Содержание
- 2. The Computer Network Arguably, the greatest advancement in technology and communication over the past 20 years
- 3. The Computer Network What is a Computer Network net·work: [net-wurk] – noun, a system containing any
- 4. Navigation Links Network Diagram – Basic Layout and map of a traditional computer network. Network Types
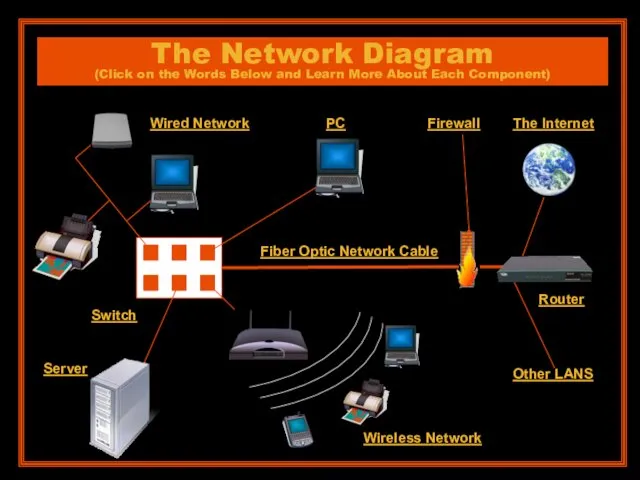
- 5. The Network Diagram (Click on the Words Below and Learn More About Each Component) The Internet
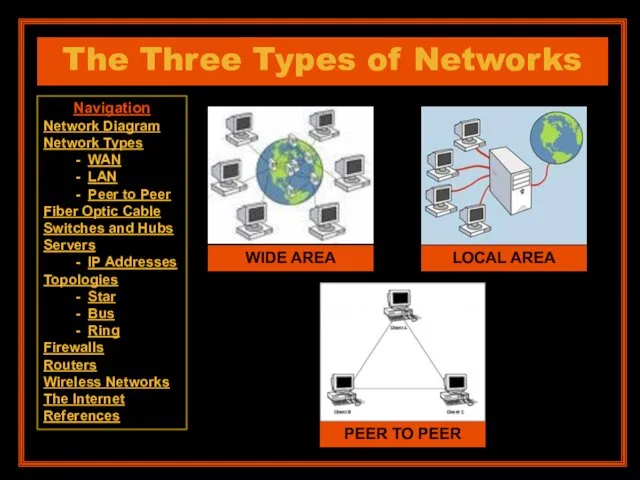
- 6. Navigation Network Diagram Network Types - WAN - LAN - Peer to Peer Fiber Optic Cable
- 7. Wide Area Network A Wide Area Network exist over a large area Data travels through telephone
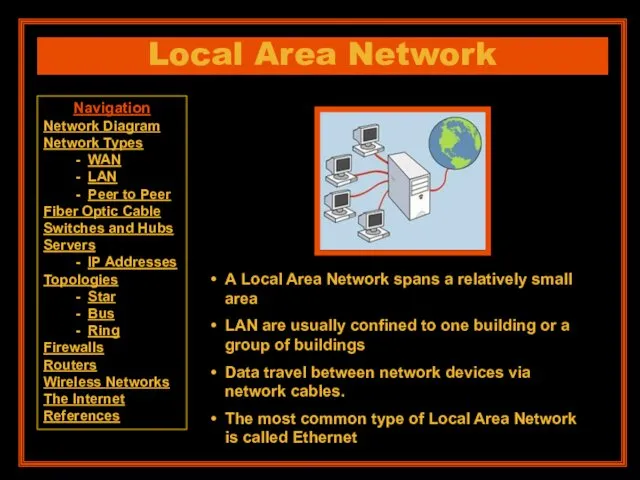
- 8. Local Area Network A Local Area Network spans a relatively small area LAN are usually confined
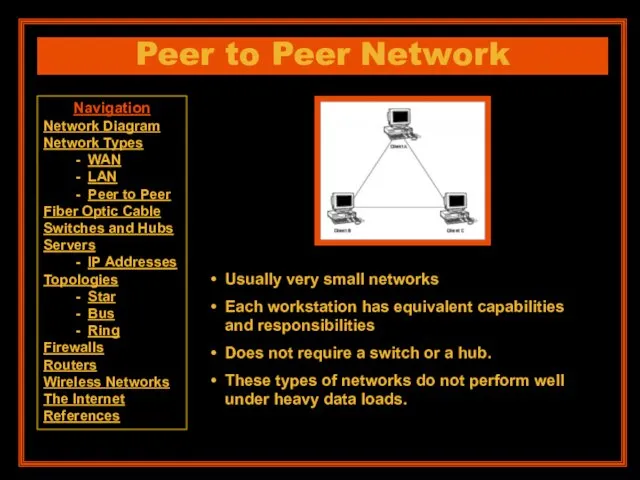
- 9. Peer to Peer Network Usually very small networks Each workstation has equivalent capabilities and responsibilities Does
- 10. Fiber Optic Cable Reduces interference in the network Transmit data faster than copper network cable Allows
- 11. Switches and Hubs Data travels faster through switches because data is not sequenced as it is
- 12. Servers Users are connected to certain servers which will fulfill the required request. There are 3
- 13. Web Servers IP Addresses “IP” stands for Internet Protocol. IP Addresses serve as the location of
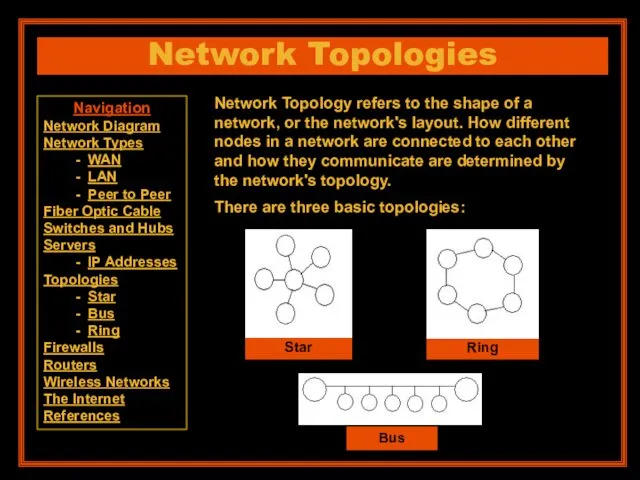
- 14. Network Topologies Network Topology refers to the shape of a network, or the network's layout. How
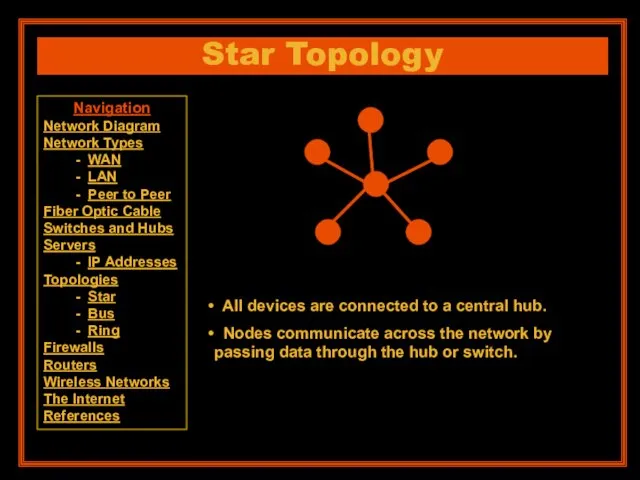
- 15. Star Topology All devices are connected to a central hub. Nodes communicate across the network by
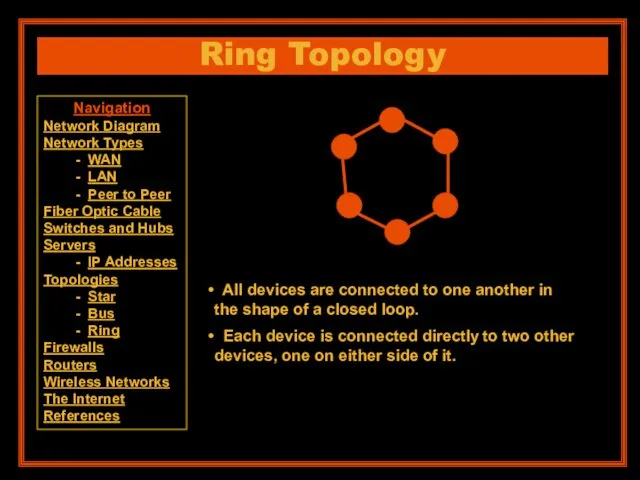
- 16. Ring Topology All devices are connected to one another in the shape of a closed loop.
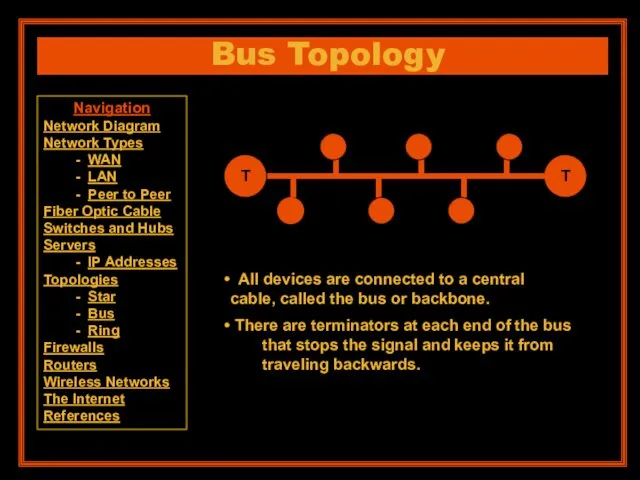
- 17. Bus Topology T T All devices are connected to a central cable, called the bus or
- 18. Firewalls A firewall is a software that can be loaded on to a network that can
- 19. Routers Whether a Router is traditional or wireless, its purposes remain the same. Routers are specialized
- 20. Navigation Network Diagram Network Types - WAN - LAN - Peer to Peer Fiber Optic Cable
- 21. The Internet The simplest definition of the Internet is that it's a network of computer networks
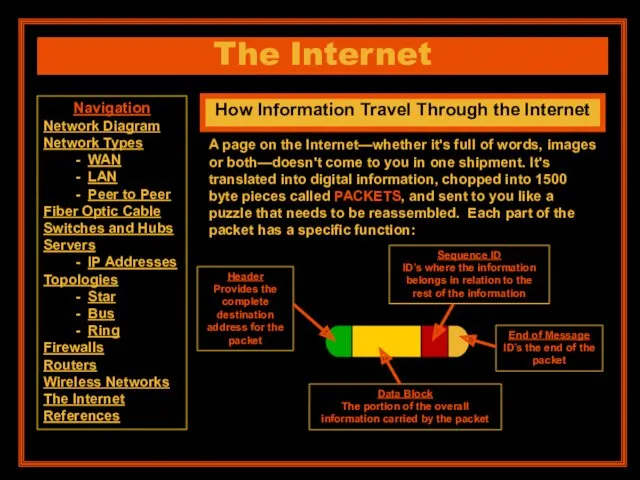
- 22. The Internet How Information Travel Through the Internet A page on the Internet—whether it's full of
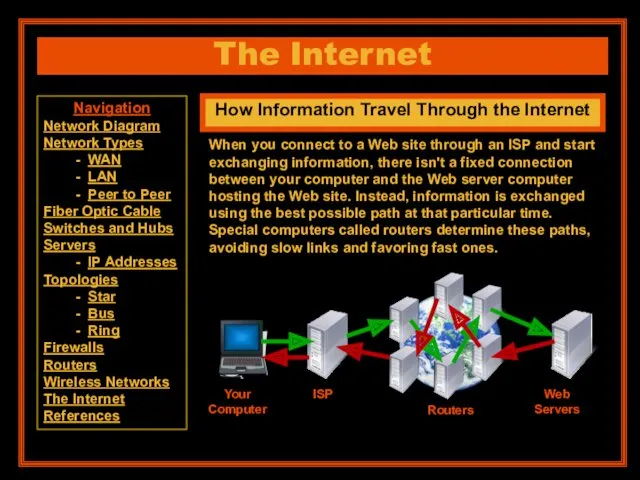
- 23. The Internet How Information Travel Through the Internet When you connect to a Web site through
- 25. Скачать презентацию

![The Computer Network What is a Computer Network net·work: [net-wurk]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/93687/slide-2.jpg)









 Представление графических данных. Форматы графических данных
Представление графических данных. Форматы графических данных Создание современного новостного сайта, с постоянным наполнением контентом
Создание современного новостного сайта, с постоянным наполнением контентом Классификация СУБД. Тема 7.1
Классификация СУБД. Тема 7.1 Развитие музеев. Конец 20, начало 21 века
Развитие музеев. Конец 20, начало 21 века Базы данных, как основа современных CALS-технологий
Базы данных, как основа современных CALS-технологий Введение в программирование
Введение в программирование Программирование мобильных приложений. Сенсоры. Кубик
Программирование мобильных приложений. Сенсоры. Кубик Понятие информационной безопасности. Основные составляющие. Важность проблемы
Понятие информационной безопасности. Основные составляющие. Важность проблемы Business designing & deploying network solutions for small and medium business. (Lecture 3)
Business designing & deploying network solutions for small and medium business. (Lecture 3) SQL. База данных
SQL. База данных Презентация Весна.
Презентация Весна. Устройство компьютера
Устройство компьютера АИС РТРС. Эксплуатация. Система мобильного мониторинга
АИС РТРС. Эксплуатация. Система мобильного мониторинга Стандарт кодирования видео и звуковой информации. MPEG-4
Стандарт кодирования видео и звуковой информации. MPEG-4 Кодирование и обработка числовой информации. Методическая разработка
Кодирование и обработка числовой информации. Методическая разработка Операционные системы
Операционные системы Работа с личным кабинетом (ЛК)
Работа с личным кабинетом (ЛК) Турботаргет. Таргетированная реклама
Турботаргет. Таргетированная реклама Комп’ютерні віруси і антивіруси
Комп’ютерні віруси і антивіруси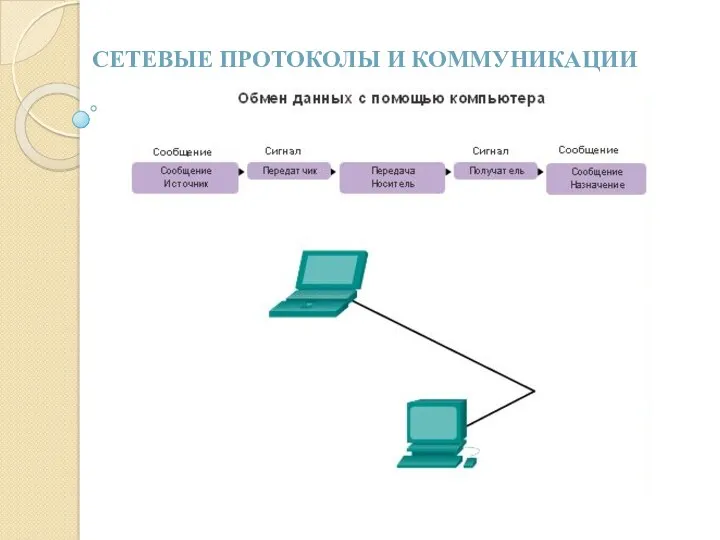 Сетевые протоколы и коммуникации
Сетевые протоколы и коммуникации Задачи
Задачи Медиаконвергенция: осмысление феномена под разным углом
Медиаконвергенция: осмысление феномена под разным углом Перечисления. Объявление и использование перечислений
Перечисления. Объявление и использование перечислений Выявление и устранение типовых неисправностей приводов, HDD, SSD, Flash
Выявление и устранение типовых неисправностей приводов, HDD, SSD, Flash Решение логических задач
Решение логических задач Чит-код социальных сетей
Чит-код социальных сетей История Tik Tok
История Tik Tok Решение задач в ALOHA
Решение задач в ALOHA