Содержание
- 2. Agenda Discussion Course Format and Evaluation About Programming and Scripting History of Programming Styles and Methodologies
- 3. Goal of CPR101 Make you a better programmer Learn how applications and system software interact Modern
- 4. Course Format Evaluation & Success
- 5. Quiz Each class will begin with a 15 minute quiz ( 5 short answer questions) You
- 6. News of the Week After the quiz there will be a 15 minute discussion on a
- 7. Weekly Lecture Lectures are 80 minutes in length and are instructor centred Ask questions anytime during
- 8. Weekly Activity Weekly Activity is a 50 minute exercise for skill development and knowledge to complement
- 9. Final Assignment The Assignment must be completed to pass the course The assignment will be worked
- 10. Graded Work Standards: 85% Attendance Record for the term (miss 4) 50% Average for all Graded
- 11. For Success …
- 12. 10 Steps For Success … Review the material each week before class Take notes on course
- 13. Programming or Scripting
- 14. What is Programming or Scripting?
- 15. What is Programming or Scripting? English like commands Written in a specific language Contained in a
- 16. Early computers First computing devices in 1800s and early 1900s were more mechanical, very basic computing.
- 17. Transistors Transistor invention in 1940s led to microchip, allowed design of smaller computers that could perform
- 18. “It would appear that we have reached the limits of what it is possible to achieve
- 19. Short History of Programming Languages
- 20. Programming Languages Do you know of any programming languages?
- 21. 1945-1959 FORTRAN (1945) First widely used high-level language LISP (1958), COBOL (1959) C (1972) Early systems
- 22. 1980-1989 C++ (1980) Still used heavily today 1990-1999 Visual Basic (1991) Ruby (1993) Java and JavaScript
- 23. Programming Levels Low-Level Programming Runs as close as possible to the hardware May include operating systems,
- 24. Types of Programming Languages
- 25. Scripting Languages Scripting Languages bash PowerShell Data-Oriented Languages SQL, MySQL dBase
- 26. Types of Languages
- 27. Embedable Languages PHP Perl Ruby JavaScript Java VBScript
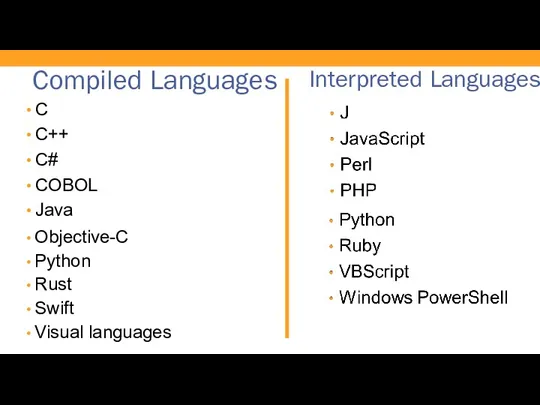
- 28. Compiled Languages C C++ C# COBOL Java Objective-C Python Rust Swift Visual languages Interpreted Languages
- 29. Other Languages The following are not programming languages HTML: Web-based markup language CSS: Design-based style sheet
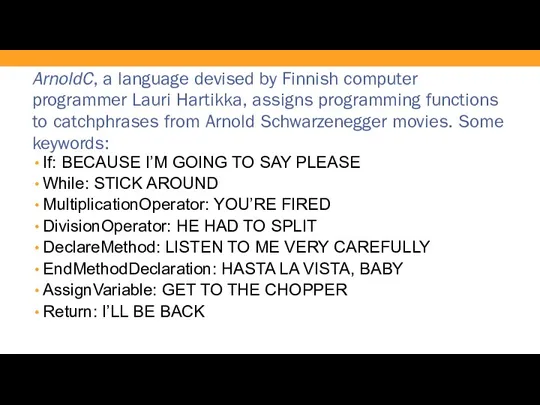
- 30. ArnoldC, a language devised by Finnish computer programmer Lauri Hartikka, assigns programming functions to catchphrases from
- 32. Скачать презентацию



























 Операторы циклов в Паскале
Операторы циклов в Паскале Создание базы данных Автозапчасти
Создание базы данных Автозапчасти Оценка производительности вычислительных систем
Оценка производительности вычислительных систем Виды системного программного обеспечения
Виды системного программного обеспечения Презентация, задание к уроку, домашнее задание к уроку информатики в 5 классе по теме Основная позиция пальцев на клавиатуре
Презентация, задание к уроку, домашнее задание к уроку информатики в 5 классе по теме Основная позиция пальцев на клавиатуре Электронные ресурсы для подготовки к Всероссийской олимпиаде школьников по русскому языку и литературе
Электронные ресурсы для подготовки к Всероссийской олимпиаде школьников по русскому языку и литературе Конструирование программного обеспечения. Контейнеры и коллекции объектов
Конструирование программного обеспечения. Контейнеры и коллекции объектов Introduction and paradigms. Programming language concepts. (Lecture 1)
Introduction and paradigms. Programming language concepts. (Lecture 1) Разработка автоматизированной информационной системы Склад
Разработка автоматизированной информационной системы Склад Таргетированная реклама #ВКонтакте от А до Я 5.0
Таргетированная реклама #ВКонтакте от А до Я 5.0 Разведка Бараша. Эпизод 6
Разведка Бараша. Эпизод 6 Подготовка к контрольной работе. Элементы алгебры логики. Математические основы информатики
Подготовка к контрольной работе. Элементы алгебры логики. Математические основы информатики Плюсы и минусы информационного общества
Плюсы и минусы информационного общества Алгоритмы и структуры данных. Алгоритмы с возвратом
Алгоритмы и структуры данных. Алгоритмы с возвратом Информация и ее виды
Информация и ее виды ITK Lecture 4. Images in ITK
ITK Lecture 4. Images in ITK Робота у локальній мережі
Робота у локальній мережі Ввод данных через клавиатуру
Ввод данных через клавиатуру Безопасный Интернет (1-4 классы)
Безопасный Интернет (1-4 классы) Особенности программных средств, используемых в разработке информационных систем
Особенности программных средств, используемых в разработке информационных систем Разработка информационно-программного обеспечения управления взаимодействием с клиентами с использованием мобильных устройств
Разработка информационно-программного обеспечения управления взаимодействием с клиентами с использованием мобильных устройств Программирование на языке Python. Символьные строки
Программирование на языке Python. Символьные строки Исполнители вокруг нас
Исполнители вокруг нас Апаратні та програмні засоби ЕОМ
Апаратні та програмні засоби ЕОМ
 Использование информационных компьютерных технологий на уроках истории и обществознания в условиях сельской школы.
Использование информационных компьютерных технологий на уроках истории и обществознания в условиях сельской школы. О компании ITFB Group
О компании ITFB Group Advantage and Disadvantage Influences of the Internet on a Human Life
Advantage and Disadvantage Influences of the Internet on a Human Life