Be a man with a “miracle”, who leads followers to ideals, initiate change and improvement
Слайд 31

IMPLICATIONS
FOR MANAGERS
Develop personal relationships and group solidarity;
Build trust;
Employ traditional approaches
and promote practices and values needed for competition (dual set of values);
Leader can evaluate subordinates, but he is responsible for their well-being;
Unacceptable for subordinates to evaluate the leader;
Use “Consultation” and “Third party” conflict resolution.






























 Уругвай
Уругвай English book analysis
English book analysis Геополитика и международные отношения
Геополитика и международные отношения Политическая жизнь современного общества. Политический конфликт ( 11 класс)
Политическая жизнь современного общества. Политический конфликт ( 11 класс) Новая экономическая политика
Новая экономическая политика Биополитика
Биополитика Політичні режими
Політичні режими Политическая власть нов
Политическая власть нов Политика. Субъекты
Политика. Субъекты Политическая жизнь современного общества. Политический конфликт
Политическая жизнь современного общества. Политический конфликт Nelson Mandela & South African Apartheid
Nelson Mandela & South African Apartheid Предварительное голосование 2023
Предварительное голосование 2023 Основы государственной культурной политики Российской Федерации
Основы государственной культурной политики Российской Федерации Political system of the USA
Political system of the USA ЛДПР - Либерально-демократическая партия России
ЛДПР - Либерально-демократическая партия России The political system of Usa
The political system of Usa Государство в политической системе общества
Государство в политической системе общества Влияние международных отношений на политическую карту мира
Влияние международных отношений на политическую карту мира Преступления против мира и безопасности человечества
Преступления против мира и безопасности человечества Дело, касающееся некоторых районов залегания фосфатных руд в Науру. Науру против Австралии
Дело, касающееся некоторых районов залегания фосфатных руд в Науру. Науру против Австралии Мировая политика и международные отношения
Мировая политика и международные отношения Цель функционирования Молодежной палаты
Цель функционирования Молодежной палаты Национализм как политическая идеология
Национализм как политическая идеология Политические элиты в фокусе отечественных исследований
Политические элиты в фокусе отечественных исследований Политические системы стран Ближнего Востока
Политические системы стран Ближнего Востока Middle East policy of the European Union in the beginning of the XXI century
Middle East policy of the European Union in the beginning of the XXI century Международный терроризм - угроза национальной безопасности
Международный терроризм - угроза национальной безопасности Политическое развитие и модернизация
Политическое развитие и модернизация