Содержание
- 2. Morphing Video: Women in Art http://www.vimeo.com/1456037
- 3. Terminator 2 Morphing (1991) Terminator 2 Clip (YouTube)
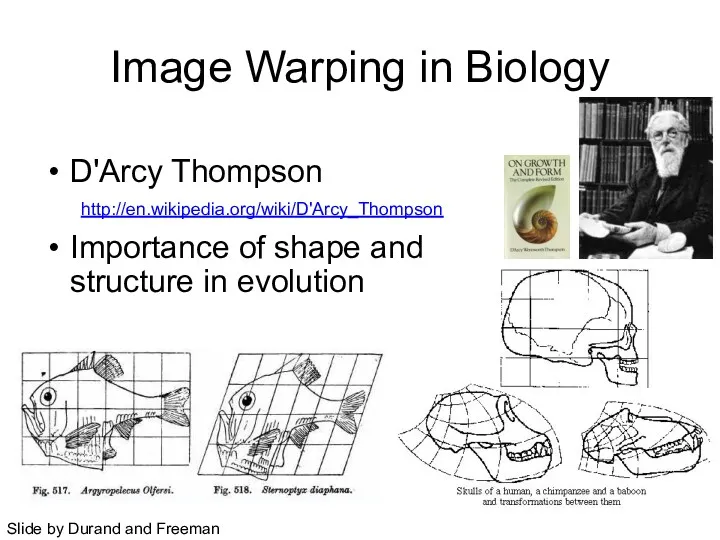
- 4. D'Arcy Thompson Importance of shape and structure in evolution Slide by Durand and Freeman Image Warping
- 5. Cambrian Explosion Source: http://www.earthlearningidea.com/
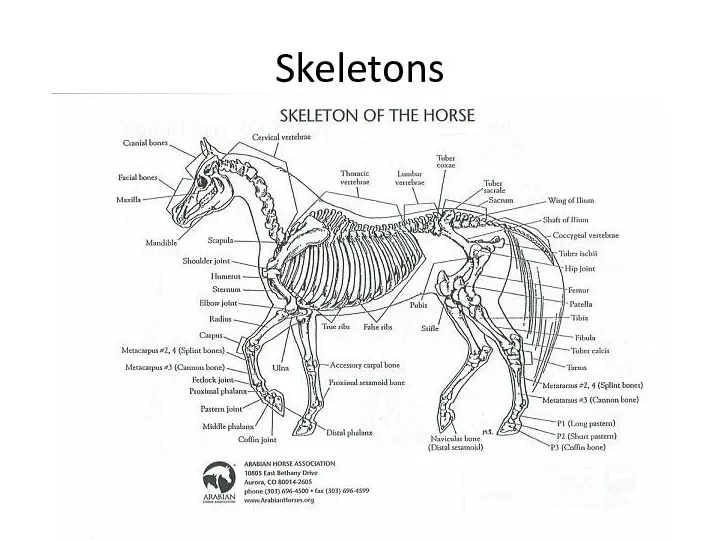
- 6. Skeletons
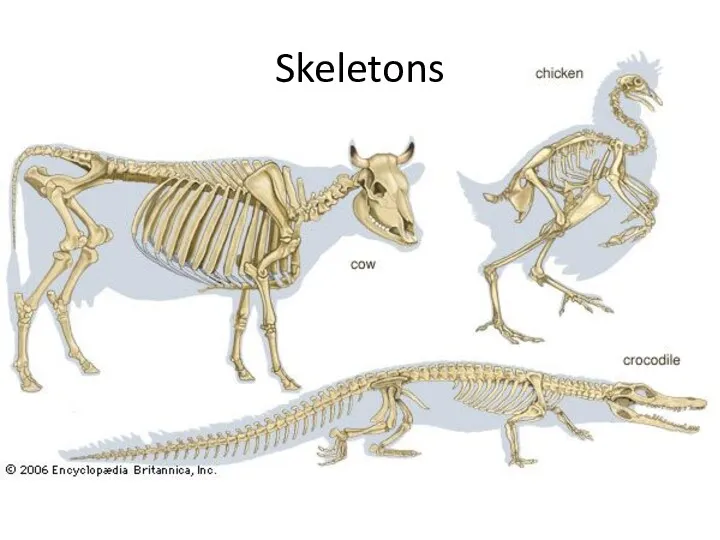
- 7. Skeletons
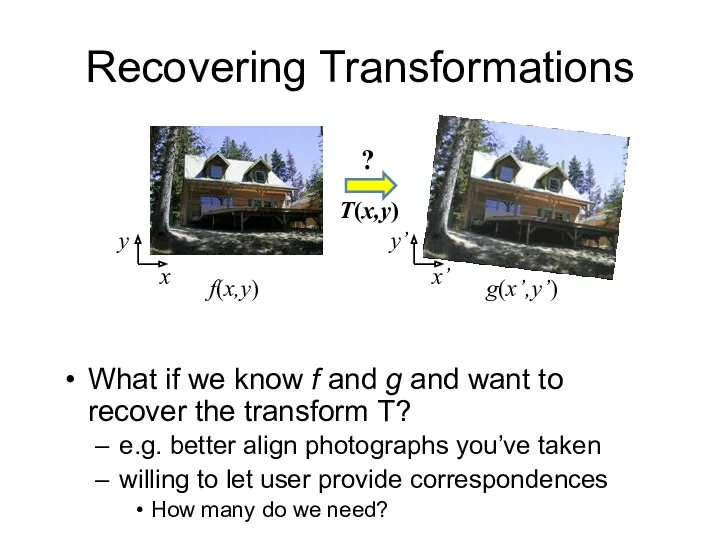
- 8. Recovering Transformations What if we know f and g and want to recover the transform T?
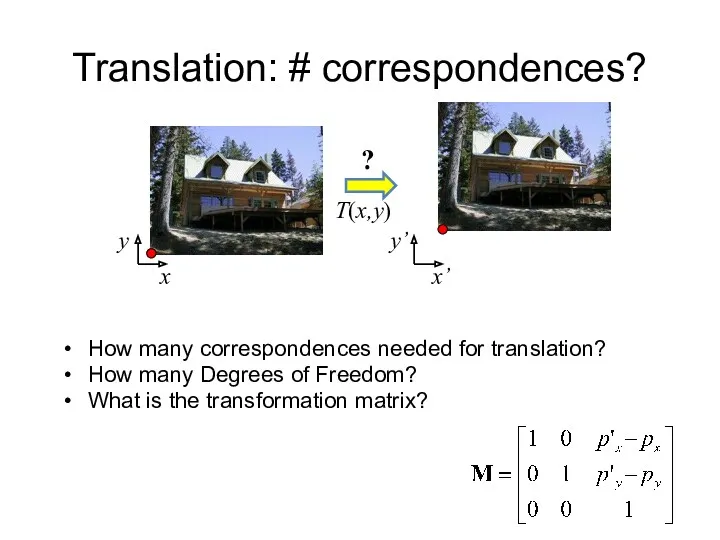
- 9. Translation: # correspondences? How many correspondences needed for translation? How many Degrees of Freedom? What is
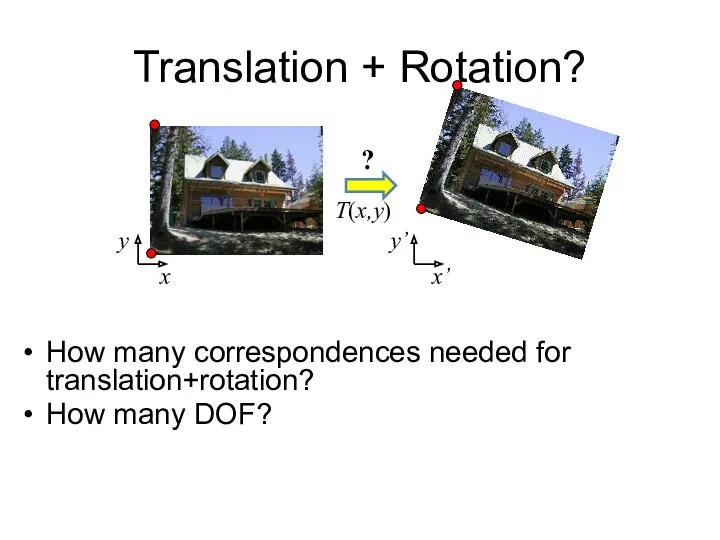
- 10. Translation + Rotation? How many correspondences needed for translation+rotation? How many DOF? x x’ T(x,y) y
- 11. Affine: # correspondences? How many correspondences needed for affine transform? How many DOF? x x’ T(x,y)
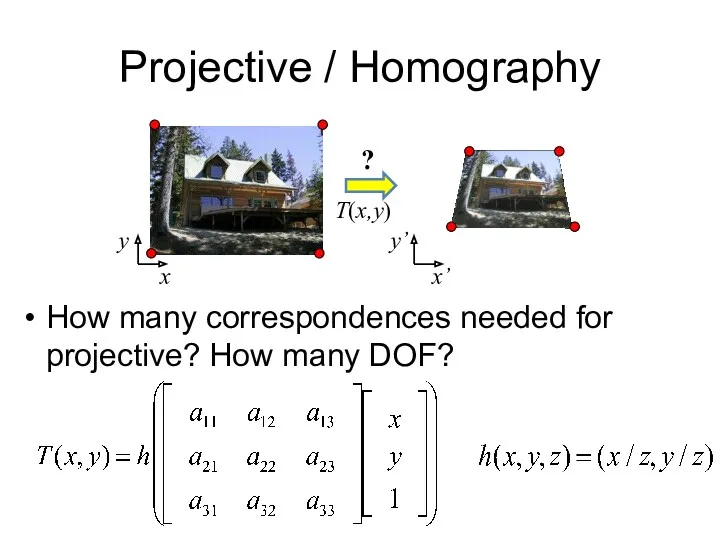
- 12. Projective / Homography How many correspondences needed for projective? How many DOF? x x’ T(x,y) y
- 13. Image Warping Given a coordinate transform (x’,y’) = T(x,y) and a source image f(x,y), how do
- 14. (x,y) (x’,y’) Forward warping Send each pixel (x,y) to its corresponding location (x’,y’) = T(x,y) in
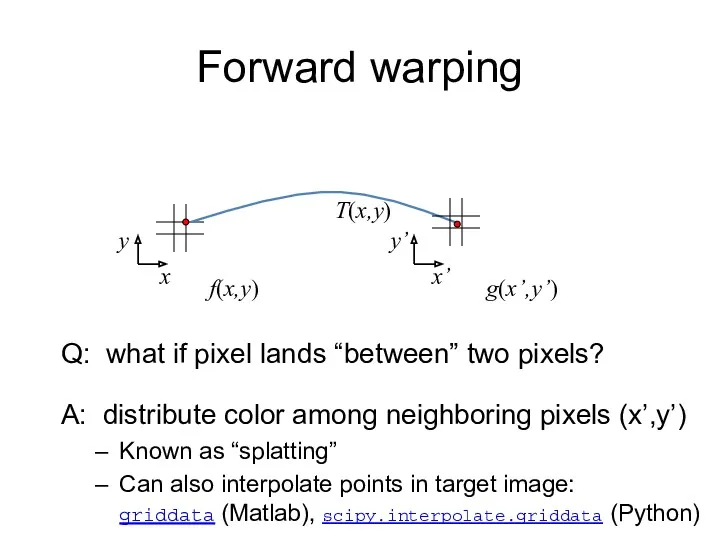
- 15. f(x,y) g(x’,y’) Forward warping x x’ T(x,y) Q: what if pixel lands “between” two pixels? y
- 16. (x,y) (x’,y’) x y Inverse warping Get each pixel color g(x’,y’) from its corresponding location (x,y)
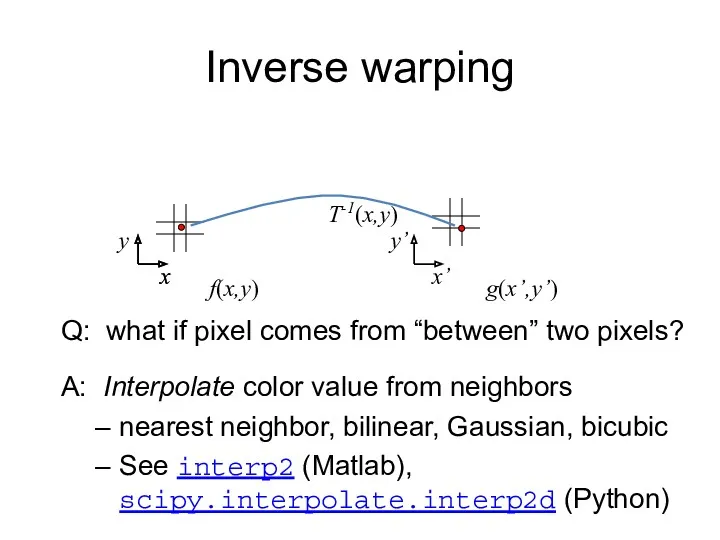
- 17. f(x,y) g(x’,y’) x y Inverse warping x x’ Q: what if pixel comes from “between” two
- 18. Forward vs. inverse warping Q: Which is better?
- 19. Forward vs. inverse warping Q: Which is better? A: Usually inverse – eliminates holes However, it
- 20. How to Obtain Warp Field? Move control points to specify a spline warp Spline produces a
- 21. Warp as Interpolation We are looking for a warping field A function that given a 2D
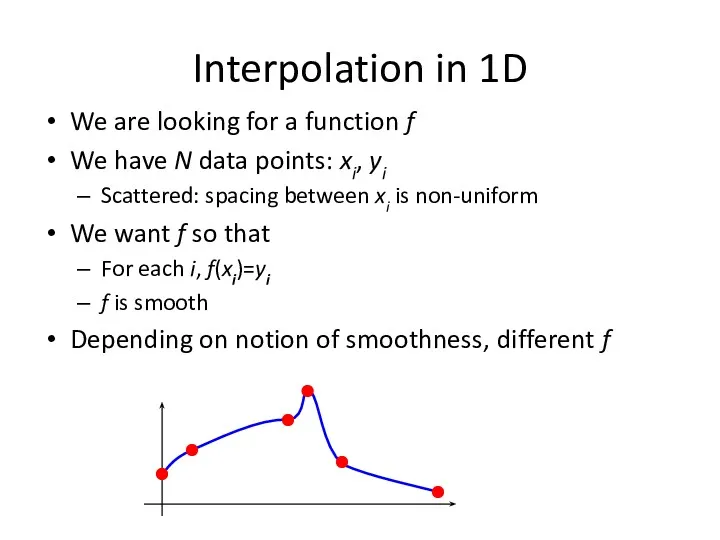
- 22. Interpolation in 1D We are looking for a function f We have N data points: xi,
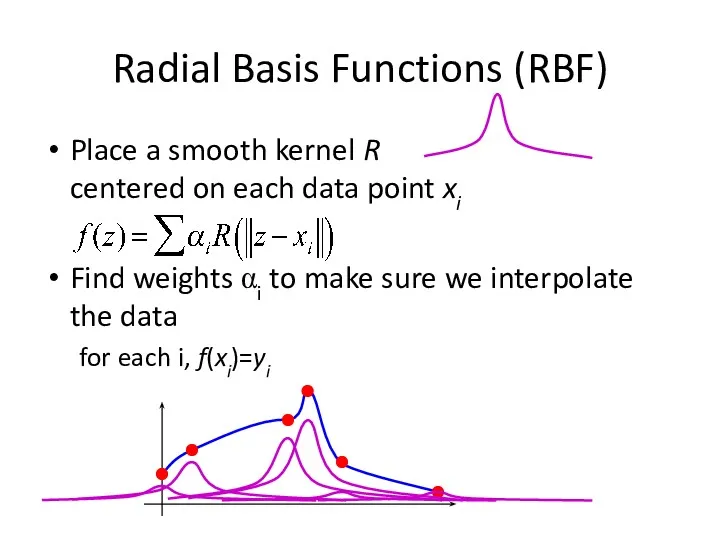
- 23. Radial Basis Functions (RBF) Place a smooth kernel R centered on each data point xi
- 24. Radial Basis Functions (RBF) Place a smooth kernel R centered on each data point xi Find
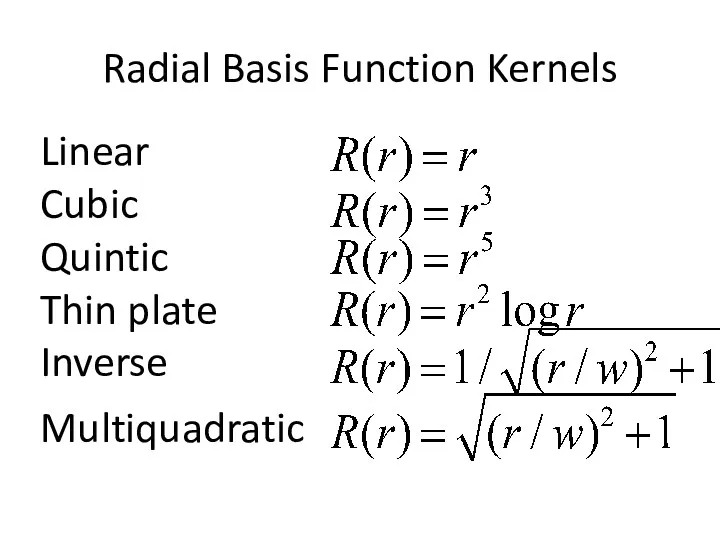
- 25. Radial Basis Function Kernels Linear Cubic Quintic Thin plate Inverse Multiquadratic
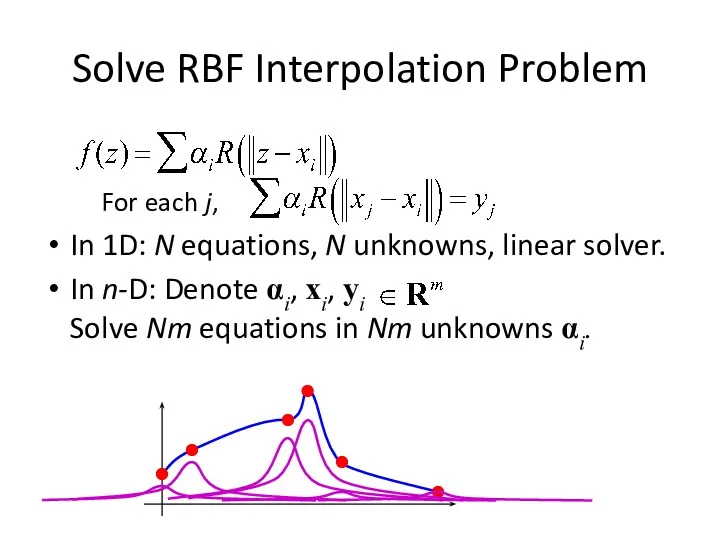
- 26. Solve RBF Interpolation Problem For each j, In 1D: N equations, N unknowns, linear solver. In
- 27. RBF Summary Interpolates “scattered data”, or data defined only at a few sparse locations. Basis functions
- 28. Applying a warp: use inverse Forward warp: For each pixel in input image Paste color to
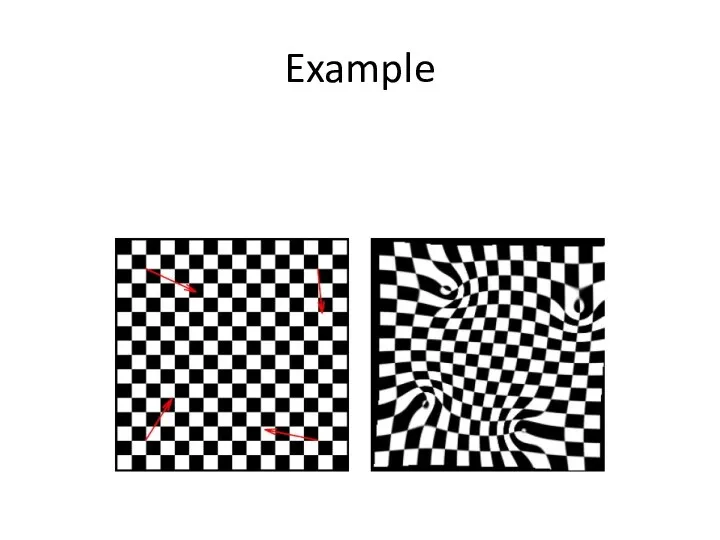
- 29. Example
- 30. Example Fold problems Oh well…
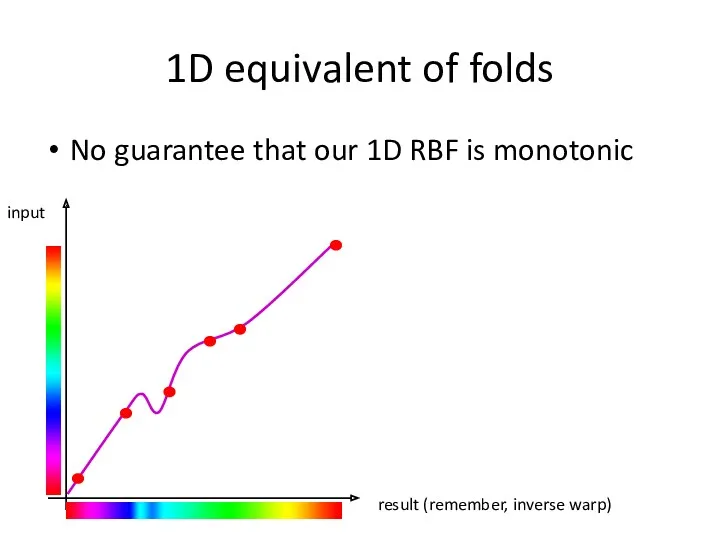
- 31. 1D equivalent of folds No guarantee that our 1D RBF is monotonic result (remember, inverse warp)
- 32. Aliasing Issues with Warping Aliasing can happen if warps are extreme. This is especially noticeable during
- 33. Aliasing Solution Use an ellipsoidal Gaussian: “Elliptical Weighted Average” (EWA) Filter is deformed based on warping.
- 34. Morphing = Object Averaging The aim is to find “an average” between two objects Not an
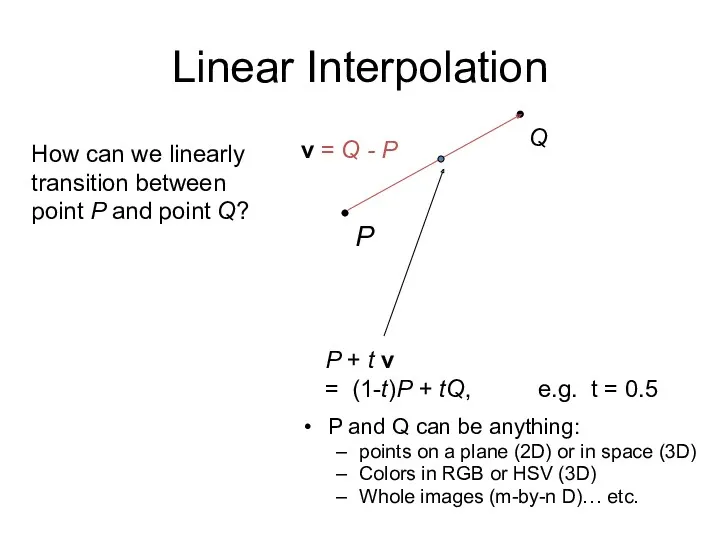
- 35. P Q v = Q - P P + t v = (1-t)P + tQ, e.g.
- 36. Idea #1: Cross-Dissolve Interpolate whole images: Imagehalfway = (1-t)*Image1 + t*image2 This is called cross-dissolve in
- 37. Idea #2: Align, then cross-disolve Align first, then cross-dissolve Alignment using global warp – picture still
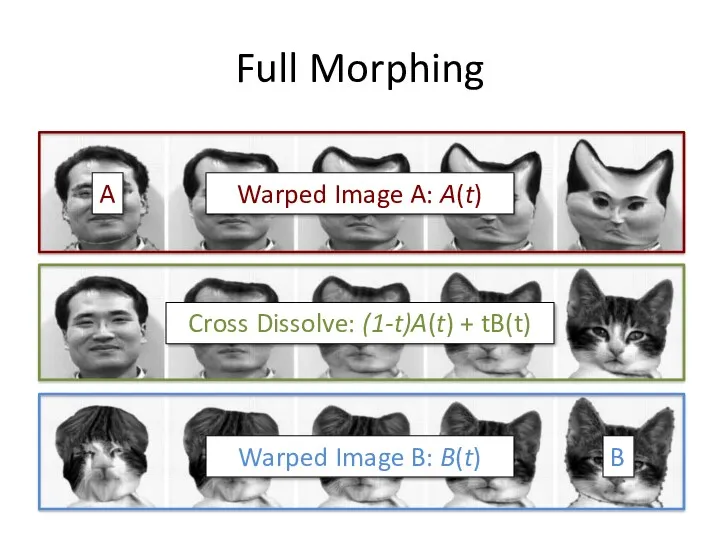
- 38. Full Morphing What if there is no simple global function that aligns two images? User specifies
- 39. Full Morphing
- 40. Full Morphing Image A Image B 1. Find warping fields from user constraints (points or lines):
- 41. Full Morphing A B Warped Image A: A(t) Warped Image B: B(t) Cross Dissolve: (1-t)A(t) +
- 42. Catman!
- 44. Скачать презентацию























 Мастер-класс по печатным СМИ
Мастер-класс по печатным СМИ Нейронные сети. Возможности применения и перспективы развития
Нейронные сети. Возможности применения и перспективы развития Prefer class hierarchies to tagged classes. (Item 20, 21, 22)
Prefer class hierarchies to tagged classes. (Item 20, 21, 22) Моделирование
Моделирование Морской бой. Описание программы
Морской бой. Описание программы Бази даних. Системи управління базами даних
Бази даних. Системи управління базами даних Принципы объектно-ориентированного проектирования
Принципы объектно-ориентированного проектирования Представление аналогового сигнала в цифровом виде (лекция 20)
Представление аналогового сигнала в цифровом виде (лекция 20) Объекты и их имена
Объекты и их имена Файлы и файловая система
Файлы и файловая система Windows System Programming
Windows System Programming Розв’язування крайових задач для звичайних диференціальних рівнянь методом Гальоркіна
Розв’язування крайових задач для звичайних диференціальних рівнянь методом Гальоркіна Електронне спілкування
Електронне спілкування Введение в PL/SQL
Введение в PL/SQL Технология быстрого описания бизнес-процессов
Технология быстрого описания бизнес-процессов Текстовая информация. Тексты в памяти компьютера. Текстовые редакторы и процессоры
Текстовая информация. Тексты в памяти компьютера. Текстовые редакторы и процессоры Creating Session Beans
Creating Session Beans Уроки по теме Одномерный массив
Уроки по теме Одномерный массив Компьютерная графика и анимация. Векторная графика
Компьютерная графика и анимация. Векторная графика Компьютерная арифметика
Компьютерная арифметика Медицинское мобильное приложение Приоритет
Медицинское мобильное приложение Приоритет Информационные технологии в профессиональной деятельности. Автоматизированные банковские системы и рабочие места
Информационные технологии в профессиональной деятельности. Автоматизированные банковские системы и рабочие места Курсовая работа по дисциплине: системное программирование. Диспетчер файлов
Курсовая работа по дисциплине: системное программирование. Диспетчер файлов Обработка информации. Создание движущихся изображений. 5 класс
Обработка информации. Создание движущихся изображений. 5 класс Интегрированный урок английского языка и информатики
Интегрированный урок английского языка и информатики Программное обеспечение
Программное обеспечение Основы логики
Основы логики 5.7. Служба каталогов сетевых серверных ОС
5.7. Служба каталогов сетевых серверных ОС