Содержание
- 2. State vs Nation: Some may believe that the state and nation are the same…, or quite
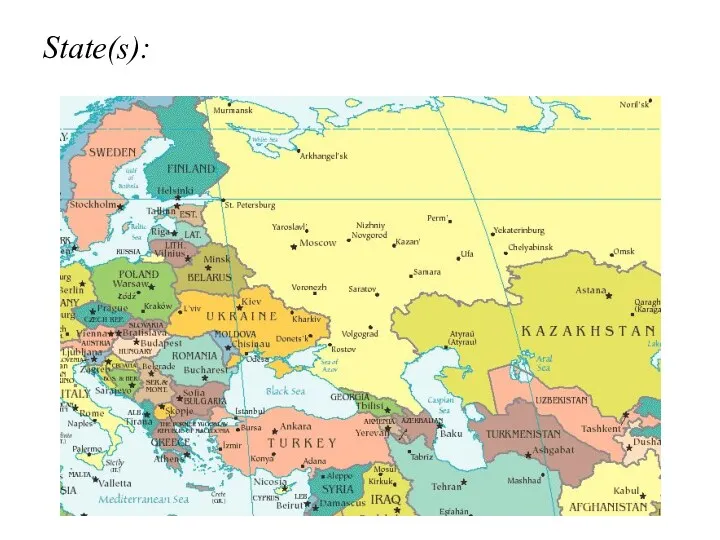
- 3. State(s):
- 4. The State and states: Meaning of the “state” I a state – a) a country; b)
- 5. State(s): state (a general definition): a complex political organization and the combination of people, territory, &
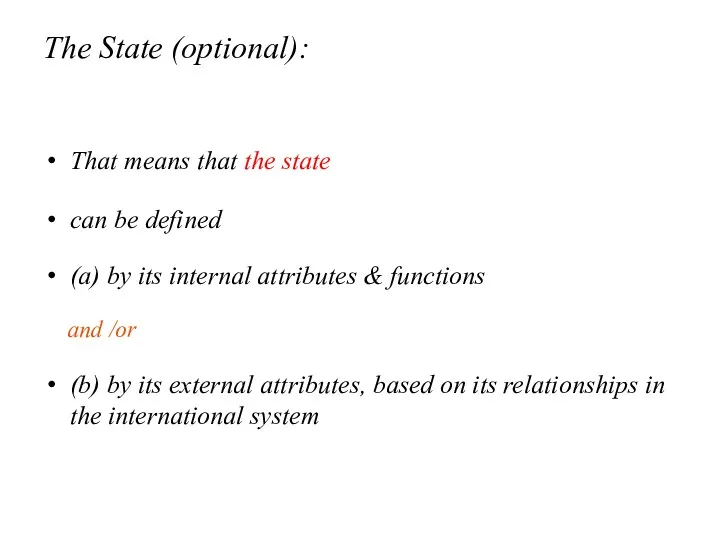
- 6. The State (optional): That means that the state can be defined (a) by its internal attributes
- 7. Attributes of the state: most important internal attributes (characteristics) of the state: 1. a territory (bounded
- 8. International attributes of the State: 1. international border recognized by other states 2. sovereignty (independence) in
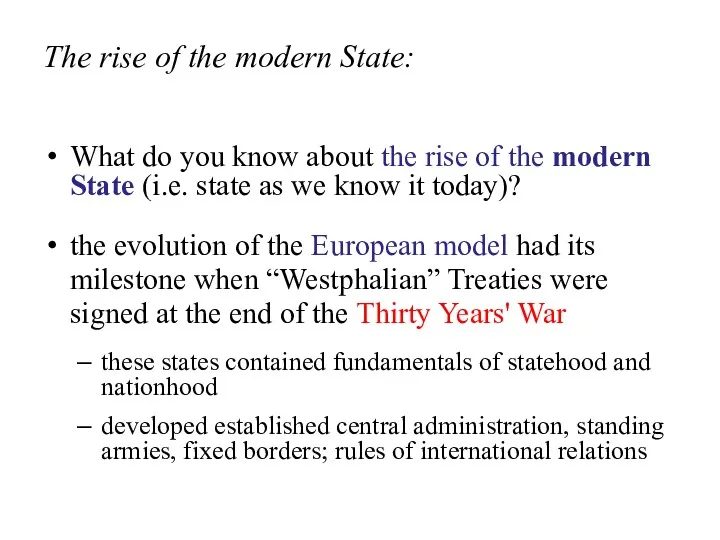
- 9. The rise of the modern State: What do you know about the rise of the modern
- 10. The State vs. Nation: How the State differs from Nation? a nation is usually defined in
- 11. The State vs. Nation: ethnic vs. civic nation ethnic n. based on ethnicity (Japan) civic n.
- 12. The State vs. Nation: How the State differs from Nation? a nation may be larger than
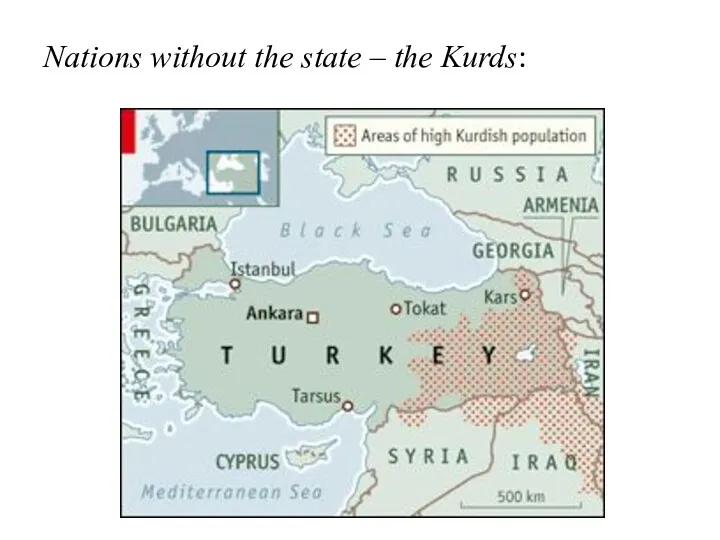
- 13. Nations without the state – the Kurds:
- 14. The State vs. Nation (optional): problems with definitions of some concepts: ethnicity, nationality… identity… these are
- 15. The Nation-State: There another important concept: the nation-state (= fusion of 2 different principles of state
- 16. Classifications of states: classifications of states – are many: i.e. we can classify states by: geographic
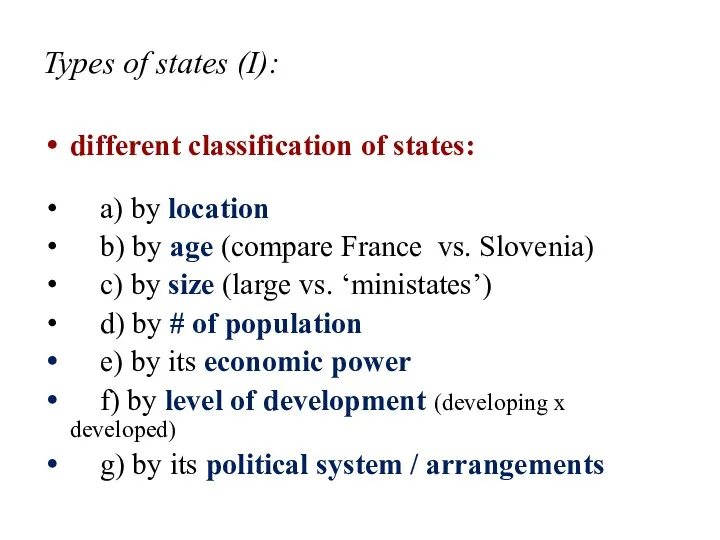
- 17. Types of states (I): different classification of states: a) by location b) by age (compare France
- 18. Types of states (II): by political system / arrangements: States are organized differently… they may have
- 19. Types of states (II): thus, there may be: democracies or non-democracies republics vs. monarchies unitary (e.g.
- 20. Forms of State: Forms of State (formal distinction): monarchy – hereditary rule by one person (king,
- 21. Images of Britain: The Queen Elizabeth II – she is liked by most of the population
- 22. Classifications of states: By different political –territorial arrangements… unitary vs. federal states [vs. confederations?] How they
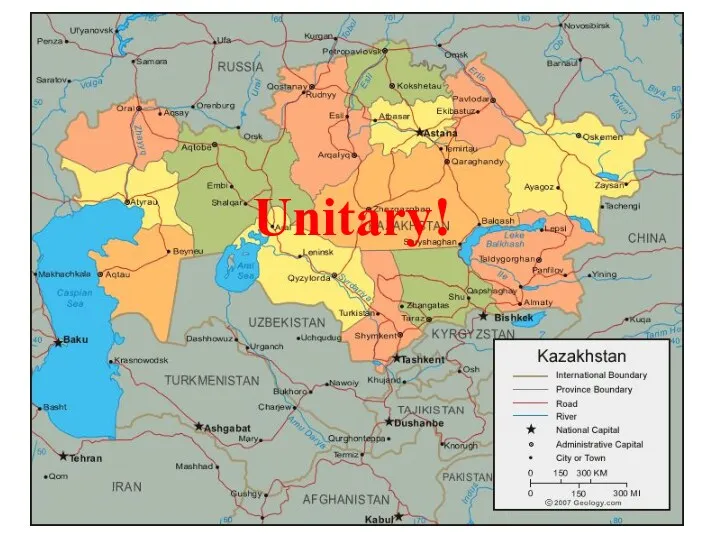
- 23. Unitary states & federations: unitary vs. federal systems unitary - a system of government in which
- 24. Federal Republic of Germany – Bundesländer Each of the 16 federal subjects has its own constitution
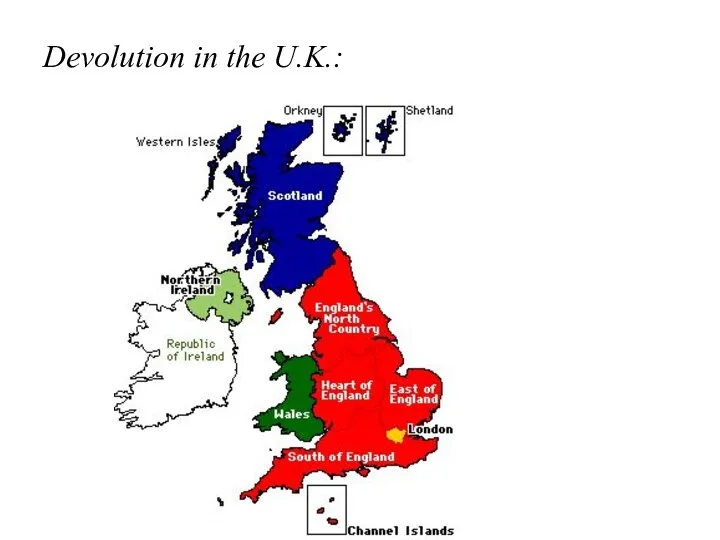
- 25. State and devolution (optional): State and devolution What is devolution? a process by which more autonomy
- 26. Devolution in the U.K.:
- 27. State and devolution (optional): Other examples of devolution / devolved Government: Spain: greater autonomy desired by
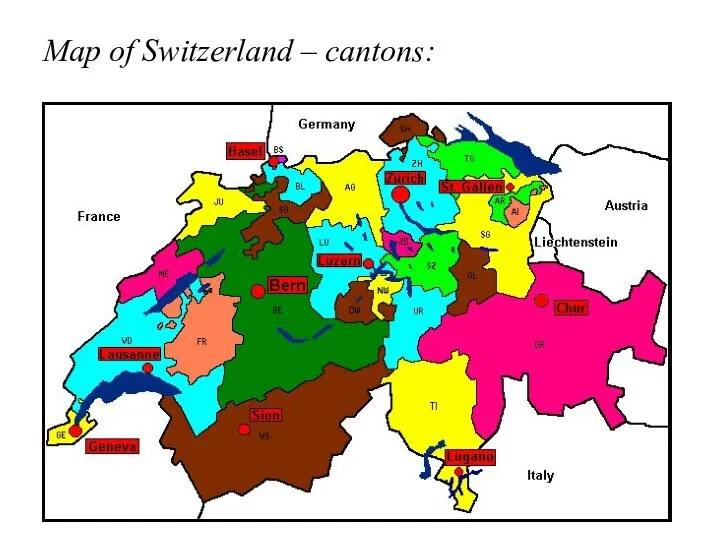
- 28. Confederations: Switzerland - a special case: Confoederatio Helvetica Switzerland is often called a “confederation”
- 29. Switzerland – a confederation: Switzerland has some unique features of the political system…: 1. significant regional
- 30. Map of Switzerland – cantons:
- 31. Switzerland: 2. participatory (semi-direct) democracy there are many mandatory referenda each year on proposed laws (or
- 32. Unitary!
- 33. Seminar (optional): What kind of federation is Russia? [a very asymmetrical one, and changing…]
- 35. Скачать презентацию























![Seminar (optional): What kind of federation is Russia? [a very asymmetrical one, and changing…]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/249081/slide-32.jpg)
 Қазақстанның сыртқы саясатының қалыптасу бағыты
Қазақстанның сыртқы саясатының қалыптасу бағыты Политические идеологии
Политические идеологии Организация Североатлантического договора (НАТО)
Организация Североатлантического договора (НАТО) Участие гражданина в политической жизни страны
Участие гражданина в политической жизни страны Политическая деятельность. (10 класс)
Политическая деятельность. (10 класс) Електоральні уподобання українців. Дослідження громадської думки. Березень 2019
Електоральні уподобання українців. Дослідження громадської думки. Березень 2019 Політична еліта і політичне лідерство
Політична еліта і політичне лідерство емлекет — белгілі бір аумаққа иелік етіп, сол жердегі халықтың еркін дамуына мүмкіндік беретін
емлекет — белгілі бір аумаққа иелік етіп, сол жердегі халықтың еркін дамуына мүмкіндік беретін Российская экологическая партия Зеленые
Российская экологическая партия Зеленые Государство: понятие, признаки, функции, виды
Государство: понятие, признаки, функции, виды Socjalizm
Socjalizm Авторитаризм и его разновидности
Авторитаризм и его разновидности Политика. Власть политика
Политика. Власть политика Типы лидеров
Типы лидеров Політична свідомість та політична культура
Політична свідомість та політична культура Central problems in international relations
Central problems in international relations Концепция разделения властей Ш. Монтескье
Концепция разделения властей Ш. Монтескье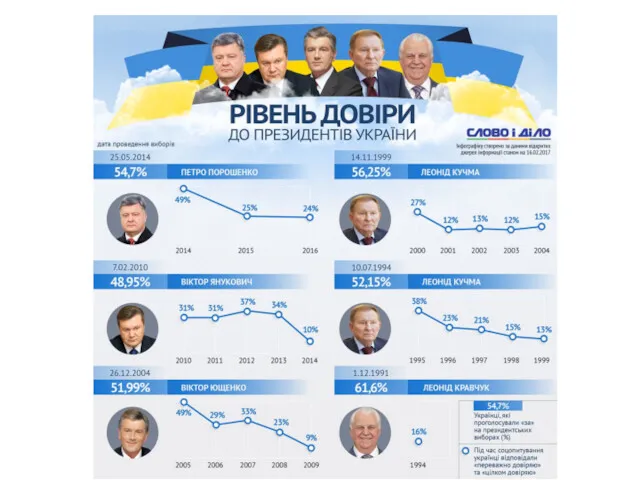 Массовые акции протеста в Украине
Массовые акции протеста в Украине Межгосударственные конфликты и попытки их решения
Межгосударственные конфликты и попытки их решения Политика. Субъекты
Политика. Субъекты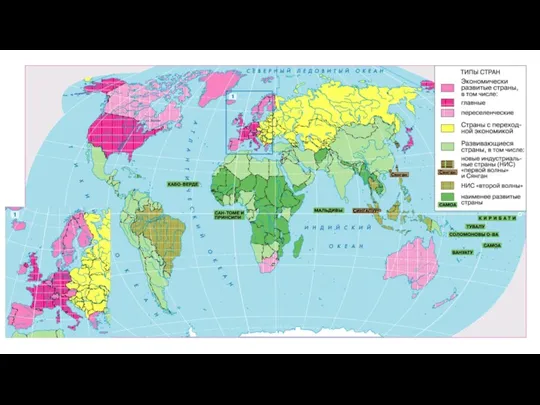 Политическое устройство мира
Политическое устройство мира The political system of Usa
The political system of Usa Исламофобия в России
Исламофобия в России Саясат және оның қызметтері
Саясат және оның қызметтері Проблема війни та миру
Проблема війни та миру Организация договора о коллективной безопасности (ОДКБ)
Организация договора о коллективной безопасности (ОДКБ) Метод прогнозных сценариев в исследовании социально-экономических и политических процессов
Метод прогнозных сценариев в исследовании социально-экономических и политических процессов Демократия. Формы демократии
Демократия. Формы демократии