Содержание
- 2. Human •a person who tries to accomplish a goal •the end-user •the member of an organization
- 3. Interface •A point where two objects meet •A point where human can tell the computer what
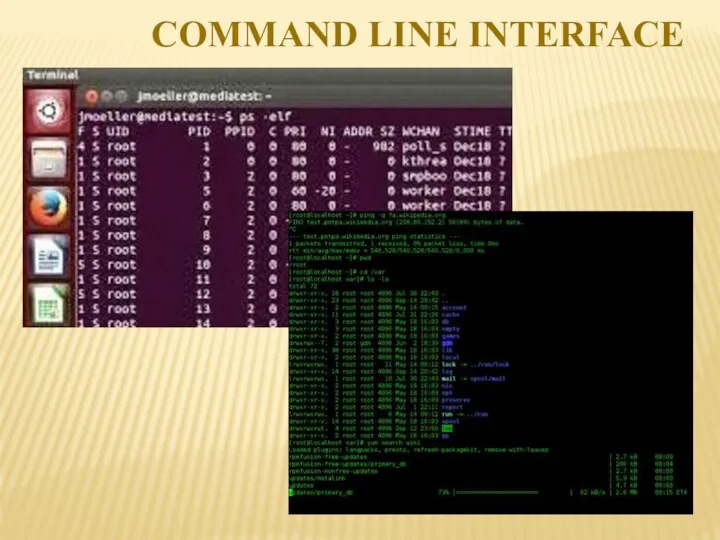
- 4. Types of Interfaces •Command Line Interface (CLI) A CLI displays a prompt, the user types a
- 5. Advantages ◦ Very flexible with the use of “switches” (options) ◦Good for “expert” users - can
- 6. COMMAND LINE INTERFACE
- 7. Advantages ◦No need to learn complex commands/language ◦Easier for a novice to learn/use ◦Ideal when there
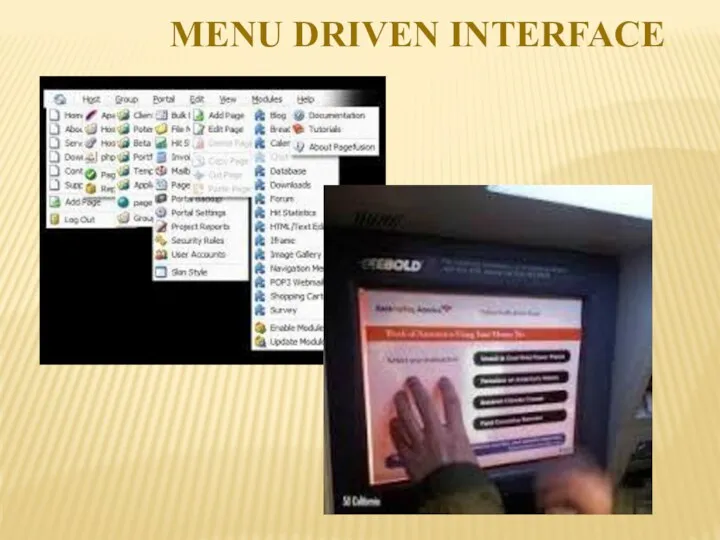
- 8. MENU DRIVEN INTERFACE
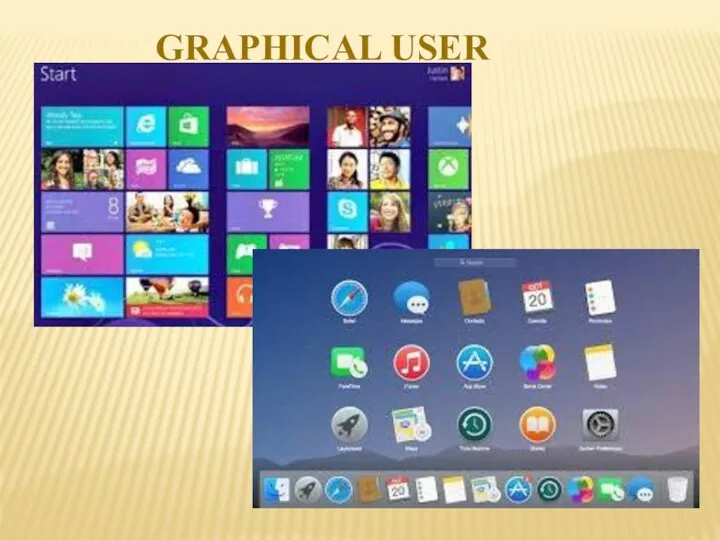
- 9. GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE ADVANTAGES ◦Most users suitable interface for inexperienced or novice ◦Many generic packages for
- 10. GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE
- 11. Advantages ◦No training required ◦Can be quicker than keyboard entry ◦Hands-free ◦Can be used by the
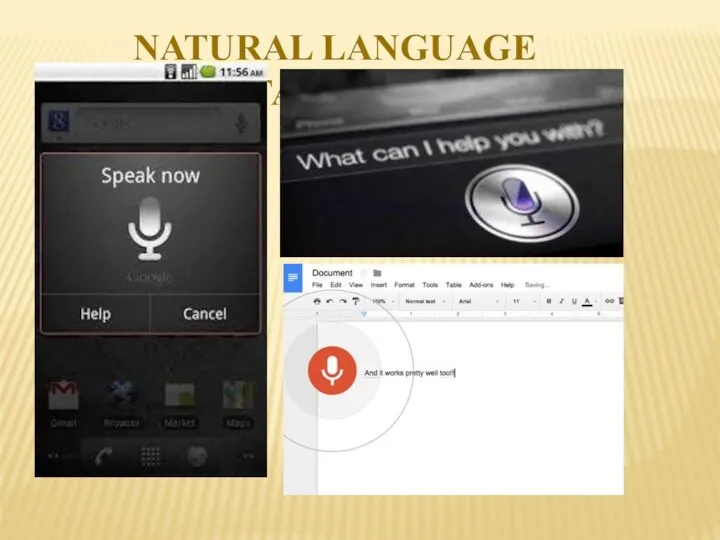
- 12. NATURAL LANGUAGE INTERFACE
- 13. Architecture • Architecture of any HCI systems is identified by: Number of inputs and outputs in
- 14. UNIMODAL HCI SYSTEM An interface mainly relies on number and diversity of its inputs and outputs
- 15. Audio Based HCI It deals with information acquired by different audio signals. information. Key components: ◦Microphone
- 16. SENSOR BASED HCI It has the wide range of applications in our day-to-day life. The common
- 17. VISUAL BASED HCI It is also called as machine vision which is the observation of an
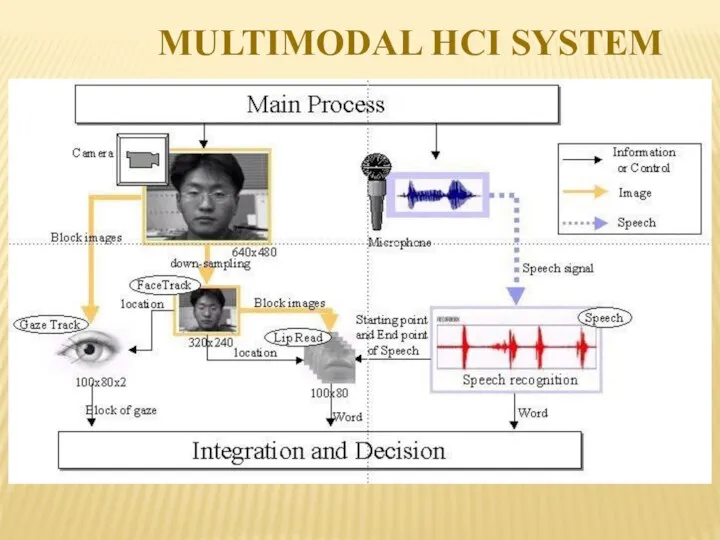
- 18. MULTIMODAL HCI SYSTEM Combination of multiple modalities, or usage of more than one independent channel signals
- 19. MULTIMODAL HCI SYSTEM
- 20. / ...... na Cll 0 N 0 0 00
- 21. Interaction design “Designing interactive products to support the way people communicate and interact in their everyday
- 22. User Experience UX User experience is the totality of the effect or effects felt by a
- 23. Usability is the pragmatic component of user experience, including effectiveness, efficiency, productivity, ease-of-use, learnability, retainability, and
- 24. Functionality Functionality is power to do work (to play) seated in the non-user-interface computational features and
- 26. Скачать презентацию
















 Создание новой базы данных в MS Access 2010
Создание новой базы данных в MS Access 2010 Базы данных. Основы проектирования баз данных. (Лекция 1)
Базы данных. Основы проектирования баз данных. (Лекция 1) Методическая разработка внеклассного мероприятия (интеллектуальная игра) по физике и информатике для учащихся 5-11 классов Кто хочет стать отличником
Методическая разработка внеклассного мероприятия (интеллектуальная игра) по физике и информатике для учащихся 5-11 классов Кто хочет стать отличником Безопасность систем баз данных. Разграничение доступа
Безопасность систем баз данных. Разграничение доступа Регулярные выражения. Библиотека regex
Регулярные выражения. Библиотека regex основы логики, построение логических схем
основы логики, построение логических схем Контент-стратегии онлайн-СМИ
Контент-стратегии онлайн-СМИ MS Excel Табличный процесс. MS Excel: возможности, достоинства и недостатки
MS Excel Табличный процесс. MS Excel: возможности, достоинства и недостатки Базы данных
Базы данных Как устроена книга
Как устроена книга Инфознайка 2014
Инфознайка 2014 Семиотика и ее основные проблемы
Семиотика и ее основные проблемы What is a computer?
What is a computer? Организация продвижения товаров и услуг в сети Интернет
Организация продвижения товаров и услуг в сети Интернет Штучний інтелект - допоможе людству чи знищить його?
Штучний інтелект - допоможе людству чи знищить його? Информационные ресурсы сети Интернет
Информационные ресурсы сети Интернет Работа с закупками малого объема в ЕАСУЗ 2.0
Работа с закупками малого объема в ЕАСУЗ 2.0 Программное обеспечение ГИС. Лекция 18
Программное обеспечение ГИС. Лекция 18 Информатика, интернет и всемирная паутина
Информатика, интернет и всемирная паутина Защита ПК от вирусов. Антивирусные средства
Защита ПК от вирусов. Антивирусные средства Средства автоматизации делопроизводства
Средства автоматизации делопроизводства Разработка информационной системы Магазин продуктов
Разработка информационной системы Магазин продуктов Mit app inventor
Mit app inventor Компьютер как унивесальное устройство для работы с информацией. 7 класс
Компьютер как унивесальное устройство для работы с информацией. 7 класс Prolog. A general-purpose logic programming language associated with artificial intelligence and computational linguistics
Prolog. A general-purpose logic programming language associated with artificial intelligence and computational linguistics Алгебра высказываний
Алгебра высказываний Методы программирования. Поиск в тексте. (Лекция 6)
Методы программирования. Поиск в тексте. (Лекция 6) Добавляем эффект свечения для изображения в Фотошоп
Добавляем эффект свечения для изображения в Фотошоп