Population: 59.6 million
Territory: 94,525 sq. miles
Year of Independence: 12th century
Constitution: unwritten;
partly statutes, partly common law and practice
Head of State: Queen Elizabeth II
Head of Government: Prime Minister Gordon Brown.
Language: English, plus about 600,000 who regularly speak Welsh and 60,000 who speak the Scottish form of Gaelic
Religion:
Anglican: 26.1 million
Roman Catholic: 5.7 million
Presbyterian: 2.6 million
Methodist: 1.3 million
Other Christian: 2.6 million
Muslim: 1.5 million
Hindu: 500,000
Sikh: 330,000
Jewish: 260,000
Other: 300,000
No religion: 8.6 million
Did not state a religion: 4.4 million
Country Biography











 Билік саяси феномен ретінде
Билік саяси феномен ретінде Республикалық референдум
Республикалық референдум Политология как наука. Возникновение и развитие политики, политических учений и политической науки: концепции власти
Политология как наука. Возникновение и развитие политики, политических учений и политической науки: концепции власти Political parties in Estonia
Political parties in Estonia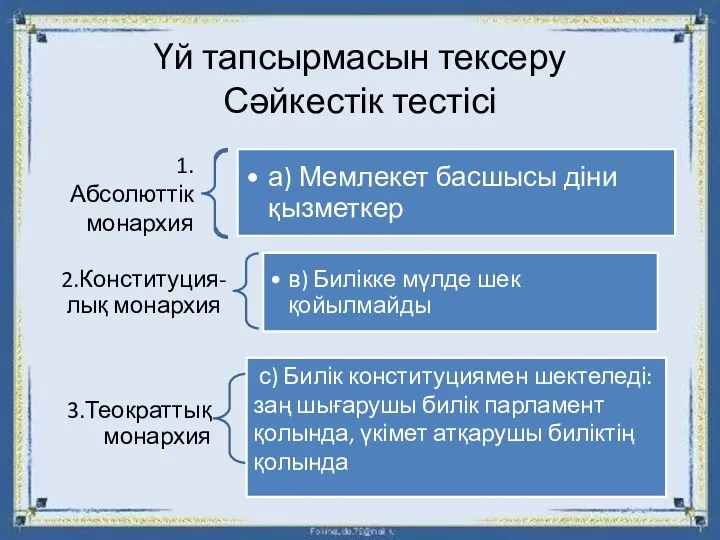 Абсалюттік монархиялы елдерді саяси картадан көрсетіңдер
Абсалюттік монархиялы елдерді саяси картадан көрсетіңдер Создание ДНР. Историко-территориальный, этно-национальный, национально-политический аспекты. Историческое возрождение
Создание ДНР. Историко-территориальный, этно-национальный, национально-политический аспекты. Историческое возрождение Социальная природа международного терроризма в современном мире
Социальная природа международного терроризма в современном мире United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization Ұлттық мүдде - халықаралық қатынастар мен сыртқы саясатты сараптаудың негіздері
Ұлттық мүдде - халықаралық қатынастар мен сыртқы саясатты сараптаудың негіздері Политический процесс и культура политического участия
Политический процесс и культура политического участия Отчетная конференция Череповецкого местного городского отделения ВПП ЕДИНАЯ РОССИЯ
Отчетная конференция Череповецкого местного городского отделения ВПП ЕДИНАЯ РОССИЯ Ідеологічно-пропагандивний блок
Ідеологічно-пропагандивний блок Дирижер симфонии внешней политики России С.В. Лавров
Дирижер симфонии внешней политики России С.В. Лавров ДНР - минский договор и закон о реинтеграции
ДНР - минский договор и закон о реинтеграции Политическая власть
Политическая власть Визначення та класифікація етнічних конфліктів
Визначення та класифікація етнічних конфліктів Президент РФ
Президент РФ Соціальна політика Республіки Польща
Соціальна політика Республіки Польща Парламентские дебаты
Парламентские дебаты Общественно-политическая жизнь СССР в 1983 – 1984 гг
Общественно-политическая жизнь СССР в 1983 – 1984 гг Компоненты политической системы общества
Компоненты политической системы общества Межведомственное взаимодействие в рамках реализации стратегии государственной антинаркотической политики РФ
Межведомственное взаимодействие в рамках реализации стратегии государственной антинаркотической политики РФ Политические партии
Политические партии Формирование нации единого будущего. Лекция № 15
Формирование нации единого будущего. Лекция № 15 Політичні режими
Політичні режими Що таке євронтеграція. Хто відповідальний за неї в Україні
Що таке євронтеграція. Хто відповідальний за неї в Україні Саясаттану пәні, ұғымдары,әдіс-тәсілдері мен қызметтері
Саясаттану пәні, ұғымдары,әдіс-тәсілдері мен қызметтері Political theory and Politics (Introductory seminar)
Political theory and Politics (Introductory seminar)