Содержание
- 2. Overview ITIL – An Introduction Key Concepts Service Management ITIL Service Life Cycle
- 3. What is ITIL? - I Systematic approach to high quality IT service delivery Documented best practice
- 4. What is ITIL? - II ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library) provides a framework of best practice guidance
- 5. What about V3? ITIL started in 80s. 40 Publications!!! V2 was introduced in 2000-02 8 Books!!
- 6. 5 Core Books Service Strategy Service Design Service Transition Service Operation Continual Service Improvement
- 7. Why ITIL Service Management? Best Practice Non-Proprietary/Non-Prescriptive Guidance, not regulations Innovative
- 8. Good Practices v.s. Proprietary Knowledge
- 9. Benefits of ITIL to the IT Provider Service Management Best Practices Lifecycle Approach Better management of
- 10. Benefits of ITIL to the Customer Focus on Business Needs Service Aligned to Business Activity Services
- 11. Some Key Concepts
- 12. Key Concepts :: Service Service delivers value to customer. How? by facilitating outcomes customers want to
- 13. Key Concepts :: Service Level Measured and reported achievement against one or more service level targets.
- 14. Key Concepts :: Service Level Agreement (SLA) Written and negotiated agreement between Service Provider and Customer
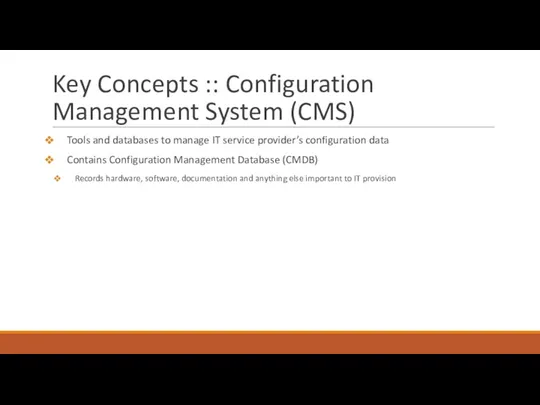
- 15. Key Concepts :: Configuration Management System (CMS) Tools and databases to manage IT service provider’s configuration
- 16. Key Concepts :: Release Collection of hardware, software, documentation, processes or other things require to implement
- 17. Key Concepts :: Incident Unplanned interruption to an IT service or an unplanned reduction in its
- 18. Key Concepts :: Work Around Reducing or eliminating the impact of an incident without resolving it
- 19. Key Concepts :: Problem Unknown underlying cause of one or more incidents
- 20. Key Concepts :: Resources Resources Things you buy or pay for IT Infrastructure, people, money Tangible
- 21. Key Concepts :: Capabilities Capabilities Things you grow Ability to carry out an activity Intangible assets
- 22. Service Management
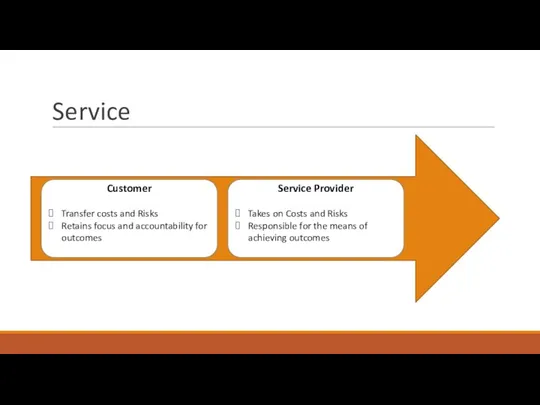
- 23. Service Customer Transfer costs and Risks Retains focus and accountability for outcomes Service Provider Takes on
- 24. What is Service Management? A set of specialized organizational capabilities for providing value to customers in
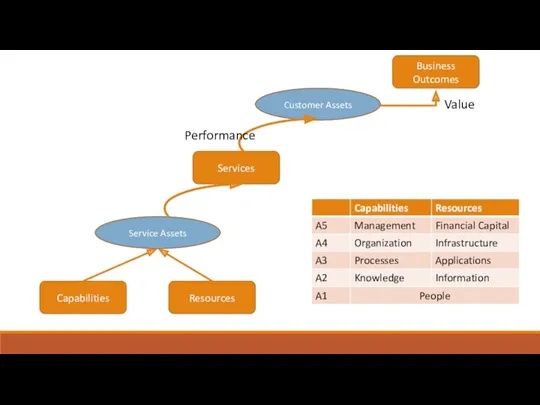
- 25. Capabilities Resources Service Assets Services Customer Assets Business Outcomes Performance Value
- 26. 4 Ps of Service Management People – skills, training, communication Processes – actions, activities, changes, goals
- 27. Service Lifecycle
- 28. Service Life Cycle (SLC) To sustain high levels of business performance, organisations need to offer competitive
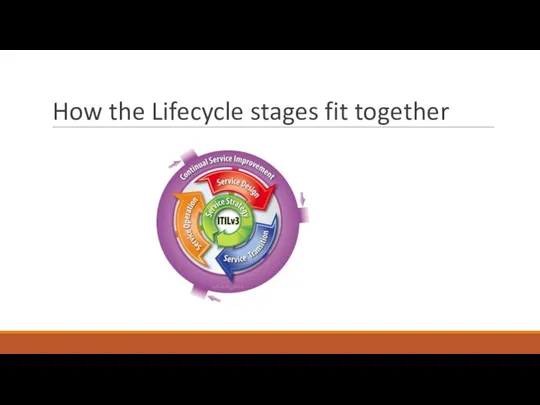
- 29. How the Lifecycle stages fit together
- 30. SLC :: Service Strategy Purpose Ensuring that our strategy is defined, maintained and then implemented. What
- 31. Service Strategy has four activities
- 32. SLC :: Service Design Purpose Converting the strategy into reality, through the use of a consistent
- 33. Processes in Service Design Availability Management Capacity Management ITSCM (disaster recovery) (IT Service Continuity Management) Supplier
- 34. SLC :: Service Transition Key Purpose To bridge both the gap between projects and operations more
- 35. Good Service Transition Set customer expectations Enable release integration Reduce performance variation Document and reduce known
- 36. SLC :: Service Operation Maintenance Management Realises Strategic Objectives and is where the Value is seen
- 37. Processes in Service Operation Incident Management Problem Management Event Management Request Fulfilment Access Management
- 38. Functions in Service Operation Service Desk Technical Management IT Operations Management Applications Management
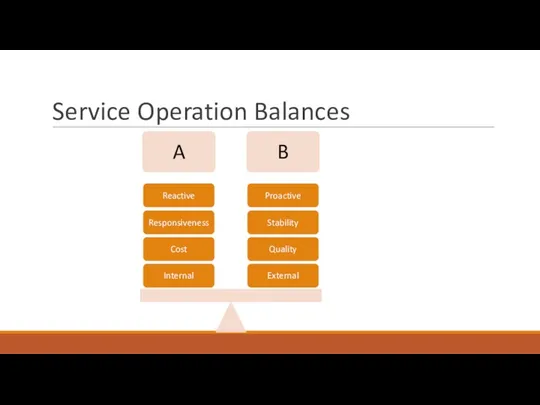
- 39. Service Operation Balances
- 40. SLC :: Continual Service Improvement Focus on Process owners and Service Owners Ensures that service management
- 41. Service Measurement Technology (components, MTBF etc) Process (KPIs - Critical Success Factors) Service (End-to end, e.g.
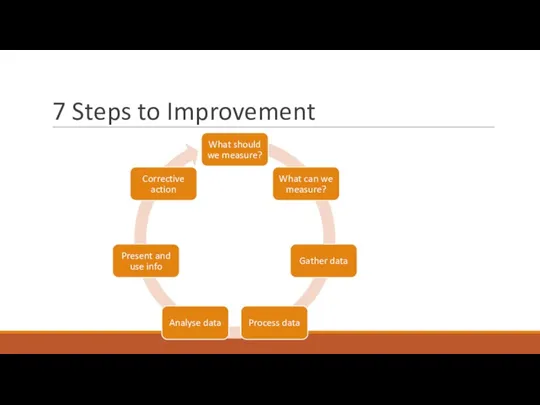
- 42. 7 Steps to Improvement
- 44. Скачать презентацию



































 Презентация к уроку на тему Моделирование
Презентация к уроку на тему Моделирование Штучний інтелект
Штучний інтелект Решение задач на компьютере алгоритмизация и программирование
Решение задач на компьютере алгоритмизация и программирование Основы трехмерного моделирования в САПР
Основы трехмерного моделирования в САПР Новые информационные технологии. (Лекция 1а)
Новые информационные технологии. (Лекция 1а) ВКР: Разработка веб сайта учебного центра
ВКР: Разработка веб сайта учебного центра Алгоритмы решения ОГЭ (Задания №1-18)
Алгоритмы решения ОГЭ (Задания №1-18) Школьный пресс-центр как средство развития духовно-нравственного и патриотического воспитания школьников
Школьный пресс-центр как средство развития духовно-нравственного и патриотического воспитания школьников Основы информационной безопасности
Основы информационной безопасности 1С-Битрикс. Сайт медицинской организации
1С-Битрикс. Сайт медицинской организации Пакет прикладных программ (ППП)
Пакет прикладных программ (ППП) Возврат не день в день. Розница. Наличные
Возврат не день в день. Розница. Наличные What is cryptocurrency
What is cryptocurrency Ветвления. Разветвляющийся алгоритмический процесс
Ветвления. Разветвляющийся алгоритмический процесс Организация отказоустойчивой сети
Организация отказоустойчивой сети Есептеу жүйесі
Есептеу жүйесі Quantum computing
Quantum computing Алгоритмы сортировки массивов
Алгоритмы сортировки массивов Пополнение личного кабинета и покупка матричного пакета
Пополнение личного кабинета и покупка матричного пакета Устройство компьютера
Устройство компьютера Переменные: тип, имя, значение
Переменные: тип, имя, значение Ідентифікація та методи визначення та фальсифікації товарів
Ідентифікація та методи визначення та фальсифікації товарів Работа с файлами
Работа с файлами Цикли з лічильником у середовищі скретч
Цикли з лічильником у середовищі скретч Системы счисления
Системы счисления Архитектура персонального компьютера
Архитектура персонального компьютера Открытый урок 7 класса, тема: Информатика. Информация, информационная картина мира, свойства информации. Виды информации и способы ее обработки. Количество информации, единицы измерения информации.
Открытый урок 7 класса, тема: Информатика. Информация, информационная картина мира, свойства информации. Виды информации и способы ее обработки. Количество информации, единицы измерения информации. League of dance
League of dance