Содержание
- 2. Why Use JavaScript? JavaScript enhances Web pages with dynamic and interactive features. JavaScript runs in client
- 3. What Can JavaScript Do? Common JavaScript tasks can replace server-side scripting. JavaScript enables shopping carts, form
- 4. JavaScript Syntax. Unlike HTML, JavaScript is case sensitive. Dot Syntax is used to combine terms. e.g.,
- 5. JavaScript Terminology. JavaScript programming uses specialized terminology. Understanding JavaScript terms is fundamental to understanding the script.
- 6. Objects Objects refers to windows, documents, images, tables, forms, buttons or links, etc. Objects should be
- 7. Properties Properties are object attributes. Object properties are defined by using the object's name, a period,
- 8. Methods Methods are actions applied to particular objects. Methods are what objects can do. e.g., document.write(”Hello
- 9. Events Events associate an object with an action. e.g., the OnMouseover event handler action can change
- 10. Functions Functions are named statements that performs tasks. e.g., function doWhatever () {statement here} The curly
- 11. Values Values are bits of information. Values types and some examples include: Number: 1, 2, 3,
- 12. Variables Variables contain values and use the equal sign to specify their value. Variables are created
- 13. Expressions Expressions are commands that assign values to variables. Expressions always use an assignment operator, such
- 14. Operators Operators are used to handle variables. Types of operators with examples: Arithmetic operators, such as
- 15. Methods of Using JavaScript. 1. JavaScripts can reside in a separate page. 2. JavaScript can be
- 16. 1. Using Separate JavaScript Files. Linking can be advantageous if many pages use the same script.
- 17. 2. Embedding JavaScript in HTML. When specifying a script only the tags and are essential, but
- 18. Using Comment Tags HTML comment tags should bracket any script. The tags hide scripts in HTML
- 19. 3. Using JavaScript in HTML Tags. Event handlers like onMouseover are a perfect example of an
- 20. Creating an Alert Message The following script in the tag uses the onLoad event to display
- 22. Скачать презентацию




















 Управление освещением витрины
Управление освещением витрины Техническая защита информации. Оценка защищённости информации ограниченного доступа от утечки по техническим каналам
Техническая защита информации. Оценка защищённости информации ограниченного доступа от утечки по техническим каналам Логические выражения и таблицы истинности. Логика
Логические выражения и таблицы истинности. Логика Искусственный интеллект
Искусственный интеллект Браузеры.Классификация браузеров
Браузеры.Классификация браузеров Конструирование программного обеспечения. Контейнеры и коллекции объектов
Конструирование программного обеспечения. Контейнеры и коллекции объектов Сервис Learningapps.org. Инструкция по работе
Сервис Learningapps.org. Инструкция по работе Основные правила Web-дизайна
Основные правила Web-дизайна Объекты в приложении Power Point
Объекты в приложении Power Point Угрозы информационной безопасности
Угрозы информационной безопасности Создание 3D-модели твердотельного объекта для печати
Создание 3D-модели твердотельного объекта для печати Маршрутизация в информационных сетях
Маршрутизация в информационных сетях Технология доступа к данным
Технология доступа к данным Проектная деятельность во внеклассной работе по информатике и ИКТ
Проектная деятельность во внеклассной работе по информатике и ИКТ Безопасность информационных систем в современном мире
Безопасность информационных систем в современном мире Искусственный интеллект
Искусственный интеллект Data Access Patterns. Three Tier Architecture
Data Access Patterns. Three Tier Architecture Методы моделирования и модели разработки информационных систем. (Лекция 3,4)
Методы моделирования и модели разработки информационных систем. (Лекция 3,4) Безопасность в сети Интернет
Безопасность в сети Интернет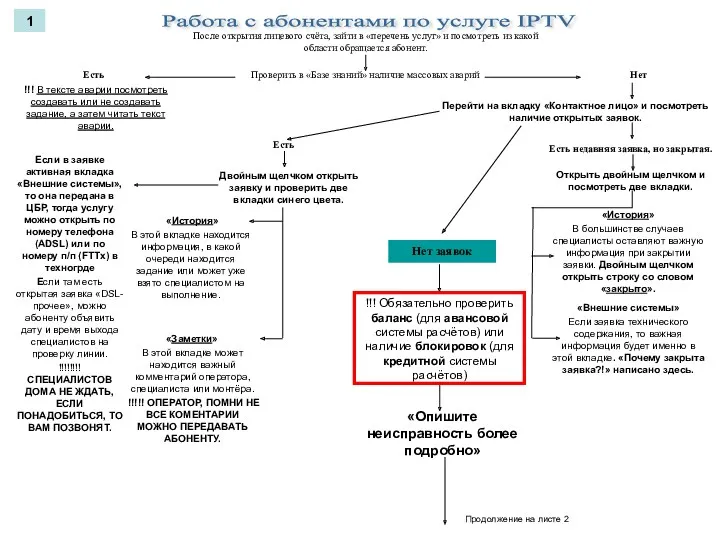 Алгоритм работы с IPTV
Алгоритм работы с IPTV Управление в логистических информационных системах (Информационные системы планирования и управления ресурсами предприятия)
Управление в логистических информационных системах (Информационные системы планирования и управления ресурсами предприятия) Четыре способа вывода бизнеса в онлайн
Четыре способа вывода бизнеса в онлайн Лекция 8. Форматы графических файлов. Формат JPEG
Лекция 8. Форматы графических файлов. Формат JPEG Обработка списков в программах на языке Пролог. Программы сортировки
Обработка списков в программах на языке Пролог. Программы сортировки Локальные и глобальные компьютерные сети. Коммуникационные технологии
Локальные и глобальные компьютерные сети. Коммуникационные технологии Основи роботи в середовищі табличного процесора
Основи роботи в середовищі табличного процесора Защита информации
Защита информации Взаимодействие со Службой занятости населения с помощью портала Работа России
Взаимодействие со Службой занятости населения с помощью портала Работа России